Pigmented nevus is a dermatological neoplasm that is usually benign in nature. This nevus is also called melanocytic or noncellular. A spot on the skin can form in early childhood, but the vast majority of moles appear in a person even before birth. Although in some cases education is formed in adulthood under the influence of certain factors. As a rule, a normal mole does not pose a danger to its owner, but under some conditions there is a risk of developing a malignant tumor called melanoma. That is why everyone needs to know the causes of the appearance, methods of treatment and removal of such age spots.
Nevi arise from melanocyte cells that have undergone changes and have melanin in their structure. First, the cells grow inside the epithelium, then an accumulation of nevocytes occurs at the border of the dermal and epidermal layers, and then the neoplasm forms on the skin itself. A mole is very often localized on the skin of the body, but it happens that it also forms on the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose or genitals. The type of such spots varies. Some types may resemble dome-shaped tumors, other types rise slightly above the skin, and others completely merge with it. Is such a formation as a nevus dangerous, when should you consult an oncologist, and whether it is possible to cure a person of melanoma-dangerous moles, any person who is worried about his health should know.
Reasons for education
If all factors are taken into account, genetic predisposition is the most basic of them.
Other causes of congenital age spots include:
- Various cell division failures;
- Toxic damage to a pregnant woman or exposure to ionizing radiation;
- Smoking and drinking alcohol during gestation;
- Diseases of the genitourinary system during gestation;
- Sexually transmitted diseases in a pregnant woman.
Secondary nevi, which occur throughout life, are also congenital, but emerge to the surface of the skin later under the influence of unfavorable factors.
Such factors may include:
- Hormonal changes, for example, during menopause, pregnancy, puberty. Also, hormonal imbalance can be caused by uncontrolled use of birth control pills and self-medication with hormonal drugs.
- Abuse of tanning under the sun, as well as in solariums.
- Frequent illnesses that reduce the body's defenses.
- Dermatological diseases of viral etiology.
- Frequent stress and emotional exhaustion.
- A history of skin cancer in any of your relatives.
Despite the fact that nevi are congenital, immediately after birth they are diagnosed in only five children out of a hundred.
They most often begin to appear during puberty and end at approximately thirty-five years of age.
In addition, in older people, pigmentation decreases, and existing moles often disappear.
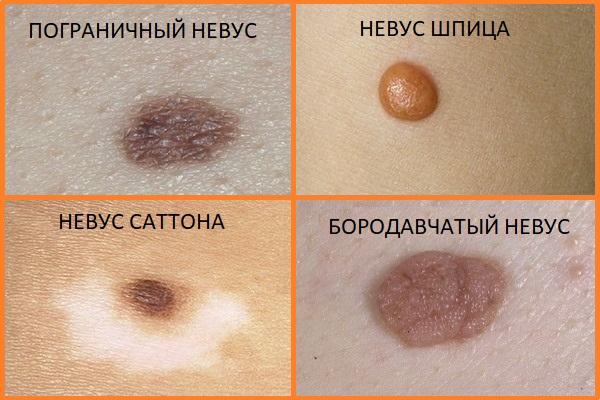
Spitz nevus
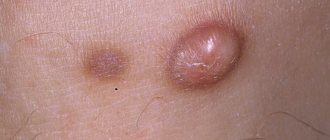
This is another pigment formation, due to the presence of which people are at risk for melanoma. Such birthmarks appear on the skin more often in children under 10 years of age, but adults are also not immune from them. A distinctive feature of Spitz nevus is its rapid growth. So, suddenly appearing on the skin, in just a few months it can increase in diameter from a couple of millimeters to a centimeter or more. Another unpleasant feature is that it can metastasize to adjacent areas of the skin and lymph nodes. But, despite this, in most cases, Spitz nevi are considered benign and can easily be treated in a timely manner.
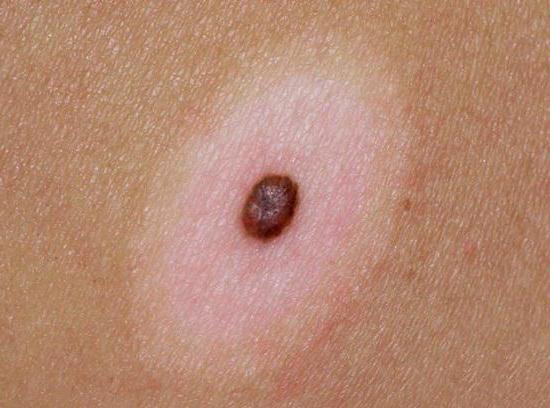
Types of nevus
Pigmented nevi are very different, it all depends on their color, appearance and the risk of degeneration into a malignant formation.
