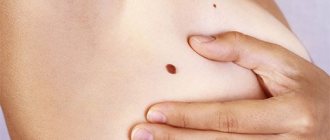
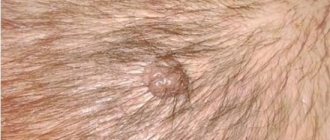
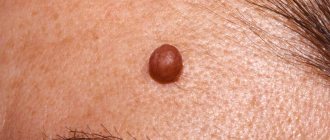
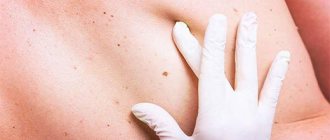
What's happened
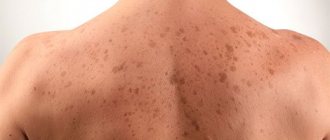
Oncological moles are a malignant formation, in the formation of which the basal layers of the dermis take part. Can be located anywhere, especially in open areas.
Melanoma is one of the most dangerous forms of cancer. It is for this reason that special attention should be paid to such birthmarks.
The disease can have either a primary development, that is, suspicious moles appear on the clean surfaces of the epidermis, or a secondary one. As a rule, they arise against the background of skin cancer or are formed from congenital and acquired moles.
Regardless of the type of disease, such neoplasms are formed from melanocytes.
The main signs of a malignant mole
Manifestations of congenital melanocytic nevus:
- The outlines are regular round or oval, with clear boundaries;
- The surface is smooth, wrinkled, nodular or warty;
- The color is uniform brown or with lighter intervals;
- Hypertrichosis (large amount of hair that is present from birth or appears in the first year of life).
Manifestations of dysplastic nevus a :
- Size from 6 mm;
- It is a nodule with a halo around it (reminiscent of a fried egg);
- The color can be brown, pink, blue-gray;
- Typical localization is the trunk and limbs.
Both congenital and dysplastic nevus are borderline conditions that can develop into melanoma at any time. However, any other moles can also become malignant, although with a much lower probability. Signs of degeneration of a mole :
- The appearance of bloody or clear discharge;
- Shape change;
- The appearance of areas with a different color;
- Formation of ulcers or erosions;
- Increasing growth rates;
- The appearance of itching, pain.
Classification
Malignant moles are divided into several types.
Borderline pigmented nevus
Presented as a small nodular formation. As a rule, it can have a shade from gray to black. The tumor is malignant and can appear on any part of the body. In most cases, this type of bad mole has a single lesion.
The structure of the nodule is represented by many cellular structures, which contain melanin, which could not come out within a certain period of time and got stuck in the space formed between the dermis and epidermis.
Such neoplasms are not predisposed to changes in color and parameters. Also resistant to ultraviolet rays.
Blue nevus
As a rule, this neoplasm does not reach large sizes. Painted in blue or dark blue. Often formed in single growths. In some cases, there may be multiple formations.
On this topic
- Oncodermatology
Prognosis for skin basal cell carcinoma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 10, 2020
These moles are characterized by a smooth, hairless surface. It is localized on the skin in the area of the face, arms and legs or buttocks, and has a slight elevation.
Blue nevus is characterized by slow development, as a result of which the pathology remains undetected for a long time.
Giant pigmented mole
Externally, cancer looks like a wart with an uneven, cracked coating. Can be painted in shades from gray to black. After a long time, the growth begins to rapidly increase in size.
This type of mole is more dangerous. This is explained by its rapid degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Nevus Ota
Presented as a single spot of dark blue color. Has an irregular shape.
In some cases, it is formed in multiple formations and merges into a group of spots. The localization site is the area around the eyes, the skin near the upper jaw, as well as areas of the cheeks.
The pigmentation process may involve the membranes and sclera of the eyes. The mucous membrane of the nasal sinuses and pharynx is also affected.
More often a unilateral lesion is diagnosed. If a nevus of Ota is detected, immediate measures must be taken to remove it.
Dubreuil's melanosis
It is a brown spot. Appears mainly on the face of people with light skin tones. It has an irregular shape with clearly defined edges.
Sometimes the appearance of the neoplasm resembles a blot in shape. Characterized by slow growth. As a rule, from one year to several decades.
Such moles are considered a precancerous condition, as they can degenerate into malignant forms.
In addition, melanomas also come in several varieties.
Superficial spreading
Formed on a nevus. It has irregular shapes and rises above the surface of the skin. In some cases, an inclusion is observed in the center, which has a different color from the neoplasm.
