Skin diseases are not uncommon in modern times. Both infectious dermatitis and non-infectious skin lesions have a negative impact on human health. Skin problems are indicated by the slightest visible defects, such as rashes, redness, and peeling. The etiology of these phenomena is different; only a dermatologist can determine the type of dermatoses.
In addition to allergic reactions, eczema, dermatomycosis, herpes, and lichen, cases of guttate psoriasis have recently become more frequent. This diagnosis frightens people who encounter it for the first time. After all, without having an idea about the disease, it is difficult to judge how serious its consequences may be.
The essence of guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis is a persistent form of psoriasis characterized by seasonal manifestations. Often the disease makes itself felt in the autumn-winter period, when it is difficult to avoid a decrease in the body’s immune reserves. Experts point out that this disease is a consequence of complications of ordinary psoriasis.
The insidiousness of the teardrop-shaped form of psoriasis is that you can never predict in which place papules with white-yellow scales may appear, which is why it is also called wandering.
Treatment of guttate psoriasis should not be delayed, as it quickly becomes chronic.
Folk remedies
Folk experience can be quite an effective method as part of the complex treatment of guttate psoriasis. In this capacity, it is expected to use medicinal plants as tea, baths with medicinal compositions, as well as lotions and compresses based on medicinal herbs.
For treatment, string, chamomile, celandine, sage, calendula and many others are widely used. Decoctions are prepared from them, which are subsequently used in the form of lotions or added to baths with water.
Flax seeds are very popular both among doctors involved in the treatment of this disease and among patients suffering from guttate psoriasis. In a thermos, infuse a tablespoon of seeds in a glass of boiling water, and the next morning drink the infusion in two doses. It is especially important to drink the infusion along with the seeds; they have no taste and over time this can be done easily.
Kalanchoe leaves or celery root are used in the form of compresses; the pulp from these plants is applied to the affected areas and secured with a napkin and adhesive tape.
Types of disease
Guttate psoriasis itself (see photo below), being a type of scaly non-infectious lichen, is classified into:
- soft – no more than three percent of the skin is affected by papules;
- moderate – the radius of skin damage exceeds three percent;
- severe - ten percent of the skin or more is covered with scaly papules.
This disease is very similar in external symptoms to guttate parapsoriasis, but is characterized by a stable course and is more difficult to treat. Completing a therapeutic course does not guarantee the absence of relapses in the future, while parapsoriasis can be cured forever.
Any form of the disease is characterized by three stages:
- sensitization – an interdependent reaction occurs between pathogenic microorganisms (antigens) and cells of the immune system (antibodies);
- latent existence - the increase in the number of antibodies exceeds the norm, cells of the immune system affect healthy cells of the skin epidermis;
- manifest rash - there is a visible rash of the skin.
It is the duration of the third phase that determines what form the disease will take—moderate or severe chronic. Each patient has a different degree of body resistance, so the phases of exacerbation of the disease and the frequency of relapses are strictly individual indicators.
Risk group for psoriasis
- The risk group for this disease includes school-age children, adolescents and adults under the age of thirty.
- Spontaneous drop-shaped lesions of the skin of the body are more typical for young people than for old people, but cases of the disease in older people are also recorded by dermatologists.
- Currently, this disease can also manifest itself in people who have never had psoriasis, but who have a congenital predisposition to this phenomenon.
Routes of infection
Guttate psoriasis cannot be infected, since the etiology of this disease is not associated with infections. Damage to the skin is associated with autoimmune processes occurring in the body. This means that the immune system begins to suppress the body’s cells, mistaking them for “enemies.”
Despite the unsightly appearance of psoriatic skin papules, psoriasis is not dangerous to others. Myths about the transmission of psoriasis by airborne droplets, contact and household contact have long been refuted by experts.
Disease prevention
- It is necessary to moisturize the skin from time to time and prevent dryness, since dryness and excessive tension of the skin causes it to crack, which aggravates the problem.
- It is necessary to protect the skin from microtraumas and damage; you should be especially careful when bathing. There is a risk of developing a secondary infection when scratching or scratching, since the skin in this case does not perform a barrier function and becomes vulnerable to viral agents.
- Increase your immunity, which is directly related to the development of guttate psoriasis. Diseases, in most cases, develop against the background of a weakened immune system.
