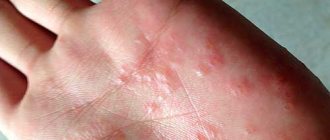
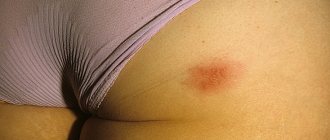
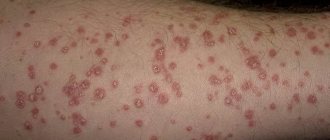
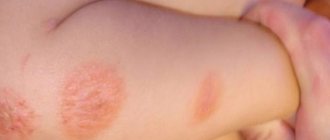
Follicular keratosis belongs to the group of non-inflammatory diseases that are a consequence of disruption of the processes occurring on the surface of the skin.
Keratification and exfoliation of the epithelium occurs excessively and manifests itself in the form of nodules on the skin. The disease does not cause pain, appearing in most cases only as a cosmetic defect.
Dermatological pathology in childhood is quite common and manifests itself in the follicular form. With the onset of puberty, the nodules disappear spontaneously, without therapy. The risk group includes children with chronic diseases such as asthma, eczema.
Follicular keratosis in a child
During the period of therapy, it is important to maintain the body’s immune functions at the proper level and carefully monitor the child’s diet, giving preference to a healthy lifestyle and nutrition.
Some experts associate the occurrence of the disease with a lack of vitamin D in the child’s body, since exacerbation of keratosis often occurs during the cold season. In the summer, there are practically no signs of the disease, the skin is completely cleared.
Causes
Follicular keratosis is one of the dermatological diseases, the causes of which are precisely unknown.
Most researchers are inclined to believe that lichen pilaris is inherited. There are many cases of the disease in different generations of the same family. Important! Follicular keratosis is not dangerous to humans and others.
Provoking factors and causes of keratosis pilaris:
- taking hormonal medications;
- cold season. In summer, the nodules on the skin almost disappear;
- deficiency of vitamins C, A, D;
- frequent stress, violation of routine;
- excess fatty, peppery, salty foods, excessive consumption of coffee.
Prognosis and prevention
Keratosis is most often inherited, so its occurrence cannot be completely excluded, but the risk of further spread can be reduced. To do this you need to follow some rules:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle , exercise and strengthen your immune system.
- Regularly take the vitamins your body lacks, especially in the spring and autumn.
- properly and nutritiously .
- Constantly moisturize the skin, avoiding excessive dryness.
- If possible, be less nervous and in stressful situations.
- Eat as many greens and fruits as possible.
- Avoid harsh effects on the skin. To do this, you should avoid rough scrubs, washcloths or brushes. After washing your face, you should not rub your face with a towel; you need to lightly blot it.
- Do not use hormonal substances, including contraceptive pills.
Types and classification
There are the following categories of disease:
- papular – associated with the formation of papules;
- vegetative;
- atrophying – can lead to atrophy of the epidermis.
Follicular dermatitis manifests itself in several forms:
- Warty. It occurs due to a genetic abnormality and is caused by inadequate production of keratin. It can be either congenital or acquired. The sore has an external resemblance to a wart. The growths tend to crack and are covered with a dense crust on top.
- Lenticular - characterized by the formation of large papules of a yellow or brown hue.
- Seborrheic. Affects the scalp and face. The rash consists of small spots with a greasy film on top. Formations tend to grow.
- Diffuse. It appears in large pathological spots and can cover parts of the body entirely.
Follicular dermatitis can be:
- primary, i.e. not related to internal pathologies;
- secondary – is a concomitant symptom of internal somatic diseases.
Pityriasis pilaris
It is an inflammation of the hair follicles. It is characterized by rashes covered with a hard crust on top, located on the inside of the knees, in the armpits. May be accompanied by itching.
Associated with the formation of red and brown pimples on the hands. If you remove the superficial crust, a depression in the middle of the sore becomes noticeable.
Devergie's disease
The rash is yellow in color, the sores have the shape of a cone with tires. They can merge with each other, forming a single horny covering.
Hyperkeratotic formations appear first in the superciliary region symmetrically to one another, then lesions appear on the forehead and cheeks. As the rash develops, it turns into scars, then keratinized crusts appear.
The variety manifests itself as papular nodules, dry skin, as a result of which cracks and wounds form on the skin, and deformation of the nail plates occurs. Localized on the feet and palms.
Darier-White disease
Accompanied by the appearance of gray crusts on the face and head, which then affect the torso and limbs. Typical for children and adolescents.
Associated with the appearance of single pimples-scales, under which black dots are visible. After removing the growths, small scars remain at their location.
