Causes
It is almost impossible to accurately identify the cause of the development of allergic dermatitis in adults and children, but the prerequisites for the appearance of this pathology may be exposure to allergens:
- latex items: gloves, baby pacifiers, condoms and so on;
- clothing containing allergenic materials (rubber, latex, synthetics, wool, etc.);
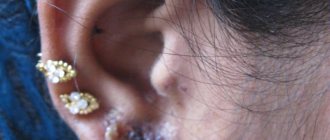
- jewelry and accessories (most often made of base metals);
- decorative cosmetics and hygiene products (creams, shampoos, soaps, gels and others);
- some medications (corticosteroid ointments, antibiotics, etc.);
- household chemicals (detergents, adhesives, washing powders, rinse aids, conditioners);
- plants (representatives of the toxicodendron genus are especially dangerous: poison ivy, sumac, oak);
- oral hygiene products (toothpastes, gels, rinses);
- dental devices for dental treatment: hooks, forceps, mirrors, burs, probe.
- food preservatives, dyes, flavors;
- other irritants (ink, house dust, pollen, drop in outside temperature, solar radiation, animal hair, etc.).
Other causes of allergic dermatitis are:
- professional activity: working with substances that provoke a reaction, for example, rubber, metal, paint, ink;
- hereditary predisposition.
to contents ^
Clinical manifestations
Predisposition to allergies is usually detected at an early age. The main signs of the disease are:
- skin rashes;
- itching sensation.
Allergic dermatitis in adults in acute form manifests itself with general and local manifestations. Common symptoms include:
- feeling of weakness;
- headache;
- slight increase in temperature.
In addition to general symptoms, local reactions are noted:
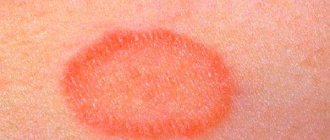
- formation of red spots;
- the appearance of a rash in the form of blisters;
- formation of weeping surfaces and erosions with the formation of crusts;
- burning and itching sensation;
- thickening of the epidermis.
After 2-3 weeks, the inflammatory disease goes away provided that the interaction with the allergen that caused the development of dermatitis is eliminated. Manifestations of dermatitis can occur on different parts of the body.
Face
The appearance of rashes on the face is often caused by the use of low-quality or simply inappropriate cosmetics. Therefore, young women are most susceptible to allergic dermatitis on the face. Food and medications can also cause an inflammatory reaction. Main symptoms:
- redness of the cheeks;
- edema formation;
- the appearance of a rash on the skin of the forehead and cheeks;
- severe itching.
Advice! In severe cases of the disease, necrosis of the facial skin may develop, followed by the formation of scars.
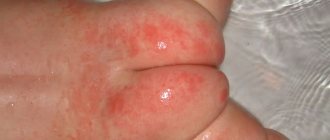
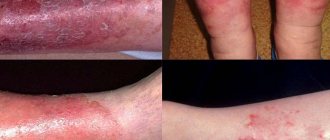
Hands
Allergic dermatitis on the skin of the hands is often observed, since this part of the body most often comes into contact with various unfavorable factors. Moreover, both acute and chronic forms of the disease can be observed.
The chronic stage develops with constant adverse effects on the skin; most often, occupational factors influence the development of the disease. The following reasons can provoke an exacerbation:
- household chemicals;
- hygiene products and cosmetics;
- medicines;
- Food;
- wool;
- plant sap and other factors.
Main manifestations:
- increased skin dryness;
- the appearance of peeling, cracks;
- thickening of the stratum corneum;
- redness.
Since severe itching is often observed with dermatitis, the patient’s skin is often covered with scratches. And the presence of damage to the skin significantly increases the risk of developing infectious diseases, for example, pyoderma.
Advice! A sign of an associated bacterial infection is the presence of ulcers.
Kinds
Allergic dermatitis is divided into several types due to its development:
- Contact dermatitis. Formed with high sensitivity to irritants. It develops when it comes into contact with the skin; rashes and redness are most often observed on the hands, eyelids, face, chest, and head. Lesions occur whenever there is direct contact with an irritating substance. Most often, allergens are aggressive chemicals such as alkalis and acids, poisonous plants, cosmetic products, accessories and metal jewelry.
