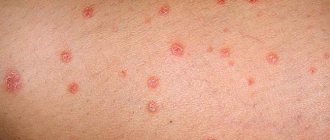
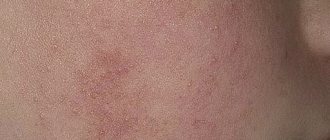
What does it look like?
The term “lichen” is a umbrella term for a whole group of different diseases with similar symptoms. There are several varieties of this disease, which are characterized by different causes, however, they have a number of similar symptoms:
- It appears as dark or light spots on various parts of the body.
- Usually they do not cause disturbances in general well-being.
- Accompanied by itching, peeling and inflammation (usually).
Signs of lichen largely depend on the type of pathogen, as well as on the form of the disease. Sometimes the clinical picture is influenced by the general health of the child. Ringworm can appear on different parts of the body:
- On the back. Most often, pink spots that are prone to growth are localized here.
- On the chest. White or pink spots may appear here.
- On foot. The lower extremities can be a target for all known types of lichen.
- On hands. Here the spots can be light or dark, can take on different shapes and itch noticeably.
Some types of lichen can also appear on the face and scalp.
What causes children's?
Viral organisms, as well as microscopic fungi of three different varieties, can provoke the appearance of lichen on the skin:
- Zooanthropophilic. Such pathogens live on the skin, as well as on the fur of pets.
- Anthropophilic. Found only on human skin.
- Geophilic. These mushrooms live on the ground.
Sometimes doctors cannot identify what causes lichen to appear on a child’s skin. In this case, we are talking about a so-called idiopathic disease.
Does it happen to babies?
Early age is not a guarantee of protection against this dermatological disease. Of course, infants have less risk of contracting lichen, since they have little contact with the environment and potential pathogens, and are also protected by maternal immunity. But many types of lichen may well appear in an infant, including those types of the disease that are highly contagious.
Diagnosis of white pityriasis
First of all, the dermatologist interviews the patient and collects data on medical history and illness. The doctor should find out about skin diseases from the patient's relatives in order to trace a possible hereditary predisposition to skin diseases.
For a medical history, the doctor must find out the duration of the disease or the time of its first manifestations. Whether the patient resorted to any therapeutic measures and whether there was a positive/negative result from them.
The patient should also be diagnosed for allergies or hypersensitivity to medications.
Next, the skin is examined in natural light.
To exclude certain diseases (syphilis, chickenpox) of the skin, the doctor may prescribe immunological tests.
Differential diagnosis
Lichen alba, first of all, must be distinguished from pityriasis versicolor, or lichen versicolor. This disease causes the formation of white spots on the body due to the growth of a fungus that affects the skin due to disruption of the functions of melanocytes. These cells produce melanin, which is responsible for the color of the skin.
Vitiligo
With multicolored lichen, the scales are pityriasis-like, but the peeling is expressed to a slight extent.
Pityriasis alba can be confused with vitiligo.
Vitiligo is a disorder of skin pigmentation due to insufficient production of melanin in certain areas of the skin. Factors that can provoke the development of the disease:
- the effect of medications;
- influence of chemicals;
- autoimmune disease;
- dermatitis;
- necrotic processes in the skin.
Vitiligo has clear boundaries. This fact serves as the basis for differentiating asbestos pityriasis from vitiligo.
Kinds
Doctors identify the following possible types of lichen:
- Shearer.
- Pink or Zhibera.
- Pityriasis or multi-colored.
- Encircling.
- White.
- Scaly.
- Red flat.
- Ringworm simplex on the face.
Parents themselves cannot determine what exactly the spot on the child’s body is. You can’t make a diagnosis by eye; you need to seek help from a doctor.
How to treat pityriasis alba
Dermatosis is a benign disease that can resolve on its own even without the use of local or systemic medications. Most often, people seek medical help only to eliminate a cosmetic defect.
If the spots occupy a small area of skin and do not increase in size, dermatologists advise not to treat them. To reduce the risk of progression of lichen, you need to limit exposure to the sun and avoid going to the bathhouse.
Diet and general recommendations
According to many doctors, dermatological disease is provoked by yeast-like fungi. To prevent their reproduction, you need to change your diet and exclude highly allergenic foods from your diet. Treatment of lichen involves following a hypoallergenic diet for at least 1-1.5 months.
