Papule, vesicle, pustule. What it is?
The primary morphological elements of the rash include:
- vesicle (bubble);
- papule (nodule);
- pustule (pustule);
- nodes;
- spots;
- tubercles;
- blisters.
The first three elements will be described in more detail below.
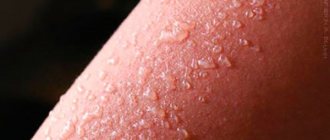
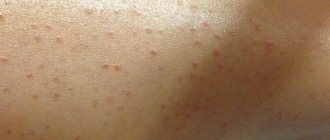
A vesicle is a spherical vesicle that rises slightly above the surface of the skin and ranges in size from a pinhead to a pea. Inside the bubble is a cloudy or clear liquid. This rash element is located in the superficial layers of the epidermis.
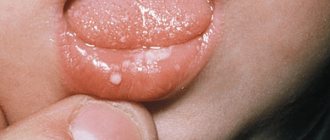
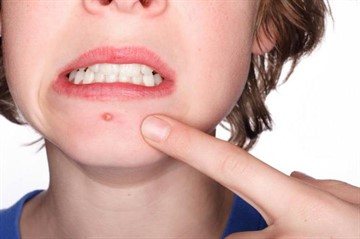
A papule is a small nodule that measures 1-20 millimeters in size. Papules often leave behind peeling and pigmentation.
Pustule is a later form of vesicle. It resembles a small ball in appearance and is yellowish in color. At the top of the ball there is a white spot, which over time bursts, forming a wet surface.
The skin around the pustule is swollen and hyperemic. After opening the abscess, its contents fall on the surface of the epidermis and form a crust. After the tissue under the lesion is restored, the crust disappears, leaving no noticeable marks.
Single pustules do not pose a particular danger to the patient’s health and usually disappear on their own after some time. The presence of a large number of pustules can be a symptom of a number of dangerous diseases (smallpox, syphilis, and so on), so in this case you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist to find out the causes of the rash.
Rashes on the epidermis are characterized by the morphological elements of the rash, which include papules, vesicles, pustules, blisters, spots and tubercles. A papule is a nodular formation with a diameter of 0.1 to 2 cm. Such elements often leave behind pigmentation and peeling.
A vesicle is a small spherical vesicle that rises above the surface of the epidermis. Inside contains a clear, colorless or cloudy liquid. The element is located in the superficial layers of the skin.
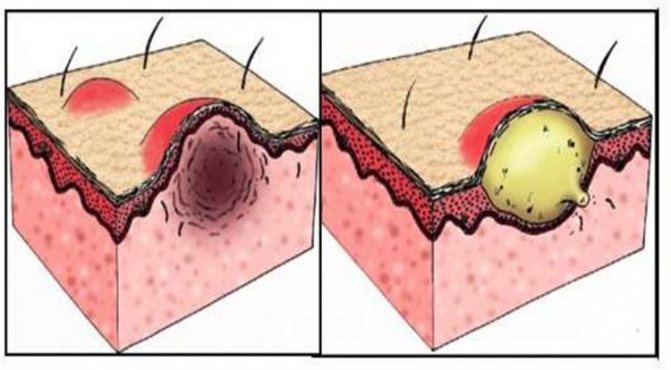
Papule (left) and pustule (right)
The pustule looks like a small yellow ball with a white spot on top and purulent contents. Over time, the formation bursts. Such elements hurt when touched. The skin around the pustule is hyperemic and swollen. After opening the abscess, a crust forms, which disappears after a while.
People often turn to dermatologists with the problem of acne and warts on the body. These formations look like papules. A wart is a keratinized solid formation with a diameter of 0.1 to 1 cm. It can be located in the papillary layer, on the surface of the dermis.
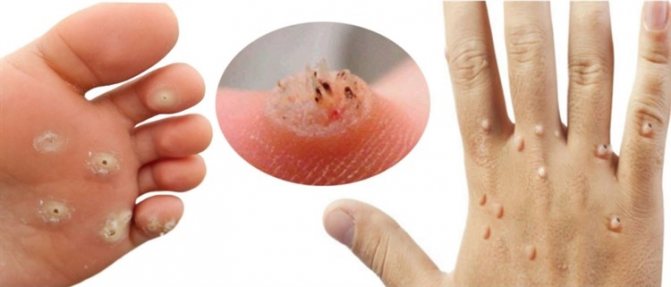
Warts
Warts do not form inflammation around themselves, do not hurt or cause itching. At first they do not differ from the color of the skin, but over time they can darken, become brown or black.