On this topic
- Oncodermatology
Prognosis for skin cancer at various stages
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
Over time, the tumor begins to thicken and form into a plaque. Gradually it takes the form of a node, the surface of which is covered with ulcers.
With this form of pathology, in half of the cases, the spread of metastases to other anatomical structures is noted.
Nodal
This type of melanoma is characterized by aggressive growth. On average, this type of mole can develop over three years. In addition, a distinctive feature of such melanoma is its vertical growth into the deep layers of the epidermis.
The surface can quickly become thinner and is often injured, which causes bleeding.
Lentiginous
This form is also called Hutchinson's freckle. In most cases, it is formed from a birthmark or an senile pigmented formation. In rare cases, its formation from a simple mole is noted.
It is most often localized in those areas that are more exposed to ultraviolet radiation. As a rule, this is the area of the hands, face, neck, and ears.
Rarely metastasizes. In addition, cases of its spontaneous resorption have been recorded.
Acral-lentiginous
Diagnosed in people with dark skin tone. It is localized in the genital area, on the palms, under the nail plate, on the foot, and also on the eyelids. Characterized by rapid development and rapid metastasis.
At the beginning of the oncological process, the tumor looks like a brown spot. As it progresses, ulcers appear on the surface. If the nail is involved in the process, its destruction is noted.
Pigmentless
It is detected in rare cases. The neoplasm has a flesh-colored or pink tint.
Features
They occur in people of any age and gender (some types have their own characteristics).
- There is a greater predisposition in people with pale skin.
- Direct relationship with the surrounding environment. Provoking factors can be chemical carcinogens, physical (ultraviolet) or biological (human papillomavirus) effects.
- This type of neoplasm can be either primary (formed on intact skin) or secondary (occurs at the site of benign formations).
- The routes of metastasis in such cases are to regional lymph nodes (distant metastases occur in rare and advanced cases).
- Skin cancer most often occurs in exposed areas of the skin (about 60% of all cases). The skin of the body accounts for about 7-10%.
- For a long time they do not have any symptoms other than external manifestations (as they progress, paraneoplastic syndrome occurs).
- It often occurs as a hereditary pathology (there is a history of cases of the disease in close relatives).
The given criteria are universal for any education in oncology. According to ICD 10, malignant skin neoplasms are coded C 43-C 44.
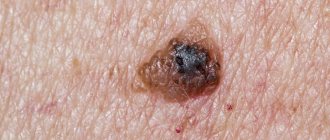
How to determine whether a mole is malignant or not
There are a number of important external signs of malignant moles (ABCDE method):
| Designation | Decoding |
| A – asymmetry | You can check this sign by drawing a conditional line through the supposed middle of the mole (in the case of malignant formations, you will get two halves of different sizes). |
| B – edge (border) | In benign formations, the edges are smooth and clear, but when malignant, the edges become torn like flames and lose their clarity. |
| C – coloring (color) | The coloring of an ordinary mole should be uniform throughout. In the case of polychrome coloring and a predominance of black tint, you must immediately contact a specialist. |
| D – diameter (diameter) | The diameter of the malignant lesion usually exceeds 6 mm. |
| E – evolution of development | All benign formations change slightly over time (increase somewhat, stretch). In the case of malignant forms, intensive growth is observed. |
Indirect bad diagnostic signs:
- itching and redness;
- disappearance of the skin pattern at the site of the lesion;
- peeling and swelling of the lesion;
- hair loss;
- ulceration and change in density;
- bleeding and weeping surface;
- screenings from the main focus (satellites).
Causes
The main provoking factor in the transformation of moles into malignant ones is abnormal development in melanocytes. With such a defect, the structure of cellular structures changes, and they degenerate into oncological elements.
Various reasons can provoke the appearance of this condition, which are combined into several categories.
Exogenous
These are factors that have a negative impact from the external environment. They are classified into a number of subspecies.
Physical
The most common causes include exposure to ultraviolet radiation. In this case, it is necessary to take into account not the duration of irradiation, but the intensity. There have been cases where sunburn after several years could lead to the degeneration of moles into a cancerous tumor.
Ionizing and electromagnetic radiation is no less important. Examples were also given when people whose professional activities involved electrical communications were diagnosed with cancerous moles.
Frequent trauma resulting from mechanical stress can also lead to malignancy. If a mole is constantly scratched, squeezed or combed, then the likelihood of malignancy increases several times.
