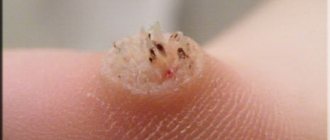
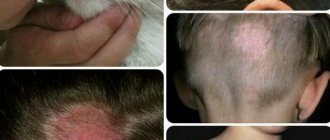
Causes of lichen
The causative agents of all types of lichen are viral and fungal infections.
The likelihood of disease increases under the following conditions:
- decrease in the level of immunity and defenses of the body;
- mental, nervous, emotional and stressful situations;
- heredity by genetic type;
- chronic diseases;
- past infectious diseases;
- tendency to allergies;
- physical and mental stress;
- long-term use of certain medications.
Transmission of infection occurs from a sick person or animal to a healthy one, through direct contact, through the use of personal items and household items. People with weak immune systems are at risk.
People with weak immune systems are most prone to shingles
A decrease in the body’s protective functions occurs due to:
- poor nutrition: excessive consumption of fatty foods, fast foods, lack of fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet, causing a deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- constant physical activity, or, conversely, physical inactivity;
- bad habits – regular drinking, smoking;
- long stay in an environmentally hazardous area;
- pathologies of the immune system;
- oncological diseases;
- injuries;
- operations;
- hormonal disorders;
- disruption of the digestive organs and circulatory system;
- chronic infections;
- the presence of damage, open wounds, cracks, erosions, ulcers on the body.
Lichen planus
The reasons for the development of this disease still remain unclear, and the same applies to the causative agents of this pathology. Lichen ruber can be considered non-contagious, although this information has not been proven by science to this day.
This type of lichen belongs to diseases that are autoimmune in nature, when the body attacks its own cells with antibodies. In order for the disease to begin to progress, a certain provoking factor must be present. Such factors may be:
- Chronic viral infections.
- Constant stress.
- Bad habits.
- The occurrence of endocrine pathologies, etc.
This type of lichen on the head of an adult is characterized by the formation of a specific rash in the form of nodules with a shiny surface. Gradually, such rashes begin to acquire a bluish tint.
This type of lichen is accompanied by severe and unbearable itching. Moreover, the whole body itches, and not just the affected areas. The rash can appear on any part of the skin, including the head, but this type of lichen is much less common.
This type of disease has several main forms:
- A blistering type of lichen planus, in which the rash appears as blisters filled with clear liquid.
- Ring form, in which the rash looks like an arc or semicircle and rapidly spreads throughout the body.
- The warty variety is a rash similar in appearance to warts.
- Lichen acuminata, where the rash may resemble sharp thorns.
- Tiperkeratic type, characterized by damage to the mucous membranes. Lichen affects the entire skin or is located on a specific area of the body.
Types of lichen in humans
The classification of lichen is based on the etiology of the disease, the mechanism of the disease, characteristic symptoms and the method of transmission of infection.
The main types are:
- pink – infectious-allergic nature (also known as Zhiber’s lichen, pithiasis);
- shingles – refers to viral diseases (herpes);
- lichen planus (erythematous) – the main factors of its development include certain diseases and heredity;
- pityriasis - damage to the epidermis by a fungal infection (other names: multi-colored, tubular, solar);
- scaly – psoriasis of non-infectious etiology;
- ringworm – fungal infection of the skin (microsporia);
- weeping – a skin reaction (eczema) to stressful or allergic irritants.
