Dermatology
Dmitry Polyanskikh
2362
Psoriasis is considered one of the common skin diseases, which usually manifests itself in people at the initial stage on the body in the form of a minomorphic rash covered with grayish scales (psoriasis photo). The pathology often develops chronically, with remission, relapses, and even psoriasis on the butt is possible. Psoriasis on the body causes suffering to a person, provokes severe itching, burning, etc. How to treat this disease?
Psoriasis: initial stage
In the initial stage of ordinary psoriasis, thickenings appear: red spots that are raised above the surface of the skin and gradually become covered with scales and crusts. Depending on the treatment and lifestyle, new rashes appear or do not appear.
The initial stage of vulgar psoriasis on the face
The initial stage of pustular psoriasis is characterized by papules - vesicles with clear yellowish or white liquid. They spread over a large area as the disease progresses, and the skin underneath is thickened and red.
Pustules with fluid
With psoriatic erythroderma, erythema first appears - areas of the skin that become red, engorged and painful. This type of psoriasis is the most dangerous; skin lesions sometimes cover almost the entire body.
Psoriatic erythroderma in the initial stage
Seborrheic psoriasis begins in most cases from the scalp, and then moves to other areas - ears, neck, nasolabial folds, beard.
Seborrheic psoriasis in the initial stage
Psoriatic arthritis most often begins with joint pain (sometimes it can last for years), a general deterioration in health, fever, and increased temperature. The disease rather manifests itself internally; externally, only the joints are deformed.
Swelling of fingers due to psoriatic arthritis
Guttate psoriasis begins with a rash of small red spots all over the body. It may appear in a child after an infectious disease (most often).
Initial stage of guttate psoriasis
Classification of pathology
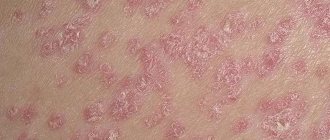
Patchy psoriasis causes patches to appear on different parts of the body, which gradually become dry, thickened plaques. Psoriatic plaques are located symmetrically, gradually increase, merge and cover wide surfaces. This is how psoriasis occurs on the back, stomach or chest.
With guttate psoriasis, individual small plaques appear on the abdomen, on the skin of the extremities, on the back or on the head under the hairline. Often they do not require treatment and go away on their own.
Inverse psoriasis is the most difficult to treat. The main areas of localization of rashes are skin folds. Smooth spots appear under the arms, in the groin area, under the breasts. In seborrheic psoriasis, the affected areas are covered with a scaly layer.
Nail psoriasis causes nail beds to peel, change color, and separate the nail bed from the top layer of skin at the fingertips. Often occurs without skin rash.
Psoriatic erythroderma
Psoriatic erythroderma often begins with fever, redness and thickening of the skin:
How to cure armpit rash in adults?
Treatment of such a pathological phenomenon depends on the causes of its development. Skin diseases such as eczema, psoriasis, candidiasis and others require a special approach. Patients are prescribed local anti-inflammatory and oral antibacterial or antifungal agents, which help eliminate armpit rash and other symptoms that accompany this pathology.
Skin rashes should be treated not only in the presence of certain diseases, but also in cases of banal allergies. After all, such reactions cause enormous discomfort to the patient, significantly reducing his quality of life.
Thus, if a person has allergic dermatitis, then he must avoid any contact with the active allergen. To identify it, you need to undergo a series of tests. Also, a patient with a similar problem may need to be prescribed a correct diet and maintain a normal daily routine. In addition, some doctors do not recommend consuming foods containing nickel, as this will only worsen a person’s already serious condition.
READ ALSO: Hormonal rash on the face of newborns: what it looks like, treatment, when it will go away
In the event that a skin rash occurs due to banal dryness of the skin, the patient is prescribed salicylic petroleum jelly. This ointment should be applied to the armpits three times a day.
If the rash is accompanied by swelling, the patient may need:
- special baths into which boric acid is added;
- various lotions, including herbal ones;
- antihistamines (for example, Suprastin and others).
It should also be noted that if you have a rash in the armpits, some experts recommend using topical hormonal ointments. However, you need to be careful when using such drugs. Very often they provide only a temporary effect, and after their use other means are ineffective.
Guttate psoriasis
If you find small red spots all over your body or in some areas, check it out - it could be guttate psoriasis.
Features of the pathology: causes
This disease is multi-etiological, with clear clinical symptoms. It is important to establish the origins of the disorder that caused the development of this disease.
