Why does the skin in my ears peel?
The reasons why the epidermis in the ears peels off can be very diverse. Among the most likely:
- increased skin dryness;
- lack of vitamins;
- fungal infections;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene;
- boils;
- eczema;
- poor nutrition or diabetes;
- allergies (in most cases accompanied by peeling behind the ears);
- large accumulations of sulfur;
- genetic characteristics;
- age factor (elderly people have an increased tendency to pathologies of the epidermis);
- stress and nervous breakdowns.
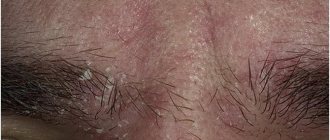
The epidermis may peel behind the ear, inside the auricle, and also on the lobe. If you have peeling skin in your ears, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Ringworm sometimes develops behind the ear and is carried by pets such as dogs and cats. Therefore, your own treatment should be combined with the treatment of your little friend.
Allergy
The manifestation begins with redness and itching. You should quickly limit contact with the irritant, otherwise the upper part of the epidermis will begin to peel off.
The causative agent of an allergic reaction is often chemicals for hair, earrings or glasses.
You can cope with the problem with the help of antihistamine ointments, which eliminate itching and make the skin soft.
If the reaction is severe, a hypoallergenic diet and a course of special medications are prescribed.
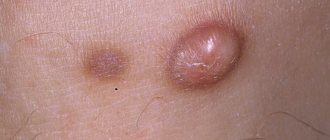
Furuncle
This is an acute inflammation of the purulent-necrotic type, which is caused by pyogenic bacteria. The cause of the disease is most often poor personal hygiene, as well as impaired metabolism, poor nutrition and skin problems.
In the initial stages, the process is accompanied by redness in the ear area or directly in the ear. Next, swelling and acute pain appear, which intensifies when touched.
You can get rid of a boil with the help of medications or surgery. Then you must undergo antibiotic therapy for a long time.
Otitis
This is a disease that represents the development of an inflammatory process in the ear cavity. Otitis often occurs in children or people with weakened immune systems. If you do not go to the hospital in time, you can not only cause serious illness, but also completely lose your hearing. Symptoms of otitis development:
- significant itching inside the ear;
- hearing impairment;
- feeling of being stuck.
The development of otitis is accompanied by the formation of purulent masses, the appearance of pain, which may result in dermatitis: the skin will itch unbearably, and peeling of the ear will occur. It is necessary to treat inflammation in children and adults under the close supervision of a doctor.
At the initial stages, boric acid is used, at the final stages antibiotics, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents are used.
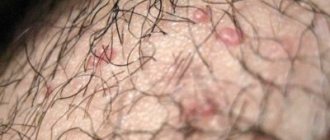
Fungus
Peeling of the skin in the ear is often caused by a fungal infection. You can become infected with harmful bacteria through the earplugs, headphones and hearing aids of strangers.
Signs of fungal infection:
- noise in ears;
- plug formation;
- presence of discharge;
- the ear itches and flakes;
- headache.
Treatment consists of using special medications, and the affected area is covered with medicinal ointments.
Eczema
The disease has a chronic and acute form. The duration of the latter is on average 3 weeks. During this time, the upper layer of the skin is damaged. With properly selected treatment methods, relapses are unlikely. Sometimes an infection can get into the healed tissue or the disease will continue to develop, which will weaken the immune system and give rise to the emergence of a chronic form.
Symptoms:
- the skin turns red;
- severe itching occurs in the area of redness;
- the appearance of a rash with blisters, which subsequently become crusty.
External and internal crusts can be removed using oil mixtures. The affected areas are treated with alcohol or ether, and sometimes aerosols containing Oxycort are prescribed.
If the surface of the skin is not moist, treatment with all kinds of anti-inflammatory ointments is supplemented with drugs that constrict blood vessels and have antifungal properties.