- Toxic-allergic dermatitis. Allergens are substances that enter the body through the skin, digestive, respiratory organs, or through intravenous/intramuscular administration of medications. Toxidermia in most cases is caused by an overdose of a drug or intolerance by the body. The most severe type of toxic-allergic dermatitis is Lyell's syndrome, which affects up to 85% of the epithelial surface. Without medical attention, the disease can be fatal.
- Phytodermatitis. Clinical manifestations of this type of dermatitis are mainly of an acute inflammatory nature on the skin (usually on the hands, sometimes the skin of the face is affected). Some types of plants, juice, milk, whose pollen contains chemicals that irritate the skin, become provocateurs. Often the causative agents of phytodermatitis are indoor plants, for example, geranium or primrose. Common types of allergenic plants are buttercups, citruses, spurge, lilies, and hogweed.
- Atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis) is observed when substances harmful to health accumulate in the blood, which give a slow immune reaction in the form of redness and rashes on the skin of the face, arms, chest, legs, and abdomen. Often this type of dermatitis is inherited, although each generation may have its own allergen. To activate it, a combination of nervous system disease, contact with an allergen and low (high) body temperature is necessary. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by frequent exacerbations that become chronic.
to contents ^
Description
Allergic dermatitis or diffuse neurodermatitis is considered an intolerance reaction with a delayed development.
That is, this disease occurs when a sufficiently large amount of an allergen that provokes the disease accumulates in the body.
Typically, an inflammatory skin reaction to an irritant develops over seven to ten days.
Allergens can be either external substances that act directly on the skin, or irritants that enter the body.
Symptoms of the disease are recorded in different parts of the body, including the skin of the face.
More sick patients live in environmentally unfavorable areas and the largest number of city dwellers are among them.
The first-time pathology can develop into a chronic form, exacerbations of which are provoked by repeated contact with an intolerable substance.
Symptoms
Different types of allergic skin dermatitis have their own symptoms, but some manifestations are similar to each other.
to contents ^
Are common
- Itching in a certain area of the skin;
- inflammation of the skin in the form of redness or rash;
- the appearance of microvesicles (small bubbles).
to contents ^
Contact
- Swelling at the site of the allergic focus;
- redness of the site of contact with the allergen;
- small blisters filled with serous fluid;
- clear outlines of the boundaries of the affected area, coinciding with the zone of contact with the allergen;
- erosion at the sites of rupture of vesicular formations at an advanced stage of dermatitis.
to contents ^
Toxic-allergic
- Peeling and itching of the skin;
- spread of red spots;
- formation of pinpoint bubbles;
- the appearance of large blisters (in rare cases);
- the localization of the affected area is sometimes on the oral mucosa and external genitalia.
to contents ^
Toxic-allergic with Lyell's syndrome
- Recurrent rashes, which may be accompanied by pain;
- dark red spots in the armpits, buttocks and groin;
- large flat blisters;
- weeping surface of the dermis, its exposure with slight friction;
- rapid formation of erosion after opening the blisters;
- dehydration and severe intoxication of the body;
- headaches and fever;
- indigestion, often accompanied by vomiting.
to contents ^
Phytodermatitis
- Burning and itching of the affected area of the skin;
- the appearance of pigmentation and redness;
- pinpoint blistering rashes or blisters.
to contents ^
Main symptoms of manifestation
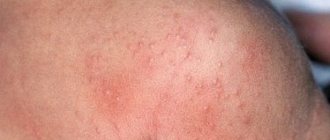
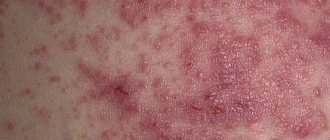
Initially, large red spots appear on the skin. Then small bubbles form against their background. There are quite a lot of them, and subsequently they will burst, leaving wet marks on the surface of the skin.
The main focus of the lesion is in the place where the allergen had an impact.
But despite this, the allergic reaction of dermatitis affects the entire body as a whole. Secondary outbreaks can appear in any other location, regardless of whether there was exposure there or not.
Using an example, you can consider an allergic reaction due to mascara. Redness from use can be so great that it affects the shoulders, neck, and chest. All rashes are accompanied by severe itching.