Psoriasis can appear in childhood or adulthood, in females or males, the first stage - the rash looks like dry red spots raised above the skin, called psoriatic plaques. Often this rash forms on the elbows, where the knees bend, psoriasis is possible on the buttocks or psoriasis under the arms - areas of strong friction. The disorder can manifest itself on the tissues of the external genitalia, on the scalp, on the soles/palms. A rash may form on the face. At the initial stage, this rash on the body itches, is characterized by a wave-like course, with exacerbations and remissions. If left untreated, the disease can spread to other skin areas of the body. The severity of the disease varies - from local damage to complete coverage of skin tissue with plaques.
The disease usually appears in people under 25 years of age. This disorder can be caused by various factors - stress, weakened immunity, heredity, etc. The exact reasons that provoke the appearance of this disease are still unknown to medical specialists.
The main phenomena causing the formation of pathology:
- Harmful addictions (alcohol, smoking);
- Allergy;
- Changes in climatic conditions;
- Long-term use of medications;
- Increased dryness of the skin;
- Various infections;
- Injury to skin tissue - burns, mechanical damage;
- Heredity;
- Stress, psycho-emotional disorders;
- Body hypothermia, overheating.
Psoriasis in children: initial stage
Guttate psoriasis is common in children; rashes often appear in the child in areas of friction (with folds of skin, under diapers).
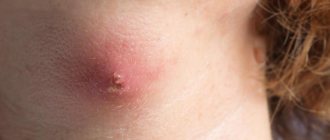
Furunculosis
It is quite difficult to call such a pathology a rash. Indeed, with its development, only one or several boils appear, which are purulent inflammation of the follicle (acute), connective tissue and sebaceous gland. A distinctive feature of such a sore is the presence of a purulent core. Very often, furunculosis affects the area under the arms. It is preceded by itching and redness in the area, as well as pain and noticeable lumps under the skin.
READ ALSO: A child has a chin rash: causes, diagnosis, treatment
conclusions
Psoriasis is a severe chronic disease that affects many systems of the body, not just the skin.
Treatment of psoriasis should be comprehensive and take into account the severity and individual characteristics of the patient. Choose methods that have fewer side effects and are closest to natural ones. Among the effective methods of treating psoriatic rashes, we recommend:
- Non-hormonal ointments for psoriasis. They help relieve inflammation, redness and itching, and remove peeling. It is preferable to use such ointments to treat a child.
- Shampoos for psoriasis on the head. Eliminate crusts and flaking from the scalp.
- When you have eliminated peeling and the first symptoms of psoriasis, use phototherapy to consolidate the results and achieve long-term remission. Ultraviolet treatment is a natural method that has been used since ancient times. The most effective and affordable methods: ultraviolet 311 nm (suitable for children from 3 years old) and PUVA therapy for the treatment of psoriasis.
- Follow a diet for psoriasis. At a minimum, exclude fried, salty, and junk foods. Ideally, follow Dr. Pegano's diet.
- Monitor your emotional state. Do more of the things that you enjoy. Walk in the fresh air, enjoy life, listen to music.
Factors that trigger the development of a rash
Why does a rash appear under the armpits in adults? Most often, this pathological condition is observed due to a number of reasons.
Neglect of personal hygiene rules. It is no secret that many people suffer from excessive sweating. Most often, this condition is associated with hormonal imbalances in the body, excess weight and working conditions. In this case, it is not enough for a person to take a bath or shower several times a day. If you do not carry out any additional hygiene procedures, then a rash under the armpits in adults will not take long to appear.
Depilation. Many women know that improperly performed depilation leads to severe skin irritation and itching. Therefore, after such a procedure, you should definitely use an emollient cream or lotion (preferably for children).
Frequent use of antiperspirants. A rash under the armpits in adults very often occurs after using roll-on, gel and other deodorants. What is this connected with? The fact is that such products can cause blockage of pores and glands in order to reduce sweating. Often this effect on the delicate skin of the armpits causes irritation, redness, burning and itching.
READ ALSO: Body skin rash - how to treat? Causes and treatment of skin rashes
Allergy to hygiene products. Some types of bath foams, body creams, and shower gels can provoke the development of an allergic reaction, which manifests itself in severe rashes on the skin. This pathological phenomenon is especially often observed after the use of depilatory creams, which are considered to be quite gentle means used to get rid of excess “vegetation” on the skin.