Based on the size of the mole, it can be:
- Microscopic - has dimensions up to 3 mm;
- Small - the diameter does not exceed one and a half centimeters;
- Medium - up to 5 cm in diameter;
- Large - 5-10 cm;
- Giant - more than ten centimeters.
We recommend reading Atheroma of the ear - signs, diagnosis, solutions
According to localization, pigment formations are cutaneous and mucous. In very rare cases, a birthmark occurs inside the eye. The cells of such nevi can be located in the conjunctiva or retina.
Complex nevus
The location of a complex nevus is dermal and epidermal. A mole appears on the skin and can look like a plaque or wart. The maturation of pigment spots occurs when clusters of nevocytes spread into the dermis, which is a benign process. The cells that are on the surface of the spot are not so mature, so they can become malignant. Complex papilloma-shaped nevi have good vascular nutrition.
Border type
This type is also called functional. The formation is localized in the epidermis and can be either congenital or acquired. Often the spot occurs in children and adolescents on the feet and palms. It is called a borderline nevus, since upon examination under a microscope it is clear that accumulations of nevocytes are located almost at the border of the epidermis and dermis. Such formation has a high risk of malignant degeneration. Over a long period, the size of the spot does not exceed three millimeters, but then it often begins to grow rapidly, often transforming into a precancerous formation - a dysplastic nevus.
Epithelioid appearance of Spitz nevus
The most common location for this type of mole is the face. It may also be called juvenile melanoma. The nodules appear flat or resemble a hemisphere. In some cases, papillomas are present on the surface of the spot. Such spots may be pink or yellowish in color. Often, dilation of blood vessels can be seen near the formation. Spitz nevus received its second name because, upon microscopic examination, it is similar to a malignant tumor of the first stage, but the epithelioid type degenerates extremely rarely.
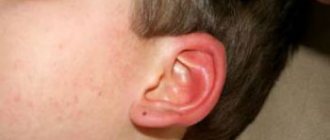
Intradermal type of nevus
This type of nevi is the most common; it is the most common and safest birthmarks, as well as moles. Moles are flat, can have any shade of brown, the color is uniform in the absence of pathology, and the texture is dense. The shape of moles is round and regular, and the boundaries are clearly defined. The outside of the mole may also be slightly convex. The accumulation of nevocytes occurs in the lower and middle layers of the dermis. These moles are often already present in a newborn baby or appear during infancy.
Galonevus
In the area of the body where the nevus of this type is located, strong pigmentation is noted. Around the spot, on the contrary, the pigment is completely absent, so the formation looks like a very dark spot with a white edge. Often pigmentation goes away on its own, leaving behind a depigmented mark. The most common location is the back. This type of nevus never degenerates into a malignant formation.
Balloon cell nevus
This species is very common. Huge nevocyte cells have light cytoplasm, which are microscopically similar to balloons. The location of the formations is intradermal, but with a complex type of balanocyte mole, it is located in two layers of skin at once.
Blue nevus
The blue nevus is popularly called Mongolian; it is located inside the dermis and is not connected to the epidermis in any way. The blue color of the spot is due to the fact that nevocytes are located deep in the tissues. Such a spot can be located in the torso, face, hands and sacrum. The formation has a pronounced boundary; it has the shape of a regular circle. Mostly such moles are flat, but sometimes they can raise the area of skin where they are located above the rest of the skin. Such nevi are practically not susceptible to malignancy.
We recommend reading Breast lipoma - causes, symptoms, treatment
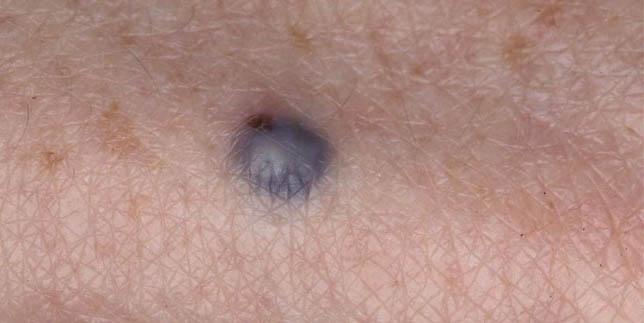
Congenital pigmented
Congenital pigmented nevi are most often giant spots. Such formations can have any location, in particular on the head. The largest accumulation of melanin is observed in the dermal layer. With this type of mole, the risk of malignancy can reach ten percent.
