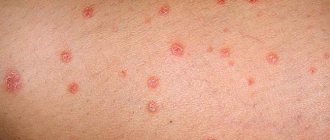
Psoriasis in children
Childhood psoriasis is a non-infectious chronic disease that affects children of school and preschool age. A characteristic feature of the appearance of this pathology in a child is the presence of inflammatory foci and the appearance of silver-white papules.
The causes and treatment of the disease largely depend on the individual characteristics of the child, as well as on the form of psoriasis and its severity. Sometimes psoriasis occurs even in newborns. If the parents of a baby suspect psoriasis, they should immediately contact a dermatologist.
Only a qualified specialist can help make the correct diagnosis and determine the necessary course of treatment.
A particular danger in treating infants is that children of this age cannot be given standard medications. Only special procedures and traditional methods can help here.
Prevention of exacerbations of the disease
The following rules and recommendations should be observed in everyday life:
- monitor the child’s hygiene;
- When bathing, use gentle products and soft washcloths;
- avoid hypothermia and overheating of the baby;
- buy clothes made from natural fabrics;
- exclude foods that may cause allergies from the child’s menu;
- avoid protracted illnesses;
- strengthen children's immunity;
- Treat cuts and cracks correctly.
If you suspect an exacerbation of the disease, you should immediately contact a dermatologist. Timely and correct treatment will ensure long remission of the disease. Older children should be taught that psoriasis is not contagious and will not limit their daily activities. Teenagers need to be given moral support.
Causes of psoriasis in children
First of all, it is worth noting that psoriasis in children occurs systemically.
The pathology negatively affects the general condition of the child’s body at a time when the immune system is not functioning properly. Despite the wide variety of opinions about the causes of the disease, doctors were unable to choose the main one, and came to the conclusion that psoriasis is a multifactorial disease .
At the same time, there are a number of scientific assumptions based on the results of studies that determine the range of main causes of psoriasis:
- Genetic predisposition of the child. In 80% of cases, a child suffers from psoriasis if the disease was observed in his parents. At the same time, only a predisposition is inherited, but the activation of the disease occurs only under the influence of external factors.
- Disturbance in the functioning of the central nervous system. Psychological trauma, stress, and frustration can also provoke the disease.
- Metabolic disease. Psoriasis develops due to a lack of vitamins and microelements.
- Infection. Most often, childhood psoriasis is the result of a previous infectious disease.
- Disruption of the endocrine system. These include hormonal imbalance and the presence of a large number of toxins in the body.
Related article:
How to cure palmoplantar psoriasis?
Photos, symptoms and treatment of psoriasis in adults
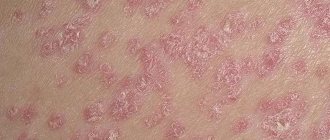
Psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of pinkish-reddish or bright red papules, covered with silvery, whitish scales, of a loose consistency. Itching of the skin may be absent or mild. Many patients report a feeling of skin tightness.
Intense itching is characteristic, as a rule, of psoriatic skin lesions of the scalp and perineum.
psoriasis of the scalp
The appearance of joint pain is noted with the development of psoriatic arthritis.
The most characteristic manifestation of psoriasis is a triad of specific symptoms of “scraping” of papules:
- the appearance of the stearin stain phenomenon (increased peeling during scraping of the psoriatic papule, as a result of which it becomes similar to a stearic drop);
- the appearance of a terminal film (the appearance of a thin transparent film remaining after all peelings are separated during scraping);
- the appearance of blood dew or the Auspitz phenomenon (the occurrence of pinpoint bleeding at the site of rejection of the terminal films).
Photo of what psoriasis looks like at the initial stage.
Psoriatic papules can be isolated or merge. The size can vary from small to covering large surfaces of the skin. The most common locations of papules are the elbows, knees, head (the scalp) and lower back.
In rare cases, plaques can affect the mucous membranes of the lips and mouth.
Children, elderly patients and people with diabetes may develop a folded form of the disease. In this case, the skin behind the ears, armpits, perineum, buttock folds, around the navel and under the mammary glands is affected.