Proper nutrition not only removes fungal waste products from the blood, but also helps replenish vitamins and microelements in the body. This has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the immune system, which promotes recovery. Dermatologists advise including the following products in the menu:
- greens and raw vegetables;
- kefir and fermented baked milk;
- rice and buckwheat porridge;
- garlic and olive oil;
- carrot juice and black currants;
- yeast-free bread and rice cakes.
If the disease worsens, you should stop drinking alcoholic beverages, citrus fruits, spicy foods and canned foods. It is also necessary to limit the consumption of smoked meats, fast food, fried fish and seafood.
Medication assistance
With lichen simplex, the affected areas of the skin often become dry and flaky, which can subsequently cause cracks to form. To ease the course of the disease in winter, you need to use an emollient ointment - Dermovate, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone. Medicines help eliminate inflammation, depigmentation and flaking.
Depending on the cause of the disease, the treatment regimen may include:
- herbal adaptogens (tincture of ginseng and lemongrass) – stimulate the immune system, which helps destroy fungal infections;
- sedatives (Adaptol, Afobazol) – increase the body’s resistance to stress that affects the functioning of the nervous and immune systems;
- photosensitizing drugs (Beroxan, Psoralen) – promote the formation of pigment in the skin when irradiated with UV rays;
- vitamin and mineral complexes (Pikovit, Vitrum) - have a stimulating effect on metabolic processes and the immune system.
Medicines can only be prescribed by the attending physician after a comprehensive examination of the patient. You should not resort to self-medication, as this can lead to an even greater deterioration in your health.
Folk remedies
Homemade ointments, compresses and applications can be used in the treatment of dermatological diseases, but exclusively as an addition to the main course of therapy. According to practical observations, folk methods in the fight against pityriasis alba show good results and speed up recovery.
You should not rely on your own strengths and the possibilities of alternative treatment; at the first symptoms of a rash or other suspicious spots on the body, it is recommended, without delay, to contact a specialist dermatologist who will perform an examination, make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
To prevent the spread of white spots throughout the body, use:
- Birch tar;
- garlic juice with lemon;
- saline solution;
- decoction of celandine;
- tincture of birch buds.
Medicinal herbs such as tansy, eucalyptus, lemon balm, thyme, oregano, chamomile, birch leaves and burdock root have excellent antifungal and antimicrobial properties. To prepare an infusion for compresses, you need to pour 1 tsp. raw materials 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 2-3 hours. In the strained infusion, gauze is moistened and applied to the affected areas of the skin for 20-30 minutes at least 2-3 times a day.
How does ringworm manifest?
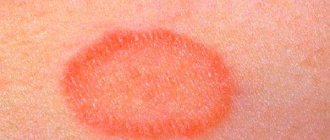
It is this deprivation that parents fear like fire, because it is contagious, can spread throughout the body and lead to hair loss. This disease is caused by pathological fungi. You can catch them from sick people, through contact with contaminated soil and unhealthy animals. The main symptoms of ringworm are ring-shaped spots on the skin that:
- They are distinguished by a reddish color.
- They itch noticeably.
- They have a diameter of up to 3 cm, and sometimes more.
- They can increase in size and even merge with each other.
- Lead to hair breaking off at the site of the lesion. Small fragments - up to 3 mm - remain sticking out above the skin.
- Covered in the central part with many scales.
- When magnified, they rise above the skin, become lumpy and turn purple.
- They can become infected, inflamed and fester.
Most often, doctors associate the occurrence of ringworm with insufficient activity of the immune system. Most doctors are confident that simple contact with such a pathogen in full health will not result in infection.
The very first signs
Usually, parents pay attention to ringworm when it reaches a size of 1 cm. But the disease usually begins as a small red nodule on the skin that can itch. Subsequently, such a papule turns into a small reddish spot and begins to grow. Apart from itching, the child usually does not worry about anything, and some children do not pay attention to such a symptom at all. As the diameter of the lichen increases, a mark with brighter edges and a lighter center is visible on the skin. At this stage of development, the disease already takes on a characteristic appearance, which helps to make a correct diagnosis. Around one lichen, others may well form - so-called daughter spots. They also increase in size over time.