Contagious diseases include pink lichen, ringworm and shingles. What skin defects of different types of dermatoses look like can be seen in the photo:
Pityriasis rosea is contagious, so do not delay treatment
Shingles is a viral disease
Heredity is often a factor in the appearance
Occurs as a result of fungal infection
Psoriasis is a chronic skin lesion
Ringworm is transmitted primarily from animals
Eczema has several forms depending on the state of the immune system
Varieties
The types of lichen in humans are presented in the table.
| View | Cause | Age category of patients | Transmission routes | Consequences |
| Pink (Giber's disease) | Allergic reactions, herpes virus | 10−40 years | Airborne | Pigmentation |
| girdling | Herpes virus (causative agent of chickenpox) | Elderly age | Sometimes transmitted by airborne droplets, causing chickenpox (common in children) | Postherpetic neuralgia |
| Shearer | Fungi of the Trichophyton, Microsporum group | 4−15 years | Contact and household | Chronic form of the disease |
| Pityriasis (multi-colored) | Mushroom Pityrosporum Orbiculare | From 10 years and older | Not contagious | Without consequences |
| Red flat | Virus, neuralgia, allergy | Women 50−60 years old | Not getting through | Without consequences |
| Weeping (eczema) | Decreased immunity, disruption of the digestive, endocrine, and nervous systems | Any age | Not contagious | Attachment of a fungal or bacterial infection |
| Scaly (psoriasis) | Violation of biochemical processes | Any age | Not getting through | Chronic form of the disease |
| Knotty (piedra) | Basiodiomycetes mold | Any age, most often women | Contact and household | Without consequences |
Photos of lichen will help determine the type of disease.
The first signs and symptoms of the disease
Skin diseases have similar symptoms, differ in the nature of the rashes, their intensity and the course of the disease.
Pityriasis rosea
The disease begins after a herpetic infection enters the body and worsens in the spring and winter.
Characteristic symptoms:
- drowsiness, weakness, fatigue;
- large, raised pink spots on the skin;
- itching;
- presence of maternal plaque;
- peeling of the surface of the lesion, formation of scales.
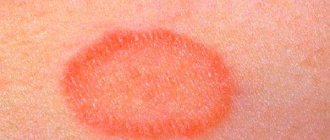
Roseola appears on the skin in the form of one large bright pink plaque with a flaky surface - maternal. After 1 - 1.5 weeks, a rash in the form of round pink pimples forms in the area of this spot.
Most often, the mother spot forms in the chest area, then the rash moves down to the stomach, bikini area, legs, and covers the hips, upper limbs, forearm and neck.
Over the course of several days, pink spots grow without merging into separate areas. The formation of a new rash continues for 15–20 days, then stops. The central part changes its bright color and acquires a golden hue. The stratum corneum of the plaque dries out, begins to peel off, and is rejected.
Regardless of treatment, the duration of the disease lasts 1.5 – 2 months. During this period, the skin color is restored and complete healing occurs.
Shingles
Dysfunction of the immune system increases the likelihood of viruses entering the body, one of which, Herpesviridae, is the causative agent of painful rashes on human skin.
General malaise, headaches, a steady increase in temperature within 37 - 38 ° C, digestive disorders, weakness, drowsiness - symptoms of herpes zoster at the initial stage.
In children, this discomfort continues for 2–3 days; for adults, this period increases to 7 days. The disease continues to progress, accompanied by severe muscle and joint pain, fever, and a rash on the body in the form of painful and itchy pink blistering spots.
After 15–20 days, the inflammatory process in the rash goes away, dry crusts form on the surface of the vesicles, which disappear after peeling.
The localization of the rash is unilateral, the damaged area is very sensitive, with severe pain, covering mainly the chest, back and lumbar region.
Relapses of the disease occur rarely - in 2–3% of cases of the general picture of the disease. In older people, pain in the dermatomal area (postherpetic neuralgia) persists for a long time - several months or years.
Lichen planus
The disease spreads to the nail plates, skin and mucous membranes.
The location of the rash, the appearance of the blisters and spots, their grouping in the affected area explains the conditional division of lichen into several subtypes, including:
- Typical - a rash in the form of red flat nodules with a crimson or purple tint and slight peeling. It affects the inner thighs, the flexion area of both types of limbs, the torso, and can be located under the armpits and on the oral mucosa.
- Warty - layers form on the surface of the plaques, reminiscent of warts in structure. Appears on the surface of the shins from the front side.
