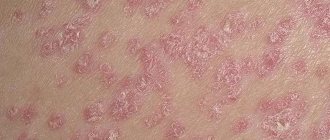
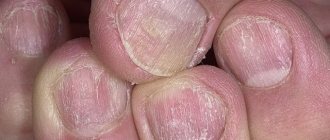
Features of the disease
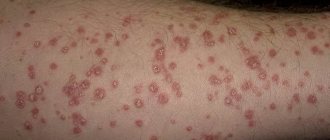
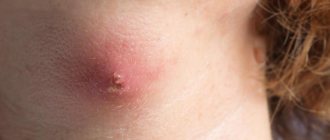
Urticaria is a skin disease in which an allergic reaction occurs due to exposure to a specific agent. It manifests itself in the form of redness and swelling of individual areas of the epidermis. A little later, blisters ranging in size from 1 mm to 5-7 cm form at this site. The foci of the pathological process are very similar to nettle burns. This disease can occur in both adults and children.
Demographic urticaria, or more precisely, dermographic urticaria, is considered a not very common pathology of the skin. Inflammation never occurs at the site of the allergic reaction. The disease is not accompanied by headaches or loss of consciousness. Symptoms usually go away within a few hours, so many people do not rush to see a doctor for help. In fact, consulting a doctor will not be superfluous. He will be able to determine the etiology of the disease, and in case of severe forms, he will prescribe the correct treatment.
Causes of urticaria
Hives occur when histamine and other compounds are released from mast cells, which are normally found in the skin. Histamine causes fluid to leak from local blood vessels, causing the skin to swell.
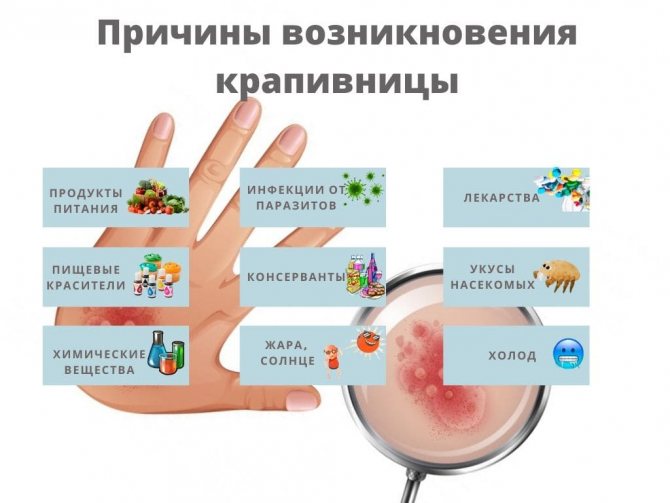
Table: Causes of urticaria
Hives are common but are not considered contagious. Despite the irritation, the hives go away on their own. Skin rashes can be caused by an allergic reaction to things such as:
- Food;
- infections caused by various organisms;
- medicines;
- food colorings;
- preservatives;
- insect bites;
- chemical substances;
- heat;
- cold;
- Sun;
Sometimes hives can occur due to changes in diet, cleaning products and cosmetics. If an infectious disease is not the cause of hives in a particular person, then it is possible that the infected contact may progress to stress, but stress itself does not cause hives.
Main Causes of Skin Disorders
The appearance of rashes on the skin is most often caused by various mechanical influences. These include insect bites, scratching and rubbing, and rubbing of clothing. Young children are also not spared from demographic urticaria. Their epidermal reaction may be a consequence of active games, during which they receive scratches and bruises.

The exact causes of the development of the disease could not be established. However, doctors identify a whole group of factors that contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- hereditary predisposition;
- frequent stress;
- pathologies of internal organs;
- taking NSAIDs;
- disruption of the thyroid gland;
- the presence of neoplasms in the body.
Often the pathological process is accompanied by diseases that significantly weaken the body’s immune forces.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by an allergist, dermatologist or immunologist . Doctors interview the patient to find out the duration and frequency of symptoms. The allergist determines what irritants the patient reacts to and whether he has been in contact with them recently. For this purpose, a survey and relevant surveys are carried out. It is important to clarify whether the patient has undergone drug therapy.
The skin is examined for other dermatological diseases. The following diagnostic methods are used:
- Complete blood count, urine test, stool test.
- Analysis for ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
- Skin biopsy.
- Study of the speed of reaction of the epidermis to impact. Press on the skin with a blunt object, leaving a mark.
- The skin is irritated for five minutes with ice or cold water.
If there is a suspicion that the cause of the disease is problems with the gastrointestinal tract, the patient is referred to a gastroenterologist. To determine the condition of the thyroid gland and the possible presence of diabetes mellitus, you will need to consult an endocrinologist. An immunologist identifies immune diseases and finds out whether the body has been weakened.
First manifestations
What are the symptoms of demographic urticaria? The disease does not affect the general well-being of a person. It is not characterized by symptoms that appear during standard allergic reactions. These include watery eyes, nasal congestion, sneezing, and difficulty breathing.