White spots on the skin of a child Komarovsky
A healthy child's skin always looks perfect. It is smooth, clean and radiates a certain radiance that is characteristic only of children's skin. But, unfortunately, sometimes the baby may develop rashes or inflammation on the body or face. Here, every caring mother already knows that such a situation is usually associated with some kind of disease, of which there are quite a few. However, it is a white spot on a child’s skin , which appears completely unexpectedly and as if out of nowhere, that causes a lot of worry among the child’s loved ones. It is worth noting that such spots can appear both immediately after birth and throughout life, right up to adulthood. Moreover, in most cases they do not in any way affect the baby’s health, but in some cases such skin pigmentation can still lead to serious consequences.
How to identify pink (Gibera)?
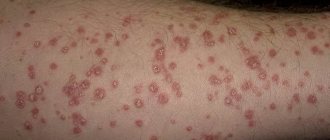
This disease rarely occurs in children; it is more often recorded in adolescents. The reasons for its development are not yet fully understood by specialists. Presumably, the development of the disease is associated with the activity of viruses (herpesviruses), and its onset can be triggered by a decrease in immunity, hypothermia and skin damage. Pityriasis rosea or Zhiber's pityriasis usually appears in spring and autumn. It is characterized by:
- Skin lesions on the abdomen, chest and back.
- Formation on the body of 1 single nodule with a diameter of up to 2 mm. It increases in size, the central part becomes yellowish and begins to peel off a little.
- The appearance of daughter light brown or pink spots on the skin.
- The presence of spots with rounded edges, up to 1 cm in size.
- Slight peeling and itching of the affected areas.
- The presence of dry, inconspicuous scales in the center of the spots, and along the periphery - an edge free from peeling.
Doctors are confident that pityriasis rosea is not contagious. The disease may disappear on its own, and then sometimes recur or never appear again.
There are various causes of hypopigmented spots on a child's face, ranging from conditions that resolve on their own within a few weeks to conditions that can last a lifetime.
Causes of white spots on a child's face
White spots can be caused by the following skin conditions:
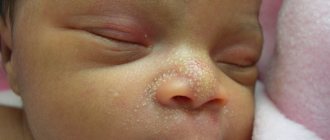
Milia
Milia are also called milk spots. These tiny white bumps usually appear on the face and rarely on the upper torso or limbs. Although milia can be seen at any age, it is common in newborns.
Causes and diagnosis of milia
Milia occurs due to entrapment of keratin (skin scales) beneath the surface of the skin. If there is no improvement after a couple of weeks, you should consult a doctor. Diagnosis is made by visual examination and no tests are required.
Prevention and treatment of milia
There is no cure for milia and it often goes away within a few weeks or months. There is no need to treat milia in children.
How can you reduce milia at home?
- Wash your child's face daily with mild soap and water.
- Pat your face dry after washing.
- Be careful not to scratch the milia to prevent skin damage and infection.
- Do not apply lotions or oils to your baby's face.
Note: Some may confuse baby pimples or Epstein pearls with milia. However, acne can cause red bumps and pustules on the face. Epstein's pearls are small, white-yellow cysts that often resemble milia, but they appear on the roof of the mouth and gums.
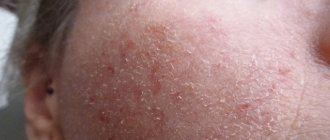
Pityriasis alba (lichen alba)
Pityriasis alba is a self-limiting skin condition that causes dry, thin, scaly and pale patches on the face. It is common in children and adolescents and is considered a type of eczema or dermatitis.
The name of this condition comes from the characteristic appearance of the skin.
Causes of white ptyriasis
The causes of white ptyriasis have not yet been clarified. However, atopic dermatitis and dry skin often coexist with it. Exposure to the sun can make it more visible by tanning the surrounding skin.
Suspected causes such as under- or over-bathing, low serum copper levels, ultraviolet radiation, or Malassezia yeast have not yet been proven to cause hypopigmentation.
Symptoms and signs of ptyriasis alba
One or more white spots, varying from 0.5 to 5 cm in diameter, are a characteristic sign of pityriasis alba. It may also cause mild itching in some children.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor
The condition can be diagnosed through a physical examination by a doctor. A skin biopsy may show mild spongiotic (fluid accumulation between cells) dermatitis with decreased melanin pigment. A skin scraping may also be taken to rule out a yeast infection.