Photo: Peeling on the face
Why is it dangerous?
- Recurrent chronic form of the disease. Its manifestations in adults significantly limit people's social opportunities and often become causes of psychological disorders and depression. Sometimes a person with skin rash problems has to change his or her field of activity to avoid contact with unfavorable production factors.
- Eczematous lesions of the skin.
- Damage to the kidneys and liver in severe toxicoderma.
- Streptoderma is an infectious inflammatory process against the background of erosions. In areas that are susceptible to scratching or other skin damage, favorable conditions are created for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Through minor injuries, fungal organisms, bacteria, and viral pathogens of papilloma and herpes penetrate into the deep layers of the skin.
- Anaphylactic shock caused by a local reaction or general intoxication after an insect bite or skin contact with toxic substances.
to contents ^
The mechanism of sensitization and skin manifestations
Allergic dermatitis occurs when the skin directly interacts with a substance that is recognized by immune cells as an allergen. Based on the mechanism of entry of the irritating factor, allergic dermatitis is also called contact dermatitis. A necessary condition for the occurrence of a specific reaction to substances that are unable to cause allergies in healthy people is the presence of a predisposition:
- weakened immunity;
- nervous tension;
- autonomic disorders;
- hereditary factor;
- concomitant/previous diseases (acute respiratory infections, mycosis of the feet, etc.);
- poor nutrition;
- deviations in the condition of the skin (decreased water-lipid barrier, dysfunction of the sebaceous and sweat glands).
Important! Dysfunction of the digestive tract, especially the liver, plays an important role in the development of any allergic reaction.
Contact dermatitis differs from the most common atopic form of skin reaction by sensitization to one specific substance from an entire group of structurally similar substances. At the same time, atopic dermatitis always develops in children, its first manifestations appear before 2 years of age. An example is a child’s diathesis for sweets.
Allergic dermatitis is distinguished from simple dermatitis that occurs from friction, temperature exposure, or contact with acid/alkali by the speed of reaction. In the first case, skin manifestations occur at lightning speed, in the second, it takes several weeks (usually up to 2 weeks) after the first contact with the irritant substance for sensitization of the body to form.
The substance, in contact with the skin, binds to proteins. Immune cells perceive this compound as an allergen. Upon first contact, immune cells recognize the substance and specific antibodies are formed. Only upon second contact does a skin reaction appear. It may take up to 3 days from the moment of contact to skin manifestations. Immune cells, lymphocytes and antibodies rush to the site of contact with the allergen. Skin inflammation is violent, often extending beyond the area of interaction with the irritant, and does not correspond to the amount of allergen and time of contact.
Diagnostics
It is based on a visual examination and laboratory test data, with the help of which substances that provoke allergic dermatitis are identified.
To identify the irritant, special skin tests are carried out, most often these are patch tests. They look like paper plates with a sticky base. Allergen substances are placed on each plate. Upon contact with the skin under a cell with an active irritant, slight redness will occur, and in the case of a strong reaction, even a blister. These changes in the skin do not cause concern and quickly disappear after removing the plate.
Diagnosis is carried out only during remission of the disease; antihistamines, especially corticosteroids, should not be taken for 3-5 days before the analysis.
In addition to skin tests, a patient with suspected allergic dermatitis is prescribed:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- blood sugar test;
- blood test for biochemistry.
According to indications, studies of the gastrointestinal tract and thyroid gland may also be prescribed to exclude concomitant diseases, the symptoms of which may be inflammatory processes on the skin.
to contents ^
Diagnostic methods
Detection of the disease is determined by the manifestation of the clinical picture. Determination of predisposing factors preceding the disease. In certain cases, a test is prescribed to determine IgE antibodies in the blood.
Identification of the allergen that provokes an exacerbation of the disease is carried out by the method of tests and samples:
1) Application of small doses of various antibodies to the forearm. If the skin turns red or a blister forms at the site where a particular allergen was scratched, then the reaction is positive.
2) Application tests - applications with special paper adhesive plates can determine a dozen provocative allergens.
The applicator is attached to the patient’s back for two days. When you remove the strip, redness or a small blister appears at the site of a certain antigen, with a sharp reaction. Changes in the skin disappear without a trace immediately after the plate is removed.