- Atrophic – sclerotic or atrophic changes in skin cells are observed in areas of rashes. In the hair growth area, areas of baldness are possible.
- Blistering - the skin tissue or the surface of the red spots is strewn with small blisters filled with serous fluid. They are located on the lower part of the legs - on the feet and lower legs.
- Moniliform - the rash forms a necklace of waxy, shiny, round vesicles. Papules are localized on the neck, behind the ears, on the forehead, abdomen, butt, and affect the tissues of the elbows and knees, on the fingers and hands.
- Pigmented - rashes are accompanied by the formation of pigment spots and brown lumps.
- Pointed - papules are a tubercle with a spine-like process of horny tissue located in the center. Formed on the shoulder blades, lower extremities, neck, elbows.
- Ring (Vidal's lichen) - pimples are connected into semicircular or round lesions, located on the back of the head, upper back, lower back, often affecting the genital area - on the penis in men and the pubic part in women.
- Erosive-ulcerative - a pathological process develops on the mucous membranes, mainly in the mouth. The rashes are small erosions and ulcers, with redness and swelling of neighboring areas.
A distinctive feature of the rash when the skin is affected by lichen planus is the presence of a network-like pattern on the surface of large plaques - Wickham's symptom. It is clearly visible when the affected area is treated with vegetable oil.
Patients complain of severe itching of the affected area. Half of the victims have damage to the skin of the genital organs and the oral mucosa. 15% of patients note the spread of rashes to the nails, as a result of which they become thinner, cloudy, and become brittle and brittle.
Pityriasis versicolor
The causative agent of the disease is a yeast-like fungus that lives in the skin of the human body. Under favorable conditions, it begins to actively reproduce, damaging healthy tissue. An exacerbation of the disease usually occurs in the spring and summer, when the activity of solar radiation increases.
Important!
The disease is also known as solar, color or multi-colored lichen due to the characteristics of its course and the color of the skin rashes.
The disease at the initial stage is manifested by the formation of milky-brown spots on the skin with clear contours. The rash appears in separate elements, gradually increasing in size and merging into groups.
The vital activity of the fungus in the affected areas disrupts the formation of melanin pigment in the cells, and under the influence of ultraviolet rays a tan appears on the skin.
Important!
In the hot season, pityriasis versicolor can be easily identified by the presence of light plaques on a tanned body.
Apart from its unattractive appearance, the sunburn rash does not cause any additional discomfort. Itching occurs in rare cases, peeling in the affected areas is almost not noticeable.
Squamosal lichen
Psoriasis, or scaly lichen, is a chronic non-infectious lesion of the skin, which is difficult to treat and causes physical and emotional discomfort to the patient.
If left untreated and the appropriate rules are not followed in everyday life, unaesthetic scaly patches can cover a large area on the patient's body.
This is what an advanced form of the disease looks like
Common symptomatic signs of psoriasis are:
- constant fatigue, fatigue, weakness;
- apathy, mood swings, emotional depression;
- itching and rashes on the skin;
- damage to the nail plate.
There are several known subtypes of scaly lichen, which are classified depending on the location and general signs of the rash.
Plaque type. One of the most common types of psoriasis. The spots can be located on the outer or inner side of the elbows and knees, on the scalp, in the lumbar region, intimate area, and buttocks.
Rash with plaque lichen has 3 stages of development:
- Progressive - small reddish spots appear on the skin, which increase in size every day.
- Stationary - the spots grow, unite into larger areas, on the surface of which light gray scales form. The affected area itches and peels.
- Regressive - the color of the plaques fades, new scabs stop forming, peeling subsides.
Periods of exacerbation, remission and the corresponding stages of development are repeated.
Drop-shaped type. Characterized by rapid development against the background of previous viral or infectious diseases. The rash appears on all parts of the body with the exception of the face. The spots look like itchy red pimples with a papule that breaks through and rots.
Just like plaque, guttate lichen is divided into 3 types:
- Mild form - small, single papules appear on the body, which without appropriate treatment increase in size, forming plaques. The rash covers no more than 3% of the total body surface.