Treatment of white lichen
Treatment is not recommended in asymptomatic cases. Moisturizers are helpful for dry skin, and mild hydrocortisone (topical steroid) creams can help reduce itching and redness in the area.
Tacrolimus ointment, pimecrolimus cream, and calcineurin inhibitors have been shown to be effective in the treatment of pityriasis alba.
The appearance of the skin may gradually return to normal over several months or two to three years.
Prevention of white deprivation
Limited sun exposure may help reduce your risk of developing this disease.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a depigmentation of the skin due to the loss of melanocytes, which are the cells that produce the skin pigment called melanin. Vitiligo can affect both sun-exposed and unprotected areas of the body. Also, with the disease, depigmentation of the lips and gray hair are often observed.
Causes of vitiligo
The exact causes of vitiligo are unknown. The disease may be associated with dysfunction or loss of melanocytes (the cells that produce the pigment melanin), which give the skin its color. This may be due to genetic factors or an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the melanocytes.
Vitiligo can occur at any age, but the onset of the disease is typical in children and adolescents.
Diagnosis of vitiligo
Vitiligo can be diagnosed through a physical examination. Rarely, a skin biopsy is performed to help confirm the diagnosis by the absence of melanocytes (pigment cells) on the skin. Thyroid disease and diabetes are checked as these may increase the risk of vitiligo in many people.
Treatment of vitiligo
Mild vitiligo may not require treatment: the spots will disappear over time. However, there are several treatments available to make your skin tone even.
Corticosteroid creams, photochemotherapy (PUVA), narrow band ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy, and depigmentation are a few treatment options. Using sunscreen can reduce tanning of the skin around vitiligo patches, and concealers can hide white spots on the skin.
Although vitiligo can be distressing to many people due to its appearance, it is not a medically dangerous condition. Vitiligo is not an infection, skin cancer, or a contagious disease.
Shingles
Shingles is a fungal skin infection that causes lighter or darker patches on the skin. The disease occurs at any age, but is most often seen in adolescents and young adults.
Causes of herpes zoster
Shingles is caused by a yeast that is usually present on the skin. Their excessive growth under the influence of environmental factors can lead to the appearance of spots on the skin. Malnutrition and excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) can also lead to yeast growth.
Note: Shingles cannot be passed from one person to another (not contagious) since most people have Malassezia yeast on their skin. This condition is not caused by poor hygiene.
A weak immune system, oily and moist skin, or hot and humid climates may increase the risk of contracting shingles. Children taking corticosteroid medications may also be susceptible to this condition.
Signs and symptoms of shingles
Although white patches can appear on the face, they are often found on the chest, back, and forearms. The spots may be pink or light brown and have scales. Skin changes are usually limited to the outer layer of the skin and often do not cause any pain or itching.
Diagnosis of herpes zoster
A physical examination is sufficient to diagnose shingles. In rare cases, doctors may collect a skin scraping to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of herpes zoster
Shampoo containing selenium sulfide is the main treatment method. If the condition does not go away, then you can use antifungal or anti-dandruff shampoos. The skin may improve over a short period of time in many children. However, it may take several months to achieve an even skin tone. To prevent relapse of the disease, monthly use of shampoo is recommended.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis (IGH) is a skin condition with small, white, oval patches.
IGH is more common in older, fair-skinned people than in children and often goes undetected.
Causes of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
The exact cause of hypomelanosis is unknown. Although this has not yet been proven, it is believed that it may be related to sun exposure.
Diagnosis of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
A physical examination is sufficient to determine the condition. Rarely are biopsy samples taken. There is usually a decrease in the number of melanocytes in the affected areas, although they are not completely absent as in vitiligo.
Treatment of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
IGH spots are benign and do not require medical treatment. Most procedures are aimed at improving the cosmetic appearance of the skin.
Home remedies may include regular use of sunscreen and physical barriers to prevent sun exposure, as it can promote or accelerate hypomelanosis.