Irritation from clothes. A rash under the armpits in adults (a photo of the problem in question is presented in this article) very often appears due to wearing too tight clothes, which strongly rub the delicate skin. As a result of such friction, a person begins to experience severe irritation and itching.
The best remedies for Psoriasis
Add to cart
Antipsoriasis cream 990 rub.
Add to cart
Magnipsor ointment RUB 1,490
Add to cart
Ultraviolet lamp Dermalight ® RUB 14,900.
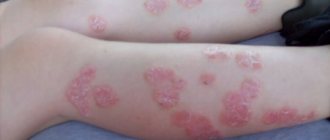
Psoriasis on the knees: symptoms and treatment (photo)
Psoriasis on the knees, the photo of which shows all the features of the pathology, is a skin disease accompanied by the formation of inflamed, scaly plaques. The bends of the extremities of the knees and elbows are most often affected. The disease is also called psoriasis vulgaris.
Psoriatic rashes on the knees and elbows bring the greatest discomfort, because in these places the skin is mobile, and this causes additional trauma to the affected areas, as a result, the inflamed tissue takes a very long time to heal.
Roughly speaking, even if it is possible to remove the signs of psoriasis from the outside and put the skin in order, inside the body the disease continues to devour the autoimmune system, which provokes severe diseases, many of which are fatal. Particularly scary is the fact that psoriasis can provoke cancerous tumors.
The only remedy that is currently available for self-use by patients with psoriasis is the special product “PSORIDEL”, which is available at a discounted price - 1 ruble. Read the details in the official source.
The essence of the problem
The disease begins as small areas of red rash. It gradually covers larger and larger areas, merges, turning into plaques with clear boundaries. Then these places dry out, dry out and begin to peel off. Skin lesions are accompanied by itching and inflammation of the plaques when they become infected.
Psoriasis on the elbows and knees has some differences compared to rashes on other parts of the body; the plaques on these areas are more covered with white scales. It is completely impossible to cure this disease, because it is a systemic pathology characterized by periods of exacerbation and attenuation of symptoms.
Treatment of psoriasis is reduced to alleviating its manifestations and prolonging the remission stage. The main feature of this pathology is that the same treatment affects everyone differently - for some, during a period of calm, all rashes and symptoms disappear, while for others, on the contrary, another relapse is provoked. The exacerbation usually lasts for several days, then a gradual decrease in the malaise begins. The duration of remission is also different for each patient - from several days to a year or more.
Psoriasis on the legs - possible causes
Currently, medicine has not identified obvious causes of the disease. There are 2 theories according to which it is based on genetic pathologies in the body. The first theory is based on the statement about the hereditary factor of the disease, i.e. psoriasis is transmitted through parents. Adherents of the second theory hypothesize that rashes are provoked by a mutation of genes in the human body itself, i.e., throughout the life of any individual, signs of the disease may appear. According to medical statistics, the pathology occurs in 15% of people of any gender and age.
Psoriasis can be triggered by various factors:
- psychological experiences, sudden nervous shock, stress;
- abuse of alcohol and tobacco products;
- general hypothermia or excessive overheating of the body;
- skin injury as a result of cuts, burns, exposure to chemical irritants;
- development of inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- weak immunity;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, pancreatic insufficiency, etc.);
- impaired metabolism;
- allergic reactions;
- long-term treatment with various drugs;
- excess weight, etc.
The disease occurs in several stages:
- The initial stage of psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of watery red papules affecting the knee or elbow bends.
The patient complains of itching in areas where the skin is affected. - At the second stage, the itching intensifies, plaque lesions become inflamed and painful. The affected skin on the moving knee and elbow joints cracks, bleeds and grows into larger spots.
- The third phase of relative calm is manifested by bluish skin in the affected areas. New rashes do not appear, but old ones do not heal well. Then regression occurs, clinical signs gradually recede, plaques disappear, and the structure and color of the skin are restored. It is important to note that treatment must be continued at all stages of the disease, especially during remission.
Treatment of psoriasis on the knees
The doctor should think about how to treat psoriasis: therapy is individual for each patient. Drug treatment is mainly aimed at healing skin plaques and preventing new ones from breaking out. Various medicinal ointments are widely used - sulfur, tar, salicylic.
The affected areas are lubricated with ointments and gels containing corticosteroids (Hydrocortisone).