Chemical
Melanocytes can also degenerate under the influence of external conditions. For example, working in the process industry. Pharmaceutical industries can also have an adverse effect on the skin.
Biological
First of all, it is worth highlighting poor quality nutrition. With constant consumption of fatty foods and animal proteins, the defect in the development of melanocytes increases.
Oral contraceptives and hormonal drugs that help normalize the menstrual cycle in women can also trigger the disease. However, this theory is only an assumption, since so far it has not been possible to establish a direct connection between these drugs and the appearance of skin cancer.
Endogenous
In most cases, the degeneration of moles into cancerous ones occurs in people with certain biological characteristics. These include:
- race ;
- pigment concentration in the skin;
- state of immunity - with a decrease in the immune system, the risk of malignancy increases;
- gender and age category - pathology is more often detected in the female half of the population, as well as at the age of 40-50 years;
- the presence of precancerous processes - this can be xeroderma, blue nevus, Dubreuil's melanosis.
Experts also highlight heredity. In other words, the risk of acquiring malignant moles increases if your immediate family has a history of skin cancer.
Examination of nevi
Pay attention to the edges of the moles (in normal nevi the edges are smooth and clearly visible). In an ordinary mole, the color does not change, there are no additional inclusions. If the edges of the newly formed tumor are uneven, torn, or have changed color, in this case it is advisable to seek help from a doctor so as not to miss the degeneration of a benign tumor into cancer. If you initially had a mole with hair or a convex one, this is normal; the only reason to worry is their degeneration and changes.
Symptoms
Despite the fact that each type of cancer mole has its own clinical signs, experts also identify general symptoms that can be used to determine whether a nevus has degenerated into a malignant tumor.
First of all, the contours of the growth begin to change, and an asymmetrical shape appears. In this case, it is necessary to exclude the formation of birthmarks in infants.
In most cases, the mole acquires fuzzy, blurry edges. The color becomes uneven. On the surface you can find a large number of stripes and dots of different shades.
On this topic
- Oncodermatology
Skin spots due to cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 5, 2020
In addition, the mole begins to grow. Its diameter, as a rule, exceeds 0.7 centimeters.
In almost all cases, malignant moles have uneven edges. However, there is a type of nevi that is not considered dangerous - these are dysplastic.
If the edges of a mole change, it will be considered dangerous if it has such signs as pronounced asymmetry, rapid growth, and jagged contours.
How to determine the oncogenicity of a tumor
Let's look at the main signs of malignant moles. First of all, various changes on the surface of the growth indicate the degeneration of birthmarks. Peeling, increase in diameter and change in structure are the main symptoms of nevus transformation. Symptoms such as itching, burning and tingling sensation in the area of moles are also important. Less commonly, various allergic reactions occur in those parts of the body that are adjacent to the growths.
Hair loss, color changes and the formation of papillomas are one of the clear signs of metamorphosis. Subsequently, new small-sized moles are added to the above-described symptoms, located close to the main growth. The appearance of small wounds and hemorrhages is also a negative symptom.
Skin cancer is a deadly disease!
Above are photos of moles that need to be removed in order to prevent the development of cancer. Each of the symptoms indicated in the list may be the beginning of pathological processes that have a destructive effect on the body
That is why it is very important to seek qualified help in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
To determine that a mole is malignant, a specialist first needs to collect all the information regarding the patient’s complaints and conduct a thorough external examination.
If a nevus is suspected of degenerating into a cancerous tumor, dermatoscopy is prescribed. This is an informative method, thanks to which in 95 percent of cases it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis. To carry out the manipulation, a special device is used - a dermatoscope.
If there is an assumption that at least one of the moles may become malignant, then a biopsy is performed. During the procedure, the doctor takes a sample of pathological tissue and sends it to the laboratory for further histological examination. This method allows you to determine the type of mole, that is, whether it is benign or malignant.
On this topic
- Oncodermatology
How to identify skin cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
To determine metastases in the lungs, kidneys and other vital organs, ultrasound examination of the peritoneum and chest x-ray are prescribed. The patient is also required to undergo a general and biochemical analysis of the blood fluid.
Based on the results of the examination, further tactics of therapeutic measures are selected.
Where to run?