References:
- Milia; Healthychildren; The American Academy of Pediatrics
- Milia; MedlinePlus; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Pityriasis alba; DermNet NZ; The New Zealand Dermatological Society
- Donald N. Givler, et al.; Pityriasis Alba; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Pityriasis alba; C. S. Mott Children's Hospital; The University of Michigan 6. Pityriasis alba; The Australasian College of Dermatologists (ACD)
- Vitiligo; The mission of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
- Vitiligo; National Health Service
- Diagnosing Vitiligo; NYU Langone Medical Center
- Vitiligo: Diagnosis and Treatment; The American Academy of Pediatrics
- Tinea Versicolor; Harvard Medical School
- Pityriasis Versicolor; National Health Service
- Falon Brown and Jonathan S. Crane; Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis; DermNet NZ; The New Zealand Dermatological Society
On Vikids you can:
Find a doctor and make an appointment
Find a clinic and make an appointment
Go to Forum
Read similar articles
Symptoms of pityriasis (multi-colored)
This type of lichen is of fungal origin, it is provoked by a fungus that normally lives on the skin of every person, but in the presence of predisposing factors begins to multiply too actively, which is accompanied by the development of unpleasant symptoms of the disease. In children, the risk of such a disease is not high, but with a genetic predisposition, hot climate, gastrointestinal diseases, reduced immunity and improper skin care, lichen versicolor may well occur in a child. You can suspect its development by:
- The appearance of small, uniform, smooth spots on the skin. They have clear boundaries.
- Pinkish, reddish, light brown and reddish-brown coloration of the affected areas.
- Localization of lichen on the neck, hips, armpits, shoulders and back.
- The affected areas are particularly bright against the background of tanned skin, as they do not darken.
- Increased sweating.
- Feeling itchy.
Pityriasis versicolor spots can merge with each other, forming large lesions. Sometimes they are present on the skin in isolation. In this case, no inflammation occurs, but the affected skin becomes covered with areas of pityriasis-like peeling.
Tinea versicolor is considered not contagious, since its pathogens are already present on the skin of every person.
How to distinguish lichen simplex alba from other skin diseases
If a person develops pityriasis alba, even if it does not cause concern, he should still visit a dermatologist's office; This is done in order to exclude similar, but more dangerous diseases.
Here is a list of diseases similar to pityriasis alba:
- atopic dermatitis;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- cutaneous mycosis;
- vitiligo, when melanin disappears in some places on the skin;
- chemical leucoderma;
- eczema.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a scraping is taken from the affected skin, after which these skin scales are examined in the laboratory using potassium hydroxide using a microscopic method. Pityriasis alba can easily be confused with vitiligo or pityriasis versicolor. With all three diseases, peeling and peeling of scales appear. But unlike white lichen, the location of the spots is not in the face area. As already mentioned, another feature of lichen alba is considered to be a predisposition to it in atopic dermatitis.
Often, when diagnosing a disease, a Wood's lamp is used; it illuminates with ultraviolet light. If this is not enough to detect the disease, a biopsy and histological examination of the spots may be performed.
girdling
Shingles is also known as herpes zoster. This disease occurs extremely rarely in children; its occurrence is possible only after the child has previously had chickenpox. After chickenpox, the virus that causes it is not completely eliminated from the body, but settles in an inactive state in the nervous system. With a significant decrease in immunity, it can become activated and cause:
- General deterioration in health: chills, high temperature, swollen lymph nodes, malaise, loss of appetite.
- Soreness, burning and itching at the affected area. Shingles most often appears on one side of the body.
- The appearance of red spots on the skin, and then blisters, as with chickenpox, which subsequently burst, crust over and fall off.
Patients with shingles can be dangerous to others who have not previously had chickenpox. It is impossible to become infected with lichen.
Children with herpes zoster are subject to mandatory hospitalization. The disease can lead to serious disorders of the nervous system.
White
This type of lichen is also called solar lichen, and the reasons for its appearance on the skin are not yet known to doctors. But some experts suspect that it is fungal in nature and occurs due to the pathogenic activity of the Malassezia fungus, which normally lives on the skin of every person. Lichen alba is manifested by the appearance of white spots on the skin, most often they are localized on the face, as well as on the lateral surfaces of the limbs. Such marks are generally not large and do not cause any discomfort to a person. However, during the cold season they can become flaky and itchy.
Lichen alba is not contagious and does not pose a health threat. However, if signs of such an illness appear in a child, you should consult a doctor.
Therapy
When the disease does not bother you, people often do not go to doctors and do not need treatment. It can go away on its own without medication in four weeks.