- Moderate form - with the same symptoms, 10% of the skin is affected.
- Severe form - the rash spreads throughout the body; treatment is long-term and requires an individual approach in each individual case.
Pustular type. This form of psoriasis is observed in 1% of people from the total number of patients. The most common areas affected are the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
The sole is a favorite location for pustular psoriasis.
At the initial stage, the skin turns red, then an itchy rash appears on it in the form of pustules with contents inside. Unpleasant symptoms worsen at night or after using detergents and household chemicals.
The pustules, increasing in size, merge into a large painful area - a round-shaped plaque covered with small whitish scales. Bursting blisters form an open wound, which can become infected and cause purulent inflammation.
2–3 weeks after the onset of the pathological process, the stationary stage begins. The spots lighten, stretch out in shape, and peeling decreases.
At the fading stage, the affected areas acquire a healthy color, and a ring of rough skin forms at their border. This period can last several months, and in complicated cases – more than a year.
Due to the stuck together scales during purulent inflammation, the pustular type is also called exudative psoriasis.
Important!
The most severe form of scaly lichen is considered to be erythroderma - a total lesion of the epidermis, dangerous to human life.
The reason for its development is advanced cases of purulent psoriasis in the absence of the necessary treatment.
Ringworm
An infectious form of skin disease caused by fungal microorganisms. Most often occurs in childhood, when the child comes into contact with sick animals.
Considering the type of pathogen, there are 2 types of ringworm.
Microsporia. The disease develops when the pathogenic fungus Microsporum enters an open area of the body, which penetrates the tissue and affects the hair, nails and skin.
A red spot with clearly defined, convex edges forms on the affected area, representing small compactions and blisters. The size of the plaque increases until it is fully mature, then a period of inflammation subsides.
The color of the spot becomes lighter, the crusts begin to dry out and peel off. The presence of 1 to 3 such plaques with a diameter of 1 to 3 cm is considered characteristic of ringworm.
Microsporia spots are located on the shoulders, neck, face; the rash can appear in the eyes, nose or ear, less often on the palms, soles or nails.
Fungal infection of the scalp is determined by the following symptoms:
- peeling of the skin at the site of the lesion;
- breaking off hairs in the infected area;
- light gray plaque on the hair (fungal spores);
- large size of lesions – up to 5 cm in diameter;
- clear boundaries;
- redness and swelling of the affected area.
Ringworm is localized in the area above the temples and the parietal part of the head. The area affected by the fungus has the appearance of short-cropped hair, hence the name of this form of lichen.
Trichophytosis. The second type of ringworm, caused by trichophyton fungi. This type is divided into superficial and infiltrative-suppurative forms.
Features of the development of superficial trichophytosis:
- irregularly shaped borders with blurry edges;
- peeling with the formation of silvery scales;
- redness of the skin inside the lesion;
- merging of small lesions into large ones;
- hair breakage;
- the formation of small bubbles and yellowish crusts.
The disease affects the occipital and temporal parts of the head, buttocks, and other parts of the body on which hair grows. Foci of the disease are located on the skin in the form of small (up to 1 cm) bald spots, contagious to others.
Trichophytosis most often affects the head and other parts of the body where hair grows.
The infiltrative-suppurative form of lichen is observed on the skin of the neck, head, face, and in men it occurs on the chin, nose, and near the mouth.
A characteristic feature is the appearance of bright red spots strewn with small pustules and scabs. Oval-shaped swollen areas form on the head, from which, when pressed, purulent contents are released. Hair lost in these places does not grow back even after recovery.
Possible enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, increased body temperature, headaches, weakness, and malaise.
If there is a suspicious rash on the body of an infant, urgently show it to a specialist to exclude the possibility of contracting lichen.
Nail trichophytosis has the following symptoms:
- formation of a pale spot on the surface of the nail;
- rejection of the nail from the skin;
- delamination and fragility of the nail plate;
- destruction and loss of the nail in complicated cases.