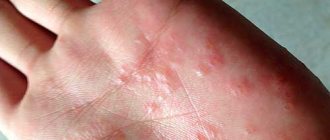
Both adults and children with demographic urticaria experience similar symptoms. First, marks appear at the site of skin contact with the irritant. These can be stripes or other shapes. In their shape, the marks accurately reproduce the pattern that remained on the skin after exposure to the irritating agent.
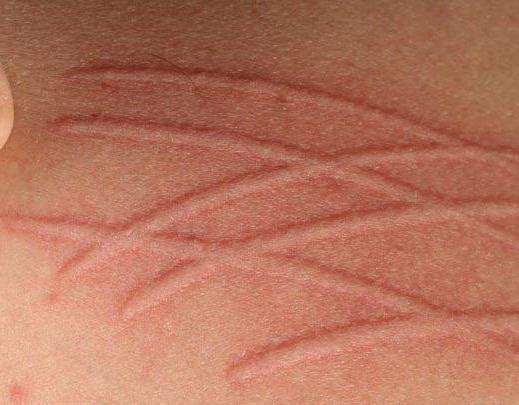

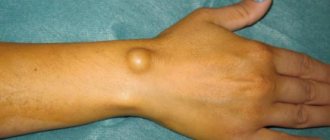
After some time, the damaged area acquires characteristic swelling. The streaks or other marks first turn red, then swell and begin to rise above the surface of the skin. Sometimes scars or blisters appear. These symptoms may persist for several hours.
Mechanical urticaria: photos and symptoms
It is worth immediately noting that the clinical picture in this case is very typical. Mechanical urticaria is difficult to confuse with other diseases.
We recommend reading: Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy: what is it, at what stage is it done, what dopplerography will show, interpretation and analysis norm
After contact with an allergen, redness appears on the skin. Subsequently, one can observe the formation of a linear, convex rash, and then blisters with transparent contents. The whole process is accompanied by very unpleasant sensations - patients complain of severe itching, burning and even pain.
When should you see a doctor?
If you suspect demographic urticaria, you can first perform a simple test at home. To do this, you need to scratch a grid in the forearm area with a well-sharpened pencil. After a few minutes, white stripes will first appear in this place, and then pink marks. They may rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Normally, such marks disappear after about an hour. In addition, the strips should not itch or hurt. This simple test allows you to determine whether you have demographic urticaria. A photo of the results of the procedure itself is presented just above.
After diagnosis at home, you must definitely visit a dermatologist. Detection of the disease usually does not cause difficulties. To confirm the final diagnosis, the doctor only needs to examine the patient’s epidermis and do several skin tests. Sometimes consultation from outside specialists is required. For example, a parasitologist helps identify the presence of pathogenic flora, and an endocrinologist evaluates the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Skin prick tests and contraindications
Another specific method for identifying allergic diseases is the prick test. This procedure helps to identify a clinically significant allergen and determine the degree of sensitivity of the body.
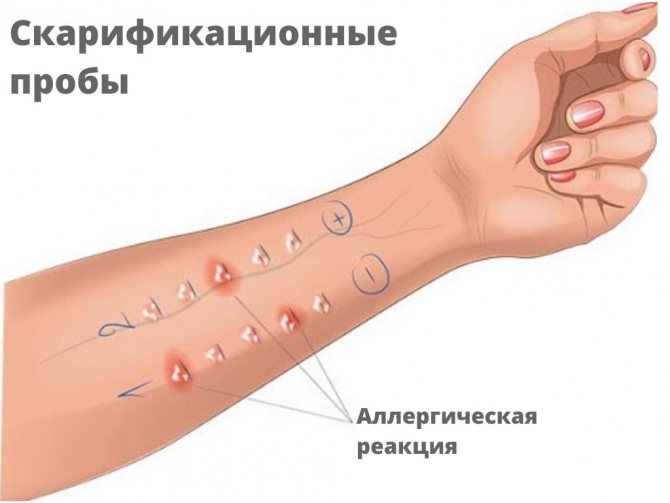
Scheme of carrying out scarification tests
A scratch test or puncturing helps determine the skin's reaction to exposure to household, epidermal, pollen and fungal allergens. This testing also allows you to identify allergies to food, pet dander, mold, soil, pollen, dust mites and others (about 40 allergens). Scarification skin tests are quite simple and can be easily tolerated by both adults and children.
Carrying out scarification tests. Before the procedure, the site where the test will be performed is treated with 70% ethyl alcohol (usually in the back in children, on the back of the forearm in adults). After treatment, marks are made on the skin at a distance of 4–5 cm from each other.
A small scratch is applied to each selected area of skin using disposable lancets with allergens fixed on them.
At the same time, tests are carried out with histamine and saline in a similar way. If no reaction to histamine is detected on the skin, the test will be negative even if allergopathology is detected. Test results appear in 15–20 minutes. If you are allergic to the test allergen, a swelling appears at the site of the incision, similar to a mosquito bite. Along with the swelling, redness and itching may occur. In some cases, a blister filled with a liquid substance forms at the site of contact with the allergen. Afterwards, the swelling is carefully treated with alcohol. How samples are evaluated:
- A negative result (-) occurs if the size of redness at the site of contact with the allergen does not exceed 1 mm.