Causes and symptoms
As a rule, this type of cell appears during intrauterine development. And the basis for their development is the neural crest. These are cells that serve as the basis for the development of certain organs and melanocytes. For some reason, these types of cells do not mature completely and remain in the dermis, and not in the deep layers of subcutaneous fatty tissue, where they should be.
Congenital pigmented nevus develops in several stages. At first, this formation is intraepithelial, but around the age of 30 it turns into an intradermal state. The congenital type is a pigmented tumor. Occurs in approximately 1% of Caucasian children.
A congenital mole usually has a brownish tint. Although there are lighter colors as well as darker ones. The growths can protrude above the surface of the skin, and then they have a warty type. The spots can have a wide variety of shapes, but their boundaries are clear. There are, however, spots with blurred boundaries. Hair may appear on the surface of such formations.
Sometimes moles can be large - even up to 20 cm
Birthmarks can appear on any part of the body. Their surface can retain the skin pattern, although tubercles or lobules often appear on it. It often happens that a large number of spots appear on the human body. Sometimes they can be large - even up to 20 cm.
The birth type has an important feature: pigment cells are located in the lower dermal layers and subcutaneous adipose tissue. And one more important note: they never disappear spontaneously.
Some varieties
There are different types of nevi:
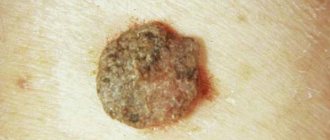
- An atypical nevus is an acquired skin formation that cannot be congenital. Moreover, it is a precursor to squamous cell skin cancer. It is equally common in men and women. There are cases when the risk of occurrence is congenital.
- A verrucous nevus is a mole that rises above the skin. Its surface consists of tubercles and lobules (sometimes similar to cauliflower). Not prone to bleeding.
- If a person develops a linear nevus, then numerous nodules appear on the skin, lining up in one line. Between the foci of altered skin there are foci of normal healthy skin. The spots come in different colors.
- Anemic nevus rarely occurs in humans. It looks like a pale spot on the skin, but it is different in color from healthy skin. Its shape is wrong. Most often located on the back, face. It can also be combined with other neoplasms.
- Basal nevus looks like pigmentless spots, with sharp boundaries, oval in shape. Most often it is formed due to reduced activity of melanocytes in the blood. A similar formation occurs in childhood.
- A recurrent nevus is a mole that appears on the body in place of previously removed ones. Typically, it occurs as a result of not being completely removed.
Symptoms
Pigmented skin nevi have only visual signs. An ordinary mole does not cause discomfort in a person; it does not hurt or itch.
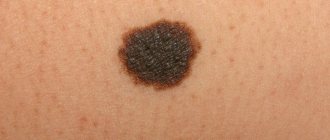
Symptoms of a spot that degenerates into a malignant neoplasm are as follows:
- change in color of the mole - it becomes very black;
- the spot begins to grow and protrude above the skin;
- bleeding begins;
- the outlines of the mole are blurred, they become unclear and crooked;
- pain occurs on the surface of the formation;
- the skin around the mole begins to tingle or itch.
If any signs of malignancy are detected, you should see a dermatologist as soon as possible. If necessary, he refers the patient for a full examination to the oncology clinic.
Types of birthmarks
There are two types of melanocytic nevus of the skin:
1. Congenital
In size, these pigment formations are small (up to 1.5 cm in diameter), medium (up to 10 cm) and large or gigantic (more than 10 cm). Congenital nevi of any size also increase in diameter as the child grows. The greatest danger is posed by medium-sized nevi, large and giant, since they most often degenerate into malignant melanomas. For what reasons are babies born with large and giant birthmarks, experts find it difficult to say exactly. According to statistics, approximately 5% of babies born with a giant nevus develop skin cancer in the first year of life or a little older. Therefore, parents whose babies were born with large birthmarks should definitely consult with a specialist. If the giant nevus is located on the face, the doctor may recommend laser bleaching, and if it is on other parts of the body, removal. The latter procedure is also recommended if the large birthmark is dark in color and has a lumpy surface.