Fold psoriasis
Patients with fold psoriasis may not have scaling. The surface of psoriatic lesions can be completely smooth and bright red. In some cases, maceration of the folds may occur.
Psoriasis of the folds
In some patients, the only manifestation of the disease may be plaques on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs.
Read further: The most effective hormonal and non-hormonal ointment for psoriasis on the skin
As a rule, psoriatic skin lesions are symmetrical, but some patients may experience unilateral rashes. The appearance of shaped psoriatic lesions (ring-shaped, arcuate, serpinginous, geographical, etc.) is also possible.
In patients with a long-term disease, long-existing plaques on the skin of the lumbar and buttock region may be accompanied by the appearance of papilomatous-warty growths on them.
Severe form of psoriasis In addition, the causes of the appearance of warty forms of psoriasis can be:
- purulent skin infections;
- improper external treatment (usually self-medication);
- excess body weight.
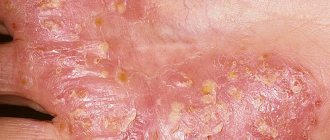
In warty forms of the disease, the scales begin to stick together, forming yellow crusts on the surface of the plaques.
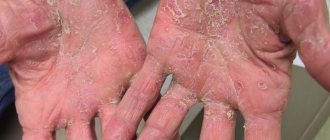
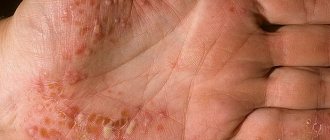
Some patients may experience isolated palmoplantar psoriasis. In this case, the patient is bothered by painful cracks, pustules, papules, erythematous-squamous plaques on the palms and soles.
Palmar psoriasis
A common manifestation of psoriasis is damage to the nail plates. In most cases, there is the appearance of pinpoint depressions on the surface of the nail (thimble-shaped degeneration). Nail deformations, longitudinal and transverse grooves, thickening of the nail plate, its loosening and discoloration, and hemorrhages under the nail plate may also appear.
With psoriatic erythroderma, which usually develops against the background of excessive insolation or improper external therapy, severe swelling of the skin, hyperemia, severe itching and peeling, fever, weakness, and loss of appetite appear. In severe cases, anemia, heart failure and impaired renal and liver function may occur, dehydration and alopecia areata may appear.
With psoriatic arthritis, asymmetric joint lesions, lesions of the interphalong joints, mutilating arthritis, spinal lesions, the appearance of periarticular osteoporosis, and bone erosions are noted. A change in skin color (purple-bluish color) is noted over the affected joint.
Psoriatic polyarthritis
Types of psoriasis in children
Each form of the disease has its own nuances, characteristics and symptoms . Based on these factors, the type of psoriasis is determined.
Let's consider how this or that type of disease begins and manifests itself in order to get a complete understanding of the pathology.
For this purpose, let's create a table:
| Type of psoriasis | Characteristic |
| Plaque-like | The most common type of disease, the first symptoms of which are the appearance of small red spots on the surface of the skin. Gradually, the formations increase in size, become dense and begin to peel off. The plaques grow quickly and after the scales are removed, a wound appears in their place. Experts say that skin lesions are found everywhere, however, most often they are located on the elbows and knees. |
| teardrop-shaped | Most young patients had a significant number of small red rashes that looked like a drop. Subsequently, they peeled off and increased in size. They are most often placed on the torso, arms, legs, and head. This type of disease goes away on its own or turns into a plaque form. Most often, guttate psoriasis occurs in children aged 4-5 years who have suffered a streptococcal infection. |
| Pustular | The most severe form of the disease, which usually occurs in adulthood. It is practically not observed in newborn children, however, cases have also occurred. The main difference between this type of pathology is the presence of bubbles with non-infectious exudate. During the course of the disease, swelling develops. |
| Generalized pustular | This variety appears suddenly and develops quite quickly. Areas of red skin appear, which later become covered with ulcers. The disease itself has an extremely negative impact on the functioning of the heart, as well as the kidneys and other internal organs. |
| Flexion of limbs | This shape suggests the presence of smooth, slightly protruding red spots at the edges. The surface of the stains does not peel off. Most often this form is observed in the genital area, in the groin or on the inner thighs. |
| Erythrodermic | This form is characterized by peeling and detachment of skin throughout the body. Typically, the patient experiences pain and itching. This type of pathology occurs as a result of a violation of the body’s thermoregulation and can cause disturbances in the functioning of the body and even death. |
| Arthropathic | Psoriasis in this form affects about 10% of patients. As a rule, the child experiences severe discomfort, swelling throughout the body, and conjunctivitis develops. Externally, psoriasis in this form resembles a strong allergic reaction of the body. |
Related article:
Heptral for psoriasis - reviews, price and instructions
Each form of the disease has its own characteristics and symptoms. Based on these points, treatment should be prescribed.
