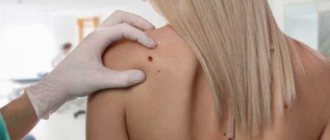
Which nevi should be removed and at what age
A small percentage of newborns are endowed with pigmented spots from birth.
Other children develop different types of nevi throughout their lives. The growth and activation of melanocytes is directly related to the following reasons: prolonged exposure to the sun (especially during a sea holiday), hormone levels, frequent visits to solariums). Gradually, the number of tumors on the skin increases. It is difficult to talk about the exact timing of the appearance of moles in childhood. The period of melanocyte activity ranges from 6 months to 1 year. Second wave - 5-6 years. It is associated with the active development of a small organism and is called a growth spurt. The third is adolescence. Hormonal imbalance is a favorable factor for the development of tumors. According to scientific data, moles can appear up to 25 years of age.
Dangerous formations (hanging, modified) should be removed. Treatment is carried out at any age in a hospital setting. Home remedies and Dr. Komarovsky’s advice are ineffective in this case. There are a huge number of effective ways to eliminate moles:
- Cryodestruction is a method of getting rid of skin growths using liquid nitrogen. During the procedure, mobile children may experience thermal burns. Cryodestruction is rarely used in childhood. It is suitable for adults and children over 14 years of age.
- Electrocoagulation is a medical procedure in which a high-frequency current is applied to the pathological area. Using a heated loop, the tumor is removed.
- Laser destruction is a harmless and painless way to treat skin growths. The formations disappear in one session of the procedure.
- Radio wave removal is carried out using a special device - a radio knife. The electrode heats the atypical tissue. They evaporate and the disease recedes. Radio wave surgery is widely used in therapeutic and pediatric practice. The manipulation does not leave any marks on the body.
- Drug therapy is selected individually in each case.
The division of neoplasms into dangerous and non-dangerous is a controversial concept. Any moles can degenerate. Pathology has a risk of death.
A child, developing in the womb, already acquires most of the birthmarks. At birth, moles are invisible, but with age, under the influence of melanin, the cells become brightly colored. According to statistics, many moles and birthmarks are observed in girls and fair-skinned children.
In pediatrics, there is no specific time frame when the appearance of moles is normal. Therefore, we can only outline the age categories when nevi appear most often:
- newborns (from 1 to 6 months) – the body encounters sunlight for the first time and, as a result, reacts to this with the appearance of moles;
- children 1-2 years old - restructuring of the body when switching to adult food;
- age 5-6 years – influence of external factors, the child spends a lot of time in the sun;
- adolescence – due to hormonal instability.
Most often, moles in children do not degenerate into malignant formations, but melanoma is a very insidious disease. Therefore, parents need to periodically visually evaluate nevi on the child’s body in order to notice dangerous changes in time.
Most children are born with slight pigmentation on the skin. It is not even always noticeable, but as the child grows up, already at 2-3 years old it transforms into dark or black bumpy formations, known as moles. No one can say how many of them are formed during life. It is known that from birth to 25 years, about 80% of all nevi usually appear. The reasons for this phenomenon are associated with:
- genetics;
- injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation;
- hormonal changes.
According to ancient beliefs, moles appear in children at birth if the pregnant woman is very frightened, but in this case they look more like birthmarks. It also happens that identical nevi can be traced in the family tree among descendants for several generations.
The formation of moles is associated with the presence of characteristic pigment cells. They are called melatocytes and are located in the inner layer of the epidermis. The formation of a mole begins with the appearance of a white formation, then it changes color and becomes brown or acquires a reddish tint.
It is believed that moles in a child form in the prenatal period or immediately after birth. During this period, birthmarks are formed. Moles are genetic in nature. Large formation of moles occurs at 6 months and 2-3 years and increases in adolescence. Until this time, there is a temporary cessation of the formation of spots, and hormonal imbalance provokes the formation of new moles.
Is the appearance of new moles dangerous?