2. Purchased
During life, age spots can appear on any part of the body, including the scalp, genitals, palms, and soles of the feet. English scientists have found that a large number of moles reduces the risk of osteoporosis by approximately 2 times and significantly reduces the appearance of wrinkles, and the degeneration of nevi into malignant melanomas is observed in approximately 16% of people with pigment marks.
Diagnostics
The very determination of the presence of a nevus on the human body requires only a visual examination, but since some moles have a tendency to become malignant, additional examination may be necessary. In this case, the doctor examines the formation under a special fluorescent lamp and takes a scraping if any fluid is released from the mole. Also, diagnosis by oncologists involves performing dermatoscopy and taking a piece of the suspicious area (biopsy) for histological examination. If malignancy is suspected, a tumor marker test is performed using venous blood. Only after carrying out all diagnostic methods can the doctor prescribe the most optimal method of therapy.
Diagnosis and treatment
In some cases, special studies must be carried out to detect the congenital type. A biopsy is least preferable, as it involves trauma to the mole. And at the same time, the risk of malignancy increases significantly. Non-traumatic diagnostic methods include:
In some cases, special tests must be carried out to detect the congenital type.
- epiluminescent microscopy (the mole is viewed enlarged in incident light);
- examination using a dermatoscope;
- inspection using an oil medium;
- Diagnostics using computer technology helps to capture the image and compare it with normal data that is already available.
The advisability of treating a skin lesion depends on its size, location and quantity. The most dangerous, considering the degeneration into melanoma, are large congenital moles. And they are advised to remove them at an early age. If they are small, have an irregular and uneven color, then it is advisable to remove them before the age of 12. Clear indications for removal are as follows:
- there is an increase in size;
- begins to protrude above the surface of the skin;
- Unnatural or incorrect coloring has appeared, pigmentation has increased;
- an inflammatory rim has appeared around the growth (or there is inflammation in the mole itself);
- the appearance of pain in the area of the mole;
- itching;
- the occurrence of bleeding or erosion on it;
- if an atypical nevus appears.
Treatment of formations
If a pigmented nevus does not have signs of malignant degeneration and does not cause cosmetic discomfort in a person, then it does not require medical measures. Treatment and removal of a mole is necessary if it has uneven edges, an asymmetrical shape, is colored in different colors, or grows quickly. Removal is also prescribed when bleeding occurs, any fluid is released from the formation, or hair grows on the spot that was not there before. For removal, doctors use various methods, the choice of which takes into account the localization of the pigment spot, its size, depth and other factors.
Removal methods
There are several ways to remove skin lesions, the selection of which is carried out individually in each specific case.

- Excision with a scalpel is used for deep nevi, and if a mole has degenerated into skin cancer. Along with the tumor, part of the fatty tissue is also excised, so a scar remains after the operation. If the nevus causes only cosmetic discomfort and is localized on visible parts of the body, doctors choose other methods.
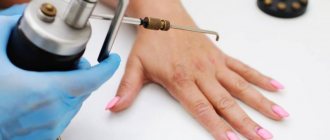
- Removal of a tumor with laser beams is carried out if a person wants to get rid of a mole on the face. With this therapy method, no traces are left on the skin, since the light beam does not touch healthy tissue. If the patient's skin has a very dark shade, then after laser therapy there may be a slight lightening.
- Treatment with radiosurgery prevents infection and is suitable for removing small pigmented lesions. Immediately after the procedure, a small burn may remain, which will go away after healing.
- Removal by electric current is called electrocoagulation. This method allows you to get rid of a nevus without blood loss, because the capillaries are immediately cauterized.
- Small formations are removed with liquid nitrogen during cryodestruction. Under the influence of high temperatures, the cells of the mole shrink, and it soon falls off.
We recommend reading Carcinoma - what it is, symptoms, causes, types and treatment
During removal, biomaterial is collected for further histological examination.
Folk remedies
You can use any traditional medicine methods to combat nevi only after consulting a doctor.
Proponents of alternative treatment recommend:
- twice a day, lubricate the mole with celandine juice mixed with Vaseline;
- lubricate the nevus with lemon juice five times a day for 2 weeks;
- treat age spots with the juice of unripe figs for three weeks;
- make compresses from garlic pulp for ten minutes, avoiding its contact with healthy areas;
- apply a mixture of a tablespoon of honey and two tablespoons of castor oil to the tumor for two minutes;
- lubricate the stain with an infusion of one clove of garlic and a glass of vinegar;
- cauterize the formation with silver nitrate twice a day.