- Quit alcohol and smoking. Avoid stressful situations and do not overcool.
Factors provoking the development of the disease
Today, experts point to multiple causes that provoke the manifestation of the teardrop form of psoriasis. Of these, both endogenous and exogenous factors can be distinguished.
Exogenous root causes of the disease
Why is guttate psoriasis a real surprise for many?
The causes of the disease, as it turns out, may include:
- people living in environmentally unfavorable areas;
- exposure to chemical and toxic substances on the human body;
- unhealthy lifestyle (poor diet, lack of exercise, taking medications for other purposes (antibiotics, vitamins, corticosteroids);
- psycho-emotional overload;
- household and professional trauma to the skin (sun and chemical burns, cuts, insect bites, frostbite, radiation).
Causes of the disease
At the moment, there are several hypotheses about the reasons for the development of this pathology, but each of them has not yet received official confirmation.
It has only been proven that psoriasis develops as a result of exacerbation of infectious, viral and bacterial diseases. In medical practice, the following causes of guttate psoriasis are identified:
- Hereditary predisposition to skin diseases;
- Changes in hormonal levels that can occur during pregnancy, menstruation, taking hormonal medications, as well as for other reasons;
- Regular stressful situations, neurological and psychological disorders;
- Metabolic disorders;
- As a consequence of viral or infectious diseases;
- Consequences of a cold climate with high humidity.
Endogenous prerequisites for guttate lichen
The endogenous causes of the disease, on the basis of which treatment is prescribed to the patient, in most cases are as follows:
- genetic predisposition to autoimmune diseases;
- disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- endocrine disorders;
- age-related hormonal imbalance;
- hormonal disorders during pregnancy;
- hormonal surge during the transition period in adolescents;
- metabolic disorder;
- gastrointestinal and liver diseases;
- individual characteristics of human skin;
- viral diseases (flu, seasonal colds, viral sore throat, pneumonia);
- bacterial infections (streptococcus, staphylococcus, bacterial tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis);
- fungal infections (dermatomycosis, keratomycosis).
Signs of the disease in adults
In an adult, guttate wandering psoriasis is manifested by a very rapid rash of pinpoint elements on the skin, very similar to droplets of water. These elements, depending on the speed of skin damage, can subsequently combine into large islands. Thus, the size of teardrop-shaped papules can vary from 5 mm to 2 cm.
Against the background of a skin rash, the patient:
- may feel unpleasant itching all over the body;
- may be irritable;
- is subject to mental depression;
- suffers from bleeding skin wounds;
- may feel joint pain;
- is more often exposed to physical fatigue compared to healthy people;
- withdraws into himself, limiting all contacts with society due to the manifestation of an inferiority complex.
Manifestations in children
Guttate psoriasis in children is an important signal for parents that the child’s immunity requires immediate correction. Psoriasis that manifests itself in childhood is much more dangerous than its manifestations at the age of 20 to 40 years and later.
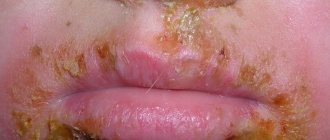
The signs of the disease are identical in both children and adults. However, the child is more sensitive to itching and the formation of wounds on the skin, which is prone to tightening due to excess moisture. Since parents are not always able to control their children in terms of compliance with hygiene recommendations, an infectious component can also be added to psoriasis, which greatly aggravates an already difficult situation.
Guttate psoriasis affects children of all age groups, newborns are no exception.
Strong arguments for urgent consultation with a dermatologist are:
- skin rash;
- irritability and capriciousness of the child;
- sleep disturbance;
- lack of appetite;
- increased body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Symptoms and signs
Very often the disease occurs in patients during the cold season. The disease is considered incurable; periods of remission are followed by exacerbations and vice versa. The first stages are characterized by the appearance of a small number of spots of not too large size. Over time, they increase and affect more and more areas of the skin. There is also tingling on the feet.
The main distinguishing feature of the disease is the absence of its precursors, such as itching or redness. The spots appear suddenly, affecting various parts of the body. The disease is called point. Symptoms are not always accompanied by the appearance of characteristic scales. The spots may simply be pink or red in color and not peel off at all.
Doctors state the facts that in most cases this type manifests itself in adolescence. It can develop against the background of infectious diseases. This could be: sore throat, flu or rubella.
