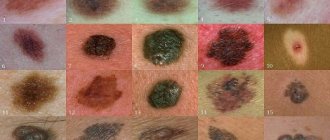
When and where does a syphilis rash appear?
A sexually transmitted disease of an infectious nature has a wave-like course. If left untreated, the disease affects all systems of the human body.
The causative agent of syphilis is Treponema pallidum
The progression of the disease and the appearance of the rash occurs in stages:
- Incubation period. The pathogen spreads throughout the body through the blood and lymph flow. There are no clinical manifestations at this stage. As a rule, the pathogen multiplies latently within a month.
- Primary syphilis. At this stage, characteristic skin rashes appear in the area of penetration of the infectious agent. Regional lymph nodes are involved in the pathological process. The stage lasts up to two months.
- Secondary syphilis. This is a long period that progresses over several years. The stage is characterized by an undulating course and the involvement of various organ systems in the disease. It is noteworthy that periods of remission alternate with regular exacerbations.
- Tertiary syphilis. The form is quite rare, which is due to the capabilities of modern medicine. Lack of timely treatment causes irreversible changes in organs. The consequences include disability and a high risk of death.
Attention! Skin syndrome is a mandatory manifestation of syphilis. The localization and nature of the rash depends on the stage of the disease.
Does the rash with syphilis itch?
The pimple is hard like cartilage tissue, for example, the ears. In the central part a crust of a grayish-yellowish hue is found. When it is removed, erosion can be seen. If such a crust is absent, the rash has a rich red color.
Important! A dense brown crust usually forms on exposed areas of the skin.
The pimple has the following forms:
- nodular;
- leaf-shaped (more often in men);
- lamellar (labia).
The papule penetrates deeply into the surrounding tissues and has smooth and clear boundaries that look like a red rim. The rash has a regular oval or round shape.
The pimple does not cause pain. There is no itching during chancre formation. Against the background of irritation, serous contents may be released, including the pathogen in significant quantities.
Spots in children with syphilis
When elements of a rash appear, such symptoms cannot be ignored.
How to distinguish spots caused by syphilis from other pathologies?
When children become ill, specific spots form at the stage of secondary syphilis.
Moreover, the rashes are similar to the rash that occurs when infected with childhood infections (rubella, measles, chickenpox).
Another symptom similar to childhood infectious diseases is fever over several days.
The main differences between spots due to syphilis from elements formed due to other reasons:
- rashes remain on the child’s body for a long time – several months;
- the presence of a wave-like course of the disease. Alternation of the appearance of rashes with their disappearance throughout the entire period of secondary syphilis.
The spots, as in adults, can have different colors.
In children, rashes due to syphilis can manifest as:
- roseola
- papules
- pustules
After antibiotic therapy, their number may decrease.
If similar elements of a rash form on the child’s body, you should be examined for the presence of syphilis.
Pediatric doctors very rarely recommend such an analysis, which contributes to the progression of the pathological process.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that not only sick parents can infect a child; infection is also possible through contact.
For example, the patient may be among the adults and children surrounding the child.
The infection can be transmitted:
- when using one pan
- through drinking water
- through close contact with the patient
If secondary syphilis is not treated, the disease will progress to the next stage.
An untreated disease poses a danger not only to the child, but also to adults.
Pathology can negatively affect the functioning of internal organs, and even cause disability and death.
Treatment of the disease includes the mandatory use of antibiotics, and if necessary, the sick child is hospitalized.
What does the rash look like and symptoms of primary syphilis?
The end of the incubation period is indicated by the appearance of a syphilitic ulcer. This rash is called chancre. At this stage, there are no changes in blood tests.
There are two types of chancre:
- sexual;
- non-sexual.
The place of introduction of the pathogen is the following zones:
- skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, mouth;
- hips;
- bikini area, abdomen, anus;
- upper respiratory tract.
Thus, there are three options for localizing rashes:
- Genital (clitoris, cervix, cervical canal, labia, vaginal walls). This location of acne is observed in 90% of cases. Certain difficulties arise in differential diagnosis. When the rash is located in the genital area, syphilis is often confused with bartholinitis.
- Anal (rectum, anus). The chancre has an atypical shape, for example, elongated, oval or slit-like. The rash appears after anal sex with an infected person.
- Extragenital. Dense pimples appear on the body. Often with syphilis there is a rash on the neck. The form can be combined with the genital one. The rash on the fingers resembles felon.
Important! In the atypical version, acne is similar to ulcers from genital herpes.
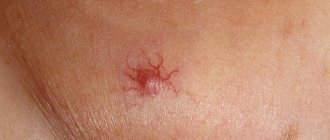
Chancre is a round-shaped erosion that appears 3-4 weeks after infection with Treponema pallidum.
The rash has smooth edges. The chancre is quite hard. In terms of tactile sensations, it can be compared to cartilage.
Initially, the rash appears as a red spot. After a few days, a painless papule appears raised above the skin level. The rash may peel a little. Gradually, growth and thickening of the papules are noted. A peculiar pimple stops growing when it reaches the required size.
Usually the chancre has a circumference of up to 5 cm. Small rashes are typical for the skin in the scalp and body area. They spread deep into the follicle. Large pimples can be seen on the pubic area, face, forearms, inner thighs and lower abdomen.
Attention! The appearance of characteristic rashes is noted in 80% of cases of infection. Multiple formation of chancre occurs when the skin is damaged.
After about a month, the rash regresses. In the absence of the necessary treatment, a pink spot remains in the chancre area, which cannot indicate recovery. The disappearance of a pimple indicates the active reproduction of Treponema pallidum and the transition of the disease to the next stage.
It is noteworthy that sometimes the rashes are secondary. This is due to the following predisposing factors:
- history of chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, anemia);
- poisoning with alcohol, toxins, chemicals;
- failure to comply with the basic rules of intimate and personal hygiene;
- elderly age.
Syphilis on the skin: photos, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods
“Behavioural disease”, “French disease”, “German disease”. The names of syphilis are varied, as are the symptoms. Modern trends are forcing society to become more literate in health and medicine. So…
What is syphilis
Syphilis is an infectious venereal disease with a wave-like course that affects all systems of the body.
The causative agent of syphilis is Treponema pallidum. The course of the disease occurs in several stages:
- The incubation period involves the spread of the pathogen through organs and tissues through the circulatory and lymphatic systems with further reproduction. This stage has no clinical manifestations. Lasts within one month;
- The period of primary syphilis begins with the appearance of characteristic skin changes at the site of penetration of the pathogen. As well as the involvement of regional lymph nodes in the process. Duration of the period is 1-2 months;
- secondary syphilis. The stage is long (up to several years) with an undulating course. Many body systems are already involved in the disease. Now periods of acute clinical manifestations will alternate with periods of imaginary well-being;
- tertiary syphilis. With modern medical capabilities, this is a rare occurrence. It manifests itself in the absence of treatment in the form of irreversible changes in organs. It ends in disability or death for the patient.