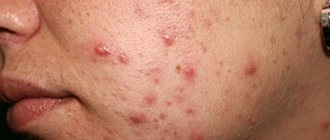
Acne papules, unlike warts, are characterized by an inflammatory process and are painful to the touch. There are pimples without inflammation - comedones.
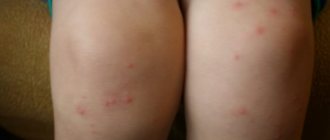
Maculopapular rash
The most important characteristics of this type of rash remain:
- Element sizes up to 2 cm.
- The process is often accompanied by peeling and inflammation of the skin. Pigment spots remain in place of the former nodules.
- Localization throughout the body.
- The timing of the appearance of the rash often helps in the differential diagnosis of the diseases that cause it.
- The color of the elements ranges from pink to brown.
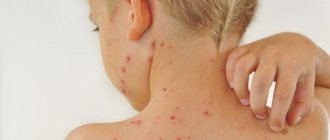
Most often, these rashes appear with a variety of infectious diseases (scarlet fever, measles, rubella, chicken pox and others). Skin elements serve as a pathognomonic symptom with which the diagnosis is established.
Photos of patients with a specific skin lesion will help you remember what a maculopapular rash looks like.
Varieties
At the moment, there are several types of papular rash. These include:
- Miliary rash. These are the smallest neoplasms that can reach a diameter of no more than two millimeters. Papules have a cone shape and are localized around the hair follicles.
- Lenticular neoplasms. This papular rash is medium in size. In diameter, such neoplasms can reach more than five millimeters. Papules are distinguished by a variety of forms. They can be either convex or flat.
- Numular. The diameter of the papules in this case can reach 2 centimeters. they are formed as a result of the merger of several flat elements. The rash eventually acquires a coin-shaped structure.
Types and classification
Papules and pustules have different locations, sizes, shapes, and colors. This allows them to be classified into certain types. Assigning a formation to a specific type allows the dermatologist to select an effective treatment regimen.
Depending on the depth of occurrence of papules, there are:
- epidermal (superficial);
- dermal (in the papillary layer);
- epidermodermal (mixed).
By size:
- lenticular (0.5x0.5 cm);
- plaques (diameter larger than a large coin)
- miliary (with a pinhead);
- numular (5-kopeck size).
The shape of papules is:
- flat;
- hemispherical;
- polygonal;
- cone-shaped (follicular).
Based on the color of the formation, they are classified into:
- pink;
- brown;
- white;
- red;
- purple.
According to the presence of an inflammatory process:
- inflamed;
- uninflamed.
Other types of papules:
- lichenoid (flaky, characteristic of lichen);
- syphilitic (round red formations on the skin and mucous membrane, capable of merging and ulcerating);
- bowenoid (red spots, related to precancerous conditions of the dermis);
- Gottron's papules (nodules located in the area of the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints);
- fibrous (formed in single numbers, localized on the nose);
- erythematous (localized on the extensor surfaces of the joints, characteristic of vasculitis and lupus erythematosus);
- piezogenic (slightly protruding round formations the color of the epidermis, formed in the heel area).
Pustules are classified according to the following criteria:
- by localization into follicular, intradermal and subcorneal;
- by pathogenesis into autoimmune, infectious;
- by the number of cameras into single-chamber and multi-chamber.
Papular necklace
One of the fairly common types of papular rashes is the “pearl ring” symptom. It is characteristic of physiological pearly papules, which are located in the area of the coronary sulcus under the head of the penis.
Unlike all previous situations, in this case small nodules are normal and do not require any treatment. Papular necklace in men is a harmless phenomenon, the cause of which has not yet been established. Most visits to doctors are due to a visual defect and the need for differential diagnosis with sexually transmitted infections.
This situation does not cause any symptoms or pronounced clinical manifestations. The characteristic features of such skin elements remain:
- Same size of papules.