Symptoms and locations
Pityriasis pilaris does not cause any particular problems. With mild rashes, some people do not pay attention to the signs of keratosis pilaris and do not consult a dermatologist.
How to recognize tinea pilaris:
- follicles become clogged with exfoliating keratin;
- multiple nodules form on the skin;
- sometimes the lesions cover a fairly large area;
- the diameter of the vesicles is 1–3 mm, with inflammation the size increases to 5 mm;
- the tubercles rise slightly above the skin;
- sometimes the tip of the hair is visible from under the crow's feet;
- shade – from translucent, flesh-colored to reddish;
- in some cases, skin hyperemia is observed in the affected area; (read about other diseases, for example, melasma here);
- itching occurs rarely;
- the development of the inflammatory process causes discomfort, reddish pimples look unesthetic;
- the inflammation disappears as suddenly as it appeared.
Localization areas:
- hips;
- buttocks;
- hands;
- stomach.
- legs;
- shoulders;
- breast;
- interscapular region.
Yellow-brown papules appear on the face, in the armpits, and on the scalp. The rash affects the mucous membranes, soles, and palms.
The patient feels discomfort, the papules itch. Treatment is strictly individual. Treatment options are determined by a dermatologist.
One type of keratosis pilaris is Darier's disease. A congenital disease of an autosomal dominant type is quite rare.
First, the rash appears on the surface of the elbow and knee joints, thighs, and buttocks. Then other parts of the body are affected (scalp, torso).
Main signs of the disease
Follicular hyperkeratosis affects hair follicles. Symptoms of the disease may be as follows:
- the skin in the area of the affected areas becomes rough and rough;
- many small bubbles in the form of pimples appear on the surface of the dermis;
- the follicles become inflamed as a result of blockage, the tubercles become red.
Most often, keratosis can be seen on the elbows, knees, outer thighs, and shoulders. That is, in those places where the skin is the driest.
Often young people with this disease are interested in the question of whether they are recruited into the army with follicular hyperkeratosis. The answer is yes. The army and hyperkeratosis are quite compatible, since the disease does not pose a threat to the patient’s life. An exception may be cases when the patient experiences severe itching and the number of rashes is constantly increasing.
Important! If symptoms of pathology appear, you should consult a dermatologist. Despite the fact that the disease is not fatal, it is still necessary to treat it.
Reasons for appearance
There are internal and external causes of follicular dermatitis. The first include:
- ichthyosis is a pathology in which small horny growths form on the skin, similar in appearance to fish scales;
- seborrhea - disruption of the activity of the sebaceous glands, accompanied by blockage of the ducts that remove secretions to the outside;
- lichen - a dermatological disease manifested in a small blistering rash;
- fungal infections, HIV;
- psoriasis;
- genetic abnormalities associated with excess or insufficient
- production of keratin;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- flat feet;
- diabetes mellitus (occurs when there is an increased level of glucose in the blood);
- overweight and obesity;
- hypovitaminosis (excess vitamin A);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (dysbacteriosis);
- erythroderma - pathological peeling of the epidermis;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances due to taking drugs that stimulate or inhibit the production of hormones;
- improper metabolism;
- neuropsychic overstrain, stress.
- Secondary causes of hyperkeratosis are:
- incorrect care: use of inappropriate cleansers for a specific skin type, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- lack of microelements in the body that affect the health of the epidermis;
- wearing excessively narrow, tight-fitting clothes made of dense materials that do not allow air to pass through;
- overweight and obesity.
The disease is caused by a deficiency of vitamins A and D, which play an important role in the formation and normal functioning of the epidermis.
In girls, the initiators of hyperkeratosis are hormonal contraceptive drugs that activate the processes of keratin formation in cells. Disturbances in the structure of the skin also result from taking medications that are prescribed to women during menopause.
The problem may arise due to the patient's unbalanced diet. Patients with follicular hyperkeratosis are prescribed a special diet.
Stressful situations and instability of a person’s mental state provoke the development of the disease and aggravate the severity of its course.
What causes follicular hyperkeratosis?
The causes of the pathology are clogging of the follicles with horny particles of the dermis. As a result, the natural function of the follicle is disrupted and it becomes inflamed. Follicular hyperkeratosis of the skin can occur in patients of different age categories. The main provoking factors are the following:
- Disruption of the endocrine system. It can develop while taking hormonal drugs, during pregnancy or menstruation.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis on the face often occurs in young people during puberty, which is also associated with hormonal disorders.
- With a deficiency of vitamin B, the skin becomes excessively dry. This may occur as a result of poor nutrition.
- Stress and excessive emotional experiences often lead to pathology.