To relieve pain and itching, oral painkillers and antihistamines (Kalovit, Claritin, Zodak, Tavegil, Zyrtec, Diazolin) are prescribed. Immunomodulators and vitamin complexes (vitamins A, E, C, D3) are prescribed as maintenance therapy. Vitamin D3 promotes rapid healing and regeneration of skin cells. To restore the patient's neuropsychological state, antidepressants and sedatives are used.
To relieve allergic reactions and remove toxins from the body, the intestines are cleansed through enemas; diuretics are also prescribed to remove waste products from the kidneys and liver, and to relieve swelling of the skin.
Have you been trying to get rid of PSORIASIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of psoriasis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Traditional methods of treating illness
Herbal medicine, in combination with traditional treatment, has a beneficial effect on alleviating the symptoms of psoriasis and increasing the duration of the calm period. Herbal teas made from St. John's wort, nettle, and dandelion leaves are very useful. For internal use, decoctions of bay leaves, dill seeds, herbal mixtures of peppermint, calendula, immortelle, milk thistle and parsnip seeds are used.
Daily compresses with birch tar with the addition of celandine and garlic tincture are recommended. On your knees and elbows you can use baths of sea salt, copper sulfate, decoctions of string and yarrow, coltsfoot, from a collection of herbs (valerian and chicory roots, celandine leaves). Homemade ointments prepared with the addition of propolis and natural honey have a good healing effect.
Prevention of psoriasis
As already noted, treatment and prevention aimed at preventing new exacerbations must be continued at all times. The basic principles are as follows:
- you should try to avoid situations that provoke nervous disorders and stress;
- follow the basic principles of a healthy diet - eliminating fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods from the diet, eating fresh fruits and vegetables high in fiber, avoiding foods with cholesterol;
- To calm the nervous system, a full, healthy sleep is required - at least 8 hours;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol, fast food, sedentary lifestyle);
- protection of the skin from various damages and chemical burns;
- wear underwear and clothes made from natural fabrics;
- regular walks in the fresh air, sports;
- control your own weight;
- Regular visits to the doctor's office and monitoring of cholesterol and blood glucose levels;
- timely treatment of all diseases.
It is important to remember that psoriasis is a chronic disease. Compliance with medical recommendations and competent treatment will help you easily endure exacerbations and enjoy a period of remission of the pathology without affecting the patient’s quality of life.
Early symptoms in different places
Traditionally, the disease first appears on the extensor surfaces of the knee and elbow joints. These are favorite places for dermatosis. First, small pathological areas are formed that rise slightly above the skin level. Over time they grow. Psoriasis appears more often after severe stress or an infectious disease.
Psoriasis and its initial stage, which is localized on the extensor surfaces of the joints, are often accompanied by redness of areas of pathologically altered skin. This is due to the constant friction of plaques on clothing.
Face and neck
The initial stage of psoriasis, the symptoms of which develop in the face and neck, have a number of features:
- Limited pathological elements. They are small and rarely merge with each other.
- Typical localization is around the eyes, on the earlobes, in the nasolabial folds, and eyebrows.
- Possibility of complete absence of itching.
The rashes look like small papules with all the features characteristic of psoriasis (silver scales and a triad of phenomena).
Scalp
Typical plaques in the early stages often appear in the scalp area, along the hair growth line. A specific reddish rim covered with scales is formed. It is called "psoriatic crown".
An additional feature of scalp psoriasis is the dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. Psoriasis on the scalp progresses like seborrhea. There is dandruff, which is difficult to treat with traditional remedies.
Body and back
The peculiarity of skin psoriasis in the back and body is a rare manifestation of symptoms in this area at the usual rate of development of the disease. The appearance of new pathological elements on the abdomen or under the shoulder blades often indicates a generalization of the process.
The first stage of dermatosis often develops in other places. Drop-shaped purple elements appear on the back and body.
Breasts and nipples
The first signs of psoriasis progress like regular plaques in the areola area. They are accompanied by itching, peeling, and covered with scales. An additional symptom is the occurrence of cracks and injuries.
This often happens to nursing mothers. A secondary infection occurs with progression of symptoms (pain, swelling, redness, increased local body temperature). This situation is fraught with acute mastitis, so urgent consultation with a surgeon is necessary.
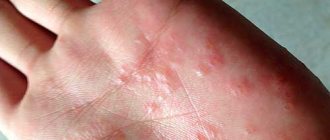
Palms and soles
The initial stage of psoriasis is accompanied by coarsening of the epidermis in the case of localization on the palms and soles. The skin becomes tough. Easily susceptible to physical injury. Bacterial and fungal infections are often associated.
