Psoriasis is a severe systemic pathology that affects not only the skin of the body, face, and scalp, but can also spread to internal organs. Unfortunately, the nature of this disease has not been fully established (it is generally considered multifactorial - that is, one in which several determinants are “to blame” for its development).
It is impossible to completely get rid of psoriasis.
Patients with the corresponding diagnosis are prescribed complex drug therapy, the main goal of which is to prevent relapses of the disease. In addition, treatment should minimize the discomfort that the notorious psoriatic plaques create for the patient.
Causes of psoriasis on the hands
Among the key causes of the disease are:
- genetic predisposition;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune mechanism;
- endocrine problems;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diabetes;
- past viral and infectious diseases;
- metabolic problems; prolonged or severe stress;
- regular contact with harmful chemical elements (including those found in cosmetics);
- skin injury.
Psoriasis can also be caused by poor diet, alcohol and cigarette abuse, and a long course of strong medications (for example, antidepressants and steroids).
The risk group includes people with a tendency to allergic reactions.
With psoriasis on the hands, the causes and treatment are closely interrelated, photos of the variety of manifestations of this disease are proof of this.
Find out more
Stages of psoriasis on the hands
Since this disease is chronic, it has a certain progression.
In total, there are three key stages in the development of pathology:
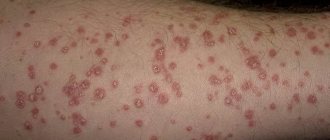
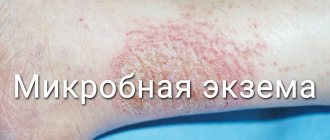
- Progressive or initial. Several reddish spots form on the hands, shoulders, between the fingers or in the fold areas. They are accompanied by peeling, swelling of the skin and intense itching. Gradually the number of formations increases. Photos of the symptoms clearly demonstrate how psoriasis begins on the hands.
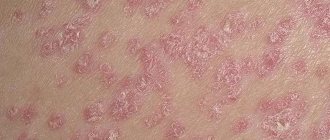
- Stationary. No other formations are formed, and existing ones are covered with silvery scales, which are easy to remove. The itching is either significantly reduced or goes away completely.
- Regression stage. External manifestations weaken and gradually disappear. Sometimes pigmentation may appear at the site of the rash.
With each new exacerbation, all three stages are repeated. You can see what psoriasis looks like on your hands in the photo.
The disease may not make itself felt from 2 months to several years.
Course of the disease
The disease is conventionally divided into 3 stages, each of which develops with different symptoms and speed of spread, regardless of where psoriasis appears - on the fingers, elbows or palms:
- The progressive stage is characterized by the fact that the papules have a bright red color, and they peel especially intensely. During this period, the skin is most susceptible to the appearance of such formations, so any damage to the epidermis leads to the formation of new rashes in these places. At this stage, the patient suffers from itching and burning in the affected areas.
- During the stationary stage, the formation of new papules stops and they begin to acquire a bluish tint and almost stop peeling. Itching and burning on the skin stop.
- The third stage is regression. When it comes, the papules resolve and the peeling stops. This leaves a pale pink spot on the skin, slightly lighter than areas of the skin not affected by psoriasis.
Subtypes of psoriasis on the hands
Hand skin psoriasis has four main types:
- Pustular form. Usually localized on the forearms and palms. The formations have the form of small reddish spots with purulent content. They are called pustules. Pustules can merge with each other to form larger formations. This subtype is considered one of the most dangerous varieties, since it can lead to complications in the form of severe swelling of the palms and the development of nephropathy.
- Drop-shaped. Usually the rash appears on the upper areas of the arm, in the shoulder area. The outlines of the formations resemble drops.
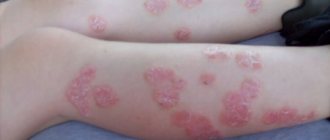
- Plaque form. Or classic. Reddish plaques appear on the skin, sometimes merging with each other.
- Nail psoriasis. Vertical or transverse lines of a light shade are formed on the plate. The skin around the nail becomes thicker and denser. Over time, the nail plate is destroyed. Treatment for fingernail psoriasis is usually no different than usual.
Among other things, psoriatic lesions are classified by location. It can affect the shoulders and forearms, palms and back of the hands, fingers, interdigital area and nails. For different types of psoriasis, photos of symptoms on your hands will help you understand the differences.
Psoriasis on the hands. Symptoms
Regardless of the subtype of the disease, psoriasis has common common symptoms:
- small or medium-sized spots that slightly rise above the skin (with psoriasis on the hands, photos of the initial stages clearly demonstrate the features of the spots);
- tendency of spots to merge with each other;
- red or pinkish undertone of formations;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- peeling of the skin and the appearance of silvery scales on top of the rash;
- cracking of the epidermis;
- itching or burning;
- joint pain;
- dry skin.