Skin syndrome in primary syphilis
One of the obligatory manifestations of pathology is skin syndrome. It is important not to confuse or substitute concepts! There is no separately existing disease “cutaneous syphilis”!
At different stages of the disease, the rash will have different characteristics and localization. Today, real photos are available for everyone to view and study.
In order not to be just scared, but to be armed, let's understand all the variety of manifestations of skin syphilis!
The end of the incubation period will be the first sign on the skin - chancre (also known as a syphilitic ulcer). At the same time, specific changes in blood tests are still silent!
According to localization, genital and extragenital chancre are distinguished. But this will certainly be the site of primary penetration of the pathogen (mucous membranes and skin of the genital organs, anal area, skin of the thighs, bikini area, abdomen, mucous membranes of the lips, oral cavity, upper respiratory tract).
Externally, the chancre has the appearance of a rounded erosion, with smooth edges. It’s not for nothing that education is called solid. Indeed, chancre resembles cartilage to the touch.
Most often, a syphilitic ulcer is single, up to several centimeters in size. It does not cause any particular concern to the patient, other than the unaesthetic appearance. The surrounding tissues and lymph nodes are still intact.
Atypical types of chancre deserve special attention.
This is a chancre-felon, when the primary focus is localized on the first phalanx of the finger and copies the symptoms of felon. The course involves pronounced inflammatory manifestations.
This is chancre-amygdalitis, simulating unilateral tonsillitis, but without the pain and intoxication component.
This is indurative edema, when the affected area does not have clear boundaries, but looks like a widespread dense infiltrate.
Skin syndrome in secondary syphilis
The spread of various types of rash diffusely, including the palms and soles, signals the transition of the disease to the stage of secondary syphilis. Many syphilitic skin lesions have led to
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, even provided a separate niche for this condition and included “Secondary syphilis of the skin and mucous membranes” as a separate unit.
Syphilis on the skin is now characterized by polymorphism (variety) of rashes: roseolous syphilide, papular syphilide, condylomas lata, syphilitic leucoderma, syphilitic tonsillitis, syphilitic alopecia. And now more details...
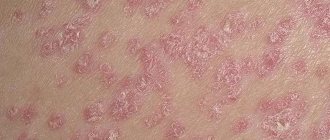
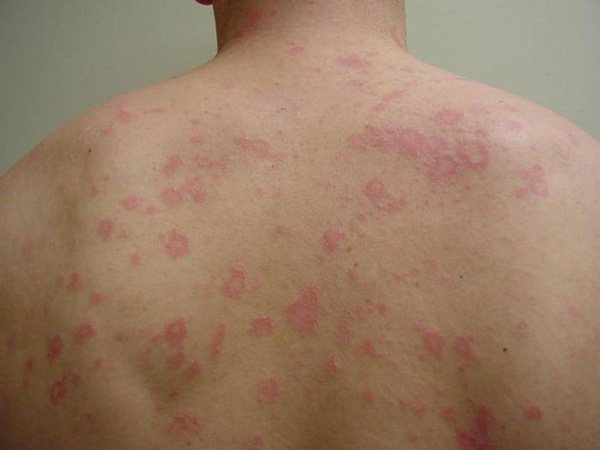
Roseola syphilide. The most common manifestation of secondary syphilis is on the skin. Occurs in 80% of patients. It looks like multiple pink spots up to 1.5 cm in diameter, which are scattered over the skin of the torso and limbs.
The spots do not rise above the skin, turn pale when pressed, do not peel or itch. Resolution of the rash occurs on average in 2-3 weeks, sometimes up to 6 weeks. But after a while the 2nd wave comes.
The rash is now larger, paler, and tends to coalesce. It should be noted that there are also rare types of roseola: follicular and scaly.
Papular syphilide. This type of rash appears both along with roseola and independently. Papules are nodules located subcutaneously.
Depending on the size, nodules are divided into types: millet-shaped, lenticular, coin-shaped, plaque-shaped. Papules are localized scattered throughout the body, often on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx.
Most of the time there is no pain. With the exception of the rash located in the folds. There is a high probability of secondary infection and the transition of papules to weeping erosions.
Important! The liquid separated from the erosion contains a huge amount of pale treponema. Therefore, in such cases, it is advisable to remember the risk of contact and household infection.
Wide condylomas. The problem of condylomas formation occurs in 5-10% of patients. Representatives of the fair sex are mostly unlucky. The favorite location is the perineum, sometimes the skin of the inner thighs.
The process begins with the grouping of papular rashes in the above areas and the gradual formation of plaques. The plaques merge into large areas, a wide stalk is formed and continues to spread to nearby areas.
The surface of condylomas is covered with scales and a gray coating. The exudate released from the surface contains a huge number of pathogens, which makes the patient very contagious.
Without treatment, the uncontrolled growth of condylomas lata can spread the formations to the mammary glands and armpits.
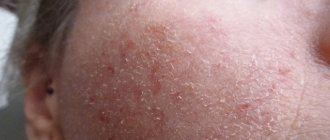
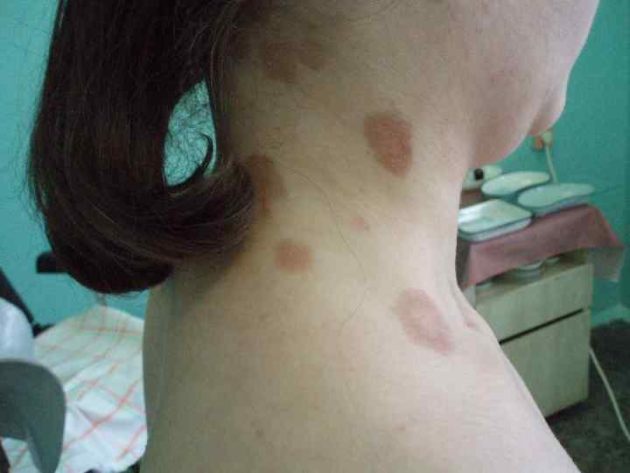
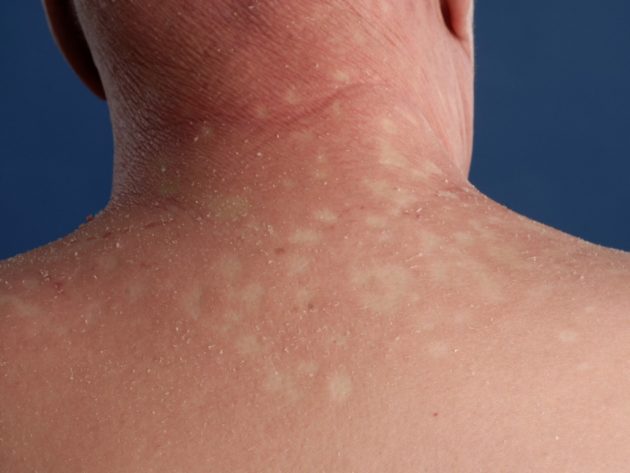
Syphilitic leucoderma. The rash appears as patches of uneven skin pigmentation. The affected areas of darkening first appear, which then transform into large white spots.