Important! Guttate psoriasis occurs suddenly, and the number of rashes can increase dramatically in just a few hours. Doctors call him unpredictable.
Experts include the following as the main provoking factors:
- heredity;
- severe stress and anxiety;
- disorders of the body's lipid metabolism;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- hormonal imbalances;
- weakening of the immune system under the influence of various factors.
The above reasons are just assumptions. In fact, there may be much more. Sometimes pathology occurs due to the development of an allergic reaction or under the influence of sunlight.
Important! Whatever the reasons, every patient should remember the need for timely and correct treatment.
Diagnosis of guttate psoriasis
- Since the triggering factor for the teardrop form of psoriasis in most cases is infections of the respiratory system, when examining a patient it is advisable to perform a bacteriological examination of smears taken from the larynx, nasal passages, and saliva in order to identify the infectious pathogen.
- Mandatory for psoriatic manifestations on the skin are detailed and biochemical blood tests to exclude the allergic factor of the disease and evaluate indicators such as: ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate (in psoriasis, increased), hemoglobin level (if the diagnosis is confirmed, low), number of leukocytes (in lichen). high). In severe cases of drip psoriasis, it is recommended to take a blood test for antigens, which allows identifying damage to the joints.
- According to the results of a urine test, a specialist analyzes the patient’s metabolic status.
- In order to exclude false diagnoses, dermatologists resort to differential diagnostic methods. Thus, a skin biopsy allows you to examine diseased areas of the skin and exclude the development of other forms of dermatoses in the patient.
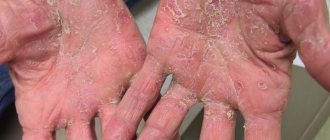
Nail psoriasis Effective treatment at home
There are several types of nail psoriasis; they can be identified by their characteristic clinical picture:
- Thimble-shaped is one of the most common forms of the disease, characterized by the appearance of many dots and pits on the surface of the nail.
- Onycholysis. The nail plate separates from the bed, and a yellowish border forms around it. The disease covers the nail completely or partially. The plate is separated in three directions - central, lateral or distal.
- Onychomadesis. It is considered one of the most severe types of psoriasis, difficult to treat. It differs from onycholysis in the absence of an inflammatory border and accelerated development.
- Hemorrhages (small hemorrhages). They appear in the form of shapeless spots and veins shining through the plate, which become almost black when large capillaries rupture.
- Trachyonychia. The nail plate becomes rough, becoming covered with irregularities. In the variety called koilonychia, its edges curl upward.
- Psoriatic paronychia is an enlargement of the nail folds, inflammation of the skin around the nail, spreading to the entire finger.
Some forms of the disease can cause a more serious problem - Zumbusch psoriasis, which requires mandatory hospitalization.
Causes of psoriasis on nails
Nail psoriasis is a chronic skin disease of an autoimmune (allergy to one's own tissues) nature. The disease has not been fully studied; there are many white spots left in it.
But it is known for sure that heredity plays a large role in its development: in one family, several people often suffer from this non-contagious dermatosis.
In recent years, assumptions about the leading importance of heredity have been confirmed by genetic research, that is, by the presence of special genes.
But not everyone who has a family history gets sick. This also requires exposure to certain general and local factors. General (affecting the entire body) factors contributing to the development of nail psoriasis include:
- any chronic diseases and foci of infection;
- endocrine and allergic diseases;
- eating only high-calorie foods;
- regular drinking, smoking;
- constant emotional tension, stress, hard physical work;
- lack of physical activity, excess body weight;
- violation of the sleep-wake pattern;
- impaired peripheral circulation - with atherosclerosis of the extremities, obliterating endarteritis, etc.;
- anemia – the nutrition of the nail plates is impaired;
- existing psoriasis of any form, especially psoriatic arthritis.
Important information: Psoriasis in dogs symptoms photo
Local factors (of no less importance):
- skin infections, especially fungal ones, affecting the nail plates;
- any mechanical and chemical effects on the nail plates.
When exposed to several causes, metabolism and immunity are disrupted. The body begins to reject its own cells, which leads to the appearance of psoriatic inflammatory process in the nail area
It is important to notice the problem in time, consult a doctor and begin treating the disease.