Accurate identification of the allergen contributes to the selection of an effective remedy for the treatment of allergic dermatitis.
Treatment
Allergic dermatitis can be eliminated at home, with the exception of cases where it develops against the background of other more serious diseases and specific conditions.
Treatment of the disease must begin with avoiding contact with the allergen; it is also important to follow a diet.
to contents ^
Drug treatment
- Glucocorticosteroids. To eliminate symptoms (even without identifying the allergen), glucocorticosteroid ointments, creams or aerosols are used. Hormonal drugs are prescribed in short courses to avoid addiction. Hydrocortisone, Dermovate, Elokom, Betamethasone, Akriderm, and others.
- Antihistamines. To reduce the severity of swelling and itching. New generation antihistamines do not cause drowsiness and do not reduce the patient’s quality of life. Cetrin, Zodak, Claritin, Suprastin, Fenkarol, Astemizole and others.
- Detoxification medications are administered intravenously or intramuscularly to reduce sensitivity to the identified allergen. Calcium chloride is used (5 milliliters of the substance intravenously using a dropper, slowly, over 4-6 minutes), sodium thiosulfate (5-50 milliliters intravenously, depending on the severity of the allergic manifestation), calcium gluconate (1-3 grams 2-3 once a day intramuscularly or intravenously).
- Enzymes are prescribed when the cause of the disease is disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas. Creon, Festal, Mezim, Panzinorm, Pancreatin and others.
- Prebiotics and enterosorbents are prescribed to restore intestinal microflora and remove toxins from the body. Linex, Laktiale, Enterosgel, Polysorb, Laktofiltrum and so on.
- Homeopathic remedies are selected individually depending on the age and condition of the patient, and the characteristics of the disease. May be prescribed: Iricar cream (for severe redness, itching), Antimonium crudum (black antimony sulfur for rashes with the formation of blisters and pustules, itching, crusts), Arsenicum album (for various rashes and skin lesions) and others.
- Antifungal drugs and products with a softening and protective effect destroy pathogenic microorganisms, moisturize, soften and protect the skin. The most effective are: Eplan, Zinc ointment, Exoderil, Bepanten, Epidel, Desitin and others.
to contents ^
Traditional treatment
The use of folk remedies for the treatment of allergic dermatitis is effective at the stage when it is necessary to alleviate symptoms.
For this we use:
- herbal decoctions for drinking from string, tricolor violet, currant bark, chamomile, viburnum bark or licorice root;
- compresses with infusions of horsetail herbs, elecampane roots, calendula, lemon balm, and felt burdock;
- homemade ointments made from chicken, pork or goose fat, sea buckthorn oil;
- baths with the addition of a decoction of nettles, chamomile flowers, oregano, blue cornflowers, wild rosemary leaves, and valerian;
- aromatherapy using geranium, lavender or sandalwood oil.
to contents ^
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of allergic dermatitis should always begin, and in some mild cases this will generally be sufficient, with eliminating its cause - identifying a specific allergen.
If doing this on your own is problematic, you can take a special blood test for allergens.
Be that as it may, it is simply necessary to establish exactly what exactly is the cause of the pathological reaction of the body - otherwise treatment simply will not make sense.
When the allergen is identified, it is necessary to try to eliminate it from the patient’s environment or, if this is impossible, reduce their contact to a minimum.
It is better not to treat allergic dermatitis on your own: by taking just one wrong step, the problem can be greatly aggravated and harm the health of the body as a whole.
Video:
In this regard, treatment at home, and especially treatment with folk remedies, can only be an addition to the main therapy prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Drug treatment of allergic dermatitis can be divided into two types:
- external treatment, in which hormonal and non-hormonal drugs are used locally in the form of all kinds of ointments, gels and creams;
- internal treatment, in which it is necessary to use antihistamines, primarily tablets, as well as various injections for allergies.
At the same time, we immediately note that only complex treatment of dermatitis is truly effective - that is, the simultaneous use of external and internal means.
Today, some of the most effective antihistamines are:
- "Claritin";
- "Citrine";
- "Zadak";
- "Dibazol";
- "Tavegil";
- "Suprastin";
- "Loratadine."