The skin in the area of the shoulder girdle, back, lower back, abdomen, and rarely the extremities is affected. Doctors distinguish spotted and lacy forms of leukoderma. With spotty, isolated foci are in familiar places.
With a lace shape, the spots merge into intricate patterns. This fusion around the neck has received the romantic name “Venus necklace”.
Interestingly, Treponema pallidum is found in the superficial layers of the dermis only in areas with leukoderma maculae.
Syphilitic alopecia. There are two reasons that cause hair loss due to syphilis. This is either the lack of hair growth in places where scars form after the rash resolves. Or their loss as a result of the course of the disease and a decrease in the body’s defenses.
In any of the cases, a characteristic sign is the focality of the lesion, scattered areas of baldness throughout the head.
In this case, the scalp resembles moth-eaten fur. And hairless skin has no specific changes. Hair growth can be restored by choosing the right treatment.
Syphilitic sore throat. A condition that occurs if, during primary syphilis, chancre is localized on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils. Then the secondary stage of development will imitate the course of a sore throat.
Initially, with the coloration of the palate and tonsils in a bluish-red color. This is followed by the appearance of erosions (ulcers) and the spread of a gray rash over the entire surface of the oral cavity.
The process is accompanied by intoxication and hyperthermic syndrome, peripheral lymphadenitis.
Skin syndrome in tertiary syphilis
Rare, but still occurring, is tertiary syphilis. Occurs in untreated or undertreated patients. Tertiary syphilides are skin lesions in the form of tubercles or gummas.
They are represented by deep infiltrates in which the body has “immured” Treponema pallidum. Nodular syphilide looks like small (5-7 mm) subcutaneous nodules scattered in large numbers.
Whereas gummas are large nodes, often not numerous. Elements of the tertiary period with a malignant course.
At the site of destruction, they will form ulcers and scars, involving the underlying bone and cartilaginous structures in the process of destruction. In this case, there are no acute inflammatory phenomena.
You've probably seen photos of a saddle nose change. So this is a clear example of the irreversible destruction of bone tissue with untreated syphilis.
Skin syndrome in congenital syphilis
I would like to dwell separately on the types of skin manifestations of congenital syphilis.
Congenital syphilis is a form of syphilis that occurs when the fetus is infected during fetal development.
Skin syndrome will be one of the clinical manifestations.
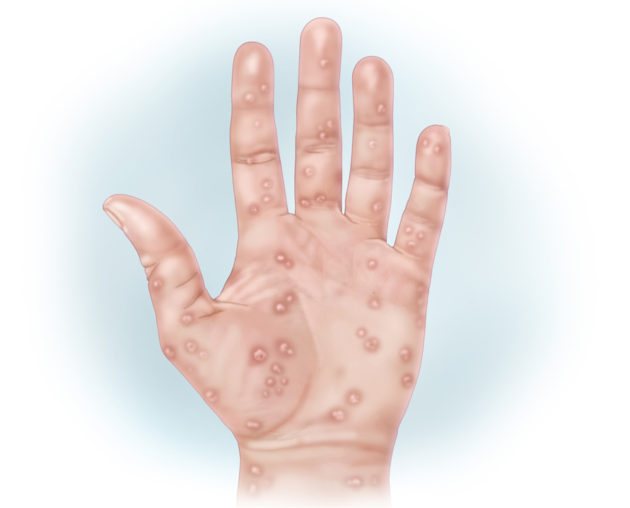
Papular eruptions. Papules are located in the perineal area, on the buttocks, palms and soles.
The mucous membranes of the oral cavity and nose are also involved. Characteristic is the radial arrangement of papules and scars after their resolution on the skin of the face, and especially around the lips.
Pemphigus of the skin. A condition characterized by blistering rashes. The favorite localization of the latter is on the palmar and plantar surfaces of the extremities.
Differential diagnosis of skin manifestations
As can be seen from the description of the skin syndrome, it is quite diverse. It is not for nothing that syphilis has been called “monkey disease” since ancient times, referring to the variety of its masks.
The clinical picture requires differential diagnosis with dermatological, gynecological, urological, dental and other diseases.
Let's look at some specific examples.
Hard chancroid is differentiated from psoriasis, lichen planus, balanoposthitis, scabies, and erosions caused by other STD pathogens.
With an extragenital location of the chancre, the latter can be regarded as a boil, carbuncle, tonsillitis, stomatitis.
Often diagnostic errors are caused by secondary syphilis. The rashes are disguised as psoriasis, different types of lichen, toxicoderma, epidermophytosis, syphilitic alopecia must be distinguished from other types of alopecia, trichophytosis.
Condylomas lata are differentiated from papillomavirus condylomas and hemorrhoids.
It is important for doctors of different specialties to remember the visual characteristics of many types of rashes to differentiate and establish the correct diagnosis. Here, specialists are helped by characteristic signs and photographs of real patients.
The best prevention of sexually transmitted diseases is the culture and literacy of intimate communication. Be healthy and loved!
Source: https://sifilis24.ru/vidy-sifilisa/sifilis-na-kozhe.html
Types of rash with secondary syphilis
The infectious disease has various manifestations. It is known that rashes occur with syphilis in most cases. The secondary stage begins about a month after the formation of a hard pimple, which is called a chancre. It is present in a third of patients with the secondary form.
The small rash of syphilis is characterized by its multiple nature and symmetrical location. Acne gradually disappears, despite the presence or absence of appropriate therapy.
Typically, relapse occurs after six months. Sometimes remission lasts up to 24 months. The number of skin rashes with syphilis decreases with each exacerbation of the disease. Pimples are characterized by an asymmetrical shape and a small area of localization.
The rash on the body due to syphilis, the photo of which is located below, has different types. This significantly complicates diagnosis. The pathology can be confused with various dermatological diseases.
The rash associated with secondary syphilis is characterized by the following general symptoms:
- gradual appearance of acne against the background of a complete absence of subjective sensations (for example, itching or temperature);
- any localization (with syphilis, rashes can even be observed in the mouth);
- oval or round shape of formations;
- no inflammation.
Attention! The color of acne has a red tint. Over time, the rashes gradually lighten.