Symptoms of psoriasis on the nails
Nail psoriasis most often develops with existing psoriatic joint damage. Much less often, it complicates the course of cutaneous forms of this disease. To understand how the pathological process spreads on the fingernails and toenails, you need to consider the structure of the nail:
Psoriasis on the fingernails is more common and progresses slowly and unnoticed. The nail plate gradually thickens due to the rapid keratinization of the surface layers.
One of the first symptoms of nail psoriasis is the appearance on the nail plates of single white spots or longitudinal lines, as well as pinpoint impressions similar to injections.
Gradually, the entire nail becomes covered with such pits (thimble symptom).
When nail psoriasis spreads, the nail matrix (the growth zone responsible for the formation of tissues of the nail plate) is affected, which leads to the melting of the nail tissues - onycholysis. The process begins with the appearance of a yellow-brown border at the free edge of the nail plate. Then the plate is separated from the bed.
Its color, thickness, consistency and shape change. Its surface becomes lumpy, grayish-brown or yellow. Further destruction of the plate leads to its atrophy (decrease in volume) or hypertrophy (increase in volume). Often it takes on the appearance of the beak of a bird of prey.
The condition may be complicated by severe itching.
When the nail bed (the layer of connective tissue under the nail plate) is damaged, subungual hyperkeratosis develops - thickening of the plate. Under the plate, spots appear that resemble oil stains (oil stain phenomenon). Important information: Differences between psoriasis and dermatitis
Single or multiple pinpoint hemorrhages also appear on the nail plates. Instead, brown longitudinal stripes sometimes appear, which also indicates hemorrhage.
Nail psoriasis on the feet is less common. Its manifestations are the same as on the hands. But this form of the disease is sometimes difficult to distinguish from a fungal infection, which has similar manifestations. Sometimes psoriatic lesions on the legs are combined with fungal ones.
Nail psoriasis can be accompanied by inflammation of the skin and periungual tissues around the nail plate - psoriatic paronychia. When an infection occurs, the inflammation of the affected area becomes purulent.
Features and reasons for appearance
Photo of psoriasis of fingernails
Psoriasis on the nails is not so common, but it causes a lot of unpleasant sensations to a person. The sore affects the nail plates, which gradually change color and collapse.
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=CncBAs4zgTM
The main task of the patient is to begin quick and effective actions aimed at treating psoriasis of the fingernails.
Psoriasis of the fingernails rarely occurs as an independent disease. It mainly appears in people suffering from psoriatic arthritis or having lesions on other areas of the skin.
The true causes of the sore have not yet been determined. But the attending physician will accurately name the factors that contribute to the development of the disease in the form of psoriasis of the fingernails. These include:
- Prolonged stress, nervous tension and nervous breakdowns;
- Disturbances in the circulatory system;
- Changes in metabolic processes;
- Heredity;
- External stimuli.
Primary signs
Photo of manifestations of psoriasis of fingernails
The course of psoriasis on the fingernails, a photo of which you can clearly see, largely depends on the origin and type of sore of a particular patient. But there are a number of common manifestations of the disease, due to which you can determine at an early stage whether you have developing nail psoriasis. These signs include:
- Pits appear on the surfaces of the nail plates;
- If you press on a sore nail, unpleasant pain occurs;
- Between the bed and the nail plate, spaces may form where dust or epidermis gets in;
- Inflammatory processes begin under the nail, caused by foreign particles getting under the nail.
Important information: What psoriasis looks like on the eyelids. Its symptoms and treatment
Reviews from people who have gone through this nail sore make it clear that untimely treatment leads to serious complications.
Curing fingernail psoriasis is not the easiest task due to the duration of treatment and the effort involved.
But if everything is done correctly, as an experienced attending physician says, then literally in 2 weeks the nail will return to its normal state, and you will forget about nail psoriasis.
Drug treatment
Treating guttate psoriasis without preliminary diagnosis is not recommended for either adults or children! The etiology of this disease has not been fully studied by specialists, and the consequences of independent intervention can only harm the patient’s body - cause irreversible acute manifestations.
Treatment of guttate psoriasis does not completely cure the patient, but only allows you to increase the duration of the inter-recurrent periods of the disease. In most cases, thanks to a competent approach to the problem, it is possible to forget about it for several years, but this does not mean that complete recovery has occurred. Any of the above factors can become an impetus for the secondary manifestation of skin lesions.