Ringworm
Eczema comes in several forms when the immune system is weakened.
True Form
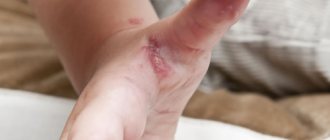
It is characterized by an acute course; in the absence of therapy, it becomes a chronic skin disease. In a short period of time, numerous vesicles cover the forearm, chest, arms, legs, buttocks, and less often the face.
After the pimples open, wet, inflamed erosions form. Soon the crusts dry out, the wounds close and heal.
Dyshidrotic form of eczema
The rashes are clearly defined, looking like dense blisters covering the soles of the feet and the front surface of the fingers. Bursting ulcers peel and flake off and are very itchy.
Microbial form
It develops at the site of damage to the skin when pathogenic microbes enter the wound. In the inflamed areas, a crust forms, under which there is cellular tissue with elements of erosion.
Coin shape
The lesions have clear boundaries, the damaged area is red with a bluish tint, up to 3 cm in diameter, the surface is wet. Localized in the bends of the elbows or under the knees, there are known cases of damage to the back of the palms of the hands.
Seborrheic form
Area of distribution: elbow joints, behind the ear area, chest, head, shoulder blades. The affected area is covered with hard yellowish scales; liquid constantly oozes from the formed microcracks, and subcutaneous swelling is observed.
Seborrheic form of weeping lichen on the chest
Hair growing in these areas becomes sticky due to the humid environment and is recommended to be removed to facilitate treatment and stop the spread of infection.
Professional (allergic) form
A characteristic feature is the presence of rashes of different stages on the skin - from redness to healing scaly ulcers. Most often observed on the hands, face, and lower extremities.
Atopic form
It immediately affects an impressive area of skin, which swells slightly, turns red, itches and becomes very dry. At the site of discomfort, bubbles containing infectious fluid form. After scratching, wounds and cracks appear, from which a wet environment is released. Pathogenic organisms entering the affected area lead to the development of the inflammatory process and inhibit healing.
Ringworm on the skin
Signs of the disease can be found on any part of the body. If they occur on the scalp, the lesions are represented by round spots up to 10 cm in size. In these places, the hair thins. Dry white or gray scales appear. Bubbles appear in the periphery, and then yellow crusts. The patient experiences slight itching.
When smooth areas of the skin are affected, spots appear that have clear contours. On the peripheral part, a pink cushion is visible, on the surface of which there are bubbles and crusts. Scales are observed in the central part. Damaged areas itch.
If the fungus infects the nail plate, it becomes cloudy, crumbles, thickens and becomes jagged.
Treatment is carried out using antifungal drugs (Nizoral, Ketoconazole), topical agents (iodine, salicylic ointment). When the scalp is affected, medicated shampoos (Dermazol) are used.
Diagnostics
Important!
It is not recommended to determine the type of disease yourself. Diagnosis is carried out in a hospital setting.
At the first appointment, the dermatologist examines the patient’s skin, affected areas, nails and hair.
The doctor first examines the skin and hair to understand the etymology of the disease
- If a visual examination fails to diagnose the disease, laboratory tests of blood serum and urine are prescribed.
- If pityriasis versicolor is suspected, iodine tests are performed. Treatment of skin plaques with iodine reveals a change in color of the affected areas.
- To confirm shingles, microscopy and serological tests are used.
- An increase in the level of ESR and leukocytes in a blood test indicates the presence of lichen planus.
- For a more detailed study of the disease picture, a biopsy of a skin sample is taken from the problem area, a culture from the throat to determine the state of the microflora, and a scraping from the surface of the spots.
- Luminescent diagnostics makes it possible to distinguish pityriasis rosea from pityriasis versicolor.
Psoriasis
Signs of the disease can be observed on any part of the body. First, a rash appears that looks like round, scaly bumps. Their color can range from pink to red. The scales are scraped off, leaving behind a damp surface. With further exposure, bleeding may begin.