- Tight location. There is practically no space left between them.
- Lack of objective changes in sensations.
- Long-term preservation. Nodules most often appear in men aged 20-40 years and remain with them for life. Over time, there is a decrease in the color intensity of the elements, which contributes to even greater invisibility.
There are several options for surgical treatment of this symptom, however, doctors perform it only at the request of the stronger sex. Papules are not transmitted to sexual partners and do not pose a threat to human health.
What to do if the rash itches and does not go away for a long time?
There are many predisposing factors. It is simply impossible to independently determine the cause of the papular rash. If new growths appear, you should seek advice from specialists. The main reasons for the appearance of a rash include:
- Diseases that are bacterial, viral or infectious in nature.
- Diseases caused by the active activity of parasites.
- Allergic reaction to certain irritants.
- Immunological reactions.
It should be noted that a papular rash resulting from an infectious disease is only one of the stages in the development of morphological types of neoplasms.
If the rash itches and does not go away, you should consult a dermatologist. It could be scabies. If itching and formations do not disappear during long-term therapy, then you should visit an allergist. It is important to identify and eliminate the factor that provokes such a reaction in the body.
Hives indicate improper elimination of toxins, disruption of internal processes, and intolerance to medications taken.
Causes
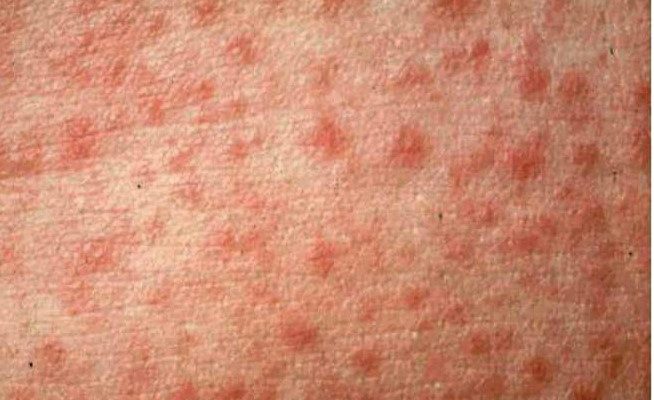
Maculopapular rashes can be explained by various factors. Among the most common reasons for this phenomenon are:
- Sudden exanthema. This is a common childhood infectious disease, which is characterized by a sudden and severe increase in temperature, not accompanied by other health problems (catarrhal phenomena). After the fever subsides, maculopapular elements appear on the child's skin - first on the chest, then on the face and limbs.
- Rubella, scarlet fever and measles. These are classic childhood infectious diseases, which are typically characterized by an increase in temperature and the appearance of a rash on the body.
- Adenoviral infection. This disease is caused by adenoviruses and is characterized by classic symptoms of ARVI. A rash with this disease does not appear in every case.
- Infectious mononucleosis. This is an acute viral illness that classically manifests as an enlarged spleen and lymph nodes. A rash is observed in about a third of patients with this diagnosis. Reddish spots appear on different parts of the body, but most often accumulate on the stomach, back, as well as the neck and limbs.
- Enterovirus infection. Enteroviruses most often affect the digestive tract, but can also attack the respiratory system and other parts of the body. Some of them cause rashes on the skin or mucous membranes. Red spots often appear in children and can be localized in different parts of the body.
- Erythema infectiosum. This disease has a viral etiology, and its main manifestation is a bright red rash, which is localized on the cheeks, as well as the torso and limbs. In addition, the patient is concerned about the symptoms of general intoxication.
- Allergic reactions. In particular, such rashes often occur due to individual intolerance to medications, for example, antibiotics.
Maculopapular rash may occur in patients with autoimmune diseases (eg, systemic lupus erythematosus), AIDS, and syphilis. Only a qualified specialist can accurately determine the cause of this phenomenon.
Localization on the body
Pustules can be located on the skin of the neck, head and torso. In men, they can be localized in the penis area. There are pustules on the lips, genitals, arms and legs, back and abdomen, heels, face, tongue.
Skin papules occur as a result of hormonal imbalance and a tumor process. The rash on the genitals is called pearlescent papule. It appears in the form of small pimples that do not cause discomfort.