Spotted form
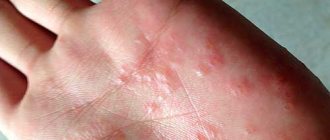
A type of secondary syphilis occurs in most cases. The color of the spots varies from red to pink. They do not protrude above the surface of the skin and disappear when pressed. The first rash may be accompanied by fever. Their size ranges from 2 to 15 mm. Pimples have an oval or round shape without clear boundaries. No peeling is observed.
With the spotted form of syphilis, the rash may persist for 1-2 months
Pimples are located symmetrically. The rash with this form of syphilis is localized on the abdomen, feet and hands, forearms, and sides of the torso. Spots on the outer thighs are rare. A rash on the face with syphilis is noted on the forehead and nasolabial folds.
With relapses, the nature of acne changes. They become larger and are located asymmetrically. Their number is less significant. The rashes can form various shapes, such as rings. This is due to their arrangement in groups.
Papular form
The variety is more common during relapses. Papules can also progress simultaneously with syphilitic spots. Papular rashes with secondary syphilis have the following features:
- formation in the upper layers of the skin;
- clear demarcation, shiny or scaly surface;
- the formations are dense and have a pointed, hemispherical, oval, round shape;
- shades vary from pink to bluish;
- enlargement of papules with irritation.
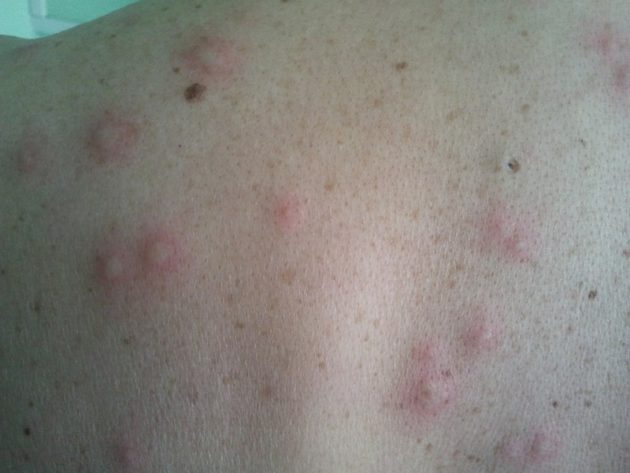
Papules regress on their own after 4-8 weeks with the formation of a pigment spot
Important! Pimples may appear.
Papular rash has several varieties:
- lenticular (psoriasiform, seborrheic, regional) and numular (cockade, blasting) - hemispherical rash on the legs, arms and torso, palms and soles, face, scalp and back of the neck with syphilis;
- miliary – round or cone-shaped dense papules on the chest, back, abdomen, which may be accompanied by itching;
- plaque-like is a fusion of lenticular and numular formations on the genitals, under the mammary glands, in the anus and armpit, between the toes (on the feet).
Against the background of infection, ulcerative, painful rashes form in the skin folds. The vegetative form occurs when papules (numular and lenticular) are irritated.
Pustular form
This is the most severe type, which develops in a small number of patients with a history of chronic pathologies. So-called pustules are often combined with spots and papules. Usually, against the background of rashes, general health worsens, which manifests itself:
- increased temperature;
- headache, joint and muscle pain;
- insomnia and weakness.
The pustular form has the following options for the development of the rash:
- syphilitic impetigo, in which rashes affect the head, face and pubis;
- acne syphilide, affecting different areas of the skin;
- smallpox syphilide, which occurs on the arms, legs, face and torso;
- syphilitic ecthyma, which appears more often on the lower legs;
- syphilitic rupee, causing necrotic decay of surrounding tissues on the body, in the area of the elbow and knee joints.
The disappearance of pustules is often accompanied by the formation of scar tissue
Pigment form
In the first six months after infection with syphilis, leukoderma may appear. The pathology has the following manifestations:
- the appearance of pigmented areas on the skin;
- the appearance of yellowish and dark brown spots;
- the same size of rashes and their gradual growth (up to 2 cm).
The pigmented form of secondary syphilis is not accompanied by pain, peeling or inflammation of the skin
Leucoderma progresses in three varieties:
- spotted, manifested by the appearance of light spots;
- reticular, implying the formation of round or oval spots prone to merging;
- marbled, indicating the appearance of white spots that can occupy a significant surface area.
Pigmentation in leukoderma occurs over a long period of time. A white rash with syphilis appears on the chest, back, abdomen, neck, lower back and shoulders. Less commonly, pigmentation occurs on the legs and arms.
Syphilitic sore throat
The disease occurs when hard chancre forms on the tonsils. The secondary stage resembles the progression of tonsillitis. The palate and tonsils take on a red-bluish tint. Then a gray rash spreads.
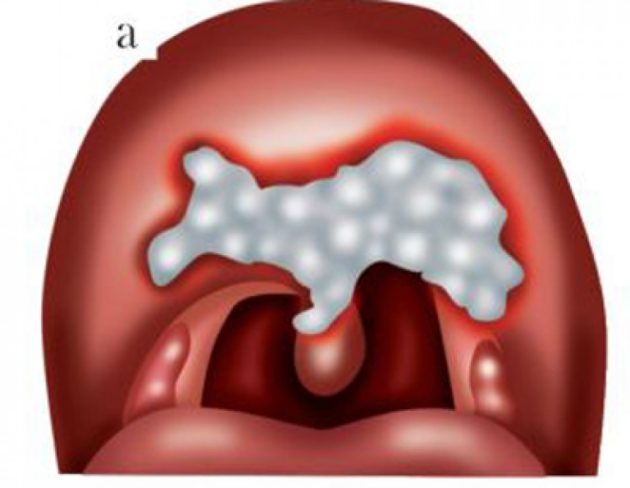
Syphilitic tonsillitis is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes and severe intoxication
Syphilide herpetiformis
This is a fairly rare form. The rash resembles blisters from a herpes virus infection. They usually develop in people suffering from alcoholism and having severe somatic pathologies.
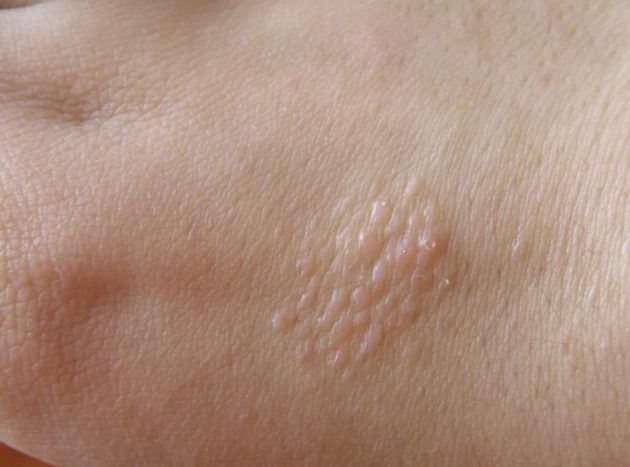
Rash herpetiformis indicates unfavorable progression of syphilis
What do syphilis spots look like at different stages?