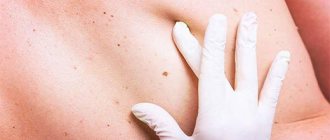
To assess the level of danger of neoplasms in children, it is recommended to fully examine the child twice a year and keep a map of the baby’s nevi, if possible including photos of moles.
All parents must know what signs of moles indicate that they can be dangerous for children:
- asymmetry. If you imagine a line in the middle of the spot, then the resulting halves should be identical; if not, you should see a dermatologist.
- edges of the spot. If they are smooth and rounded, then there is no need to worry. If the edges are sharp and jagged, see a doctor.
- color transition. Regardless of the color itself, it must be uniform, which indicates the safety of the nevus.
- size. Spots up to 6 mm in size are considered safe.
- growth rate. If the size of the spot has not changed in a month, it can be considered safe.
Today there are several ways to remove nevi in children:
- Radio wave - using high frequency radio waves.
- Surgical: the nevus is cut out with a scalpel along with the surrounding skin, after which the tissue is sutured. This method is used for malignant tumors; after healing, a scar remains.
- Electrocoagulation - using electric waves.
- Laser is the least traumatic of all methods and leaves an almost invisible scar.
- Cryodestruction. The stain is removed using liquid nitrogen - at a very low temperature, after removal there is almost no scar left. This method is recommended if there is no suspicion of cancer.
Reasons for the development of tumors on the skin
The main reason for the development of moles is genetic predisposition. If the father or mother has many spots on the body, then most likely the baby will also develop them over time. The period of appearance, number and location of moles depends on genetics.
Other reasons for the formation of nevi:
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- individual development of the child;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- viruses and injuries (in diseases, melanocytes accumulate in one place);
- hormonal disorders (observed during puberty).
Changes in the functioning of the endocrine system at the age of 13-15 years affect the formation of a special substance - melatonin. It is involved in the process of skin pigmentation. Melatonin provokes the rapid formation and disappearance of moles. This is a normal physiological process, so parents can be calm about the health of the child.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays promotes the appearance of age spots and affects their size and shape. Such processes can be pathological in nature, since nevi can change from exposure to the sun and turn into malignant neoplasms. Changes are observed at any age.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Tablets for allergies during pregnancy: what can you take and what antihistamines are prohibited?
The most susceptible to the formation of moles are:
- girls (it has been noticed that boys develop fewer spots);
- children with fair skin;
- premature babies.
Types and distinctive features of moles
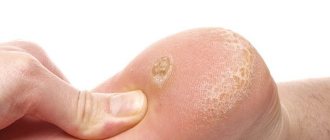
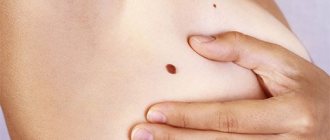
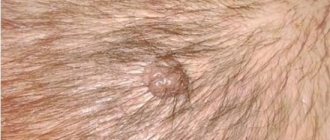
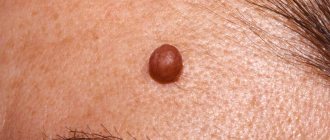
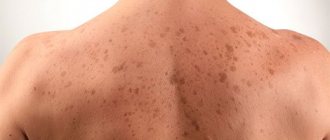
Common tumors have a smooth surface and are brown or black in color (see photo). They appear on different parts of the skin in the first year of a baby’s life. Particular attention should be paid to moles that appear on the feet and palms of children. Such neoplasms are easily injured, which causes their modification.
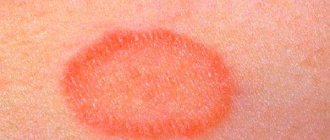
Vascular moles are characterized by a collection of blood vessels. Their color varies from scarlet to red. The spots may be raised or not palpable. As a rule, they are removed due to their unaesthetic appearance.
Types of vascular nevi:
- Hemangiomas. Appear immediately after birth or in the first year of life on any part of the skin. They are benign in nature, so they are not harmful to health. Hemangiomas have an unaesthetic appearance (sometimes black), various shapes and sizes. They are able to increase over time. Growth rate does not indicate modification, but can cause significant discomfort. As a rule, over time, the mole becomes lighter and then disappears. There are strawberry and cavernous hemangioma. The first has a convex surface of strawberry color. It is soft to the touch. Appears at the age of 1 year (congenital moles can rarely be found) on the head, face and other places, including internal organs. Cavernous hemangioma is purple or red in color and has a firm texture. Disappears on its own by age 12.