Localized around the head of the penis. Develops due to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
Hemorrhagic rash treatment
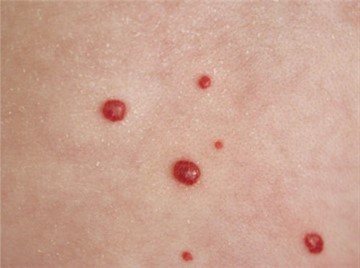
There are a huge number of diseases in the world that manifest themselves in the form of a rash. It is difficult to call the rash itself a disease; it is rather a symptom of something more serious. In general, rashes vary. Its appearance and location can tell us about the reason why it arose. When blood capillaries rupture, a hemorrhagic rash occurs. Usually the rashes are not palpable, and when pressed they do not turn pale or disappear.
The size and color of the rash depends on the cause of its appearance. They can be black, blue, purple, violet, red, in the form of spots, dots or stripes. Petechiae are small rashes, and purpura are large rashes. The most common is a hemorrhagic rash on the legs. It is difficult to name the exact cause of its occurrence, because this localization is characteristic of many diseases.
Diagnostic methods
Treatment of papular rash should be prescribed strictly by a specialist doctor. It is impossible to determine the reasons for the development of this phenomenon at home. Only a doctor can prescribe adequate treatment for neoplasms.
It should be remembered that papular rash occurs as a result of certain diseases. Often it is a sign of a more serious illness. To diagnose the disease, it is necessary to conduct a certain series of studies. When making a diagnosis, the doctor must:
- Assess the general condition of the patient.
- Examine the affected areas of the skin.
- Order laboratory tests.
- Palpate the papular rash.
If papules, pustules, or vesicles appear, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist, consult with an infectious disease specialist, venereologist or allergist. At the appointment, the doctor interviews the patient, examines the skin using a dermatoscope, and prescribes a series of examinations.
The following diagnostic techniques are used:
- liver tests;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- skin allergy tests;
- bacterial sowing;
- biopsy;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- chest x-ray;
- HIV test;
- plasma analysis for hormone levels;
- skin scraping microscopy;
- urine test.
Most dermatological research techniques are painless. They allow you to identify the disease and select a treatment regimen.
Treatment
Since the rash can have different etiologies, there is no universal treatment. It is worth remembering that the appearance of rashes should alert a person. You definitely need to see a doctor.
A dermatologist should evaluate the condition of the skin. A medical history will also be required to evaluate the causes and additional symptoms of the disease.
A mandatory step is taking tests. During the study, the doctor can determine the presence of a virus or bacteria that has caused problems in the body. Only depending on these indicators, treatment of the disease is prescribed.
If the disease is infectious, as is the case with rubella or measles, then specific therapy is not required. It will be enough to take medications prescribed by a doctor to treat the underlying disease.
Causes
Papules and pustules occur for various reasons. Most often they are formed as a result of the active activity of microbes, viruses, and fungi.
Also, the reasons for the formation of papules and pustules are:
- disruptions in the functioning of the stomach, liver and intestines. Observed in certain pathologies of internal organs, with improper and irregular nutrition;
- hormonal imbalance. Hormone levels change during puberty, pregnancy, menopause;
- physical, emotional fatigue. Lack of wakefulness and rest, insomnia, and stressful conditions lead to weakened immunity. This reduces the body’s resistance to diseases, including those of an epidermal nature;
- blockage of the sebaceous glands. Occurs with cholesterosis, impaired metabolism, poor hygiene;
- allergies to hygiene products, food, animal hair, insect bites.
Types of rash
A person may experience papular urticaria in different ways. The types of rash differ in:
- localization;
- symmetry and asymmetry of the pattern;
- the presence or absence of itching;
- color;
- intensity of damage;
- provoking factor.
To suggest one or another type of neoplasm, you can look at the photo of each below.
Epidemiology of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. What's new about Rocky Mountain spotted fever? Pathogenic mechanisms of diseases caused by Rickettsia. Early signaling events associated with the entry of Rickettsia conoria into mammalian cells. Reactivation of Rickettsia rickettsia in Andersey Dermacentrum ticks: ultrastructural analysis.