Syphilis is an infectious disease, in 99% of cases it is transmitted through sexual contact and affects the entire body. The causative agent of the pathology is Treponema pallidum, a bacterial pathogen, one of the signs of whose presence is characteristic spots. What are the spots on the body with syphilis? And what are the ulcers of syphilis?
Spots in primary syphilis
The primary period of syphilis is from the moment of infection to 2-3 months, when a hard chancre forms in the area of infection:
- First there is a slight redness, in place of which a bulge forms after a few days.
- In the middle of formation, cell death occurs, so the chancre soon turns into an insensitive ulcer surrounded by a hard ring.
The first stage of syphilis ends with characteristic rashes all over the body - the result of the vital activity of Treponema pallidum. Skin problems are accompanied by intoxication phenomena:
- general weakness and joint pain;
- decreased vitality.
The combination of all signs indicates the beginning of the next stage in the development of syphilis.
Spots in secondary syphilis
The second stage is longer. It lasts up to 4 years and manifests itself on the skin in a wide variety of ways. Surface elements of this period are classified into:
- Roseola syphilides , the appearance of which indicates that the body contains a huge amount of the causative bacteria. The coloring of the spots is weak, the outlines are slightly blurred, the shape resembles an oval or circle with a diameter of up to one and a half centimeters. Roseolas do not unite and are at the same level with the surface of the skin. The area of their localization is the sides and stomach.
- Papular syphilides , resembling nodules (papules). They look like a circle or hemisphere the size of a lentil grain, dense to the touch. Initially, the papules are smooth and shiny, but soon signs of peeling become visible on the surface, and a border forms around the perimeter. The localization area for papular syphilides is the entire body, including the groin, palms and feet.
- Palmoplantar syphilides are one of the forms of the elements discussed above. Outwardly they resemble dark red callus spots. An increase in the volume of formations causes them to crack in the center, which leads to the formation of a flaky halo around the perimeter of the circle. Patients often confuse palmoplantar papules with ordinary shoe rubs, so they do not rush to see a doctor and start treatment late.
- Condylomas lata . Essentially these are vegetative papules. They can combine to form hypertrophied areas. They are covered with a white layer of swollen horny epithelium, under which there is a serous infiltrate. Condylomas lata in some cases may be the only skin symptom of secondary syphilis. The favorite place of localization is the perianal area, therefore, when examining a neoplasm, it must be differentiated from anal warts and manifestations of hemorrhoids.
- Syphilitic leucodermas . They are observed infrequently and are considered a specific manifestation of syphilis. Doctors romantically call clusters of rash elements on the chest and neck the “Necklace of Venus.” Taken separately, leucoderma looks like a light oval on a dark brown spot. In addition to the front of the upper body, the rash may cover the arms and armpits.
Syphilitic leucodermas
Skin formations characteristic of tertiary syphilis lead to the development of conditions such as:
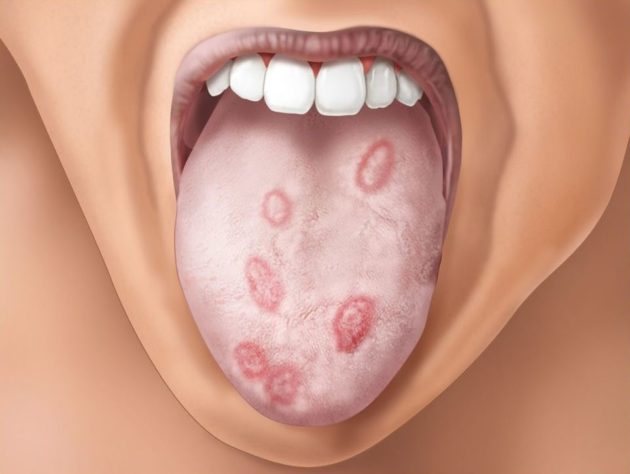
- Erythematous tonsillitis . Its characteristic feature is considered to be spots on the body of roseola, covering the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. They are distinguished by a dark red hue, a smooth surface and clear boundaries. Roseola on the mucous membrane does not hurt, but can make it difficult to swallow saliva and food. Syphilides in the mouth during relapses in the third stage of syphilis may be the only external manifestation of the disease;
- Syphilitic alopecia. This is baldness caused by a large number of specific elements on the scalp. My hair breaks down and falls out unevenly, like pieces of moth-eaten fur.
It is important to understand that a person who has syphilides on his body is dangerous because of his ability to “share” the infection upon contact, since the elements of the rash contain a large volume of the causative bacteria.
So, a syphilitic rash can be represented by spots and other elements of various types.
In this case, the severe course of the pathology is accompanied by pustular (pustular) syphilides, reminiscent of smallpox, acne or impetigo.
A characteristic feature of the secondary period is also that with each new relapse the number of spots on the body decreases, but the elements themselves become larger and form clusters resembling circles and arcs.
In the absence of treatment or improper therapy, secondary syphilis enters the next stage.
Spots and ulcers in tertiary syphilis
This degree of pathology is stated 7-10 years after Treponema pallidum enters the body. Currently, tertiary syphilis occurs in patients who neglect doctor's prescriptions, partially or completely violating them.
Do you think there is a chance to be cured at the third stage of syphilis?
Skin manifestations of this period - tertiary syphilides - develop over months and years, without giving symptoms of inflammation or causing discomfort. Unlike formations of secondary syphilis, these are compactly located, occupying a limited area of the body and gradually regressing, transforming into skin scars.
External manifestations of tertiary syphilis include:
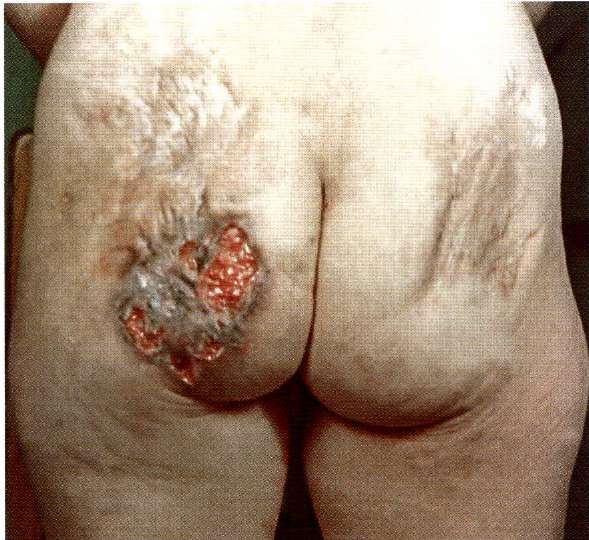
- Tuberous syphilides . These are dense syphilis spots-bulges of a brownish tint containing infiltrate. They have up to 7 mm in diameter. In a cluster of syphilides, elements of varying degrees of development can be distinguished. After a while, the tubercle becomes necrotic, forming syphilis ulcers containing infiltrate. It takes weeks or months to heal, leaving a small area of atrophy or scar on the body.