All of these drugs quickly suppress the production of histamine in cells, but they all have side effects - they cause drowsiness, dizziness, and sometimes nausea, and are contraindicated during pregnancy.
Preparations for allergic dermatitis in the form of ointments:
- "Prednisolone";
- "Hydrocortisone";
- "Sinalar";
- "Advantan";
- "Elokom";
- "Fenistil-gel".
These hormonal drugs are prescribed, as a rule, during an exacerbation, when it is necessary to quickly relieve inflammation and somewhat normalize the condition of the skin.
When the acute period has passed, non-hormonal ointments are used as restorative therapy. Such preparations are designed to soften and moisturize the skin and activate its healing.
Photo:
A good effect can also be achieved if allergic dermatitis in adults is treated with special injections.
The following allergy injections are effective:
- "Diprospan";
- "Prednisolone hemisuccinate";
- "Ruzam";
- "Decortin N 20";
- "Solyu-Decortin N 50" and others.
In addition, in recent years, it has become possible to quickly cope with allergies if you treat them with a new generation of drugs - cromones, which strengthen the membranes of mast cells, due to which histamine is practically not released.
Diet
A person prone to allergic skin reactions must follow a special diet. Proper nutrition is the prevention and treatment of dermatitis at the same time.
Moreover, it is not enough for the patient to exclude the main allergen from the diet; one must try to completely avoid foods that contain aggressive substances.
It is prohibited to use:
- juices, nectars in paper bags;
- marinades and preserves, smoked meats;
- whole cow's milk, condensed milk;
- mustard, spices, ketchups, mayonnaise, ready-made sauces, and so on;
- chocolate, coffee;
- berries and fruits of red and orange color (strawberries, strawberries, oranges, tangerines and so on);
- confectionery products (rolls, cakes, pastries, etc.);
- seafood in any form;
- vegetables (tomatoes, onions, garlic, bell peppers);
- sauerkraut;
- eggs;
- nuts;
- honey;
- mushrooms.
Recommended Products:
- green vegetables and fruits;
- rice, buckwheat, semolina, oats;
- dried fruit compotes, rosehip decoction;
- weak meat and vegetable broths, soups made from them;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- homemade jelly and jelly;
- pasta (hard varieties);
- egg white omelettes;
- boiled (stewed) chicken, rabbit, beef;
- bread with bran or rye flour.
It is also necessary to reduce your salt and sugar intake. It is better to steam or stew all dishes; it is advisable to completely exclude fried and fatty foods.
to contents ^
In children
Allergic dermatitis has 3 successive age stages:
- infant – up to 2 years;
- children - from 2 to 13 years;
- teenage – from 13 to 18 years.
The manifestations in each of these phases are different.
Most often, the pathology occurs in children under 1 year of age. Symptoms in the form of rashes appear on the face, on the inside of the knee and elbow joint. In this case, a small rash can spread throughout the body.
Symptoms of common dermatitis include skin redness, weeping, crusting, and dry skin. In most cases, pathology occurs after the introduction of complementary foods, during teething, and in bottle-fed babies.
In children from 2 to 12 years old, the skin rash appears mainly in the elbows and knees, on the back of the hand, and on the neck. In areas where the skin is affected, swelling appears, hyperemia may occur, and plaques, papules, cracks, erosions, scratches and crusts often form. Cracks are very painful on the soles and hands.
In adolescence, most cases of pathology occur in boys. The disease occurs with periods of remission and exacerbation, the affected area may increase. This stage is characterized by rashes on the face, neck, chest, and sometimes the hands and elbows are affected. Next, all skin folds, feet, fingers, and the back of the hands are gradually captured.
If a child of any age develops a rash that does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to seek help from a doctor. Without proper treatment and identification of the allergen, the disease can progress and lead to the development of bronchial asthma. Treatment of children with allergic dermatitis should be under the supervision of a doctor.
If an allergy occurs in a baby, the mother needs to carefully monitor her diet. This reaction is called a food allergy and it occurs most often to milk, citrus fruits, seafood, tomatoes, and chocolate. In this case, allergenic foods are completely excluded from the mother’s diet, and then gradually introduced into the child’s menu according to pediatricians’ recommendations for complementary feeding.