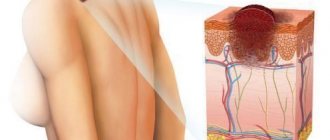
Otomycosis
This is a disease of the outer ear. In both adults and children, it most often occurs against the background of a weakened immune defense of the body. This condition is caused by:
- lack of essential vitamins and minerals in the diet;
- chronic course of infectious diseases;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- constant nervous tension.
The fact is that otomycosis is caused by fungi that are constantly included in the microflora of the human body and occupy a certain position in the upper layers of the epidermis. With healthy immunity, their number is stable, and the life process does not have a negative impact on humans. If the body's defenses are weakened, the fungus, penetrating through any microtrauma of the upper layers of the epidermis of the ear canal, begins to actively multiply and intensively saturate the surrounding tissues with decay products. Quantitative accumulations of these substances foreign to the human body serve as the beginning of an acute allergic reaction, which becomes protracted.
First, itching appears in the inner part of the outer ear, the ear canal becomes inflamed, and the skin on its surface cracks. Liquid fragments similar to ichor are released from the cracks. Then, the process involves: the open and posterior part of the auricle:
- the pigmentation of the skin changes (from pinkish-red to burgundy);
- swelling is observed, especially the lobe increases significantly in size;
- the ear is very itchy, and touching it causes pain;
- the skin dries, cracks, flakes and flakes.
Without timely treatment, otomycosis can be aggravated by dermatitis of infectious pathology.
Otomycosis
Dermatitis
Peeling inside or on the surface of the ear is often a sign of one of the skin diseases. Each type of dermatitis is accompanied by specific symptoms.
Psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of red nodules with white scales on the surface of the skin, so the outside of the earlobe may peel. At first the formations are small in size, but over time they develop into large plaques. Depending on the stage of the disease, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Neurodermatitis is a dangerous type of dermatitis that can affect the lymph nodes. A red rash and unbearable itching appear on infected areas. In severe stages, neurodermatitis causes darkening of the dermis and the formation of a dry crust on it.
Eczema is a disease characterized by skin rashes and itching in places where they are localized.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease caused by infectious and inflammatory processes, which mainly affects areas of the skin with an abundance of sebaceous glands. The cause of dermatitis is fungi, which, while on the surface of the skin, feed on the secretion product of the sebaceous glands.
For the treatment of each type of dermatitis, a comprehensive treatment is selected, which consists of the use of medications, dietary nutrition and increasing local immunity.
Prevention
The main goal of prevention is to prevent the possible occurrence of itching and flaking of the ears.
To achieve this, the following measures are being taken:
- First of all, it is necessary to exclude all sources of allergies that can cause a reaction. For each person, everything is purely individual, for some it is animal hair, for others it is food, for others it is medicine. If you get rid of the allergy trigger, the skin will stop peeling.
- In addition, it is very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene, paying special attention to the ears and face, since this is where the largest number of sebaceous glands are located. They, in turn, become clogged with a mixture of sebum and dirt, and cause unwanted manifestations on the epidermis.
- Another point concerns existing chronic skin diseases. It is important to monitor your general condition and prevent relapses and exacerbations. This will significantly reduce the incidence of itching.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that the earlobe can peel off both from external irritants and from internal problems of the body. If a person cannot cope with the disease on his own, he should definitely visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
Symptoms
We looked at the reasons why the earlobes peel. How does pathology manifest itself?
Symptoms differ in the appearance of:
- peeling and peeling of scales;
- itching;
- slight burning sensation at the site of irritation;
- dry skin.
Diagnosis includes an initial examination, taking an anamnesis, determining a tendency to allergies, and excluding chronic pathologies. Further examination may include a blood test and a skin sample.
Possible complications of the symptom
Ignoring a symptom increases the risk of developing serious complications!
Complications can arise not only in the absence of treatment, but also in the event of improper treatment. The severity of complications depends on the disease that caused the peeling process in the ear.