As the pathology develops, the tubercles increase in size and turn into plaques, which then merge. Their resorption occurs from the central part. As a result, something like a garland is formed on the skin. The disease is accompanied by itching.
Any form of psoriasis is characterized by damage to the nail plate. If this happens, the nails become cloudy and thick. On the palms and feet, the disease is accompanied by redness, the formation of crusts and cracks. Scales and psoriatic plaques also appear.
It is impossible to completely cure psoriasis because it is a chronic disease. It is characterized by periods of exacerbations and remissions. To get rid of symptoms during periods of exacerbation, complex therapy is recommended. Hormonal ointments (Lorinden, Mometasone), external agents based on tar (Kolposedin), and preparations with solid oil (Antipsor) are used. Spa treatment, physiotherapy, and proper nutrition are recommended.
Treatment of deprivation in humans
The main drugs for the treatment of dermatological skin diseases are:
- Clotrimazole-Fitofarm. It has a wide spectrum of action, eliminates all types of fungal infections, suppresses their reproduction. Used in the form of creams, ointments and tablets. Effective for ringworm and pityriasis versicolor.
- Mycoseptin. The action of the ointment is aimed at deactivating the growth and destruction of fungi.
- Dermazol. Affects all types of fungal spores that cause lichen. Skin rashes are treated with ointment, and shampoo is applied to the hair growth area on the head.
- Acyclovir. An antiviral drug that has a selective effect on herpes virus infections. Prescribed for herpes zoster.
- Panavir-gel. It has a detrimental effect on viruses and stimulates the body's immune system.
- Lamicon. A long-acting drug that kills yeast and mold fungi and promotes rapid healing of affected areas. Used to treat multicolored ringworm.
- Lamisil. It is used for damage to the nail plates, hair, and skin with solar, pink and red types of lichen.
- Mikofin. The cream is applied to the elements of the rash for ringworm, tinea, and herpes zoster. The components of the drug destroy the cell structure of the pathogenic fungus, leading to its death.
→ Read more in the article “How to treat lichen”
Lamisil is used depending on the type of disease in sprays, creams, ointments and tablets
Antihistamines are used to suppress allergic reactions:
- Suprastin;
- Eden;
- Loratadine;
- Hifenadine;
- Diazolin;
- Bepotastin.
In addition to ointments and creams for external treatment, antiviral medications are used for oral administration:
- Famvir;
- Virolex;
- Gerpevir;
- Medovir;
- Valtrex.
Important!
All drugs must be used in accordance with the dosage indicated in the instructions.
Remedies for ringworm
When combating this skin lesion, various groups of medications can be used: ointments, gels, sprays, tablets. Traditional medicine can also be used. However, all appointments must be made by a dermatologist. He knows how to treat shingles. If necessary, this specialist can refer the patient for a consultation with an immunologist and infectious disease specialist. Self-medication is dangerous! It is important to remember that different types of lichen occur in people; treatment is individual in each case. It is tailored to the type of pathogen involved.
Ointment for ringworm
This is a group of medications created to combat dermatological problems. Before treating lichen, it is important to understand the nature of its origin. More often, the pathology is provoked by viruses and fungi. In this case, the drug used must destroy the pathogenic microorganism that caused the problem and remove the accompanying unpleasant symptoms: inflammation, itching. If the disease is non-infectious (an autoimmune reaction of the body or an allergy), other medications are selected to combat it.