Actin-based rickettsial motility: behavior and involvement of cytoskeletal regulators. Hemostatic changes in Rocky Mountain spotted fever and Mediterranean spotted fever. Rocky Mountain spotted fever familial cluster. Tick rickettsios around the world: emerging diseases challenging old concepts.
Maculopapular
When a maculopapular rash occurs, papules with a dense consistency appear on the surface of the skin. They are distinguished by their significant size, so the diameter exceeds 1 cm.
The rashes can have different shades. Flesh-colored, burgundy and purple growths are often observed.
The rash appears quickly. Suddenly you can find it in the area:
Life-threatening eruptions due to infectious agents. Fever and rash in a 3-year-old girl: Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Rocky mountain fever: clinical, laboratory and epidemiological features of 262 cases. Fatal cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in familial clusters—three conditions.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever - United States. Research into homini piroplasmosis. Life-threatening rashes: dermatological signs of four infectious diseases. Rocky Mountain "Flawless" and "Almost Flawless" Fever: A Wolf in Sheep's Clothing.
- faces;
- torso;
Depending on the causes of the disease, the location of the papules may vary. A distinctive feature is a viral infection of the body. In case of an allergic reaction, bacterial or fungal infection, or immunodeficiency, the rash appears mainly on the hands and feet.
Maculopapular rash occurs with measles, rubella and other infectious diseases
Rocky mountain spotted fever, mimicking acute cholecystitis. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: Mimicking Appendicitis or Acute Surgical Abdomen? Clinical and laboratory features, hospital course, and outcome of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in children.
Myocardial involvement in rocky mountain spotted fever: a case report and review. Echocardiographic M-mode abnormalities in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Involvement of the lower respiratory tract in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Clinical manifestations of Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Maculopapular rash can be caused by various factors. Among them are:
- measles, rubella and other infectious diseases;
- enterovirus;
- adenovirus;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- sudden exanthema;
- allergies to food irritants, medications, streptococcus, staphylococcus toxins;
- damage by bacteria and fungus;
- helminthiasis
Most often, the rash does not cause itchy skin. But if the reason lies in an allergic reaction, this symptom often appears.
Rocky mountain spotted fever: a clinical dilemma. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: A Seasonal Alert. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: A disease requiring microbiological concern. Sensitivity of various serological tests in the diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Therapeutic delay and mortality in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Use of polymerase chain reaction as a diagnostic test for Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Diagnosis and treatment of tick-borne rickettsial diseases: Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. United States: A practical guide for physicians and other health and public health professionals.
Erythematous-papular
The rashes are localized in the area:
- faces;
- limbs;
- lower back.
Most often the elbows and knees are affected. The boundaries of the rash are clear, and a symmetrical pattern is visible.
In the central zone, darkening of the papule is observed. The edges of the neoplasm have a bright red tint. The rashes are large in size, up to 1 cm. When papules merge, large lesions are formed.
Rocky mountain spotted fever during pregnancy: differential diagnosis and treatment. Rocky mountain spotted fever in pregnancy. Rocky mountain spotted fever and pregnancy: a case report and review of the literature. Tetracyclines and permanent teeth: relationship between dose and tooth color.
Treatment of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in children. Use of doxycycline for rickettsial disease in pediatric patients. Treatment of tick-borne diseases. Predictors of prognosis and risk of acute renal failure in patients with spotted fever in the Rocky Mountains.
The appearance of such a rash can be caused by:
- lupus erythematosus;
- atopic dermatitis;
- syphilis;
- rosacea;
- allergic reaction;
- trichinosis;
- vasculitis;
- scabies;
- diathesis.
The nature of the rashes of the disease differs slightly. Therefore, this symptom can be used to make the correct diagnosis.
Long-term effects of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Neurological complications of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Continued deterioration after Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: Case Report. Persistence of Rickettsia rickettsia in a patient with Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Brazilian spotted fever: a case series from an endemic area in southeastern Brazil: clinical aspects. This rash usually begins on the wrists and ankles, spreads inward toward the torso, and also affects the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The rash may become papular, petechial, or purpuric, i.e. hard bumps, flat red dots that do not bleach under pressure, or large flat spots of red or purple 3mm-1cm that also do not bleach under pressure.