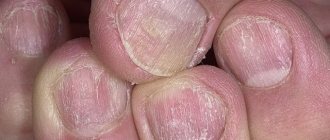
Nails
Symptoms of nail psoriasis manifest themselves as onychodystrophy. Damage to the nail plate occurs. Typical signs of the disease in the early stages:
- thickening or thinning of the nail plate;
- the appearance of transverse or longitudinal lines on its surface;
- change in the color and consistency of the nail. It may crumble. The worst case scenario is onycholysis with complete detachment of the plate.
Symptoms of the onset of psoriatic rashes are varied. It is important to be able to recognize them in time and seek help from a dermatologist. He will select a treatment. Early contact with a doctor often leads to rapid stabilization of the condition.
Causes of psoriasis
Many people are interested in the question, is psoriasis contagious or not? First, it’s worth understanding the causes of psoriasis. They cannot be infected by contact, through shared towels, hygiene items or handshakes. Most often, the disease occurs in young people, aged 18-25 years.
The main factors contributing to the development of the disease are:
- Genetic predisposition. The disease can develop in first-degree relatives;
- A common cause is stress, nervous tension, severe emotional shock;
- A possible cause is a disease of the endocrine system;
- Metabolic disorders, in particular, lack of silicon in the human body, vitamin deficiency;
- Intestinal diseases and viruses.
It is worth noting that an immune imbalance in the body provokes the appearance of a rash. This is a condition when one’s own cells show aggression towards tissues, this is reflected in the skin. There is a direct connection between the development of the disease and the condition of the intestines.
People with intestinal parasitic infections are more likely to develop skin diseases. The causative agents of intestinal diseases, when present for a long time, release toxins into the blood that provoke immune imbalance. The result is psoriasis.
Treatment methods for psoriasis
The method of treating psoriasis is determined by the form of the disease, symptoms and sensitivity to medications. First, local treatment is carried out on the affected areas. This avoids the occurrence of an adverse reaction. There is a technique according to which patients are prescribed soft drugs. If there is no effect, they are replaced with more potent ones. Even if the chosen product is effective, it is changed periodically to avoid addiction. Taking systemic medications gives good results. Their use is advisable for severe and moderate forms of pathology. The disadvantage of this treatment is the high likelihood of serious adverse reactions. Main groups of drugs used:
- Retinoids (Tigason, Neotigazon) - eliminate impaired maturation of the surface layer of the skin.
- Immunosuppressants (Cyclosporin A) - reduce the activity of the immune defense and the activity of T-lymphocytes, which provoke intensive division of skin cells.
- Cytostatics - drugs for the treatment of malignant tumors (Methotrexate) - stop the proliferation of atypical epidermal cells and their growth.
Physiotherapeutic methods are also used:
- photochemotherapy;
- selective phototherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrosleep;
- ultrasound therapy;
- hyperthermia.
Psoriatic triad - photo
The initial papules can be very small, only a few mm in diameter, or they can grow up to 5 cm. Outwardly, they look like bright red spots that are completely covered with white scales. An untrained eye will easily mistake them for lichen.
It is not for nothing that psoriasis is sometimes called “squamositis”.
Related article:
Dermovate for psoriasis - instructions for use
But there are three significant signs by which these plaques can confidently be attributed specifically to psoriatic manifestations:
- “Symptom of stearin stain” - white scales from the skin are easy to scrape off, like a drop of stearin dripping from a candle;
- “Terminal film symptom” - after the white “stearic” film is removed, a thin, shiny, slightly moist skin is exposed underneath;
- “Bloody dew symptom” - if you try to remove the exposed terminal film, small blood droplets will appear.
The unique “psoriatic triad” in pictures will help in making a more accurate diagnosis.
What is psoriasis
Psoriasis is a pathological model of dermatosis, accompanied by profuse skin manifestations in the form of large spots that merge into itchy and scaly plaques. The disease is cyclical and has a chronic course, so it is not possible to cure it. However, it is necessary to follow a daily set of measures to maintain a stable period of remission. Active drug treatment must be carried out at the progression stage. The localization of psoriatic manifestations is quite extensive:
- head and face, neck, eyelids, ears;
- elbow and knee bends;
- lower back;
- feet and palms;
- arms and legs;
- groin area and genitals.
Psoriasis
In severe cases, psoriasis affects the nail plates, joints and affects the activity of the central nervous system. The disease can occur in any person under the influence of genetic factors, as well as external pathogenic manifestations.