Treatment of pityriasis alba is necessary if:
- manifestations on the face cause discomfort in the patient;
- the addition of another disease is possible;
- There are more affected areas on the skin.
For white lichen, treatment does not involve the use of medications. Often, using a moisturizer will suffice. It is better to buy baby cream, as it does not cause allergies, does not contain dyes or various flavors that can cause adverse effects on the skin.
In the summer, it is better not to sunbathe in the open sun, because the difference between healthy skin and one that is susceptible to pigmentation will be very noticeable. Sometimes such manipulations will be enough for a quick recovery.
How to treat lichen during the inflammatory process? Therapy will include the use of hydrocortisone ointment and antiseptics.
It is allowed to use herbal compresses that have soothing properties, such as:
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- calendula;
- sage.
But before using them, you should consult a doctor, since even harmless herbs can cause allergies, which can lead to a worsening of the condition.
Therefore, the question of how to treat the disease remains little studied. It's hard to predict what will help for sure. For severe manifestations, doctors recommend using hormonal ointments. But they cannot be used for a long time. They have serious side effects. Before you start using them, you should weigh the pros and cons and decide what is more important, a cosmetic defect or complications after the ointment.
Treatment for children is slightly different. Children's skin requires constant care.
There are rules that must be strictly followed:
- wash only with warm water without using soap, as it dries out the skin;
- bathe in a bath only with warm water, use soap with glycerin;
- Constantly maintain your skin with moisturizer;
- When you are on the beach with your child, do not forget to use a special sun protection product;
- treat pityriasis alba with corticosteroid hormones.
Treatment with folk remedies is also allowed. But this must be done with caution. Because some herbs can cause pigment production, which will increase the appearance of white spots. It is best to make a decoction and apply lotions to the affected skin.
Lotions made from the herbs chamomile, St. John's wort, oregano and calendula are popular. Rosehip oil can be an excellent moisturizer. But all these products should be checked for the presence of an allergic reaction before use. To do this, you need to place a couple of drops of oil on the skin and wait a while. If redness appears, the use of this product is not recommended.
Good results can only be achieved by using such products for a long time.
Scaly
The popular name “scaly lichen” is one of the names of psoriasis, which is a chronic dermatological disease. This disease can develop in children for reasons unknown to science and can cause children a lot of discomfort. Psoriasis is characterized by excessively active division of skin cells, which causes the following to appear on the body:
- Sharply defined bright pink areas. Upon careful examination, you can find small flakes of dead epidermis on them.
- Small papules (nodules) covered with many grayish scales.
The affected areas grow, protrude above the surface of the skin and often merge with each other. They itch and may crack.
Psoriasis in children requires timely diagnosis and proper therapy under the supervision of a qualified doctor. Attempts at self-medication are very dangerous.
Treatment with traditional methods
In general, traditional methods for lichen are not used. Unless you can prepare a medicinal decoction that will improve skin pigmentation and the general condition of the body's immune system. This tea is prepared with the addition of several herbs, such as:
- St. John's wort;
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- plantain;
- oregano, etc.
For the decoction to give a positive result, this treatment should be used for a long time.
Prevention.
Due to the fact that this disease has more questions than answers, preventive measures are also impossible to predict, since there is no specific cause for the onset of the disease. Children who are predisposed to skin diseases should strengthen their immunity.
Red flat
This disease is quite rare in children; doctors suggest that its development is associated with abnormal activity of the immune system - the disease is most likely of autoimmune origin. The disease is characterized by the appearance of rashes:
- Violet (purple color).
- In the form of papules and plaques.
- From 2 to 3 mm (at the beginning of appearance).
- With angular outlines, a purple tint and a distinct shine.
- On the wrists, legs, torso, and mucous membranes.
- Symmetrical localization.
- Accompanied by intense itching.
Lichen planus is difficult to treat. The disease is prone to constant relapses.
Prevention of exacerbations
Chronic lichen alba is prone to recurrence, so after recovery it is recommended to take preventive measures. All of them are aimed at strengthening the immune system and eliminating provoking factors. To get rid of the disease and prevent exacerbations, it is recommended:
- treat even minor damage to the skin with an antiseptic;
- treat colds and exacerbations of chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- monitor the functioning of the immune system and take immunostimulating drugs on time;
- avoid stressful situations, overheating and hypothermia;
- include foods with phytoncides in the diet (onions, garlic, blueberries, radishes);
- use personal care products - towels, combs, washcloths, etc.