If the disease affects the nails, their color and structure change. In this case, photos of the symptoms of psoriasis on the hands and treatment can be found on the Internet.
If the formations are damaged, painful ulcers may form in their place. Often the patient experiences internal discomfort.
Symptoms of psoriasis
The main symptoms of psoriasis are papules that appear on the bends of the elbow on the outside of the arm. These formations look like small tubercles no larger than 2 mm in size. Their surface is covered with light white scales, which fly off when touched by hands or clothing. A number of symptoms are precisely associated with these papules:
- When the papule is scratched, white scales become abundant, even if there were practically none before the mechanical action. This phenomenon is observed if a stearin stain is disturbed. The effect with papules is called the stearin stain effect.
- After the papule is freed from the scales, a thin film is found underneath them.
- If you remove the thin film covering the papule, blood will begin to appear on its surface, which appears on the surface in the form of small droplets. This is called the blood dew effect.
Psoriasis papules tend to grow very rapidly; they unite into large spots and spread to the palms of the hands, fingers, sometimes completely covering them.
Treatment of psoriasis on the hands
For psoriasis on the hands, treatment is carried out comprehensively, combining several measures at once. Among them:
- Local medications. Ointments or creams containing active ingredients. Previously, cytostatics and hormone-containing compounds were used. Now preference is given to retinoids and all kinds of sedatives. The main tasks of local preparations are to exfoliate dead skin particles, eliminate swelling and inflammation, and relieve redness and itching. The products are actively used for psoriasis on the hands at the initial stage.
- Systemic medications. Products for internal use. Affects the immune system and inflammatory processes. They are used less frequently - in advanced cases or when local therapy does not produce the desired results.
- Physiotherapy. Procedures such as laser exposure, PUVA therapy, cryo- and ozone therapy, bioresonance therapy and ultraviolet irradiation are used. There are photos of psoriasis on the hands before and after physiotherapy.
- Diet. It is of an eliminative nature. Potential allergens and harmful foods such as sweets and smoked foods are removed from the diet. Ideally, the menu is drawn up by the attending physician.
Treatment is usually self-administered with periodic hospital visits. However, if the disease is severe, the patient may be transferred to a hospital.
Treatment of psoriasis on the hands. Help with folk remedies
It is better to resort to traditional methods only in the first stages of the disease. In the case of psoriasis, photographs of the initial stage on the hands can be found in abundance on the Internet.
Home remedies include the following recipes:
- Herbal collection. Chamomile flowers, St. John's wort, parts of yarrow, calendula flowers, string and leaves of celandine are taken in equal parts. Mix everything and pour boiling water over it. Afterwards, the composition is kept in a water bath for 20-30 minutes and cooled. The decoction is used as lotions, compresses and baths. It can also be taken orally - 50 ml three times a day. Plants relieve inflammation, relieve itching and help improve metabolism.
- Egg ointment. Take the yolks of boiled eggs and place them in a frying pan over low gas. The yolks should become oily. They are then allowed to cool and applied to the rash areas for 15-20 minutes. Rinse off with lukewarm water. You can replace it with a decoction of herbs.
- Propolis ointment. Take 200 grams of pork fat and 100 grams of propolis. The ingredients are placed in the oven to completely melt. Then take everything out and mix it with two tablespoons of sea buckthorn oil. The cooled mixture is applied to the affected areas up to 6 times a day. The course is until the skin becomes clear.
It is worth remembering that before using any of the folk recipes you should consult a doctor. Otherwise, side effects may occur.
Treatment of psoriasis on the hands with medications
Hand psoriasis is treated with the following categories of medications:
- Soothing and moisturizing creams. As well as gels and ointments. They soften the skin of the hands, prevent the formation of cracks and alleviate symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments. Increases local skin immunity and stops inflammation processes.
- Antibacterial ointments. Additional means that prevent infection from entering the body.
- Antihistamines. Local or systemic use. They weaken the immune response and fight inflammation.
- Corticosteroids. Hormonal drugs. Indicated in severe and advanced cases. May be in the form of ointment or tablets.
- Hepatoprotectors. Medicines to support liver function.
- Sorbents. Cleanse the body of poisons and toxic substances, including potential allergens.
- Immunomodulators. Needed to harmonize the functioning of the immune system.
- Sedatives. This category includes sedatives and mild antidepressants. Needed to calm the nervous system and relieve symptoms.
- Monoclonal antibodies. They are antibodies to factors that provoke inflammation. These substances find the cells that cause psoriasis and “tag” them so that they are subsequently destroyed by the immune system. Antibodies are administered intramuscularly and only in severe cases of the disease.
How to treat psoriasis on the hands should only be determined by a doctor. Self-medication is fraught with consequences in the form of worsening symptoms and complications.