- Salmon-colored spots (flaming nevus). A frequent formation that has a pink or reddish tint. Appears on the baby's head or face. Disappears a year after birth.
- Port-wine stains (stork bite). Sometimes children are born with flat moles, which are called port-wine moles. They cover the baby's head and face and are bright in color. Appear due to dilation of blood vessels. Such formations grow with the newborn without changing color. Some parents believe that the stain can be hidden by tanning. This is a misconception, since when exposed to sunlight, the color of the mole becomes brighter. You can disguise a mole using cosmetics or use laser or infrared therapy.
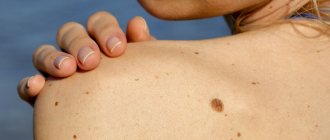
- Hanging mole (convex). Appears in the armpit, on the back or neck. It is dark in color and protrudes above the surface of the skin. Such a nevus is easy to injure, so if it forms, you should consult a doctor about the possibility of removal. At first, parents should monitor the size of the mole.
Let's look at each variety in more detail.
Hemangiomas
Hemangiomas are benign growths caused by broken capillaries, which is why they are mostly red in color. The nevus develops over several months. Hemangioma can increase as the child grows, but with age it changes less intensely.
Red nevi located on the child’s head pose a serious danger. Inside the red hemangioma, thrombosis of blood vessels constantly occurs, as a result of which blood clotting is reduced, so if it is damaged, bleeding is possible. A mole located on a child’s head is constantly exposed to injury by a comb, and this is very dangerous.
Hemangioma on the head
Hanging moles
Hanging moles can be benign or malignant. They are formed by epithelial cells and pose a danger to the child’s health, as they can be constantly injured. If a hanging mole is detected, it is better to show the child to a dermatologist, who will determine its malignancy and the cause of its appearance.
A blue nevus is formed by subcutaneous pigmentation and is a type of birthmark. However, unlike them, the accumulation of melanin occurs deep in the dermis. They can be either benign or malignant.
Another type of pigmented nevi are Mongolian spots. They appear in newborns and disappear over time almost without a trace.
Factors leading to the formation of moles
Parents can find out why moles appear in children from their pediatrician.
The reasons for the appearance of these neoplasms:
- Moles on a baby’s body develop due to a genetic predisposition.
- The child has hormonal imbalance. This reason is relatively rare in infants, but failures of this type can occur in older children.
Doctors can predict the birth of a baby with moles, since nevus at birth immediately appears in children with fair skin and premature babies. Most often, girls have moles.
Although no one takes newborns to the beach, it cannot be ruled out that children may develop birthmarks from exposure to sunlight.
How to distinguish dangerous from non-dangerous moles
Of course, Luna Fenner's story is exceptional - not only because of the size of the nevus, but also because of its extremely unfortunate location, which makes surgery difficult. But many mothers of newborns notice strange spots and moles on their babies that don’t look safe at all...
Which birthmarks need surgery and which ones don’t? When should you see a doctor? And in general, do you need to take any measures if your child was born with a spot? Let's figure it out and make sure that stain is different from stain!
Moles can be of two types: formed by pigment cells (from pale brown to black, like the Moon), or resulting from vascular changes (from pink to purple). Both types occur in newborns, although with different frequencies.
Every skin growth poses a danger to the child's health. Any nevi can eventually degenerate from a benign tumor to a malignant one. There are the following types of harmless moles:
- Red spots are observed in babies up to one year old. Their typical location is the forehead, back of the head, nose. The mechanism of appearance of these neoplasms is associated with friction against the maternal bones. The baby's head is large in the womb. When passing through the birth canal, the protruding parts of the skull rub against the pelvic bones for a long time. Red spots do not require treatment. In a one-year-old child they completely disappear.