Still, doctors do not advise doing amateur activities. In case of suspicious symptoms or a simple desire to get rid of an ugly mole, it is better to immediately visit a dermatologist.
Diagnosis of nevus
A dermatologist examines and determines the exact type of skin formation. A doctor can easily identify a congenital melanocytic nevus even if it is small in size. Dermatological equipment allows you to determine the danger of skin formations for humans. If necessary use:
- The procedure of smearing the surface of a mole.
- Accurate computer diagnostics.
- Collection of analyses.
- Fluorescent microscopy - inspection and removal of formations.
Melanoform nevus of the trunk or other place may not be removed. Depending on the degree of danger and predisposition to treatment, the doctor prescribes antibacterial and antiseptic medications, as well as hormonal ointments and creams.
If the reason for your visit to a dermatologist is mechanical damage to a mole, then you need to take a more careful approach to treatment. Such damage can cause the development of a malignant tumor.
A person may even simply not notice that his skin growth is rubbing against his outer clothing. The danger from untimely deterioration of the condition only increases. The transformation of an ordinary mole into melanoma can occur due to: excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays, rubbing, trauma, burns, etc. This cancerous disease is capable of spreading its infected cells throughout the human body. This type of cancer is one of the most severe. Treatment for this is grueling, expensive, and most importantly, does not guarantee a 100% recovery.
If a mole is injured, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination by a dermatologist.
Pregnant women only have a tendency to form pigmented formations. For them to begin to grow, one hormonal imbalance is not enough. When diagnosing these, a dermatologist pays attention to:
- recent injections;
- taking medications;
- increased use of harmful products;
- excessive intake of vitamin A;
- alcohol addiction;
- blood sugar level.
The active growth of a nevus on the skin of a pregnant woman may be associated with a lack of beneficial microelements or a hereditary predisposition. Research by scientists has shown that DNA contains information about the nevus. The tendency to form age spots passes from generation to generation. Often there are similar locations of the nevus in the mother and child. In 70% of cases, the formation on the neck, face and genitals is repeated genetically, with the first heir of the family. The location of these pigment spots is not identical, but has a similar size and shape.
A less common factor influencing the growth of nevus on human skin is radiation. Exceeding the received dose occurs due to various reasons. Some are related to working conditions, others to being in high-risk areas. For radiation effects on the skin, the influence of an X-ray machine is sufficient.

Vitamin A abuse can cause moles to grow
Prevention of malignancy
Pigmented nevi can become malignant due to damage (for example, a cut while shaving), constant friction, and exposure to ultraviolet radiation. People with fair skin color, blue eyes and blond hair have less melanin, but it is they who most often experience malignant degeneration of the spot. The reason is that melanin protects the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, so naturally dark-skinned people are less likely to experience skin cancer.
To prevent malignant degeneration of the nevus, it is necessary to protect it from injury, sunbathe in the sun during the period of least radioactivity (before eleven o'clock in the morning and after four o'clock in the evening), go to the solarium less often, use sunscreen with an SPF level of at least 50. Once a You should visit a dermatologist for a year and periodically conduct an independent examination of moles. Do not forget that if a mole is healthy, but is a cosmetic defect, it can only be removed surgically and not at home.
Course and prognosis of dysplastic melanocytic nevus
This virus can be stable, regressive, or progressing to melanoma. The factors that are responsible for progression to melanoma are still unclear. Scientists give preference to genetic factors, as well as the influence of environmental factors. The probability of a dysplastic melanocytic nevus developing into melanoma in people, taking into account genetic predisposition, between the ages of 20 and 60 years is 56%, and after 75 years the probability is 100%. Therefore, it is better to treat at an early stage. At the same time, people with white skin and those who have often been burned while having this type of melacytic nevus have a much greater risk of developing into melanoma. For other people, the risk of developing a tumor is 17%.
Methods for treating nevi
Treatment is allowed only in patients over 2 years of age. Therapy has 4 main directions:
- surgical removal;
- laser excision;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation.
As a rule, nevi that have grown deeply into the tissue are surgically removed. Giant neoplasms are removed in several stages, but the disadvantage of this method is the formation of scars at the site of the nevi.
Laser coagulation is used to remove dysplastic pigmented nevi and other clinical types of spots. The method allows removal of the formation without pain and without subsequent scarring.
Cryodestruction involves exposing the affected area of skin to very low temperatures. As a result, the altered cells die and are replaced by healthy ones. After cryodestruction, a small crust appears, which quickly disappears.