Drip psoriasis is not a death sentence if its treatment and periods of recovery of the body after therapeutic courses are accompanied by:
- compliance with dietary nutrition;
- moderate psycho-emotional stress;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- active lifestyle;
- hardening of the body.
Treatment of guttate psoriasis
To achieve a lasting effect from the treatment, a patient with psoriasis needs to tune in to a long-term treatment process. It provides for the use of medications, special procedures with PUVA therapy and plasmaphoresis, as well as dietary nutrition with the replenishment of essential vitamins.
Drug therapy in the treatment of psoriasis is aimed at achieving the following goals: antibiotics are intended to suppress the infectious process, local drugs with hormonal properties eliminate the external manifestations of psoriasis, drugs with a sedative effect normalize the psycho-emotional state of the patient, and immunomodulator drugs increase the body's defenses.
Medicines used in the treatment of guttate lichen
| Name of the drug | Current substance | Pharmacological group | Form release |
| Treatment for adults | |||
| "Triderm" | betamethasone, clotrimazole, gentamicin | corticosteroid in combination with an antibiotic | cream, ointment |
| "Betazon" | |||
| "Triacutan" | |||
| "Celestoderm" | |||
| "Kremgen" | |||
| "Diprosalik" | betamethasone, salicylic acid | corticosteroid | lotion |
| "Dermabin" | |||
| "Advantan" | methylprednisolone aceponate | cream | |
| "Prednisolone" | prednisolone | ointment | |
| "Sinaflan" | fluocinolone acetonide | ointment | |
| "Calcetriol" | calcetriol | antipsoriatic agent | ointment |
| "Forcal" | |||
| "Hemosol" | salicylic acid | dermatological product | ointment |
| "Davonex" | calcipotriol | biogenic stimulant | cream, ointment |
| "Psorkutan" | |||
| "Glenriaz" | |||
| Vitamin complex | vitamins A, B, P, C, E, D | a drug that replenishes vitamin deficiencies in the body | dragees, pills |
| "Polysorb" | silica | enterosorbent | powder for the preparation of emulsion for oral use |
| "Atoxil" | |||
| Activated carbon | activated carbon | pills | |
| "Enterosgel" | methyl silicic acid | oral paste | |
| "Dexamethasone" | dexamethasone | corticosteroid for systemic use | pills |
| "Methylprednisolone" | methylprednisolone | pills | |
| "Tsetrin" | centrizine hydrochloride | antihistamine | pills |
| "Zodak" | pills | ||
| "Phosphogliv" | phospholipids | hepatoprotector | capsules |
| "Geparsil" | silymarin | capsules | |
| "Lifemoon" | cyclosporine | immunosuppressant | capsules |
| "Imusporin" | capsules | ||
| "Vero-Methotrexate" | methotrexate | injection | |
| Treatment for children | |||
| Sulfuric ointment | sulfur | antimicrobial agent | ointment |
| Salicylic ointment | salicylic acid | dermatological product | ointment |
| Papaverine ointment | papaverine hydrochloride | ointment | |
| "Tavegil" | clemastine | antihistamine | pills |
| "Diazolin" | mebhydrolin | pills | |
| "Enbrel" | etanercept | immunosuppressant | injection |
| "Pyrogenal" | bacterial lipopolysaccharide | broad-spectrum immunomodulator | injection |
| "Prednisolone" | prednisolone | corticosteroid | ointment |
| "Flucinar" | fluocinolone | ointment | |
| "Sinaflan" | fluocinolone acetonide | ointment | |
| "Valerian" | valerian extract | sedative | tablets, tincture |
| "Motherwort" | motherwort extract | tincture | |
| "Pyridoxine" | vitamin B | vitamin preparation | injection |
| "Cyanocobalamin" | vitamin B12 | injection | |
| "Riboflavin" | vitamin B2 | injection | |
| Pangamic acid | vitamin B15 | dragee | |
| Folic acid | vitamin B9 | dragee | |
| "Retinol" | vitamin A | dragee | |
| Ascorbic acid | vitamin C | pills | |
Drug treatment for severe disease may be accompanied by blood purification (plasmopharesis) or physiotherapeutic procedures (UVR, selective phototherapy, PUVA therapy).
Guttate psoriasis: 9 photos, causes, symptoms and treatment
About the Editor
Guttate psoriasis is a chronic inflammation of the skin in which reddish, itchy teardrop-shaped papules form on the skin. The disease mainly affects children over 6 years of age and young people, but it also occurs in older people. The rash appears spontaneously and is not contagious.
An alternative name is macular psoriasis and lichen planus.
Why does guttate psoriasis appear?
The exact reasons are not known. However, it is believed that the main trigger factor is infection. In this case, most often - streptococci. This hypothesis is supported by scrapings from papules - usually this pathogen is always found in them.
Psoriasis can also develop against the background of other disorders:
- advanced infectious diseases (tonsillitis, sinusitis, ARVI, fungal infections);
- weakening of the body's immune forces;
- physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- endocrine problems;
- metabolic disorders;
- HIV;
- hereditary predisposition;
- regular contact with harmful chemicals; frequent use of low-quality cosmetics;
- a long course of certain medications (usually hormonal);
- skin damage;
- allergies and systemic lupus.
The risk of developing the disease also increases in people with chronic diseases. Reviews about the treatment of guttate psoriasis vary due to different causes of the pathology.
Find out more
Symptoms of Guttate Psoriasis
Main signs of pathology:
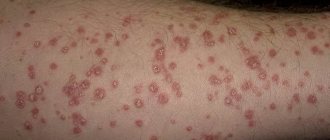
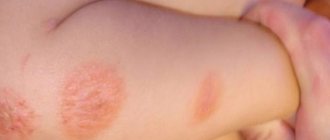
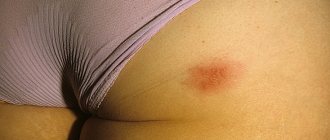
- rash in the form of pinkish or reddish drops (can merge with each other, forming larger spots);
- silvery scales on top of the rashes, which can be easily removed;
- intense itching;
- the formation of small ulcers when the skin is injured (sometimes visible in photos of guttate psoriasis, and although when these ulcers go away depends on the degree of damage, it usually happens slowly).
In most cases, the rash appears on the torso, legs and shoulder area.
Attacks of rashes occur in waves. Papules appear spontaneously and randomly. They pass just as quickly and suddenly. Often attacks occur during weakened immunity. Seasonal exacerbations are sometimes possible.
Photos are better than simple descriptions in providing a more complete understanding of drip psoriasis.
Also, the external manifestations of this type of psoriasis can be classified based on the stage:
- Progressive or initial stage. Several papules appear on the skin, which gradually increase in number and sometimes in size. The formations are peeling off. The patient is bothered by severe, never-ending itching.
- Stabilization stage. The itching sensation becomes weaker or disappears completely. No new papules appear. The degree of pigmentation around the formations begins to weaken slightly.
- Regressive or resolution stage. Papules gradually resolve, but may leave behind weakly pigmented areas.
With each relapse, all of the above stages are repeated.
The disease can progress to another form of psoriasis. Most often - plaque-like.
Treatment Strategies for Guttate Psoriasis
The pathology is chronic and cannot be completely cured. Therefore, the key goal of therapy is to weaken the external manifestations of the disease and reduce the likelihood of relapses.
For drip psoriasis, treatment methods and strategies are complex. Therefore, several of the following means are used at once:
- Taking systemic medications. As a rule - in the form of tablets. In severe cases, injections may be prescribed. Medicines act comprehensively against the pathogen, relieve inflammation, and also reduce itching and the degree of redness.
- Physiotherapy. It is highly efficient. Among physical procedures, ultraviolet irradiation, excimer laser exposure, PUVA and selective phototherapy, cryotherapy, plasmaphoresis, as well as treatment of damaged areas with darsonval are more often used. On the Internet you can find photos of the treatment of guttate psoriasis using procedures.
- Use of external medications. In the form of ointments, gels and creams. Designed to eliminate symptoms such as itching and redness, and also reduce inflammation and swelling of the skin. Sometimes, for guttate psoriasis, treatment can be supplemented with ointments with an antibacterial effect. They are prescribed to avoid infection of the patient through microdamages in the skin.
- Diet. The diet is hypoallergenic and is aimed at eliminating provoking foods. First of all, fast carbohydrates (pasta, sweets, baked goods) are removed from the menu. It is also recommended to exclude preservatives, products with dyes, fried and fatty foods, spices, too spicy and salty foods. Quitting alcohol and smoking is mandatory. The basis of the diet should be foods such as vegetables, lean fish and meat (cooked or boiled), berries (except strawberries and wild strawberries), fresh fruits (except citrus fruits) and low-fat fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, milk). It is optimal if the menu is compiled by the attending physician.
- Elimination of stress. This is necessary to harmonize the activity of the nervous system and the emotional state of the patient. For this purpose, sedatives such as motherwort and valerian infusion or mild antidepressants may be prescribed.
Features of treatment depend on the degree of damage and the general condition of the body. This information can only be obtained by a doctor - after a thorough diagnosis. Therefore, self-medication is excluded.
Treatment of guttate psoriasis with folk remedies
Treatment of guttate psoriasis at home is used only after consultation with a doctor and exclusively as an additional measure. You cannot refuse to take medications.
Popular recipes:
- Motherwort tincture. Take 1-2 times a day for calm.
- Herb tea. Suitable plants include mint and chamomile, linden, lavender and St. John's wort. They can be drunk separately or mixed.
- Infusion of celandine. The plant is poured with boiling water and left for several hours. The composition is lubricated on plaques.
- Herbal bath. A decoction is made from celandine, the root part of white willow or juniper berries. Add it to the bath and take it for 15-20 minutes. Additionally, you can add two tbsp to the water. spoons of olive oil and one tbsp. spoon of milk.
- Sea buckthorn oil. It can be taken orally or applied to areas with rashes.
- Chicory compress. Two tbsp. spoons of chicory are brewed with a glass of boiling water. Soak sterile gauze in the mixture and moisten the rash from time to time.
- Garlic lotions. Pumpkin tails are baked in the oven until ash forms. Take garlic and squeeze its juice onto the affected areas, and sprinkle pumpkin ash on top.
- Salt bath and onion compress. The procedure is done at night. Take a bath with sea salt for 20 minutes. When leaving the water, do not dry yourself, but let your body dry on its own. Rub the onion, grated to a paste, into the affected areas and leave for 15 minutes. Then they clean everything up with a napkin and go to rest. In the morning, prepare a strong infusion of celandine and wipe the areas with the rash with it.
Traditional methods are best used only in the first stages of the disease.
Treatment of guttate psoriasis with medications
In guttate psoriasis, the causes and treatment of the disease with medications are interrelated.
In most cases, the following types of medications are prescribed:
- Antihistamines. Reduce the degree of inflammation and symptomatic manifestations such as itching and redness of the skin. Usually come in tablet form.
- Antibiotics. They are prescribed only when it is confirmed that the patient has streptococci.
- Cytostatics. Indicated in serious cases when the disease is particularly severe. Drugs of this type reduce the rate of cell division.
- Ointments. Hormonal or non-hormonal. The latter are prescribed in the first stages or when the pathology is mild. Hormone-based products are rarely used due to many side effects. Sometimes ointments containing dithranol are also prescribed - they slow down cell division and reduce the degree of inflammation.
- Systemic glucocorticoids. Hormone-based tablets. Prescribed in moderate to severe cases.
- Vitamin complexes. Especially those containing vitamins A, E and D.
Also, in advanced situations, an injection of sodium thiosulfate solution into a vein may be prescribed.
Preventive measures
To avoid relapses, the following conditions must be observed:
- Moisturize the skin. Special creams and gels. Especially taking a bath or shower.
- Avoid damage to the skin such as wounds and scratches.
- Follow a healthy menu. Give up bad foods and habits, do not eat fried, smoked, too fatty and sweet. Give preference to vegetables, berries and fruits. It is also recommended to add fish and fish oil to the menu. The omega-3 acids they contain reduce the degree of inflammation.
- Try to monitor your immune system. Do gymnastic exercises regularly, follow a daily routine, and harden yourself.
- Take baths more often with the addition of herbal infusions.
- Drink plenty of fluids. About 1.5 liters per day. However, you can’t overdo it either - it’s important to monitor your well-being.
- Try to eliminate stress. Or change your attitude towards some stress factors. In particularly difficult situations, it is advisable to make an appointment with a psychotherapist.
Compliance with the above measures and rules will seriously reduce the likelihood of new attacks of the rash.
(1 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Source: //www.dermatit.net/psoriaz/kaplevidnyj-prichiny-i-strategii-lecheniya/