- Flat brown formations do not protrude above the skin level. They rarely get injured. Brown spots may disappear without a trace over time. Sometimes they last for the rest of your life. The formations do not malignize and do not pose a serious threat to the health and life of the patient.
- Strawberry hemangioma is a convex pigmented growth of red or burgundy color. Soft to the touch. Strawberry hemangioma appears in the first weeks of life. It may be congenital. The pathology brings discomfort during movement if it is located on the palms or heels. Dermatologists and oncologists do not recommend removing the formation using known methods. Minor injuries can cause hemangioma to transform into cancer.
- Cavernous hemangioma is formed by blood vessels. It has unclear boundaries and an uneven shape. The growth disappears on its own during puberty.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Ichthyol ointment for boils: instructions for use and properties
Dangerous moles include:
- Setton's nevus is a small red nodule. The neoplasm differs from other growths in the presence of depigmented light skin around it. It has an oval shape with clear boundaries. It often degenerates into melanoma. Sometimes the tumor disappears on its own. Typical localization is arms, back, stomach, feet, fingers, navel, lips.
- Papillomatous nevus visually looks like a malignant tumor. It is characterized by an irregular shape, blurred edges, dark color, and large size. The growth is localized on the head. Hair grows on it. One type of papillomatous nevus is verrucous. On its surface there are cracks and pigmented inclusions.
- Fibroepithelial nevus is characterized by slow growth. It has a dark brown, blue color. On the surface of the mole there is stubble or vellus hair. Several formations appear on the skin at once. Fibroepithelial growth should be differentiated from borderline growth. The latter is distinguished by smooth borders and dull coloring.
- An intradermal nevus is a formation that looks like a birthmark.
- An atypical nevus grows more than 1 cm. It is characterized by typical signs of malignancy: irregular shape, unclear boundaries, black color.
- The Mongolian spot comes in blue and brown colors. The typical location is in the spine. Education disappears during adolescence.
Any skin growths can degenerate. Symptoms of malignancy include:
- The growth began to grow rapidly.
- The shape of the growth has changed.
- The mole has become asymmetrical.
- It has blurred boundaries.
- The color of the growth has changed. It can be black or white.
- Vesicles with transparent contents appeared around the neoplasm.
- The mole has festered.
- Benign neoplasms do not hurt or itch. The appearance of unpleasant symptoms indicates degeneration. If the lump begins to itch terribly, seek medical help immediately.
- Crusts, peeling, ulcerative defects, bulges on the mole indicate malignancy of the formation.
- Location in frequently traumatized areas can lead to the development of melanoma.
- An increase in the number of nevi indicates pathology.
Small nevi, as a rule, are completely harmless and are benign formations. However, this cannot be said about medium, large, hanging and vascular moles. Some nevi require specialist supervision.
Sometimes parents don't know who to turn to. In such cases, you can consult a pediatrician. He will conduct an examination and refer you to a dermatologist or oncologist. The most dangerous nevi that require emergency care include the following:
- injured;
- fast growing;
- mutating.
Benign and malignant moles
When do the first moles appear?
Some newborns are born with pigmentation on the body; the formations are birthmarks that arise for various reasons. Nevi appear throughout life in places where melanocytes accumulate, which were formed during the prenatal period. The first pigment spots are visualized in a child by his first birthday; with age, the number of spots increases, and the size increases in proportion to the baby’s growth.
During puberty and hormonal imbalance, nevi appear in large numbers in adolescents. Acquired moles are considered to be pigmentation that appears after acne, dermatoses, and mechanical damage to the skin.
From the point of view of medical science, a nevus is an accumulation of melanocytes (cells that produce melanin), which arose as a result of the migration of melanoblasts, the cells from which melanocytes are formed, disrupted during the development of the embryo. It is impossible to influence this process either during pregnancy or after. As melanocytes mature, melanin synthesis begins, turning the nevi brown.