- Gummy syphilides , which are represented by one or more single elements on the body. Gumma, in fact, is a painless node under the skin, the localization of which can be the forehead, legs and forearms, elbows and knees. At the initial stage of formation, the node is movable. Over time, it grows and fuses with surrounding tissues, turning into a static subcutaneous formation. A hole appears in the center through which gelatinous discharge flows. Soon the depression takes the form of a crater, at the bottom of which there is a necrotic core. After its release, the ulcer quickly heals, forming a concave, star-shaped scar. There are cases when gummas resolve without going through the ulcer stage: the node simply becomes smaller and is eventually replaced by connective tissue.
In addition to the thickness of the skin, gummous syphilides affect:
In the long term, this leads to the inevitable destruction of the body.
Rash due to congenital syphilis
The form occurs due to infection of the fetus during intrauterine development. With this type of syphilis, a rash appears on the palms. Acne is often noted in the perineum, feet and buttocks. The pathological process involves the mucous membranes of the nose and oral cavity. After the rash disappears, scars remain.
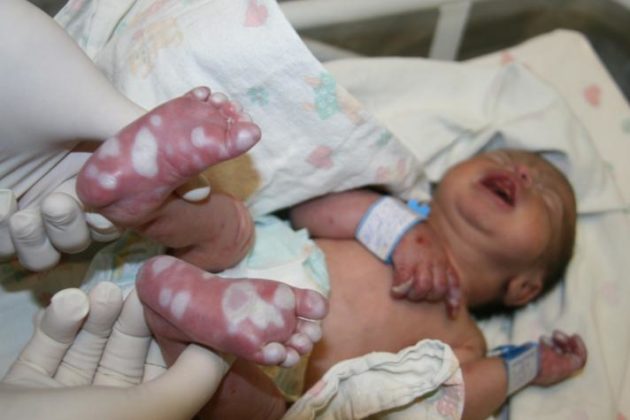
Skin manifestations are the main symptom of congenital syphilis
Important! As the infectious process progresses, the general condition is usually not disturbed.
Characteristic locations of spots in syphilis
Elements of the rash can appear on various parts of the body and mucous membranes.
But the most favorite places for localization of spots on the body with syphilis are:
- chest and neck
- stomach and back
- face
- shoulders
This feature of the location of syphilitic elements is taken into account by the doctor when making a diagnosis.
But this does not mean that there will be no such spots on other parts of the body.
For example, spots may appear on the legs, which is atypical for syphilis and can cause difficulties in making a diagnosis.
How long does a syphilis rash last?
The appearance of acne may indicate the primary stage. In this case, the pathogen actively multiplies at the site of penetration, which leads to the formation of hard chancre. The body begins to produce antibodies as the pathogen further spreads through the bloodstream. Rashes characteristic of secondary syphilis appear due to the release of biologically active substances due to contact between the immune system and the microbe.
During the tertiary stage, internal organs and bones are affected. This period is also manifested by the appearance of a rash. Each phase of the disease has its own characteristics of skin manifestations.
The rash (chancre) with primary syphilis progresses over seven weeks. Their healing is accompanied by the formation of scar tissue.
Approximately 10 weeks after direct infection, a rash appears and secondary syphilis is diagnosed. Relapses of the disease are observed for three years. The rash lasts up to two months. The tertiary form develops 3-30 years after infection.
Important facts about syphilis
The causative agent of syphilis is called “treponema pallidum”. It is a Gram-negative spirochete that gets its name because it stains pale pink when using the Romanowsky-Giemsa method.
Syphilis is a chronic systemic venereal infectious disease that affects the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs, bones and nervous system. In Russia, the disease was first recorded in 1499. Like most serious pathologies, syphilis has its own classification.
The following groups are distinguished:
- primary;
- secondary (early and late);
- tertiary;
- congenital.
Note! It was found that early forms of syphilis are more contagious; syphilides can resolve without a trace. In later forms, the degree of contagiousness is less, but syphilides are accompanied by irreversible destruction of parts of the body.
In more expanded classifications, syphilis can also be:
- seronegative;
- seropositive;
- fresh;
- hidden;
- recurrent;
- active;
- early or late congenital;
- visceral;
- nervous system;
- fetus
Cases in which fetal syphilis or congenital syphilis is observed almost always result in the birth of a stillborn child, or the death of the child in the womb.
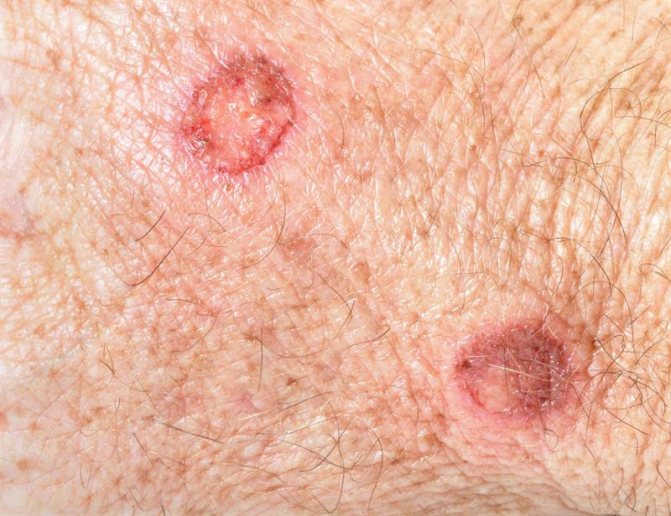
What kind of ulcers with syphilis depends on whether a secondary infection has occurred
Transmission routes
Almost all known transmission routes are available to this disease, and therefore the frequency of cases of syphilis among the population is steadily increasing.
Known routes of transmission include:
- Sexual – the disease is transmitted through contact with an infected person, the risk of infection is about 50%. Syphilis is transmitted through all types of sexual contact.
- Domestic - occurs in cases where one of the partners is infected, and the second is not aware of this, or neglects the rules of hygiene. Infection occurs through common objects, saliva from kissing.
- Blood transfusion - cases of infection are observed when blood is transfused from someone infected with syphilis to a healthy person. However, this is a very rare occurrence, because The donor undergoes a thorough screening before donating blood. More often, this route of infection occurs among injection drug users, when using one syringe.