Darkening is observed in the center of the erythematous papule
Maculopapular
Maculopapular rash is presented in the form of very large neoplasms up to 2 cm in size. It can be distinguished by its characteristic features.
- The rashes are inflamed and flaky. After the persistent rash disappears, pigmented areas may be noted on the surface of the skin.
- Papules form in the face, body, upper and lower extremities.
- The stage of the disease can be tracked by the timing of the rash. First of all, the facial part is affected, and then the rash spreads to the torso. Also, the degree of development is determined by the size of the papules.
- The color of the new growths is predominantly pink, but brown and red colors are allowed.
This type of rash is divided into several subtypes depending on the type of disease. Highlight:
Differences between Rickettsia and Lyme disease
Early flu-like symptoms and skin rashes can make it difficult to diagnose Lyme and Rickettsia disease and co-infections. In progressively severe cases of untreated or unresponsive rickettsia infection, the patient may develop vasculitis throughout the body, leading to blood clots and even death. Symptoms of Lyme disease that differ from those include rickettsia arthritis, myalgia, and a type of rash that occurs with infection. The neurological symptoms of Lyme disease are also different from those of Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and they can begin soon as Bell's palsy, and can become meningitis and encephalitis, with subacute encephalopathy, axonal polyneuropathy, and even leukoencephalopathy possibly. Symptoms of neuroborreliosis can be very are similar to diseases or conditions such as multiple sclerosis, depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and even schizophrenia, which can lead to misdiagnosis, especially if co-infections like Rickettsia throws the question.
- scarlet fever-like rashes accompanying rubella, chickenpox, scarlet fever, allergies to medications;
- morbilliforms, which appear as a result of late stages of rubella and measles;
- flaky, noted with seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis.
With measles, the papules have a whitish tint, with a red rim along the borders of the rash. Due to increased symptoms, the papules merge.
Some sleep disorders and mood disorders may also occur with Lyme disease, and symptoms may persist for several years if left untreated. Patients with rickettsia usually recover within a few weeks or months, while Lyme disease can cause arthritis symptoms for years with or without treatment.
A 52-year-old woman was consulted for an asymptomatic papular rash of the chest and upper extremities for 6 months, accompanied by a morning dry cough and mild shortness of breath in the past month. There were dozens of lenticular maculopapules with an erythematous violet tone, with fine superficial scaling distributed scatteredly on the hands and forearms. Similarly, in the posterior neck and atrial zone they isolated and penetrated much more into erythematous papules.
Rubella rash starts from the forehead area. Next it moves to the body. The person feels unbearable itching. Also, similar symptoms are observed with toxic damage to the body by drugs.
Many diseases appear as a maculopapular rash. Therefore, the doctor must conduct a thorough examination before making a diagnosis.
Rice. — Lyphenoid papules, distributed in the upper extremities. Rice. - Inflammatory erythematous lesions in the atrial region. Skin biopsies were performed in a “punch” for histological examination and microbiological cultures. A CT scan of the chest was also performed.
Rice. — Histological detail of the damage. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Histological examination of one of the lesions showed a granulomatous infiltrate located mainly in the papillary dermis. These are necrotizing granulomas consisting of histiocytes, some multinucleated giant cells and a few lymphocytes in the periphery.
Therapy of the disease
The treatment plan for papular rash depends on the underlying disease. If the neoplasms represent an allergic reaction, then first of all it is necessary to eliminate the irritants. For therapy in this case, antihistamines should be used. Special skin care products are also recommended.
If a papular rash occurs as a result of an infectious disease, then in this case anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics are used. When choosing a medicine, the doctor, as a rule, is guided by the infectious agent.
Papular urticaria
The peculiarity of this pathological condition remains the reason for its appearance. Unlike infectious pathogens, in this situation the main role is played by the body's allergic reaction to antigens.
As a result of allergens entering the bloodstream or local contact with the body, a local response progresses with the release of large amounts of histamine, which leads to the accumulation of fluid in the affected areas. The result of this is papular urticaria. The photo shows the characteristic elements that appear after contact with the antigen.
The best method to overcome the problem remains the complete exclusion of interaction with allergens. If it is impossible to limit contact, persistent papular urticaria may progress. To reduce its manifestations, it is necessary to use specialized antiallergic agents.