A big problem with this pathology is severe itching of the skin. Children become whiny, restless and sleep poorly. To eliminate these unpleasant symptoms, doctors prescribe antihistamines and glucocorticosteroid ointments, moisturizing body creams (Bepanten and Physiogel cream and others), and a suspension with the emollient effect of Tsindol. Before applying ointments, the affected area must be treated with an antiseptic (Chlorhexidine, Fukortsin and others).
If symptoms remain after a course of treatment, you will have to undergo allergy tests. In case of frequent exacerbations of the disease, it is recommended to undergo a course of immunotherapy with the drugs Polyoxidonium, Ismizhen, and so on.
When dermatitis is complicated by a purulent process, antibacterial drugs are added to treatment.
Calcium supplements and vitamin complexes will help alleviate the child’s condition.
To avoid worsening symptoms, parents of a sick child are advised to:
- do not take the child outside at very low air temperatures;
- ensure a high level of humidity in the child’s room;
- exclude contact of the patient with pets;
- do not put woolen clothes on his naked body;
- protect the baby from exposure to cigarette smoke, dust, and chemical odors;
- If possible, remove down pillows and soft toys;
- use hypoallergenic detergents for baby hygiene;
- carefully monitor the sterility of the child’s damaged skin to avoid infection.
to contents ^
Treatment of allergic dermatitis in adults and children
General therapy for the treatment of allergic dermatitis and their symptoms in adults and children includes several points:
identification and exclusion of the provoking factor; selection of a hypoallergenic diet; prescription of sedatives, enterosorbents, vitamin therapy and probiotics; use of antibiotics, systemic corticosteroids and antihistamines (especially in children).
Drug therapy
1) Particular attention is paid to glucocorticosteroid drugs in the form of systemic treatment - oral administration and superficial treatment of allergic dermatitis with an ointment based on the drugs "Deymovate", "Hydrocortisone" or "Elocom".
2) To prevent itching and swelling, eliminate redness, antihistamines are very effective - injections and tablets “Loratidine”, “Suprastin” and “Clemastine”.
3) The use of medicinal moisturizers is due to the thickening of the skin caused by the disease. They are based on thermal waters and animal wax. The most effective are Lipikar, Atoderm, Topikrem and Trixera.
4) Treatment of allergic dermatitis with Actovegin, Solcoseryl or Cynovit creams solves the problem of skin peeling (freeing it from scales), inflammation and irritation, promotes rapid healing of weeping wounds and elimination of itching.
5) Paste or ointment - “Bepanten”, “Advantan”, “Pentanol” - contribute to the rapid healing of dry wounds.
During pregnancy
Allergic dermatitis in pregnant women is becoming more common and makes the newborn predisposed to this pathology in the future. The increase in the number of allergy sufferers among expectant mothers is associated with poor environmental conditions, food products with nutritional additives, and the need to take medications.
Treatment of dermatitis during pregnancy is carried out according to the standard regimen. Its goal is to quickly stop the immune response to the allergen, that is, to identify the irritant and avoid contact with it, and prescribe antihistamines.
Pregnant women are most often prescribed:
- external agents - they reduce itching, alleviate symptoms, eliminate discomfort, disinfect and soothe the affected area;
- enterosorbents for rapid removal of the allergen;
- probiotics to improve intestinal function.
to contents ^
Is it possible to wash with allergic dermatitis?
Allergic dermatitis requires particularly careful hygiene. You can and should swim regularly, but following important rules:
- Avoid extreme temperature changes (very cold water, then too hot). It is better to take a shower and bath in water of moderate temperature, which will not burn the skin.
- At the end of the hygienic procedure, you should wipe yourself thoroughly, but with light circular movements, without rubbing or squeezing.
- Use an individual and clean (after washing, not drying from previous use) towel each time.
Prevention
- Use of hypoallergenic cosmetics and household chemicals;
- maximum elimination of contact with irritants;
- replacing down pillows and feather beds with their analogues with artificial fillers;
- dietary nutrition;
- regular moisturizing of the skin with special emulsions and creams;
- wearing loose-fitting clothes made from natural fabrics;
- treatment of foci of chronic infection;
- careful body hygiene to reduce sweating;
- strengthening the immune system;
- reduction of stress load;
- eliminating bad habits;
- regular walks in the fresh air.