Article on the topic
Dermatoscopy of moles will help identify melanoma in the early stages
If you notice an unusual mole on your body, be sure to go to a dermato-oncologist. If this doctor is not available, you can consult a dermatologist, surgeon or oncologist. An experienced specialist can visually determine the nature of the nevus. A special device called a dermatoscope helps him with this. Essentially, this is a powerful magnifying glass; by examining a mole through it, the doctor can notice the smallest details that are simply impossible to see with the naked eye. If there is doubt about the diagnosis, the doctor will conduct a histological examination to determine the characteristic signs of benign, premalignant and malignant neoplasms.
By the way, if you want to remove a mole for aesthetic reasons, then the decision should also be made by a dermato-oncologist after dermatoscopy, which allows you to choose the optimal method, determine the boundaries and depth of removal.
Even if degeneration into melanoma has not occurred, for medical reasons those moles that are subject to constant friction, pressure, and injury are removed. And also those that are in the groin area and under the arms, under the chest, on the belt, and in men - on the face at the shaving site.
If a mole that has degenerated into melanoma is removed at an early stage, the probability of complete recovery reaches 95%; if time is lost, it is only 20%.
Treatment
One of the most reliable and effective methods of therapy is surgical removal of cancerous moles. Before the operation, an anesthetic is administered. After this, an incision is made on the skin parallel to the drawn lines. If the tumor is small in size, then the entire procedure takes no more than half an hour.
The resulting fragment of pathological tissue is sent to the laboratory for further examination, which makes it possible to determine the extent of the oncological process.
Malignant moles are removed according to sequential steps. First, up to one centimeter of unaffected tissue that surrounds the tumor is excised. Layers of skin are removed until fatty tissue appears.
On this topic
- Oncodermatology
What tumor markers indicate skin cancer?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
If invasive melanoma is diagnosed, then the skin must be removed with an extension of up to 10 millimeters. All layers of the skin up to the fascia are also excised.
For an oncological mole that reaches more than 2.01 millimeters in thickness, up to two centimeters of skin is removed.
If metastases have spread, experts also recommend excising regional lymph nodes.
In more advanced stages, when the mole is inoperable, immunotherapy or chemotherapy is prescribed.
Cryodestruction
Liquid nitrogen is used to remove the tumor. Under the influence of low temperatures, the mole freezes, which leads to the destruction of pathological cells. This procedure takes no more than 10 minutes.
Laser
The nevus is burned out. The advantage of this technique is that during its implementation there is no bleeding, since the vessels are simultaneously sealed.
Radio wave method
Used only for small moles located on the surface of the skin. Removal is carried out with a special device. A wound appears at the location of the mole, which disappears in a short period of time.
How to get rid of dangerous moles
Hazardous formations can be removed if indicated. They are:
- convex shape;
- localization in traumatic places (head, neck, face);
- pain upon contact with clothing;
- moles that are constantly exposed to direct sunlight;
- formations with a diameter of more than 5 mm;
- change in color, contours;
- the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the area of the tumor;
- bleeding
Removal should be carried out by an experienced surgeon in an oncology center or a specialized department of a hospital or private medical center.
The choice of treatment method is determined by a specialist, and the cost depends on the size and number of moles.
Removal methods:
- Surgical operation (400-600 rubles). Excision of deep and extensive (more than 5 cm) neoplasms with a scalpel under local anesthesia.
- Electrocoagulation (RUB 700-1,200). Removal using an electric knife with low frequency current.
- Laser therapy (900-2500 rubles). Painless and layer-by-layer removal with a laser beam.
- Radio wave (800-1500 rubles). The mole is cut off under the influence of high-frequency current, and the remaining part is burned out.
- Cryodestruction (800-1500 rubles). Low temperature freezing using liquid nitrogen.
- Photodynamics (900-1300). Irradiation of the problem area with ultraviolet light.
Article on the topic: Diet after prostate biopsy - allowed foods and nutritional rules
Why you can’t rip off a mole
Removing the lesion on your own is unsafe and ineffective. It can lead to the following consequences:
- prolonged bleeding if blood vessels are affected;
- reappearance of a formation, often malignant;
- growth of the remaining part of the growth;
- activation of pathological tissue processes (malignization).
If a mole is completely or partially torn off, a number of recommendations should be followed. Algorithm of actions:
- Stop bleeding if present using hydrogen peroxide.
- Disinfect the wound with Chlorhexidine, Iodine or alcohol solution.
- Apply a sterile bandage with adhesive tape.
- Place the torn mole or part of it in a sterile container and take it to the doctor for histological analysis.
- Immediately contact a dermatologist or surgeon to get help and determine the nature of the torn nevus.