The alba type of lichen can progress in the summer due to increased activity of yeast-like fungi. To prevent the spread of white spots, you need to treat the areas with sunscreen. In addition, antifungal ointments prescribed by a doctor can be used.
Lichen simplex often goes away without drug therapy, without causing much discomfort. After recovery, the functions of melanocytes are restored, due to which the skin acquires a normal shade. Therefore, dermatologists do not recommend resorting to intensive treatment if only a few white spots up to 4 cm in size appear on the body.
Simple on the face (dry streptoderma)
The culprit of this disease is bacteria - streptococci. Infection with such infectious agents leads to the appearance on the body of pinkish round spots with a flaky surface. Foci of the disease are covered with small-plate scales, their size reaches 3-4 cm. They can be localized on the back, buttocks and limbs, and elements of lichen simplex often appear on the face.
This skin disease is contagious. Most often it is recorded in boys aged 7 to 10 years. The elements of the disease do not bother the patient, but sometimes they itch and cause a feeling of dry skin. Under the influence of ultraviolet light, the spots disappear, leaving behind areas devoid of pigment that disappear over time.
Dry streptoderma often occurs chronically and periodically worsens. The disease requires targeted antibacterial treatment.
Symptoms
Lichen alba has its own symptoms, by which the type of this disease is easily determined, for which no special treatment is used. The main symptom is the appearance of light-colored spots on the human epidermis; in rare cases, slight itching may be present. Statistics show that children aged 3 to 16 years are susceptible to this disease.
Boys are more susceptible to this disease than female children of the same age. May be chronic, but by the time one gets older, symptoms no longer appear. It is important to correctly diagnose the disease. This type of disease can go away on its own as soon as a person passes childhood, so treatment is not necessary.
They try to treat mainly for cosmetic purposes. The doctor determines the disease by visual examination, and then prescribes treatment for the patient. If a visual examination is not enough, the doctor will refer the patient to undergo various laboratory tests.
How to find out what spots on the body are?
If you find any spots on your child’s body, you should consult a qualified dermatologist as soon as possible. The doctor will be able to:
- Collect anamnesis by interviewing parents and the child himself.
- Carry out a visual inspection. The presence of pink, oval spots allows one to suspect the presence of lichen.
- Conduct special tests to diagnose pathology. Most often, to recognize the essence of the existing disorder, a simple scraping of the skin is sufficient, but additional research may be necessary.
Usually the diagnosis can be established in 1 visit. After the doctor determines whether he is dealing with lichen or not, he will be able to select special treatment and tell him what to do to achieve a speedy recovery.
What does the scraping show?
To conduct such a study, the doctor, using a special instrument (scalpel), carefully scrapes tissue from the skin and transfers it to a glass slide. Such material is examined in the laboratory, and it can be found:
- Pathogenic fungi or bacteria. The laboratory can determine which pathogen we are talking about.
- Abnormal cells that should not normally be on the skin. Sometimes the content of a large number of keratinized cells, etc. is revealed.
Skin scraping can be performed at any dermatology clinic. This is a fairly simple study, the effectiveness of which, however, largely depends on the professionalism of the doctor and laboratory assistant.
How does this happen?
It should be noted that the epidermis has three layers:
- Surface layer.
- Middle layer (dermis).
- The third layer is subcutaneous fat.
In the space between the first and second layers of skin there are special cells that produce a substance that determines skin color (pigment), usually it has a brown tint. The intensity of the color depends on its quantity. For unknown reasons, which can only be speculated about, this pigment begins to be produced less in certain skin areas. In common parlance, this disease is called pityriasis alba, but such a disease is not included in the medical classification at all.
Features of treatment
Treatment methods for lichen in children are selected individually after the correct diagnosis has been established. Most often, children are diagnosed with ringworm, which requires:
- Proper skin care.
- Compliance with the diet. Food should be predominantly plant-based. Sweet and starchy foods are prohibited.
- Special hygiene. It is extremely important to wash the patient’s clothes and bedding at high temperatures, as well as iron them. It is necessary to further disinfect the room.
- Use of local and systemic drugs.