Alternative Methods
Patients with psoriasis benefit from phototherapy—exposure to ultraviolet rays of a certain spectrum and power on the affected epidermis. The method combines the following procedures :
- Narrowband irradiation. Suppresses cell growth, like hormonal ointments, but is not addictive.
- Selective phototherapy. Effective for exudative lesions of the epidermis.
- Photochemotherapy. Helps cure all forms of psoriasis on any part of the body.
- Shortwave irradiation. Used for minor damage to the skin.
Treatment of psoriasis can be supplemented with natural remedies. The following recipes can achieve a positive effect:
- Combine a tablespoon of herbal mixture, composed of equal parts of chamomile, sage, valerian, calendula and celandine flowers with 1 liter of water, bring to a boil and let cool to 37 °C. It is necessary to pour the broth into a shallow container and immerse your hands in it for 20 minutes. The procedure should be performed every other day.
- Combine 5 g of baby cream, 1 egg white, ½ tsp. dried and powdered celandine. The prepared ointment should be lubricated on the affected areas of the epidermis.
- Melt 300 g of butter in a water bath, combine with 20 g of propolis and boil the mixture until smooth. The cooled mass can be applied to rash-covered skin or used for compresses.
- Exacerbation of psoriasis of the fingers can be eliminated by taking baths with sea salt. To do this, you need to dissolve 1 tbsp. l. salt in 500 ml of warm water and immerse the brushes in the liquid for 15 minutes.
Preventive measures
After familiarizing yourself with the photo of psoriasis on the hands, treatment and possible consequences, it is natural to want to extend the period of remission.
To avoid relapses, you must:
- stop using soaps and gels with sulfates;
- limit skin contact with any aggressive cleaning agents;
- do not use rough washcloths and towels;
- regularly apply moisturizers;
- protect hands from frost, wind and strong sun;
- give up alcohol and cigarettes;
- monitor your diet;
- Rest often and avoid stress.
And the most important thing is to consult a doctor in time in case of relapses.
Causes
Despite the not fully known causes of psoriasis, doctors identify the main factors:
- Alcohol consumption.
- Skin contact with household chemicals, aggressive agents, building mixtures.
- Working with hands (carpenters, masons, builders).
- Nervous tension, stress.
- Insect bites (mosquitoes, wasps, bees).
- Overwork.
- Skin injuries.
- Long-term treatment with medications.
- Poor quality cosmetic products.
Psoriasis on the hands most often occurs in people who work in hazardous industries with chemicals, poisons, and household chemicals. Due to the negative effect on the skin and together with immunological disorders, disturbances occur in the process of renewal of epidermal cells.
Stages
There are the following stages of psoriasis:
- Stationary.
- Progressive.
- Regressive.
Initially, a red or pink papule appears, which is covered with moist scales. The area has its own clear boundaries and itching is observed. Most often, the surfaces of the elbows, the space between the fingers, shoulders, and hands are affected. Characteristic signs of psoriasis: terminal film, stearin spots and pinpoint bruising at the site of inflammation, when removing the scales. There are few rashes at the first stage, papules quickly grow and take on shape. The edges are free, and there is a scale in the center.
In the stationary stage, plaques arise and are fixed in one place . The itching goes away or is absent. The scales spread over the entire surface, the skin looks light and thinned. The disease may remain in this stage for many months.
With regression, there is a decline in the papules, cleansing of the skin, and dark spots persist for some time. After a relapse, psoriasis symptoms may worsen. Long-term progression of the disease leads to roughening of the skin on the hands, elbows, and nails.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of psoriasis is carried out by a dermatologist. The disease is easily distinguished by external signs from other dermatoses. To exclude the spread of a fungal disease, a tissue fragment is taken and examined under a microscope.
Symptoms of psoriasis:
- Stearic stains - when the plaque is removed, a clear liquid appears on the surface, and peeling increases.
- Terminal film - after removing the scales, there is shiny and thin skin underneath.
- Bloody dew - after scraping the plaque and the phenomenon of terminal film, stearin stain, drops of blood appear on the surface.
If these three symptoms are detected, we can say that it is psoriasis. Additionally, a comprehensive examination is performed to identify the causes and extent of skin damage, and predict complications.
Impact of psoriasis on quality of life
Psoriasis can reduce the quality of life. Plaques located on open areas of the body repel others with their appearance. Itching during periods of exacerbation deprives a person of sleep and peace, knocking him out of the usual rhythm of life. It is difficult for patients suffering from psoriasis on their hands to find work. They are forced to give up doing what they love . The owner of a cafe, restaurant, or beauty salon will not hire such an employee. Many people do not know that psoriasis is not contagious, which often leads to conflict situations. Psychological pressure, self-doubt, refusal to communicate with loved ones, negatively affects the course of the disease. Depression is a common cause of exacerbation of the disease.
Modern medicine makes it possible to control any stage of psoriasis. And with an experienced specialist, exacerbations are rare and short-lived.