The elevation of moles above the skin level depends on which layers of the skin contain melanocytes. In convex nevi, pigmenting cells lie inside the dermis/epidermis and are called epidermal/intradermal; in flat skin types, melanocytes are localized at the border of these skin layers and are called mixed. Over the course of life, flat moles tend to bulge due to cell migration, which is considered normal.
A child is born with birthmarks or receives them in infancy. Congenital formations vary in shape and size, have pronounced outlines, often do not rise on the skin, color ranges from pink to brown, and localization is different. There are 2 common types of birthmarks: ordinary, consisting of melanocytes, vascular - angiomas. The second type can begin in utero or grow during life.
Which moles are dangerous?
Moles themselves, even black ones, do not pose a risk to children's health. Their formation is a normal physiological process. Large moles protruding above the skin should alert parents, as the child begins to show interest in the new growth, scratching and picking at it. These actions lead to injury, which is the main reason for the modification of the mole.
Complications can result from a malfunction of the immune system and sunburn. As a result, the child develops melanomas, which grow rapidly and spread malignant cells throughout the body. Without timely treatment, melanoma can damage vital organs, leading to death.
Symptoms requiring consultation with a dermatologist:
- Asymmetry. Moles should have an even, symmetrical shape. If one of the halves of the spot begins to grow faster than the other, there is a possibility of its modification.
- Uneven borders. The first sign of melanoma development is blurred, jagged edges.
- Color change. A mole of unusual color or its change during growth (if it turns red), as well as the appearance of various inclusions on the spot indicate changes.
- Big size. All nevi with a diameter greater than 6 mm must be shown to a dermatologist. If the mole has enlarged, then there is a risk of developing a modification.
Features of moles in newborns
Spots form on the skin of infants either before birth or in the first weeks of the baby’s life. They belong to congenital benign formations. Pigmentation can be differentiated into vascular formations and pigmented ones. Pigmented birthmarks include birthmarks; vascular angiomas are divided into hemangiomas and lymphangiomas.
Hemangiomas are hypertrophied vascular formations that look like flat moles or convex roundness from pinkish to red, of various shapes. They do not itch, do not irritate the baby, and can be located on any part of the body. Over time, they fade and disappear, increase in size as the child grows, and normally retain their original shape.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the scientific name of a mole.
Lymphangiomas in children are a rare disease; depending on the type of disease, the tumor can be pronounced (cystic) or in the form of nodules rising above the surface of the skin (cavernous). The tumor cells are benign, symptoms appear immediately after birth or in the first years of life, mainly up to 3 years. The disease is caused by intrauterine developmental defects, is localized in the location of the lymph nodes, treatment is surgical.
On the back of the baby's head, eyelids, bridge of the nose, forehead, and eyebrows, the mother notices pink or red spots of irregular shape. The formations are caused by vascular hypoxia during the perinatal period or during childbirth. Tumors are not dangerous, they fade over time, they are removed if they are located on visible areas of the body and represent a cosmetic defect.
Red-haired babies are born without freckles on their cheeks. The spots appear at 3-5 years of age, reaching a maximum in number by the age of 25, when the formation of body systems is completed. Later, the spots do not appear, and the old ones fade.
In childhood, nevi do not carry the risk of degeneration into a malignant formation. This usually happens later, but formations require careful attention and specialist supervision. The following symptoms serve as a signal to remove pigmentation defects:
- the nevus has become asymmetrical and irregular in shape;
- the edges of the formation spread out, became jagged, the boundaries blurred;
- the nevus bleeds, there is discharge;
- the color of the spot has become uneven, inclusions of colors unnatural for the skin are visible;
- the size of the formation has increased over 6 mm;
- the dynamics of symptoms, sharp growth and deformation can be traced.
What should you pay attention to?
All benign moles have clear outlines and regular shape. They are light brown, red or black, flat or convex in shape, and small in size. Parents should seek help if:
- the child has many moles;
- nevus changes color, shape and size too quickly;
- diameter of large moles or birthmarks over 10 cm;
- the mole disappeared on its own, leaving a barely noticeable spot;
- an injured nevus takes a long time to heal, but the wound constantly bleeds, ichor is released or pus appears;
- the mole turned red.