Even ordinary dermatitis can lead to undesirable consequences if it is started:
- Deep mycosis. Otomycosis (fungal infection of the ear) in severe cases can lead to deep mycosis. This is a dangerous disease when the fungus begins to penetrate inside the body, affecting organs and tissues. It is very difficult to cure this disease; it is often accompanied by relapses throughout life. The fungus can affect the mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, upper respiratory tract, liver, and lymph nodes. Mycosis is usually self-limiting, but can be fatal in people with weakened immune systems, such as those infected with HIV.
- Sepsis. Otogenic sepsis leads to infection entering the blood and spreading throughout the body. Sepsis is severe, accompanied by high fever, profuse sweating, dehydration, and a drop in blood pressure. When the membranes of the brain are damaged, meningitis develops.
- Otoanthritis. This complication usually occurs in small infants, when inflammation from the middle ear during otitis spreads to the mastoid process. The disease can occur in a latent form or be accompanied by characteristic symptoms: fever, ear pain, active discharge of pus, and pus accumulates very quickly after its removal.
- Perforation of the eardrum. Inflammatory processes, ear rinsing procedures, and improper hygiene lead to damage to the eardrum. As a result of perforation of the membrane, hearing function is impaired, noise and buzzing in the ear, discomfort, and pain occur. If there is perforation, drops should not be instilled into the ear, as they can get on the auditory nerve, which leads to serious hearing impairment.
- Destruction of the auditory ossicles. The destruction of the auditory ossicles begins with long-term and severe inflammatory diseases of the ear. With this disease, hearing loss can be significant and quite long-lasting, as well as severe pain in the ear, a feeling of fullness, noise, and dizziness.
Peeling ears in a child
Many of the reasons why adults' ears may itch also apply to children. But if a child’s earlobes are flaky and itchy, then the cause may be hidden in diathesis. This is an innate predisposition of the child’s body to respond incorrectly to stimuli. Main symptoms: redness and peeling of the skin (often in the facial area).
In addition, the skin on the outside of the ears will itch if the infant is constantly dressed warmly and sweats frequently.
Causes
Why do my earlobes peel? People often come to dermatologists with this question, but in fact, the cause may not be hidden in a skin disease.
- Allergic reaction. The situation becomes clear if the ears begin to peel after eating foods that provoke allergies. If you have constant itching, you need to pay attention to your diet.
- A bite of an insect. Some insect bites can cause this problem.
- Lack of vitamins. With a lack of vitamins A or E, dryness occurs in certain areas of the skin, including the ears.
- Elderly age. Due to the characteristics of the body of older people, problems with the epidermis may occur, especially in sensitive areas.
- Ear dandruff. This phenomenon is not uncommon. It appears under the same circumstances as on the head. If the itching is accompanied by detachment of scales, then we are most likely talking about this problem.
- Inflammatory processes in the inner layers of the skin. In this case, noticeable redness appears on the surface of the epidermis.
- Neglect of hygiene. If hygiene is not observed, the dermis begins to peel and itch.
- Stress and neuroses. If there is excessive stress on the nervous system, itching and irritation of the skin may occur.
- Diseases. If your earlobes are flaky and itchy, the cause may be some kind of disease. Since there are a large number of diseases with such symptoms, we need to talk about them separately.
It doesn’t matter whether the earlobe is peeling on the inside or outside, it is equally unpleasant and can be dangerous to health.
Treatment for ear peeling
Correct diagnosis means effective treatment!
Treatment for ear peeling can begin only after the cause of the peeling has been established. Typically, treatment is aimed at eliminating both unpleasant symptoms and the root cause itself.
You cannot start treatment on your own before the examination and drip any drops available at home into your ear. The use of folk remedies such as herbal decoctions and natural juices is also dangerous. They can not only be ineffective, but also intensify the allergic reaction and lead to burns.
Symptom treatment method:
- Antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial infections, purulent discharge from the ear, and otitis media. They can be local or general. In case of serious infection, oral antibacterial drugs are combined with the use of topical agents. The most famous antibiotic ear drops are Otipax, Anauran, Otofa, Otinum. They have a complex effect: they relieve itching, relieve pain and act on pathogenic bacteria. The drugs have contraindications and age restrictions, so it is advisable to consult a doctor before using them.