Diseases with papules
Rashes are characteristic of the following pathologies: psoriasis, measles, scabies, anthrax, syphilis, atopic dermatitis, herpes, typhus, eczema, Kaposi's sarcoma, streptococcal impetigo.
The diseases differ in the appearance of the papules, their location and other associated symptoms:
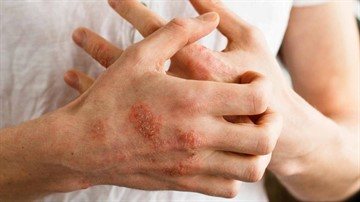
psoriasis. It is an autoimmune chronic disease that affects the skin. Manifested by weakness, fatigue, depression. The main symptom is spots that rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Red psoriasis papules vary in size and shape: teardrop-shaped, coin-shaped, and dotted. Initially, the size of the formation is 3-4 mm, but as the disease progresses, the papules increase to 10 or more centimeters. Morphological elements affect the entire body and can merge;- eczema. This is a neuro-allergic recurrent pathology that manifests itself in the upper layers of the dermis. This disease is characterized by a rash that causes itching and burning. At first the skin turns red. Then small pink-red papules form. As inflammation progresses, they transform into vesicles and pustules. After opening the formation, weeping eczema occurs. When the inflammatory process subsides, the skin turns pale, erosion becomes crusty;
- scabies. The disease is contagious and is caused by parasitic scabies mites on the skin. Elements of the rash are represented by scabies. They look like dirty gray lines of a straight or curved shape. Elongated papules and pustules can form under them. The formations cause severe itching. When scratching, erosions occur;
- Kaposi's sarcoma. These are multiple malignant neoplasms on the skin. First, papules form, similar to rashes caused by lichen ruber. Places of localization are the arms, legs, and feet. Papules peel, increase in size (can reach 5 cm), and are painful. After resorption, the nodules leave pigmented impressions. Kaposi's sarcomatosis can metastasize to the lungs, bones, and liver. In this case, the person experiences a bloody cough and diarrhea, and a high fever;

syphilis. This is a sexually transmitted systemic disease of an infectious nature that affects the mucous membranes, skin, nervous system, bones, and internal organs. Papular syphilides appear during the period of exacerbation of the disease. They can be meliar, lenticular, numular, plaque. In primary syphilis, the formation looks like a round ulcer with a smooth bottom and even edges. Erosion is painful. Small ulcers appear on the mucous membranes. Chancres up to 5 cm in diameter are observed in the abdomen, thighs, chin, forearms and hands. Secondary syphilis manifests itself as nodules, spots, papular-pustular rash, and vesicles. Formations can occur on any part of the body; they do not merge. Their color and shape vary. The skin around the syphilides does not swell or become inflamed;
- streptococcal impetigo. This is a contagious pathology of streptococcal nature. Initially, bluish-red papules appear on the skin, which can be eroded. Then they transform into vesicles with an edematous and hyperemic base. Localized in the area of the buttocks, thighs, back and abdomen;
- atopic dermatitis. This is a non-contagious, chronic inflammatory skin disease. It manifests itself as follicular papules and plaques on the extensor surface of the limbs and trunk. In adults, atopic dermatitis is characterized by pigmentation, secondary leukoderma. Whitish spots form in the cheek area.
Characteristic symptoms of the rash
When a disease, allergic reaction or infection occurs, a rash appears on the skin. It is not accompanied by an inflammatory process or severe itching.
It is worth noting that there is also no peeling of the skin. If such signs appear, accompanied by itching, then skin damage may be suspected.
A characteristic symptom of a maculopapular rash is an inflammatory process in the glands behind the ears and swelling of the lymph nodes. They help to quickly diagnose a particular disease.
If the rash spreads throughout the body, covering unusual areas of the skin, then diagnosis becomes difficult. After all, similar symptoms can appear with various skin diseases.
Some patients who develop a maculopapular rash report minor pain or itching. But still, these signs cannot be considered characteristic of this type of rash.
At the initial stage of occurrence, papules are small areas that rise above the surface of the skin. Their diameter does not exceed one centimeter. The rash has a light red tint.