- Transplacental - involves the transmission of syphilis to the child from the mother through the placenta during pregnancy. Leads to congenital syphilis. In addition, infection can occur during breastfeeding or passage through the birth canal.
- Professional – occurs among medical workers who come into contact with the biological fluids of a sick person. A doctor can become infected during surgery if there is damage to the skin during the process.
From the information received, it follows that in order to avoid infection, one should not neglect protection during sexual intercourse, and also use an individual set of utensils and hygiene products when living with a patient with syphilis.
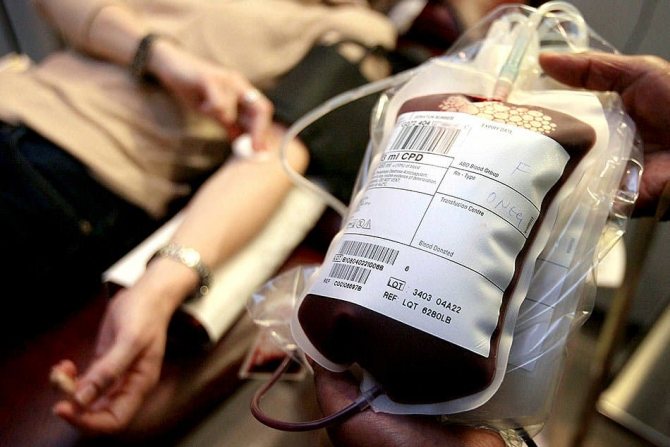
Infection can occur through blood transfusion
From the birth of syphilis to chronic disease
Syphilis can be transferred from mother to child during pregnancy, which negatively affects the fetus during the prenatal period.
Modern medicine has identified the main indicators by which it can be judged that syphilis affected intrauterine growth:
- Interstitial keratitis is an inflammation of the outer mucous membrane of the eye and the eyeball. This can be observed as significant redness and suppuration of the eyes. After completing the course of treatment, traces of surgical intervention will remain on the eyeball, and leukoma (white mesh) will also appear on the eyes. Typically, such changes also lead to a significant decrease in vision, pain and tearing of the eyes.
- Chronic lack of hearing - the fetus during intrauterine growth is subject to an active attack by Treponema pallidum, as a result of which hearing loss is one of the main symptoms of a woman suffering from syphilis during pregnancy;
- Hutchinson's teeth are unfinished development of dental tissue during pregnancy in the fetus. In this case, the teeth have an unpleasant appearance, may grow sparsely, and are not completely covered with enamel. And all this leads to their early destruction.
If a woman has undergone a course of treatment and got rid of Treponema pallidum, the child will still have a chronically weakened immune system.
But with incorrect and untimely treatment, the child will definitely have external abnormalities after birth.
Breastfeeding in the presence of syphilis is strictly prohibited for mothers; milk with Treponema pallidum bacteria automatically passes to the child, causing only harm.
A woman after treatment for syphilis can have children, but for a more accurate conclusion, you need to get a referral from your GP for the two main tests described above.
Signs
During the incubation period, there are no clinical signs of the disease; the primary signs of syphilis are characterized by chancre, the secondary ones (lasting 3-5 years) are spots on the skin. The tertiary active stage of the disease is the most severe and, if not treated promptly, leads to death. The patient's bone tissue is destroyed, his nose collapses, and his limbs are deformed.
Primary signs
After several weeks from the moment of infection, the first symptoms of syphilis appear, which include signs:
- specific round-shaped ulcers - chancre;
- chancre disappears after a few weeks, but this does not mean a cure, but the penetration of bacteria into the body;
- characteristic damage to the lymph nodes;
- Primary syphilis affects internal organs and systems.
At the 11th week of infection, clinical symptoms of secondary syphilis appear. This is characterized by the appearance of syphilitic infections in the form of spots, rashes, ulcers, and nodules on the skin. These formations are painless; if left untreated, they disappear and the disease enters a latent stage. Over time, secondary recurrent syphilis occurs, characterized by repeated manifestations. The stage lasts up to four years, accompanied by deterioration of the condition.
Five years after infection, tertiary symptoms appear. This is already a severe form, there is damage to internal organs, the formation of lesions (threshing areas) on the skin, mucous membranes, heart, liver, brain, lungs, bones and eyes. Often the disease affects the nasal mucosa, which can lead to destruction of the nasal septum. At this stage, dementia and progressive paralysis appear. She is not undergoing treatment.
As for women, after an asymptomatic period (about a month after syphilis enters your body), the time comes for the disease to manifest itself in all its glory.
The first sign is the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, labia or anus. An ulcer (chancre) manifests itself as a response of our immune system to the invasion of harmful bacteria.
A chancre is an inflammatory area of the skin or mucous membrane, usually round in shape and having a flat base.
At first, the growth on the skin will not show painful spasms, but later it will definitely be accompanied by a rash on different parts of the body and mucous areas.
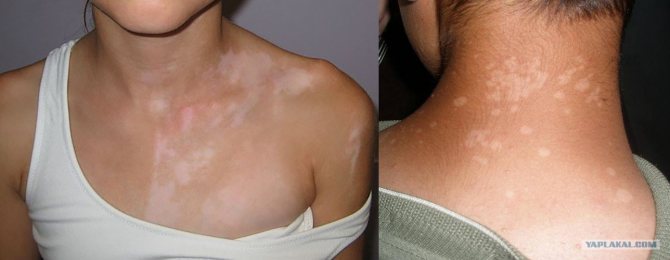
But, despite this, ulcers (chancres) can also occur in the above mentioned places (oral cavity, anus).
The subsequent treatment regimen is not divided according to genital characteristics; the treatment is the same for men and women.
Skin syndrome in tertiary syphilis
Rare, but still occurring, is tertiary syphilis. Occurs in untreated or undertreated patients. Tertiary syphilides are skin lesions in the form of tubercles or gummas.
READ ALSO: Red cheeks and rashes on the body of a child: is it an allergy or an infection? | Medical Note blog about health and digital medicine
They are represented by deep infiltrates in which the body has “immured” Treponema pallidum. Nodular syphilide looks like small (5-7 mm) subcutaneous nodules scattered in large numbers.
Whereas gummas are large nodes, often not numerous. Elements of the tertiary period with a malignant course.
At the site of destruction, they will form ulcers and scars, involving the underlying bone and cartilaginous structures in the process of destruction. In this case, there are no acute inflammatory phenomena.
You've probably seen photos of a saddle nose change. So this is a clear example of the irreversible destruction of bone tissue with untreated syphilis.
When, after infection with syphilis, elements appear
After the infection has entered the body, there are no symptoms of the disease for 1-3 months.
At the end of the incubation period, chancre forms.