Treatment of other types of lichen has its own characteristics, in particular:
- There is usually no treatment for pityriasis rosea and pityriasis alba. Signs of such diseases can go away on their own, but doctors recommend avoiding friction and pressure on the elements. If the disease is accompanied by itching, antihistamines and topical hormonal agents can be used.
- Pityriasis versicolor is quite easy to treat with antifungal medications. At the same time, it is very important for a small patient to strengthen the immune system.
- Herpes zoster requires mandatory use of antiviral drugs. Additionally, special analgesics, vitamin preparations, physiotherapy techniques, etc. can be used.
- Psoriasis requires mandatory comprehensive treatment, in particular, diet and special skin care. To lubricate the elements of the rash, keratolytics, hormonal agents and other drugs that suppress rapid cell division and inflammation are used.
- Streptoderma is an indication for the mandatory use of antibacterial ointments. In addition, patients need to take special care of their skin.
The treatment regimen for lichen is selected exclusively on an individual basis. Self-medication of a child can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
What is the cure from medicines?
Single manifestations of ringworm in a child (for example, on the arm or stomach) can be easily managed with the help of local remedies. It is recommended to smear the affected areas with antifungal agents:
- Terbinafine.
- Miconazole.
- Clotrimazole.
- Ketoconazole.
- Mycoseptin.
Such medications are used exclusively in accordance with the instructions for the time recommended by the doctor. Additionally, the doctor may recommend anointing the affected area with an iodine solution (5%), but parents need to remember that excessive application of such a product can lead to a skin burn in the child.
If ringworm is widespread or localized on the scalp, it can also be treated using tablets. Children are usually prescribed griseofulvin.
There is no quick cure for ringworm. This disease requires daily therapy for 1-2 weeks until symptoms disappear completely and another 1 week after that to exclude relapses.
Is it possible to treat with folk remedies?
Many parents are interested in how to remove lichen from children using alternative medicine methods. But doctors recommend refraining from such amateur activities, since the lack of proper therapy can lead to the spread of a fungal infection to healthy areas of the skin. If a single plaque on the body can be dealt with with an ointment, then several affected areas will require longer and more difficult treatment with pills for the body.
When wondering what is the best way to treat lichen on a child’s arm or leg, you should trust your doctor’s recommendations. In addition to the prescribed treatment, you can use general strengthening traditional medicine that activates the immune system.
How to get rid of white spots?
When developing a treatment regimen, the doctor takes into account the factor that provoked the appearance of spots. Solving the problem takes an integrated approach. In addition to eliminating the external signs of this phenomenon, mandatory treatment of the underlying disease, against which the spots appeared, is required. The doctor prescribes treatment after making a final diagnosis.
General recommendations
If depigmented areas appear on a child’s skin, it is recommended:
- reduce the baby’s stay outside to a minimum during peak solar activity;
- protect from stressful situations;
- include a large amount of fresh vegetables, fruits and berries in your daily diet;
- exercise regularly;
- Strictly follow the dosage and duration of medication prescribed by your doctor.
Medications
In addition, the specialist must assess the risk of any negative effects while taking the following groups of medications:
| Main disease | Group of drugs | Properties of drugs |
| Lichen | Salicylic acid | Antifungal and anti-inflammatory |
| Ointments based on birch tar | Wound healing and bactericidal | |
| Antihistamines | Soothing, decongestant and antipruritic | |
| Vitiligo (cannot be cured) | Topical creams, photosensitizers, drugs that stabilize the endocrine system and liver, medications based on psoralen followed by exposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays, alcohol tincture of placenta extract | Increase sensitivity to light, restore metabolism, normalize skin tone |
| Hypomelanosis | B vitamins | Immunostimulating |
| Immunostimulants | ||
| Photosensitizers | Strengthen the effect of light, trigger a chain of physical and chemical processes in the body | |
| Corticosteroid ointments | Anti-inflammatory |
Traditional medicine
The most effective methods of traditional medicine for eliminating depigmented areas of skin as a result of vitiligo and lichen:
- rubbing with a decoction of dill, parsley, or St. John's wort;
- applications with a mixture of sulfur ointment, birch tar and goose fat;
- compresses with propolis and olive oil or jojoba and lavender oils;
- lotions made from apple cider vinegar or wormwood solution.