How to treat lichen in humans:
- Yam ointment
is a drug that has antifungal and acaricidal effects. This drug contains salicylic acid, Lysol, zinc oxide, and so on. This ointment is recommended to be applied in a thin layer to the areas affected by lichen, covering 2-3 cm of nearby healthy tissue. This product should be used twice a day for 1-2 weeks. - Zinc ointment
is a medicine with a drying and antiseptic effect. This medicine is used externally. It is applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the body. You need to do this procedure 2-3 times a day. The duration of therapy depends on the intensity of the lesion and is determined individually for each patient. - Sulfur ointment
is an effective medicine that has a disinfecting effect. This medication destroys fungi. For lichen, it is recommended to treat the affected area with salicylic alcohol, and then apply a thin layer of sulfur ointment to the body. The maximum allowable duration of therapy is 10 days. - Terbinafine
is an ointment that is highly effective against almost all fungal agents. This drug is applied to the area affected by lichen a couple of times a day. The course of therapy lasts from 3 to 6 months. - Oxolinic ointment
is a drug with high antiviral activity. It is applied 2-3 times a day in a thin layer. Duration of therapy is 2-8 weeks. - Acyclovir ointment
is a medication that has high activity against herpes. Its main component interacts with agents, interrupting the process of their reproduction. This product is applied to the skin up to 5 times a day for 7-10 days. - Streptocide ointment
is an antimicrobial agent that is effective in combating infectious skin lesions. This medication is applied to the skin in a thin layer. The procedure is done at night. The duration of therapy is determined individually.
Tablets for lichen
Several groups of drugs are used to combat this pathology. Most often these are painkillers, antiviral and immunostimulating drugs. Depending on what type of lichen is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed.
In most cases, the following tablets are prescribed:
- Valtrex;
- Acyclovir;
- Fluconazole;
- Nystatin;
- Pimafucin;
- Cetirizine;
- Fexadine;
- Griseofulvin;
- Lamisil;
- Chloroquine;
- Fulcin.
Folk remedies for lichen
Non-traditional methods of therapy are also effective in the fight against skin lesions. Tar gives a good result. This remedy is effective for any type of lichen. It is an excellent antiseptic that destroys pathogenic microflora. In addition, tar stimulates the process of restoration of damaged tissue. It is actively used in both traditional (part of ointments) and folk medicine.
Tar ointment for lichen
Ingredients:
- birch tar – 1 part;
- fish oil or softened butter – 1 part.
Preparation, use
- The components are combined until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
- The finished folk remedy for lichen is spread in an even layer on gauze folded in two.
- The compress is applied to the affected area for a couple of hours. Such procedures should be done for 4-5 days in a row. To enhance the effect, it is recommended to use tar soap for lichen before applying a compress. As an alternative, Zinc ointment can be used. After removing the compress, treat the surface with this preparation.
How to get rid of ringworm with garlic vinegar?
Ingredients:
- garlic – 1 clove;
- apple cider vinegar – 200 ml.
Preparation, use
- The peeled clove is poured with vinegar and left in a dark, cool place for 10-12 days.
- Soak a gauze bandage in this solution and apply it to the affected area overnight.
- The procedure is performed until no trace remains of the skin problem.
Mysterious pityriasis rosea
Pink lichen, or, as it is also called, Zhiber's lichen, has not yet revealed its secrets to doctors. No one can say what exactly causes this unpleasant disease. It is only known that it is not contagious, and most often affects people aged 10 to 35 years. It is usually preceded by a severe cold, severe stress, or a general decrease in immunity.
Ringworm manifests itself as follows: first, a so-called maternal plaque about 2 cm in size appears on the body. Then it dries out and begins to peel off, and after a few days small pink spots spread throughout the body. After 6-8 weeks (sometimes after 12), the disease goes away spontaneously. The rash may be accompanied by itching, slight fever, nausea and headache.
Scientists are still searching for the causative agent of the disease and ways to treat it. It has been suggested that pityriasis rosea is associated with the reactivation of the herpes virus 6 and 7, which causes roseola infantile (after recovery, it does not disappear, but remains in the body in an inactive form). But these are just assumptions for now.
During the first week of illness, swimming is prohibited, as this leads to increased spread of lichen to the entire surface of the body. Treatment may include zinc liniment and ultraviolet irradiation. If the itching becomes unbearable, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroid medications. But even if you do not take any action, the lichen will definitely disappear after 12 weeks.