If the disease develops, characteristic changes in the rash can be observed. Papules can merge together, affecting large surfaces of the skin. With maximum development, the rash becomes dark in color, spreading throughout the body. When the disease passes, the rashes become lighter.
After the rash disappears, no traces remain on the surface of the skin. There will be no redness, peeling, scars or scars.
Personal hygiene
Often a papular rash occurs as a result of improper skin care. In such situations, a careful selection of personal hygiene products is carried out. This takes into account the patient’s predisposition to allergies, as well as the type of skin.
In addition, the specialist can give the patient certain recommendations related to caring for damaged areas, as well as keeping the body clean. It is worth noting that following all the rules specified by the doctor can prevent the occurrence of a papular rash in the future.
Almost every child goes through this.
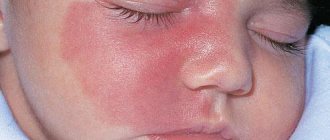
Almost every child experiences inflammation and itching of the skin due to household allergies. Especially often the cheeks “bloom” in the first six months of life, when the baby’s body “gets acquainted” with various new substances and develops defensive reactions to what it does not like.
It is believed that in babies who are breastfed, allergic reactions are less common (if the mother does not abuse chocolate, oranges, etc.) than in “artificial” babies. And the point is not so much that the formula may be of poor quality, but rather the fact that when a child is bottle-fed, he often eats more than he needs. This causes a lack of enzymes for digestion, hence the retention of food in the intestines, its rotting and the absorption of harmful substances into the blood, which give rise to allergic reactions.
Why shouldn't you overfeed allergy sufferers?
Therefore, allergic rashes occur more often in well-fed than in thin, undernourished children and adults. Treatment of household allergies consists of following a dietary regime, eliminating completely or partially allergenic products (food and household chemicals), observing temperature conditions (the air temperature in rooms for allergy sufferers should not be higher than 20°C) and taking personal and household hygiene measures.
A person wearing airtight, dirty clothes in hot weather can cause a phenomenon called heat rash (widespread in infants). In this case, small red blistering spots with transparent contents may appear on the neck, shoulders, and back, which are slightly itchy, but there is no fever or any other painful signs. Miliaria itself is not dangerous, but inflamed skin provides an opportunity for various microbes to enter the body. Therefore, in the heat, you need to take water treatments in a timely manner, use soda compresses (a teaspoon of soda per glass of boiled water) to reduce itching. For antiseptic treatment of prickly heat elements, a weak (slightly pink) solution of potassium permanganate is suitable.
How to treat?
To treat papular and pustular rashes, different methods are used: medications, folk remedies, and herbal medicine. The choice depends on the type of disease diagnosed.
For greater effectiveness, complex treatment is indicated. After eliminating the acute condition of a skin disease, spots and scars may remain on the body. To remove them, biorevitalization, mesotherapy, laser therapy, and grinding are used.
To treat dermatological diseases, medications of different effects and release forms are used. Bacterial, viral, and fungal skin lesions are treated with antimycotics, antibiotics, and antiviral agents.
To relieve swelling and redness, anti-inflammatory and healing gels and creams are prescribed. To increase the body's defenses, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes.
For liver, intestinal and gastric disorders, medications are used aimed at restoring the functioning of the organ (hepatoprotective drugs, probiotics).
Alternative medicine also provides a good healing effect. Herbal medicine is carried out and the healing properties of various products are used. Traditional healers recommend many recipes to combat spotty rashes on the skin.
The most effective folk remedies:
- one nutmeg, a little galangal and ginger, pour alcohol. Place in a warm place for a couple of days. Wipe the affected areas of the body with the prepared tincture. Additionally, it is recommended to drink a decoction of elderberry and yarrow flowers, one cup per day;
- Pour a tablespoon of oak bark into a glass of boiling water and simmer for a quarter of an hour. After cooling, strain the liquid. Wipe damaged tissues three times a day;
- lubricate the spotty rash with viburnum juice. Additionally, you should take an infusion: grind the berries and pour boiling water over a tablespoon. Leave for five hours and strain. Drink 150 ml 4 times a day;
- mix 100 g of purified sulfur and 300 g of pork fat. Apply to the affected area of skin until the spotty rash disappears.