Electrocoagulation affects the nevus with high temperatures. Typically this method is used to remove small and medium-sized stains.
What is nevus?
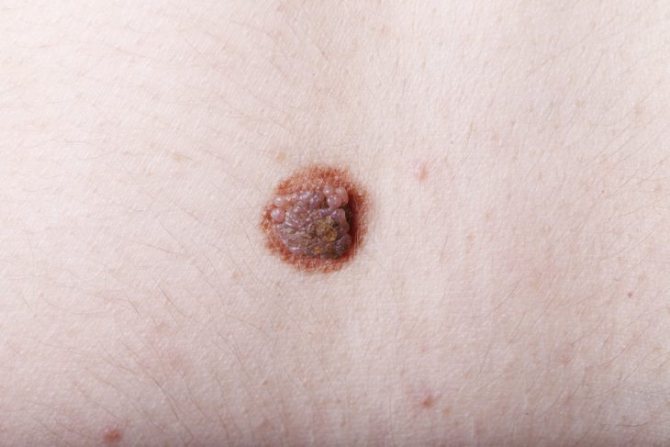
A dark neoplasm that appears on the skin in the form of a nodule or flat surface is called a mole, or nevus. Often the neoplasm is benign with a high risk of degeneration into a tumor. Skin compaction is of a pigmented nature. They grow as single or multiple neoplasms. A benign nevus does not require treatment and is not dangerous, but the owner must be systematically diagnosed by a doctor. Moles are either subcutaneous or can rise above the epidermis. The diameter of nevi is varied: from a small and invisible point to spots that fill large areas of the body.
Nevus does not have “favorite” locations; it can be located on the hands, nose, foot, eyelid, forehead, temple, neck and mucous membranes. The color of a mole can be yellow, brown, lilac, blue, pink, red and even black, in different shades. Since such appearances are not dangerous, there is no need to undergo any manipulations if the patient does not have negative symptoms or mental rejection of the neoplasm (an unpleasant dermal defect).
The edges of a mole that is not melanoma-dangerous are smooth, clearly defined and not blurry. They have a symmetrical contour. Moles can be either deep or located in the upper layers of the epidermis. Ignoring changes in a mole causes dangerous complications of skin disease. New growths are distinguished by color (colorless, yellow, black, red), size (small, medium, large, giant), shape (convex, smooth, round). There can be a deep nevus or a flat one.
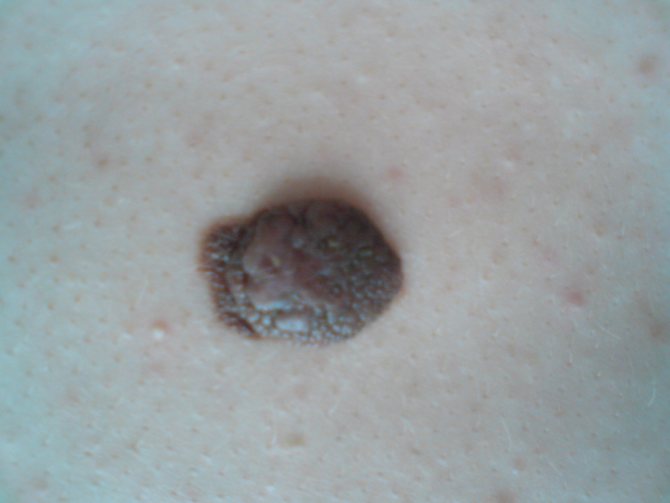
The growth of nevus is provoked by external factors or changes in the body.
What do nevi look like?
It is difficult to say for sure what a nevus looks like. Even scientists have not finally decided which formations are classified as nevi and which are classified as tumors. A mole, from the size of a pea with a diameter of 1 mm to a spot of 30 cm, can protrude greatly above the skin, or merge with it, have a round or irregular shape with smooth or ragged edges.