- Antihistamines. Antiallergic drugs are prescribed for allergies, dermatitis, and eczema. They are usually prescribed in tablets. These drugs block receptors that respond to the irritant and relieve all existing symptoms of an allergic reaction. Such drugs include Zodak, Cetirizine, Loratadine, Tavegil, Suprastin, etc. The drugs differ in composition and have contraindications. When treating eczema, you must also adhere to a diet.
- Antifungal topical agents. If a fungal infection occurs, topical medications are usually used. Medicines are prescribed depending on the type of fungus: mold, yeast, pathogenic. Typically, agents such as Terbinafil and Nitrofungin are recommended. For serious infections, oral medications such as Fluconazole are recommended.
- Surgery. Only boils usually require surgical treatment. If the drugs do not help, the boil increases in size, matures and does not break through, it is opened with a scalpel after local anesthesia, and then treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent complications.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy for flaking in the ears should be selected exclusively by the attending physician. Treatment may include the use of a variety of drugs:
- Symptomatic remedies to relieve pain and fever (for example, with otitis externa).
- Antihistamines to suppress itching. Such remedies help with various conditions, even those not related to allergies.
- Anti-inflammatory creams and ointments.
- Moisturizing and regenerating local ear care products.
- Antibacterial drugs in the form of ointments, creams, ear drops, and tablets (if necessary). Such drugs are used only when the bacterial etiology of the disease is confirmed.
- Antimycotic agents in the form of local or systemic drugs. Such therapy is necessary for otomycosis.
- Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs containing hormones. Such treatment allows you to suppress the strong inflammatory process in eczema.
- Retinoids, keratolytics, steroids and other local medications. Such drugs are used in complex therapy of psoriasis.
All medications used in dermatological and otolaryngological practice are selected individually, taking into account the available indications and individual characteristics of the patient.
The best remedies for flaking ears
Depending on the reasons that caused the peeling, doctors prescribe different groups of drugs. Bacterial infections of the inner ear require the use of antibiotics. Mycoses and otomycosis - antifungal ointments or creams. Dermatitis, eczema and other inflammatory skin diseases are treated with steroid ointments.
Therapy for flaky skin behind the ears is carried out with creams and pastes containing zinc, sulfur, and salicylic acid. Ointments with selenium disulfate or ketanazole can be used.
After consultation with a doctor, treatment can be supplemented with folk remedies:
- Place onion juice into the ear canal two or three times a day.
- A clove of garlic wrapped in gauze and inserted into the external auditory canal will relieve inflammation and reduce pathogenic microflora.
- Aloe vera juice will relieve swelling and irritation of the skin. Freshly squeezed juice (no more than 5 drops) is instilled two or three times a day.
Sunburn and frostbite are treated with panthenol and other vitamin B6-based products that stimulate skin restoration. If ear dandruff is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations - itching, burning, pain, they can be treated independently.
How to cure excessive peeling of the ears in an adult - vitamin compresses are effective. It is necessary to mix the contents of capsules with vitamins A, B, E, C in equal proportions. Place a moistened cotton swab in the ear canal for 30 minutes.
To facilitate the removal of keratinized scales, use rose and rosehip oil. Vegetable or olive oil will also work. A piece of bandage or a cotton swab is moistened in them and the flaking skin is gently wiped. The oils are left for 20 minutes, then removed along with the scales with a cotton pad.
Treatment
Treatment should begin when the exact cause is identified. If this does not pose a threat to the health of an adult or child, then treatment can be carried out at home as prescribed by a doctor.
Allergic reactions to food, medicine or insect bites are treated with antihistamines, soothing ointments and compresses. When determining the cause of an allergic reaction, the allergy provocateur must be eliminated (discontinue the medication or eliminate the food product from the diet).