Types of moles
The following types of moles are most often found in children:
- Borderline nevi. They are small nodules (diameter from several millimeters to centimeters) of regular shape, painted in a dark color. They protrude above the skin and are not accompanied by painful sensations.
- Intradermal moles. They can look like spots on the skin or folded formations protruding above the surface (they resemble blackberries in appearance). Color - from flesh to red or black.
- Mixed form. These are dense nevi that have a spherical shape. Their size is about 1 cm, color is dark.
- Congenital nevi. They form during fetal development, when normal skin cells are converted into melanin .
Diagnostic methods
If a neoplasm is detected on a child’s body, you should consult a dermatologist. After the examination, the doctor will determine the possibility of modification and, if necessary, refer to other specialists - an oncologist and a surgeon. Basic diagnostic methods:
- Dermatoscopy. The procedure involves a detailed examination of the structure of the spot using a special magnifying device - a dermascope. (Previously, a regular microscope was used for these purposes). As a result of the examination, an accurate photograph of the mole and its full description are obtained.
- Computer diagnostics (digital dermatoscopy). A more accurate examination, making it possible to examine the spot under high magnification. This allows you to determine color changes, inclusions of melanin and the condition of blood vessels.
- Biopsy (histological examination). It is carried out after removal of the tumor. Using this method, you can detect malignant cells that indicate oncology.
What to do if a mole grows?
Moles in children are a fairly common and common occurrence. A small dark spot that appears in infancy can gradually grow and change. Hair may appear on it, it increases in size and even becomes black and slightly convex. This is quite natural if the change in the size of the mole occurs in proportion to the child’s growing up.
Types of nevi that grow like warts (see also: warts on the legs of children)
It’s another matter if the nevus begins to change greatly, actively and rapidly growing. Why does this happen and what should parents do? In this case, you should not delay your visit to the doctor. The child will need to be shown to a dermatologist, who will examine the pathology and, if necessary, refer to an oncologist. After examining the baby and doing the necessary tests, the doctor may suggest removal of the mole.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with acne on the back in men: causes and treatment
As a rule, moles do not cause discomfort and do not harm the child’s health. A baby can live with a pigment spot for the rest of his life. However, there are cases when nevi need to be removed. The main symptoms indicating the need for surgery:
- bleeding of a mole after touching;
- redness and peeling of the surface;
- severe itching;
- getting injured.
Main methods of therapy:
- Cryodestruction. The procedure involves applying cold to the wart for a few seconds.
- Hormonal influence. Treatment with hormonal drugs is allowed from 2 months under the strict supervision of a doctor. Use Prednisolone in an acceptable dosage.
- Sclerosing therapy. In this case, special agents are injected under the skin without touching the top layer. They lead to the death of mole cells. In this way, spots on the face are removed.
Laser is often used to remove moles. This method is safe and painless, does not leave scars or scars. However, there is a risk of burns. Laser therapy eliminates the risk of developing tumor metastases.
Moles in children: in what cases removal is required
Removing tumors requires a serious reason. It won’t work to just go to a specialist and ask your child to remove a mole that they don’t like. However, there are a number of main reasons , if identified, surgical intervention is no longer necessary.
- The indication for removal is the presence of constant itching, pain, pain and discomfort in the child in the area of the nevus.
- Trauma to a mole, leading to severe bleeding and pain, which occurs even at the slightest contact with the neoplasm.
- Surgery is required when there is severe inflammation and peeling on the surface of the mole.
Thanks to modern methods of surgical removal of moles, you can get rid of pathologically dangerous nevi quickly and painlessly.
Which nevi should be removed and at what age
Finally, we come to the case of Luna Fenner. The “Batman mask” on her face is a giant congenital melanocytic nevus. Actually, melanocytic nevi - clusters of cells with excess pigment, melanocytes - each of us has, these are ordinary moles. However, if you remember, most of them appeared in your childhood, and most likely in adolescence, during puberty, against the background of intense hormonal changes.
Unlike other birthmarks, moles “prefer” the lower part of the body. As a rule, these are benign neoplasms that do not require any intervention, with one exception: size matters.