Initial psoriasis
- Initial stage of psoriasis
- Signs of psoriasis
- Treatment of psoriasis in the initial period
- Preventive actions
- Psoriasis - how to get rid of a deadly autoimmune disease?
Initial stage of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a disease commonly known as lichen planus. It is this concept that personifies all the full clinical symptoms of the disease. In terms of its structure, the disease in question is the most common type of dermatological disease, characterized by a disruption of the process of normal cell division, as well as the formation of keratin in them. It is important to note that the initial stage of psoriasis and the appearance of scales are quite easy to diagnose.
In modern times, the causes of the disease have not been precisely established. There is an opinion that the main dominant factor is a hereditary predisposition to pathology, which is realized due to certain points:
- Various injuries of a traumatic nature;
- Infectious diseases;
- Endocrine system disorders;
- High level of exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- Excessive consumption of multiple alcoholic beverages;
- Psychological trauma and so on.
Signs of psoriasis
The onset of psoriasis is caused by the formation of papules, similar in appearance to pimples. This element has clear lines and boundaries, standing out with its rounded shapes. The standard colors are pink and red. However, on the lower extremities, papules may also be bluish in color, since these parts of the body are endowed with the slowest blood flow than other organs.
The fundamental criterion for the initial stage is the appearance of silver-white scales on the papules. They bind quite poorly to the skin. That is why they are easy to separate at the moment of touch. It is noted that most often the plaques appear on the head, elbows and knees, gradually merging with each other. Of course, we should not forget about possible formations on the tips of the nails. These manifestations can become quite aggravated in winter, exposed to the influence of cold weather. In this case, the patient begins to actively feel an unpleasant itching.
Initial psoriasis can develop in a variety of ways:
- Acute manifestations;
- Subacute manifestations;
- Chronic manifestations.
The whole process naturally begins with the acute form, which occurs suddenly. Timely detection of these signs will help make treatment more effective.
Treatment of psoriasis in the initial period
Experts say that psoriasis is a disease that cannot be completely cured. However, mild psoriasis can be eliminated without bringing the body to a critical condition. In the first stages, doctors recommend using specialized drugs that suppress the human immune system. These include a variety of creams and ointments containing hormonal components. In addition, agents such as tar, naftalan oil, and synthetic retinoid can have an anti-inflammatory, improving, regenerating, disinfecting and normalizing effect on lesions.
The use of the above medications allows you to remove the external signs of psoriasis. However, over time, plaques can appear with renewed vigor. It is systemic drugs, together with local treatment, that will not only temporarily clear the skin, but also prevent the disease from developing into a more serious subacute and chronic form. Thanks to such methods, there is a real chance to eliminate external skin symptoms and manifestations as much as possible, while restraining the active development of the disease.
New generation medicine recommends many means to combat psoriasis. But it is worth noting that intervention on the part of doctors is not enough. Great importance is given directly to the patient, who is more able to prevent various relapses.
Preventive actions
Psoriasis, like any identical disease, requires correct preventive actions.
The basic rules include:
- Proper skin care;
- Normalized lifestyle.