At this stage of development of the process, an ulcer forms at the site of infection.
It is saucer-shaped with a hard cartilaginous base of red color and edges that rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane - chancre.
With atypical syphilis, red spots may form in the mouth, anus and anus.
If the oral mucosa is affected by infection, the rash can be localized:
- on the tonsils
- palatine arches
- in the language
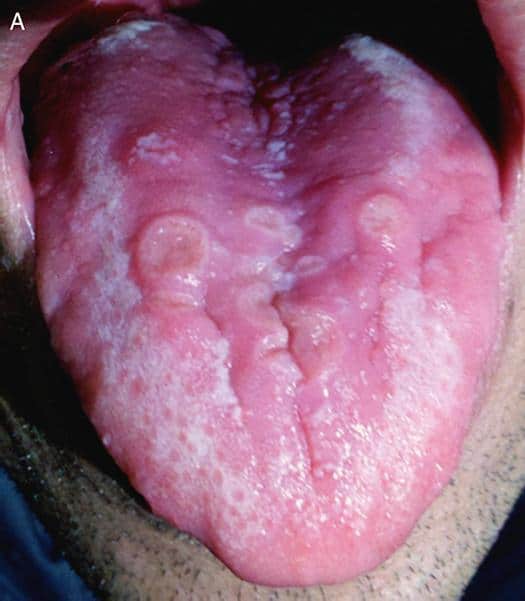
Syphilis spots in the oral cavity can only appear if pathogens have entered the body through the mouth.
In children, infection of the oral mucosa through domestic means occurs in extremely rare cases.
With secondary syphilis, chancre disappears, and pink spots form on the body - syphilitic roseola.
If the patient has not started a course of treatment, then the elements are capable of relapses at regular intervals.
Characteristic manifestations of syphilis during this period are:
- Roseola forms over the entire surface of the skin.
- Formation of leukoderma - a white rash “necklace of Venus”.
- The occurrence of condylomas in the anogenital zone.
- Formation of papules on the skin, including the scalp, and mucous membranes.
- Formation of pustular syphilides.
- Complete or focal alopecia “crown of Venus”, loss of eyelashes and eyebrows, hair in the pubic area and throughout the body.
- Erosive and ulcerative elements form on the tonsils, papules form in the corners of the mouth, and smooth red spots devoid of papillae form on the tongue - a symptom of a mown meadow.
- On the mucous membrane of the genitals in women, on the penis in men (on the glans, frenulum, foreskin) - roseola, papules.
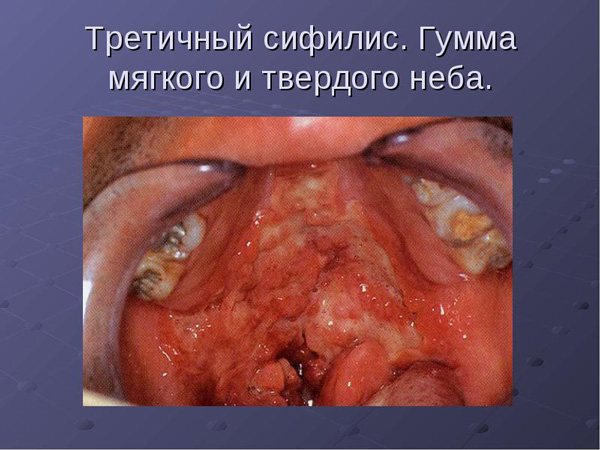
The tertiary stage of syphilis is characterized by the appearance of tuberous syphilides and gummas on the skin.
During this period, tertiary roseola is formed, which is a large red spot.
The rash is localized on the torso, lower back, and buttocks.
After it disappears, a scar remains on the skin.
The main symptoms of tertiary roseola are as follows:
- scanty rashes
- large element sizes
- symmetrical location of the rash
Attention, abnormal!
After the incubation period, the time comes for the formation of ulcers and, accordingly, the disease enters the first stage.
But, despite the presumptive outcome for each phase, abnormal phenomena on the skin are possible.
Based on this, unexpected manifestations are divided into several categories:
- Damage to skin vessels that occur around syphilitic chancre. This symptom changes the color of the penis, scrotum of men and female genitalia to a darker color with a blue tint. Women are more likely to experience syphilis on the lips. It is often confused with other gynecological inflammatory processes. However, only syphilis is characterized by swelling, which during diagnosis will not show any deviations from the norm, but the person’s lymph nodes will be inflamed.
- Idiopathic syphiloma is an inflammation that causes Treponema pallidum on the three main fingers of the hand. Pieces of skin peel off at the affected areas, which leads to slight blood loss, more similar to a recent moderate burn.
- Syphilitic amygdalitis is an inflammation of the submandibular or cervical tonsil. With this anomaly, the structure of the tonsil itself does not change, only an inflammatory process is present, which makes it difficult to swallow saliva and food. All accompanying symptoms are more reminiscent of a sore throat (fever, pain, pain when swallowing), but in our case, inflammation is present in only one tonsil.
Syphilis bacteria
We have known about syphilis since the beginning of the 20th century, when this disease was the most common, and every 5 people were infected with it.
At that time, this disease went by the more typical name for that time, “French disease.”
After a while, scientists concluded that this disease is bacterial in nature, and this significantly helped in its timely diagnosis and treatment.
Treponema pallidum first received this name due to the fact that when studying it under a microscope, scientists simply could not identify it.
After all, its entire structure, in fact, had no color, was simply transparent and at the same time very poorly painted by various methods.
To expose it, they used silver staining, the Gizma method, and a microscope with dark lenses.
With the help of further studies over time, it turned out that treponema can function and replicate only in a living organism.
The optimal temperature for the reproduction of this bacterium is the body temperature of a living organism 37 ° C; under optimal conditions, it divides every day.
Thanks to these data, a new treatment method was created: forcibly increasing body temperature to the maximum level, using the malaria virus.
Thus, it was easier for the patient to tolerate the manifestations of the underlying disease.
What tests for syphilis are needed for spots
In order to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to identify the cause of the appearance of the elements, i.e., identify the pathogen.
To do this, you will need to undergo an examination.
To diagnose syphilis, the following tests are performed:
- Microscopic examination of biomaterial taken from rashes. Elements of the rash can be located on the surface of the skin, oral mucosa, tonsils, and rectal mucosa. The technique is low sensitive and often gives a false negative result.
- Bacteriological culture of the contents of chancre and other elements of the rash.
- Lymph node biopsy.
- Serological reactions, ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), RIF, RIBT make it possible to determine the presence of antibodies to the pale spirochete in the patient’s blood.
- Histological study of syphilides.
- PCR from the surface of the spots. This diagnostic method is the most reliable, as it allows the detection of Treponema pallidum DNA in a sample.