The danger of any melanocytic nevus is the potential for degeneration into a malignant tumor, melanoma. Much, however, depends not only on the area of the spot, but also on its location: trauma to the nevus, the likelihood that it will be exposed to ultraviolet irradiation (in other words, it will end up in the sun), all these are factors contributing to degeneration. Such spots require constant medical supervision and, whenever possible, surgical removal.
6.11.2019
Prepared by Alena Novikova
physiology,
symptoms and diseases
The question of whether nevi should be removed or not depends solely on the specialist’s prognosis. When children develop small moles that do not interfere with their normal lifestyle, they should not be touched. If the nevi are located in dangerous areas, where they are subject to constant trauma, are large in size, or have too many of them accumulated in one place, it is better to remove these moles.
Removal methods
Let's look at each method:
- Radio wave. Removal of moles in children is carried out using high-frequency radio waves.
- Surgical. The mole is removed with a scalpel along with the surrounding tissue. The wound is usually sutured. This method is used in cases of suspected cancer, large convex tumors, where it is necessary to remove a large area of skin. The wound takes a long time to heal and a scar remains.
- Electrocoagulation. This method is similar to the radio wave method, only here the removal occurs using electric waves. The wound takes a long time to heal and requires care.
- Laser. It is considered the least traumatic for the skin and is popular when removing moles. Barely noticeable scars remain, and the wound heals quickly.
- Cryodestruction. Liquid nitrogen at ultra-low temperatures has a destructive effect on nevus tissue. There are practically no scars left. However, unlike the above methods, this method does not allow sending a tissue sample for histology, so it is not used if oncology is suspected.
After removing a mole, you must adhere to certain rules for treating the skin.
Post-operative care
The doctor who performed the operation must give the child's parents special recommendations for caring for the wound left behind. If it is not deep, it is treated with brilliant green and kept open. When removing large, deep nevi, the surgeon may stitch the area. After such an operation, you should treat it daily with brilliant green and change the bandage. It is advisable not to wet the operated area until complete healing.
To avoid developing cancer, a child’s moles must be constantly monitored. The following preventive measures will help protect against the degeneration of nevi:
- Avoid direct sunlight. The best time in the summer for walking with a child is considered to be before 10:00 in the morning and after 16:00 in the evening. If you need to go outside at lunchtime, when it is too hot outside, the baby should wear things that cover the body, as well as a hat. This is especially true for infants.
- When relaxing near bodies of water, the child must be thoroughly dried so that the water remaining on the body does not cause sunburn.
- Monitor any changes in moles and seek advice from specialists. If the nevus turns red, begins to quickly increase in size, changes its outline, color, shape, you should not put it off until later, as this may be a signal of oncology.
- If a nevus is injured, the wound should not be cauterized with alcohol tinctures. It will be enough to put a bandage on it and see a doctor.
- Try to avoid mechanical or any other impact on moles.
Reasons for removing moles
Usually moles are not dangerous and if they are not in places where they are subject to permanent damage, then there is no need to remove them. But when exposed to unfavorable factors (weakened immune system, hereditary predisposition to cancer, burns, injuries), nevi can degenerate into a malignant formation - melanoma. This is a very dangerous disease and the mortality rate from it is very high.
It is necessary to constantly monitor pigment formations in a child. If there are few moles, but they are large in size, if it changes or has been injured and begins to bleed, you should urgently consult a doctor to carry out the necessary tests.
Mole removal occurs using a laser and does not pose any harm to health.
What does Dr. Komarovsky say?
The famous children's doctor E. O. Komarovsky recommends that parents, when moles appear in children, carefully monitor the neoplasms and contact a specialist if any changes are detected. Only a doctor will be able to determine what an increase in size or color means and what threat the symptoms pose to the child.
Komarovsky draws the attention of parents to the fact that the sun’s rays have a negative effect on the mole, so when in the sun it is better to cover the spot. Parents need to ensure that the baby does not injure the mole. It doesn’t matter how many moles there are on the body, what matters is their modification, not the number.