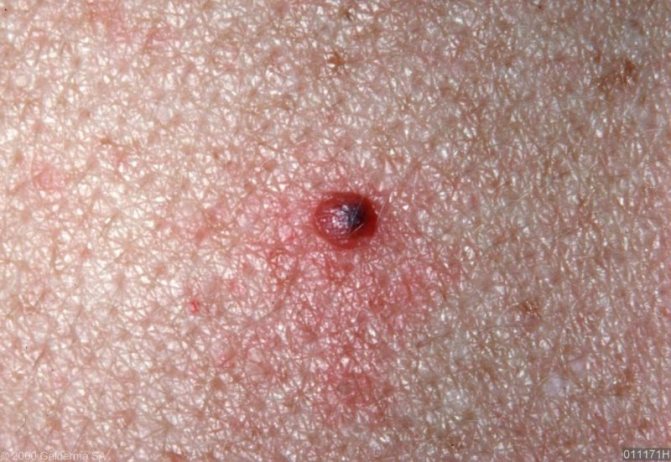
Causes
There is no consensus yet on the reasons for the appearance of melanocytic nevi. A number of experts believe that congenital moles are formed during the period of embryonic development, and acquired ones - under the influence of some external or internal provoking factors. Other dermatologists believe that all melanocytic nevi, even those that appear throughout life, are due to genetic mutations.
However, all experts are unanimous in the opinion that certain factors can cause the formation of acquired moles and their degeneration into cancerous tumors. These include:
- hormonal imbalance in adolescence, during pregnancy, taking contraceptives and menopause;
- genetic disorders;
- frequent exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin;
- allergic and inflammatory diseases of the skin (dermatitis, acne, etc.).
All these factors cause disturbances in the development of special skin cells, melanoblasts, which are the source of melanin synthesis. They transform into nevocytes, accumulate in certain areas of the skin and form moles.
What to do with moles?
If the nevi do not bother you in any way, and if they are located on safe areas of the skin, you just need to watch them. If they are located where they can often be injured (on the palms, on the feet, on the neck, on the head, on the waist) or on the face, which causes cosmetic defects, it is recommended to remove them. Such operations should be entrusted only to doctors - a surgeon, a dermatologist. Epidermal nevi are recommended to be removed only by surgery. It is performed under local anesthesia and is therefore painless. Papillomatous melanocytic nevus of the skin, especially those located on the stalk, is sometimes more appropriate to remove with liquid nitrogen. In recent years, laser treatment of moles and their excision with a radio knife have also been successfully used.
After surgery, the doctor, as a rule, sends the removed fragments for histological examination to be completely sure that there is no cancer.
It is completely unacceptable to remove nevi on your own using traditional methods. Especially often, people try to get rid of papillomatous nevi on the legs by tying them with thread. This leads to blocking the blood supply to the mole, and it may actually fall off. But in most cases, this method of “treatment” provokes the development of changes in the cells of the epidermis or dermis and leads to disastrous consequences.
Methods for diagnosing nevus
Only a doctor can diagnose a nevus on the stomach or in another area. You can contact a dermatologist, oncologist or surgeon. After the necessary tests, the full clinical picture and causes of occurrence are established. Initially, the doctor conducts a visual examination and questioning of the patient. Determines what a mole looks like and what it feels like on palpation. Using dermatoscopy, the structure of the surface of the nevus is determined.
Computed tomography is carried out using a zoomed-in image and characterizes the surface of the tumor. Ultrasound determines the pathology of tumor development, the depth of its growth, and the effect on tissues and organs. A biopsy is performed extremely rarely, since this analysis requires trauma to the skin of the tumor. Histological analysis for the presence of cancer cells is possible only after surgical removal of the mole. Diagnostics are carried out in laboratory conditions using special equipment.
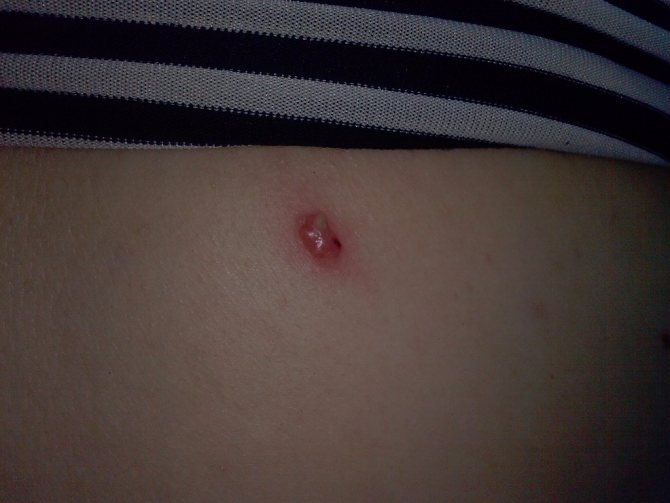
If a mole is injured, there is a risk of melanoma formation.