It is important to note that each person should monitor the hydration of their own skin. However, the selection of funds must be extremely careful. All lotions, creams and other preparations aimed at optimally maintaining the water balance in the skin should contain only natural ingredients that are not capable of provoking multiple allergic reactions.
In addition, mechanical damage to the skin, that is, burns, scratches, punctures and other cuts, must be carefully and carefully treated, since they can easily serve as causes of exacerbation of psoriasis.
Among other things, various chemicals, that is, varnishes, household chemicals, paint, are a certain type of external irritant. Close contact with the compounds in question may result in severe psoriatic skin reactions.
Symptoms of the disease in a child
The degree of complexity of a disease such as psoriasis can be determined taking into account the signs of pathology.
Can you have psoriasis without symptoms? The answer is no. This disease has pronounced symptoms. The following signs of psoriasis in children can be identified:
- The initial stage of the disease in most cases is accompanied by a reaction such as the appearance of a uniform red rash with a silvery-white coating;
- The child feels unwell, looks sick, and is weak;
- Subsequently, the scaly plaques crack and minor bleeding occurs due to damage to the capillaries. This may cause secondary infection of the patient;
- In infants, symptoms such as diaper rash or eczema are observed.
In general, the symptoms of psoriasis in children are classic and there are no special signs characteristic of this pathology.
Diagnostics
It is difficult to diagnose a child under one year of age based solely on external examination and general symptoms. Psoriasis in children occurs without the characteristic psoriatic triad, expressed by the appearance of a thermal film and pinpoint hemorrhage when the scales peel off.
Infants may not have peeling in the first days of illness. The suspected diagnosis is confirmed by examining a scraping taken from the surface of psoriatic elements.
READ MORE: Small pimples in the groin of a baby
Elucidation of hereditary predisposition and past infections is important in diagnosis. During examination, it is necessary to differentiate psoriasis from dermatoses that have a similar clinical picture.
Mechanism of disease development
The disease progresses in different ways.
Psoriasis is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. There are several factors that trigger the development of the disease. These include:
- temperature changes;
- change in climate zone;
- damage to the skin in any form;
- the presence of a viral or infectious disease;
- poor nutrition;
- influence of external negative factors;
- long-term treatment with medications;
- constant stress and insomnia.
It should be noted that if parents have a predisposition to this disease, it is not at all necessary that it will appear in their children. Each child is individual and his body tolerates this or that load in its own way.
In this regard, one child has enough malnutrition to provoke psoriasis, while another will easily tolerate all the above-mentioned moments and will not suffer from these diseases.
How to treat psoriasis in childhood
Treatment of psoriasis in children should be carried out under the guidance of the attending physician.
Only a specialist will be able to accurately diagnose and determine what kind of help a small patient needs. First, you need to make an appointment with a specialist and, when visiting the consultation, talk about the first manifestations of psoriasis in your child. Also, the doctor will ask several questions regarding other points in order to find out the causes of the disease.
For example, it is important for a specialist to know whether parents or any relatives have this disease and in what form. When did the first manifestation occur and after what?
Related article:
Psoriate in the treatment of psoriasis
Answers to these questions will allow you to get a more accurate picture of the appearance and development of the pathology in order to give the doctor the opportunity to determine the form and cause of its occurrence.
Of course, the research does not end there and the baby will have to pass several mandatory tests, as well as undergo an electron microscopic examination of the epidermis. Only this diagnostic technique will allow us to determine the form and stage of development of the disease.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor draws up a treatment course taking into account the patient’s characteristics, namely his intolerance to individual components or substances.
The course of treatment for a child includes procedures such as:
- PUVA therapy;
- phytotherapy;
- use of retinoids;
- a course of immunosuppressants;
Experts recommend alternating treatment methods to achieve good results. Treatment of psoriasis in infants causes particular difficulties, since babies cannot be given complex medications.
In this case, it is very important that the doctor constantly monitors the treatment process, and that the parents carry out all necessary procedures. Only then can treatment give a positive result.