If irritation is caused by insufficient hygiene, then the solution to the problem is very simple. You just need to wash the affected areas of the epidermis with soap.
Peeling due to nervousness quickly stops when the root cause (stress or neurosis) is eliminated. It is necessary to avoid situations that irritate the nervous system.
Ear dandruff can be easily treated with medicated hair shampoos.
If the cause of peeling ears lies in a lack of vitamins or nutrients, then you need to change your diet and take vitamin complexes to make up for the deficiency.
Diseases, the symptom of which is peeling of the ears, must be treated by a specialist. Most often this is a dermatologist. When visiting a doctor, it is necessary to indicate all symptoms, even minor ones. Since itching of the epidermis may be caused by a hidden insidious disease (for example, diabetes). That is why a specialist should make a diagnosis.
After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. For skin diseases, it consists of taking pills, applying ointments and visiting a physiotherapy room, where there are special light lamps.
Under no circumstances should you prescribe treatment for yourself without making an accurate diagnosis. This may result in aggravation of the problem; the disease may become chronic with exacerbations. In this case, it will become much more difficult to get rid of peeling.
When to see a doctor
If your ears begin to itch, itch severely, flake off profusely, or there is discharge from the ear canal, consult a dermatologist before starting self-treatment. Such symptoms indicate a fungal infection of the skin.
If the auricle inside and outside is covered with a crust that becomes wet or peels, a consultation with a dermatologist is necessary. Eczema often manifests itself in a similar way to other skin diseases that require special treatment.
When your ears begin to itch, accompanied by flake-like skin peeling, severe pain, a feeling of stuffiness, or significant hearing impairment, you should consult an ENT specialist. Most likely, otitis has developed, which requires immediate treatment with antibiotics, which only a doctor can correctly prescribe.
In adults, itching of the ear with peeling, with the formation of papules and redness of the skin on the outside may indicate dermatitis or fungal infection. These diseases require contacting a dermatologist and treatment under his supervision.
There are many reasons why the skin in the ears peels. If the problem is caused by vitamin deficiency or improper care, incorrectly selected cosmetics, it is easy to solve it yourself.
But if accompanied by peeling, severe itching, pain, the appearance of crusts or discharge, you need to consult a doctor. Self-medication in such cases will only worsen the situation.
Prevention of ear peeling
Cleaning your ears correctly!
Various ear diseases can be avoided if you follow simple rules. Even healthy ears need proper care. Ear diseases are much easier to prevent than to treat.
Preventive actions:
- You need to clean your ears correctly. Many people strive to cleanse their ears of wax as often and effectively as possible, thinking that it is the cause of disease. But the body cleanses the ear canals of wax on its own. It is eliminated by chewing and talking. You only need to clean the outer part of the ear canal, but under no circumstances should the stick penetrate deep into the ear. This can lead to injury and complications.
- Those who wear hearing aids should clean them regularly and use special ear rinsing drops. These people are especially prone to dermatitis and inflammation in the ear.
- Swimmers and people who regularly visit the pool should protect their ears from water (which also contains chlorine). There is a special cap for this. After the pool, your ears should be rinsed with a solution of sea water.
- When bathing small children under one year old, you need to make sure that water does not flow into the ears. For this purpose, cotton swabs are used, which are inserted during bathing. If a child needs to clean his ears, it is better to use special children's cotton swabs with a limiter.
- Ears need to be protected not only from water, but also from cold air. Walking in winter and in windy weather without a hat is highly discouraged. This is dangerous not only due to otitis media, but also other inflammatory infectious diseases.
- A good prevention of ear disease is timely treatment of colds. ARVI, influenza and other infections often lead to otitis media with a long chronic course.
- Do not use any metal objects such as hairpins or hairpins to clean your ears. Do not scratch or clean your ear with them. They leave scratches that can become inflamed. When using headphones, it is also advisable to wipe them periodically.
If you follow the basic rules of prevention, most diseases can be avoided. It is especially important to monitor the hygiene and health of the ears of young children, since complications are much more common in them.