- In a child, the disease can occur due to insufficient hygiene or incorrectly selected cosmetics.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis on the shoulders, face and other parts of the body can develop due to a lack of vitamins A, D and C. These components are very important for the normal functioning of the dermis. Vitamin A supports normal healthy renewal processes of the dermis, C promotes the production of collagen, D ensures the normal renewal process of skin cells.
In addition to vitamin deficiency, an excess of vitamins – hypervitaminosis – can also have a negative effect on human skin.
How to get rid of the disease
How to treat keratosis pilaris? Most people want to get rid of pilaris because of the unsightly appearance of the skin. Therapy includes:
- local remedies – creams, ointments;
- traditional medicine recipes;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Recommended:
- adherence to diet during treatment;
- respect for the principles of healthy eating after recovery;
- normalization of the regime;
- strengthening the state of the nervous system.
Helpful Tips:
- take an oil solution of vitamins A and E;
- Vitamins C and D increase the body's resistance;
- Buy regular fish oil at the pharmacy. This natural product is an excellent way to strengthen the immune system;
- use cold pressed oil. Replace some of the sunflower oil with olive, flaxseed, pumpkin, and amaranth oil.
Therapy for hyperkeratosis
Follicular hyperkeratosis is a pathology of a chronic nature that cannot be completely cured. It can regress with age. Self-therapy only causes a deterioration in the condition of the integument.
Dermatologists advise following certain skin care rules to reduce inflammation and improve the overall condition of the stratum corneum..
- It is necessary to balance the diet and normalize the intestinal microflora.
- Pure water helps restore optimal functioning of the epidermis.
- It is necessary to correct the functioning of the endocrine system.
- Any mechanical damage to plaques should be avoided. This provokes infections.
- The effect of a bath or sauna helps smooth out goose bumps. Emollient herbs or milk should be added to a regular bath.
- Products saturated with fruit and lactic acids are well suited for hygiene. Lotions and creams moisturize the skin.
- It is forbidden to sunbathe for a long time, as the sun dries out the skin excessively.
To combat pathology, there are alternative methods based on traditional medicine.
A hot bath with salt or chamomile softens the skin and cleanses the pores of dead elements. It is allowed to use a soft sponge or washcloth.
- For hyperkeratosis, honey massage is used, which softens the skin and cleanses the pores.
- Redness can be relieved with celandine juice, but you should first do an allergy test.
- Masks made from fermented milk products, potatoes or aloe are an effective treatment.
Skin care
Human skin consists of many layers and is constantly renewed. In the deep layers of the dermis, new cells form and mature; the outer layer consists of keratinized cells, which die over time and are replaced by new ones.
In some cases, the process of death of old cells is disrupted, and a disease such as keratosis develops. The pathology has various forms, but the most common of them is keratosis pilaris.
This disease can occur at any age, but most often it occurs in children. Follicular keratosis in a child has specific symptoms and often gives the baby a lot of unpleasant sensations. Although the disease itself is not threatening to the health and life of the child.
Follow the rules:
- Moisturize problem skin regularly. Use Vaseline based formulations. Before applying the cream, take a soothing bath with a decoction of medicinal herbs - chamomile, string, sage, calendula. Carry out the procedures daily;
- Protect your skin from direct sunlight during treatment. Dried epidermis easily cracks, wounds appear - a gateway for pathogens;
- choose suitable cosmetics. Do not use thick foundation to cover up blemishes.
Treatment of keratosis pilaris
The disease is chronic and it is impossible to completely get rid of it. However, modern medicine has a set of tools and methods that can improve the condition of the skin, make the manifestations of pathology less noticeable, and prevent inflammation.
Treatment of follicular hyperkeratosis should be comprehensive. First of all, weight control and adherence to a special diet are necessary. Food should be rich in vitamins A, B, and C.
Your daily diet should include:
- sea fish;
- liver;
- wheat sprouts;
- beets;
- carrot;
- bran;
- sea buckthorn;
- oatmeal;
- parsley;
- beans;
- bananas;
- sorrel;
- buckwheat;
- strawberries;
- apricots;
- cabbage;
- pumpkin;
- peaches;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- cherries;
- vegetable oil;
- mushrooms;
- bell pepper;
- corn;
- tomatoes;
- lean meat.
In addition to diet, you need to take pharmaceuticals prescribed by a dermatologist and undergo cosmetic procedures.
Drugs
The basis of drug therapy for keratosis is retinoids - analogues of vitamin A).
Here are some of them:
- Acitretin is a synthetic retinoid. Prescribed to slow down the process of cell death and accelerate the formation of new ones;
- Alitretinoin is a drug of natural origin. It has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Effective for severe forms of dermatological disorders;
- Etretinate is a synthetic analogue of retinoic acid.