- A questionable result (±) if a papule (swelling) forms on the skin.
- A weak positive result (+) if a papule or blister with a diameter of up to 3 mm forms on the skin.
- A positive result (++) if the papule and blister reach a diameter of up to 5 mm.
- Strongly positive (+++) if the papule and blister reach a diameter of 10 mm.
- Very strongly positive (++++), if the diameter of the swelling and blister exceeds 10 mm, extensive redness develops, and general reactions are observed.
Sometimes, scarification tests give false results. This may be due to violations of the technique of performing skin allergy tests, methods of storing and transporting allergen extracts. Contraindications:
- Exacerbation of an allergic disease;
- Acute infectious pathologies;
- Exacerbation of foci of chronic infection;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Oncopathology;
- Psychosomatic disorders;
- AIDS;
- A history of acute reaction to a specific antigen;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Early childhood;
- Taking antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids and mast cell membrane stabilizers.
If symptoms are mild, treatment may not be needed. However, treatment may help relieve severe itching, severe discomfort, or lingering symptoms.
Drug therapy
As mentioned above, specific treatment for this disease is extremely rarely required. Symptoms usually disappear on their own within a few hours or days. However, for many patients they still cause aesthetic discomfort. Therefore, they are interested in the question of how to treat demographic urticaria.
Therapy should begin with first generation antihistamines. These include the following medications: Zyrtec, Tavegil, Claritin, Cetirizine. They relieve the symptoms of the pathological process, and noticeable relief occurs after 2-3 hours. Therapy is usually reduced to a single pill before bedtime.

If for some reason the patient refuses to take the tablets, they can be replaced with ointments. For example, Fenistil gel perfectly relieves itching and inflammation. "Drapolen Cream" effectively fights scars and small scars characteristic of such a pathology as demographic urticaria.
Treatment of the chronic form of the disease is recommended with second-generation antihistamines. These are drugs such as Tagamet, Zantac and Bricanil. When the listed medications do not give a positive result, the prescription of oral steroids and physiotherapy is considered appropriate.
It should be noted that only a doctor can select specific drugs for treatment. Self-therapy often ends in disastrous results.
Treatment
If, as a result of the diagnostic measures carried out, it is established that dermatographic urticaria occurs against the background of a chronic disease, then it must be cured first. In general, the mechanism for eliminating the symptoms of autographism does not differ from the treatment of other forms of urticaria and includes the following components:
- taking antihistamines;
- use of external antiallergic agents;
- the use of drugs to eliminate general symptoms;
- folk remedies.
Antihistamines
For uncomplicated forms of urticarial dermographism, first-generation antihistamines are prescribed to eliminate redness, skin rashes, swelling and itching:
- Diphenhydramine;
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Diazolin;
- Fenkarol.
Having a quick effect, these medications help get rid of the symptoms of urticaria in 3-4 days. The disadvantage of first generation antihistamines is the large number of side effects that make their use impossible if urticaria is diagnosed in a child or a pregnant woman.
In the case of chronic recurrent urticaria, it is more advisable to resort to second or third generation antihistamines. These include the following tablets and syrups:
- Clarotadine;
- Kestin;
- Claritin;
- Rupafin;
- Zyrtec;
- Gismanal;
- Desal;
- Xizal;
- Erius.
These drugs have a prolonged effect, so they need to be taken once a day. Claritin and Zyrtec can be used during pregnancy, but only under the supervision of a physician for a short time. Desal and Erius in syrup form are used in pediatric practice. Contraindications are problems with the cardiovascular system and chronic liver diseases.
In the absence of the expected result from the use of these medications, as well as in severe cases of the disease, hormonal medications are used - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone.
Help from traditional medicine
A mild form of the disease often does not require specific therapy. To eliminate unwanted symptoms, you can use recipes from traditional healers.
A decoction of the string is particularly effective. It should be brewed like tea and consumed in small portions throughout the day. Celery juice is no less useful. You should drink 1/3 cup of this delicious medicine every day. You can also soak a cotton pad in this juice and treat the affected areas with it.

Prevention measures
Specific measures to prevent the disease have not been developed, since the exact causes of its occurrence are still unknown. To prevent allergic skin reactions, doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- give preference to outfits made from natural fabrics;
- minimize stressful situations;
- refrain from visiting saunas;
- do not use hard washcloths;
- undergo preventive examination.
Remember that if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, it is easier to cure any disease. Be healthy!
Diet
- Fish and seafood;
- Various types of cheeses, in particular hard ones, as well as dairy products;
- Strong alcoholic drinks and drinks containing caffeine;
- All types of smoked meats.
We recommend reading: Tablets for gastritis: a list of effective medicines
In addition, if you exclude the above products, doctors recommend diversifying your diet with such products as:
- Coarse bread products;
- All types of nuts except coconut;
- Green olives;
- Pumpkin (can be eaten raw or cooked) and avocado.
Nutritional adjustments are not strictly necessary, but are still recommended for complete recovery.
This video will tell you how to cure hives: