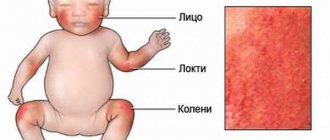
Eczema refers to a group of skin conditions that can cause itching, cracked skin, and painful blisters. People with eczema typically experience periods of flare-ups and remissions throughout their lives.
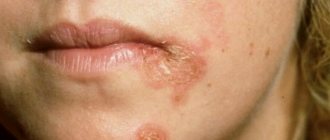
People can get eczema on their lips as a result of genetic influences or as a result of environmental factors such as irritants in lip products or habitual lip licking.
In this article, we will look at the causes, symptoms and treatments for lip eczema.
What is eczema on the face, photo
eczema on the face photo
Eczema on the face is a widespread inflammatory disease of the human skin.
It is characterized by the presence of various rashes on the face, hyperemia, peeling and swelling. Most often the chin, cheeks, nasolabial triangle are affected, and less often the eyelids. Eczema occurs in people of all ages and belongs to the category of multifactorial diseases. Eczema belongs to the category of multifactorial diseases, that is, the causes that can provoke the disease are numerous. The causes of the disease can be both external and internal. External causes of the development of eczema are certain chemical substances with which a person comes into contact during his life. Thus, very often eczema is provoked by household chemicals (soap, washing powders), cosmetics (both decorative cosmetics and care products), clothing made of synthetic materials, and jewelry.
Also, eczema on the face can be a result of eating poor-quality food with a large amount of dyes and emulsifiers, taking pharmaceuticals, especially antibiotics. Internal causes of the development of eczema are low immunity, dysbacteriosis, vitamin deficiency, parasitic and infectious diseases, as well as malfunctions of the endocrine system.
Internal causes also include genetic predisposition, various pathologies of pregnancy, and even artificial feeding. The disease looks very unaesthetic (especially during an exacerbation), its symptoms are quite pronounced. Interestingly, the disease manifests itself differently in different areas of the facial skin.
So, if the eyelids are affected, they become very thick, itchy and flaky. If eczema is localized on the lips, then the lips constantly dry out and crack, and periodically bleed.
Each stage of the disease has its own symptoms. At the same time, the manifestation of eczema of several stages at once can be observed on human skin (for example, weeping wounds and dry crusts). Doctors assign one or another stage of the disease based on which stage has more signs.
According to the nature of the disease, acute, subacute and chronic eczema are distinguished. In the acute form of the disease, all the signs are very pronounced, and the duration of the above-described cycle does not exceed 6 weeks. The doctor may also order a histological examination of tissue from the affected area to make sure that the disease is not autoimmune in nature.
Only compliance with all these measures guarantees that the treatment will be truly correct. Treatment of eczema, wherever the disease is localized, should always be comprehensive. However, before you begin to treat the disease, the factors that provoke it should be eliminated.
For example, if the manifestation of eczema on the face is caused by the use of a particular cosmetic product, this product and its analogues should no longer be used. If the cause is other diseases, for example, the presence of parasites, then before treating eczema, you need to get rid of the parasitic infection.
When the provoking factor has been eliminated, direct treatment of eczema can begin. As a rule, treatment of eczema is carried out in several directions. This includes taking antihistamines, using hormonal and non-hormonal ointments (if necessary, ointments containing antibiotics are also used), immunomodulation, following a special hypoallergenic diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Treatment of eczema on the face involves the use of solutions with calcium chloride (10%), sodium bromide (10%) and sodium hyposulfite (20%). Injections with ascorbic acid, cyanocobalamin and thiamine are also indicated. These measures help reduce the body's sensitivity to irritating factors.
At the final stage of the disease, retinol is injected, which accelerates the processes of completion and epidermization. The disease in its initial stages should be treated using lotions based on silver nitrate or resorcinol, which have an antiseptic effect and relieve inflammation. It is most difficult to treat the disease at the weeping stage.
At this time, compresses with an antibacterial solution and glucocorticosteroids are needed. And, of course, treatment of the disease is impossible without local agents, which can take the form of ointment, gel, or cream.
At the same time, in order to treat the disease, both hormonal (but in small quantities and for a certain period of time) and non-hormonal ointment should be used. Among the hormonal agents of external influence, the most popular are: Prednisolone ointment (0.5%) and Lokoid ointment - these drugs have practically no restrictions on their use, and are indicated even for children and pregnant women.
Fast-acting drugs that are used in particularly advanced cases and are used only for a limited period of time under the supervision of a specialist are Dermovate ointment, Galcinonide ointment, and Advantan cream ointment. As already mentioned, treatment of eczema on the face involves the use of non-hormonal external medications.
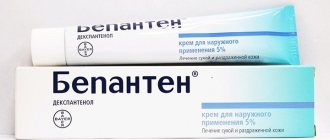
Thus, in the initial stages, good results are achieved by using such agents as indomethacin ointment and Meshchersky ointment. In the stages of weeping and crust formation, Eplan and Panthenol are recommended, which have a softening effect and promote rapid healing of the wound surface.
The advantage of non-hormonal ointments is that they can be used for a long time. If laboratory tests reveal the presence of infections, Exoderil and Losterin are prescribed - zinc-based ointments with an antibacterial component.
Finally, we note that the prognosis for a complete cure of chronic eczema is unfavorable. In this regard, in order to prevent the disease from becoming chronic, it is better to begin treatment of the disease in the early stages. In this situation, you can get rid of the disease forever.
Source: zabotaokozhe.ru
Reasons for development
Eczema on the face, as well as on other parts of the body, can be caused by various factors. They are similar to each other in both adults and children. The disease itself can have a wide variety of origins.
Causes of eczema:
- An allergic reaction of the body to any irritants, which include: pollen, wool, food and other substances. In such a situation, it is recommended to carry out an allergy test.
- Parasitic infestations. Worms and other parasites in the human body can cause a lack of vitamins and disrupt the metabolic process. As a result, the immune system becomes weaker and more susceptible to infection.
- Skin infection due to fungal infection.
- Insect bites.
- Heredity.
- Violation of the integrity of the skin.
- Nervous disorders, stressful situations.
- Systemic autoimmune diseases, disorders of the digestive system.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
If the patient has at least one of the listed provoking causes of eczema, then it is worth consulting with a specialist and starting therapy.
Types of eczema
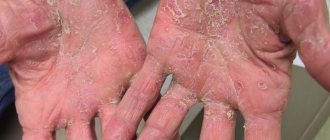
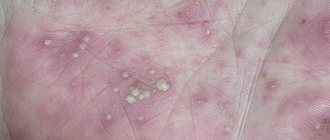
Depending on the causes of the appearance and localization of the disease, experts distinguish the following types of eczema: true (idiopathic) eczema is an inflammatory skin disease characterized by the formation of multiple mottled rashes mainly on the skin of the soles and palms.
When the bubbles open, weeping areas, crusts and scales form; itching appears. As a result of the appearance of more and more new blisters, the eczema lesion increases in size, and gradually it can spread to other parts of the body.
Microbial eczema usually asymmetrically affects the skin of the legs, the back of the hand and the scalp. The causative agent of the disease is a yeast fungus of the pyococcal flora, which causes the appearance of greenish-yellow rashes, serous-purulent crusts and erosions. Exacerbation of the disease leads to bleeding of the affected area and increased itching.
Occupational eczema is characterized by damage to exposed areas of the body by chemicals; it usually appears in industrial workers against the background of allergic dermatitis.
Infantile eczema develops in children usually due to a hereditary predisposition, or against the background of exacerbation of diathesis. The disease is localized on the face, scalp and gradually spreads to other parts of the body.
Abundant red rashes, peeling, burning sensation and itching appear on the child’s skin. Seborrheic eczema affects the scalp, face, chest and interscapular area.
This species is characterized by the presence of yellowish-pink rashes, an abundance of layered yellowish crusts and scales. The course of eczema is long and capricious: for no apparent reason, the inflammation either worsens or subsides.
Source: abia-spb.ru
Symptoms
This skin disease not only develops in stages, but each type is accompanied by severe symptoms. Common signs of pathology include the following factors:
- Redness. In most cases, it occurs at the initial stage of eczema on the face. The boundaries of the inflammatory process will depend on the type of pathology.
- Bubbles and pustules.
- Wet areas with inflammation.
- Peeling.
- Crust formation.
- Itching, burning.
- Ulcers and ulcers.
After this pathology, the patient may have scars on his facial skin, which, as a result, leads to infection. In parallel with the listed symptoms of eczema on the skin of the face, the patient may also complain of symptoms such as increased irritability, insomnia, fatigue, and exhaustion of the body. Children may be more restless, have partial paralysis, and eat poorly.
Causes of eczema on the face
According to doctors, there are many reasons for the occurrence of eczema, but the specific cause of its occurrence is not known for sure. With eczema, just like with many other allergic diseases, an antigen-antibody reaction occurs, i.e. the entry of some foreign substance into our body.
Antigens, entering the body, promote the release of antibodies to eliminate these harmful substances. In this case, the following happens: eczematous blisters form at the points of contact of the antigen with the antibody, inflate and at a certain moment burst.
It is this characteristic of eczematous vesicles that actually served as the basis for the name “eczes” (from the word to boil). Factors predisposing a person to eczema: Heredity, this factor plays a very important role in the manifestation of not only eczema, but also other allergic diseases.
Liver condition, dysfunction of intoxication, i.e. the accumulation of toxins in the blood also provokes the appearance of allergic processes. And the liver, which is supposed to perform a detoxification function, cannot cope; toxins and allergens accumulate in the body.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia, with it the permeability of the vascular wall increases. The vessels become labile and therefore all some anti-inflammatory substances and water lead to increased oxidation and an increase in the corresponding inflammatory reaction. Oxidation is the perspiration of liquid through the vessels, through an unstable vascular wall, and therefore weeping, bubbles, and all the ensuing negative consequences occur.
An endocrine disorder is not only a disorder of the adrenal glands, but also a disorder of the thyroid gland, and in women it is often associated with sex hormones.
The state of immunity in allergic people, as a rule, has increased activity, but not in a beneficial direction, but in a pathological one, i.e. It should not react to an agent that penetrates a healthy body; in people prone to allergies, the immune system reacts incorrectly. Simply put, a perverted immune reaction occurs.
Environmental factors, the main causes of occurrence, such as hypothermia, cosmetics, contact with detergents or some other irritating substances. In patients whose eczema manifests itself on the skin of the hands, it is very important to maintain a skin protection regime, i.e. limit contact with these products, protect yourself from the cold.
Source: budizdorov.com
Symptoms and signs, photo on the face
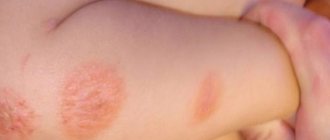
There are two types of eczema based on the nature of the rash: Dry eczema - characterized by dry skin, cracking, redness, peeling, itching. Localized on the arms and legs. Weeping eczema is characterized by severe redness of the skin, a rash of small blisters or a wet spot.
Appears on the head under the hair, on the inside of the elbows and knees and on the chest. Accompanied by severe itching and burning.
Each type of eczema has its own symptoms. True eczema: acute inflammatory redness of the skin followed by a rash of tiny blisters that quickly burst. In place of the burst bubbles, erosions form, forming a weeping surface. Then it dries out and becomes covered with gray-yellow crusts.
These stages are accompanied by severe itching. It occurs in clearly visible stages - erythematous (redness), papulovesicular (vesicular), weeping and crusting. It is almost always possible to observe all these stages simultaneously (in different areas). True eczema most often affects the face, hands and spreads throughout the skin.
Microbial: often occurs in damaged areas (wounds, including infected ones, cuts, ulcers). The onset is acute, the lesions are numerous and tend to increase. It has a clearly defined shape with a stratum corneum along the edges. The area affected by eczema is covered with a lamellar crust, under which there is a continuous weeping surface. Localized on the back of the hands, face and neck.
Mycotic (fungal): the symptoms are in many ways similar to the true one, but the edges of the lesions are sharply defined. This type of eczema is more difficult to treat and requires qualified medical supervision.
Seborrheic eczema: develops against the background of seborrhea, in areas where the sebaceous glands are located (in large quantities): nasolabial folds, scalp, area between the shoulder blades. Pinkish-yellow nodules covered with fatty scales; over time, plaques form, which merge to form large lesions.
Dyshidrotic: its localization is the palms and soles. The redness is barely noticeable. The bubbles can form erosions, but they can also merge to form larger blisters. In the absence/incorrect treatment, eczema is accompanied by changes in the nail plate.
Occupational eczema: symptoms are similar to those of true eczema. Occurs as a result of exposure to an external chemical, physical or mechanical irritant. It is characterized by the absence of exacerbations and is quickly cured.
Source: cytomed.ru
Principles of treatment
To effectively combat eczema, you must first contact a dermatologist. During the examination, the doctor takes into account not only visual symptoms. To determine an accurate diagnosis, additional research is necessary. This includes a blood test, taking allergy samples and scales from the affected areas of the skin.
The most effective is complex treatment, which is based on a combination of approaches such as medication, physical therapy and diet.
Medicines. To combat eczema, tablets, injections and special ointments are used. Treatment is carried out using the following groups of drugs: Antihistamines - antiallergic systemic drugs. Sedatives – calm the nervous system and reduce itching. Steroid topical ointments – relieve inflammation.
Antibiotics – protect the face from bacteria and germs. Vitamins – groups B and C. Physiotherapy. Today, methods such as electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, and reflexology are actively used. Diet. It is recommended to drink more water; all foods that can cause allergies in the patient are excluded from the diet.
Folk remedies. Additionally, treatment with traditional methods is used. It is recommended to apply grated raw potatoes wrapped in gauze to the affected areas, especially in the dry form. A mashed cabbage leaf soaked in apple cider vinegar can relieve itching. You can also lubricate your face with a mixture of dry celandine and butter in a ratio of approximately 1:5. An infusion of yarrow is used internally: 2 teaspoons of herbs per glass of boiling water. You need to drink throughout the day an hour and a half before meals. An adult is able to independently carry out these procedures. A small child needs the help of his parents. In addition, not all drugs are used at a young age, especially potent anti-inflammatory ones.
Treatment of eczema in children on the eyelids and face is complicated by the fact that the child can rub the greased area of skin and lick his hands. Therefore, infants should be swaddled tightly before applying the cream. Only by combining these methods will the treatment be effective and efficient. In addition, the face should always be clean, and it is better not to use cosmetics temporarily.
Source: jkrasa.ru
Traditional methods
At the first symptoms of the disease, a person should consult a dermatologist. He will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe pills for eczema. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate. If you are diagnosed with eczema, the first thing you need to do is determine the cause of the disease.
Having determined the cause, you need to get rid of it, because eczema is only a consequence of some existing diseases.
When fighting eczema itself, complex treatment is necessary, which includes the use of the following drugs: the very first tablets for eczema are antihistamines, which block the effects of substances such as histamine on the body and help fight allergic processes: severe itching, burning.
Among these drugs are used: Suprastin, Loratadine, Fenistil, Cetriliv, Zyrtec, Zodak, etc. Note: it is better to use anti-allergy drugs before bed, as they have a sedative effect, inducing sleep, inhibiting nervous processes; desensitizing drugs that suppress the effects of allergenic agents on the body.
Such drugs are salt solutions of calcium gluconate and sodium thiosulfate, which are administered intravenously. These saline solutions help fight inflammation. There are frequent cases when a secondary infection is added to the primary disease: viral, fungal or bacterial.
Then you can use the following tablets for eczema:
- for mycotic or fungal infections: Flucostat, Clotrimazole, Fucis, Fluconazole;
- for bacterial infection: broad-spectrum antibiotics Doxycycline, Amoxil, Loprax, Norfloxacin.
However, when using antibiotics, in parallel it is necessary to use drugs that eliminate the symptoms of dysbiosis and help restore the beneficial intestinal microflora. Such medications are Hilak-forte, Enterosgel, Acidolac. You may also need to take medications that improve liver function: Gepabene, Karsil, Smecta, white or black activated carbon.
To improve the effect of treatment, vitamin preparations and immunomodulators may be needed: Neurovit, Supradin, Aevit, Decamevit, Ascorbic acid, B vitamins. Vitamins for hand eczema should only be prescribed by a dermatologist, since taking some of them can cause allergic reactions in the body and worsen the progression of the disease.
Often, people suffering from eczema lose sleep and become emotionally exhausted due to the struggle with the disease. Then the doctor may prescribe sedatives and sedatives: Sedavit, Glitsed, Persen, Novopassit.
In addition to all the listed medications, for dry hand eczema, it is good to regularly use moisturizing creams, oils, emollients, the molecules of which penetrate deeply into the cells of the epithelial tissue and nourish it. When using eczema pills prescribed by your doctor, it is important to undergo a course of physical procedures that will improve the recovery process and rehabilitation of patients with eczema.
Among the most used and effective physiotherapeutic procedures are the following: balneotherapy - treatment with mineral waters. These could be medicinal hydrogen sulfide baths. Taking such procedures for eczema is very useful, as they reduce itching and flaking, thereby improving the condition of the skin.
Such baths help you relax and calm down. Thalassotherapy - treatment with sea products: sea salt, mud, algae. By taking baths using seafood, you can enrich your body with essential microelements that penetrate through the skin pores, producing a healing effect.
Ozone and plasma therapy, when the blood or plasma of a sick person is taken, enriched with ozone and returned back.
This procedure helps in the fight against inflammatory processes, increases the formation of new epithelial tissue, and has the effect of drying problem areas of the skin. However, this procedure has contraindications if a person suffers from epilepsy, hyperthyroidism, bleeding or poor ozone tolerance.
Some may not agree to such a procedure due to their beliefs. Therefore, the decision is entirely yours; laser therapy, when a chronic source of infection is eliminated using a laser, improves the process of blood circulation and regeneration of skin areas affected by eczema.
Laser therapy mobilizes the physiological systems of the body, helps to cope with insomnia; cryodestruction is a freezing process that uses liquid nitrogen or solid carbon dioxide. This procedure relieves pain and improves the healing of ulcerated parts of the skin due to eczema.
However, it is better not to carry out magnetic therapy if a person has diseases of the endocrine system, severe hypertension, or other cardiovascular diseases; irradiation with ultraviolet rays, which has an antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effect.
UV rays have a positive effect on cerebral circulation, the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. This procedure can be used at home if you purchase a UV lamp; Electrosleep blocks the excitability of the nervous system, improves the metabolic process; for dry eczema, you can use paraffin treatment, which accelerates the metabolism of useful substances and has an analgesic effect.
Eczema pills and physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect in treating eczema, but to prevent the progression of the disease and cases of relapse, in addition to traditional medicine, the suffering person must adhere to a diet. Proper nutrition will strengthen a person’s physical and emotional health and give strength to fight the disease.
It is important to exclude from your diet foods that are allergic, which can increase itching and burning. These include: chocolate, oranges, lemons, tangerines, berries. Also vegetables and fruits containing an abundance of carotene: tomatoes, red peppers, strawberries, etc.
You need to refrain from fried, fatty, spicy foods, mayonnaise, smoked foods, carbonated water, and alcohol.
Eat less baked goods and sweet pastries. Eczema tablets play a major role in treatment, but it is also very important to teach yourself to eat right. This will help reduce the number of relapses, reduce itching and prevent the progression of the disease.
Source: vysypanie.ru
Help from folk remedies
Potato.
Grate the raw potatoes and place on cheesecloth, wrap carefully. It needs to be applied to areas of inflammation, and can be secured with a bandage in the form of a bandage. After two hours, the bandage is changed to a new one. Good results are obtained by additional consumption of potato juice internally. Potato juice can be squeezed through cheesecloth or a juicer. Take two tablespoons of potato juice twice a day. Do not forget that beneficial substances disappear from potatoes very quickly, so they must be drunk immediately after cooking. Cabbage. The anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties of cabbage have long been known. You can apply raw white cabbage leaves to the inflamed areas or prepare a compress. A compress is made from three tablespoons of chopped cabbage and raw egg white. This mixture is wrapped in gauze and applied to the sore spot, secured with a bandage. The dressing is changed once a day.
Carrot. Like potatoes, carrots can be used both internally and externally. The juice from one carrot is squeezed out, a cotton pad is soaked in it and eczematous areas are regularly treated with it, without washing off the juice. When drinking carrot juice internally, you need to remember that the healing drink retains its nutritional and medicinal properties for no more than 10 minutes.
Garlic. This vegetable contains phytoncides that dry out eczematous erosions. It can be used internally and externally to treat eczema. Grate the garlic on the finest grater or squeeze it under a press. Mix three crushed garlic cloves with half a teaspoon of honey and rub into the rash area.
The second option for using garlic is a mixture of chopped garlic and half a teaspoon of butter, wrapped in gauze, applied to a painful area on the hands or feet and left overnight. Repeat the procedure for a week.
Decoctions from tree bark. Grind the oak bark and pour into a glass. Brew one liter of boiling water and bring to a boil. Now add two tablespoons of dried burdock root. Turn off the heat and steep the broth under a closed lid for half an hour. Place your hands in the hot broth until the liquid cools. Do not wipe your hands after this.
Take a piece of willow bark and chop it. Pour two cups of boiling water. Let the broth brew and cool. Wash the eczema areas with this liquid. Aloe and Kalanchoe juices. Apply a cut Kalanchoe or aloe leaf with the pulp itself to the affected skin. The skin should immediately turn pale.
Or soak a cotton swab with juice squeezed from Kalanchoe or Kalanchoe leaves and wipe as often as possible. If pure juice causes a burning sensation, then mix it with a teaspoon of honey and then apply. For a week, wipe the inflammation center with the juice of these plants twice a day, and you will see the healing of existing erosions.
Celandine has long been used in dermatology to relieve fresh ulcers, purulent lesions, lichen, acne and eczema. The most important effect of celandine is antipruritic. The fastest results are obtained by using pure celandine juice. Soak a cotton pad with celandine and apply to the eczema.
There may be a slight burning sensation, which will later disappear along with the inflammation. You can prepare an infusion for external use based on the celandine itself. Pour two tablespoons of celandine grass and roots with a glass of boiling water. Leave for half an hour, then cool for an hour and strain. Apply this infusion of celandine to the inflammation several times a day.
Salt bath. Pour three liters of hot water into a bowl and add three to four tablespoons of coarse rock or sea salt. Place your hands, feet or elbows in the solution and hold until the water cools. Then dry your hands with a towel and apply nourishing cream. It is advisable to carry out the procedure daily before bedtime.
Ointment with chicken egg. Take three transparent glasses. Pour a raw chicken egg into the first glass, note for yourself how many milliliters it takes up. Measure the same volume of water and pour it into the second glass, add the same amount of vinegar into the third. Pour the contents of three glasses into a jar and close the lid.
Shake the contents of the jar vigorously until it becomes creamy. Use the resulting mixture to lubricate eczema-affected skin on your arms or legs.
Put on cotton socks or gloves and sleep in them until the morning. In the morning, wash your hands or feet without soap. Repeat the procedure in the evening. After just a week of using the ointment at home, peeling and the appearance of young pink skin on the arms or legs are observed.
Ointment with baby cream. For weeping eczema, try preparing a rich ointment in the following way. Mix 70% baby cream (you can use lard) and 30% fir oil or beeswax. Mix until smooth and apply to the area of inflammation (on the hands or feet). It is recommended to lubricate the eczema-affected areas of the skin three times a day for two weeks.
Sunflower oil ointment. In a glass of vegetable oil, add two tablespoons of rosin, grated laundry soap, aloe juice, and beeswax. Heat the composition in a water bath until the components are completely dissolved. Apply the resulting ointment to the affected areas of the skin.
Aromatic and vegetable oils are successfully used to treat eczema, especially dry eczema. Among vegetable oils, shea, sesame, jojoba, rose hip, wheat germ, sea buckthorn, amaranth and flaxseed oils show good results. There is no need to dilute them; they can be applied in their pure form to areas of inflammation (hands, feet).
For example, to treat dry eczema, use 3 ml of sea buckthorn oil orally and in the form of a 5% sea buckthorn oil ointment. The ointment prevents peeling and eliminates skin itching. Essential oils against eczema - ylang-ylang, patchouli, lavender, sandalwood, myrrh, tea tree, fir oils.
Unlike the previous group, these oils are diluted in the following proportion: 5 drops of aromatic oil per 1 tablespoon of base oil (olive, sunflower, flaxseed, grape seed). After mixing, apply this composition with your finger to the areas of inflammation (on the hands, feet) or apply a soaked cloth. There is no need to rinse with water.
It is difficult to imagine external treatment of eczema without herbal therapy from within the body; the phytocomplexes given below must be used before meals for a month.
Now you know how you can cure eczema on your hands and other parts of the body with folk remedies prepared at home. Try these simple remedies and you will be pleasantly surprised by the speedy healing of inflammation and cracks in the skin.
Source: dermatyt.ru
How to treat?
It is quite difficult to choose an ointment for eczema on the hands; the list of effective remedies is quite extensive, but not all of them can help each specific patient.
Usually, the doctor has to select drugs for local treatment and their dosage individually.
List of the most commonly prescribed ointments for eczema:
- Dermovate (corticosteroid with anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and analgesic effect);
- Advantan (contains corticosteroids, most effective against allergic manifestations);
- Dexamethasone (one of the most popular topical corticosteroids);
- Celestoderm;
- Triderm;
- Ointments against some symptoms - zinc, sulfur.
To relieve exacerbations, anti-inflammatory drugs, antipruritic drugs containing corticosteroids are used, and antihistamines and sedatives are prescribed orally.
Also, lotions with antiseptic agents are prescribed for local treatment. If the exacerbation is severe, the patient may require sick leave.
If the patient has dyshidrotic eczema of the hands, treatment with topical remedies is very important. The main task is to prevent infection from entering, so antibiotics in the form of ointments are widely used; bandages can be applied to the affected areas, if they are large.
- In severe cases of the disease, hospitalization may be required with plasmapheresis, antibiotic prophylaxis, and the administration of detoxifying drugs. In rare cases, severe eczema can lead to disability.
- Outside of exacerbations, it is recommended to use special skin care products recommended by your doctor, avoid contact with allergens, if possible, lead a measured lifestyle, and minimize the amount of stress. If possible, you need to organize a hypoallergenic lifestyle, i.e. Avoid known allergens in food, clothing, and household chemicals.
It is not advisable for patients to keep animals and plants at home, or to have a lot of soft toys, carpets and other objects that collect dust. It is necessary to carry out wet cleaning of the room daily - dusting, washing the floor, wiping various surfaces.
Alternative medicine remedies are used as auxiliary or preventive measures during periods of remission. Before this, a consultation with a dermatologist is required for each prescription.
Potato
Raw potatoes have anti-edematous, regenerating, anti-inflammatory properties. The vegetable draws excess water from the skin tissue, resulting in improved microcirculation and local metabolism. Carrots and white cabbage have similar properties.
To treat eczema, use finely grated raw potatoes or squeezed juice from them. During the day you need to apply lotions to the affected areas 4-5 times, and at night apply a compress, wrapping the potato pulp in gauze.
When eczema is combined with disorders in the gastrointestinal tract, the juice of the vegetable is taken orally. To do this, drink 250 ml of juice in the morning on an empty stomach for 10 days.
Garlic
Garlic is one of the most powerful natural antibiotics, which additionally has antiseptic and drying properties. The vegetable is used to treat microbial eczema.
To prepare the ointment, a paste of 3 cloves of garlic is mixed with ½ teaspoon of honey. The product is applied to the affected areas 3-4 times a day. The mixture can also be used as a compress at night.
Vine
Grapevine juice has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties.
The sap is collected before the leaves bloom in April. To do this, select the strongest vine and make an oblique cut on it, place a container on the base and secure the stem above it.
The juice is used as part of lotions, moistening gauze cloth in it. Lotions are applied 3-4 times a day to lesions pre-treated with an antiseptic.
Sea salt
Sea salt contains a large amount of minerals. Together they have antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, regenerating, immunostimulating and antipruritic effects on the skin.
During the wet stage, dry compresses are used. To do this, salt is ground to a powdery state, sprinkled on eczematous elements and secured with a bandage for 2-3 hours. To enhance the therapeutic effect, you can add a mixture of components crushed to a powder state: yarrow leaves, licorice root.
The procedure is carried out once a day every 3 days. After each compress, the skin is washed with antiseptic decoctions of herbs: calendula, chamomile.
An ointment based on sea salt is suitable for treating any stage of the disease. To do this, crushed sea salt (1 tbsp) is mixed with red clay (100 g), gradually diluted with boiled water, and brought to a creamy state.
The ointment is applied to the inflamed elements and left to act for 20 minutes, after which the residue is removed with a gauze cloth and washed with an antiseptic solution. The procedure is carried out 2-3 times a day.
Herbal complexes
Medicinal herbal infusions have anti-inflammatory, drying, antiseptic and wound-healing properties.
- Mix the crushed roots of burdock, yarrow, and dandelion in equal parts. The mixture (60 g) is poured with boiling water (1 l) and left for 1 hour. Take 2 tbsp. l. per day separately from food.
- A mixture (60 g) consisting of chicory root, chamomile, creeping thyme (1: 1: 1), pour boiling water (0.5 l) and leave for 30 minutes. Use as a lotion on wet surfaces for 15 minutes 3-4 times a day.
- Calendula flowers, horsetail, oak bark (50 g) mixed in equal parts are poured with boiling water (0.5 l), left for 1 hour and filtered. Used as part of compresses at night and lotions 3-4 times a day.
During periods without acute inflammatory processes, therapeutic baths will be useful, strengthening the barrier functions of the skin. For this purpose, decoctions and infusions of chamomile, calendula, elderberries, nettles and pine needles are used.
It is important for patients with eczema to adhere to specific hygiene. It involves the complete elimination of factors that irritate the skin and the prevention of re-infection.
During the acute course of the pathology, water procedures should be completely avoided. Cleansing of the skin is carried out with a gauze cloth soaked in distilled water with the addition of zinc or herbal decoctions with antiseptic properties.
For minor lesions, remissions of chronic forms of eczema, subacute conditions of the pathology, warm shower and daily washing procedures are recommended. It is recommended to use washing gels with medicinal ingredients: salicylic acid, naphthalan, plant extracts, urea, natural oils. Hygiene products should not contain aggressive components.
During water procedures, use only soft sponges or washcloths made from natural materials. You cannot make peelings and scrubs with products containing abrasive components.
The body must not overheat and become overtired. Baths, sun, and strong physical activity are excluded. Patients need to avoid stressful situations.