Attention: any drug should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
The dosage, as well as the duration of the course, are selected by the dermatologist individually for each patient. An excess of vitamin A in the body can cause kidney or liver pathologies, increased blood cholesterol levels, and urinary problems.
Ointments
Ointments for follicular hyperkeratosis are selected taking into account the degree of development of the problem, the nature of the course of the disease, and concomitant pathologies.
Typically, products containing salicylic acid, urea, and AHA acids (for example, anthralin, tazarotene, daivonex) are used. They have the following effects on the body:
- stop inflammation;
- disinfect;
- stimulate cellular restoration.
In the acute period, corticosteroid ointments are used:
- diprospan;
- prednisolone;
- flucinar;
- hydrocortisone ointment;
- sinalar;
- dermovate;
- sinaflan.
Such creams combine anti-allergenic, anti-inflammatory, exfoliating, and immunostimulating effects.
For hyperkeratosis of a fungal nature, ointments that eliminate the pathogenic factor (such as exoderil, clotrimazole) are recommended.
Cosmetology procedures
You can improve the appearance of problem areas with hyperkeratosis and remove keratinized layers using cosmetic procedures.
Here are the most effective methods for solving the problem:
- Phototherapy destroys dead cells under the influence of light flashes. Before this, the skin is treated with a photosensitive composition;
- brossage - cleanses the dermis with a device with special attachments with a disinfecting gel or fine scrub;
- Laser resurfacing destroys altered hair follicles, their growth stops, and nodules disappear. Depending on the degree of development of the disease, superficial or deep treatment is selected;
- cryotherapy is performed with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of low temperatures, the upper layer of the epidermis dies and is rejected, local metabolism accelerates, skin cells receive sufficient hydration and nutrition;
- Ultrasonic cleaning provides quick but gentle removal of dead tissue.
Attention: mechanical peelings are contraindicated for hyperkeratosis!
In some cases, the cosmetologist recommends chemical peeling using acid-based compounds that act gently.
How to get rid of it at home
Treatment can be supplemented with traditional medicine. Note that they do not fight the problem itself, but reduce keratotic manifestations, moisturize the skin, and stop inflammatory processes.
Here are some effective recipes:
- Wash the lower leaves of aloe and freeze in the refrigerator for several days. Grind the pulp, apply it to the problem area overnight, cover the top with cling film and gauze. Carry out the procedure every other day;
- Grate raw potatoes, wrap the resulting mass in cotton cloth, and apply to your face for a couple of hours. Potatoes can be replaced with beets;
- Apply a thin layer of propolis to the face, cover with cellophane, then with gauze. Keep it for a day. The frequency of manipulations is once every three days.
Before carrying out the procedures, it is advisable to steam the affected area in a soda bath to soften the crusts. This will increase the effectiveness of the formulations.
Folk remedies
Home recipes are aimed at reducing inflammation and cleansing the epidermis. Most components for the treatment of pilaris are easy to find in every home. Be sure to get the go-ahead from your dermatologist to use traditional medicine recipes.
Starch baths Dissolve 0.5 kg of starch in cold water. Take warm water and pour in the solution. Take a bath for 30 minutes. After the procedure, rinse your body, wipe dry, and apply moisturizer.
Aloe treatmentChoose a plant. Which is at least five years old. Trim off the thick, fleshy leaves. Immerse in boiling water for 10 seconds, wipe, wrap in dry gauze, and put in the freezer for three days.
Take out the aloe leaves, defrost, cut as thin as possible. Apply the plates to the affected areas and cover with plastic wrap. Keep it until the morning. Remove the leaves and wipe the skin with salicylic alcohol.
The frequency of procedures is 3 times a week. Be sure to let your skin breathe, otherwise diaper rash will appear.
Potato compressSimple, accessible, cheap! Grate the potatoes on a fine grater and apply the mixture onto clean gauze. Apply the compress to the rash. After an hour, remove and apply a fresh compress. After the end of the same period, another one is needed.
Carry out the procedure every day. The skin becomes fresher and the number of rashes is reduced.
Beetroot compresses Take richly colored root vegetables, chop in a blender or grate. Leave the mixture in the bowl for 2 hours. There is no need to clean it in the cold.
The difference from potato compresses is that the beet mass is applied once. The duration of the procedure is 5–6 hours. Wash your skin with warm water, apply a light moisturizer.
Masks with propolisHealing product is widely used in cosmetology and dermatology. Apply the valuable substance to the rash areas. After a while, the body will be covered with a film. Do not wash it off for two or three days.
Wash your face and give your skin a rest. Repeat the procedure with a break of 3-4 days.