How does papillomatous nevus differ from papilloma?
- Unpleasant sensations. Pain, tingling, itching are characteristic only of papillomas. If such sensations occur in an ordinary mole, this is a sign of malignancy.
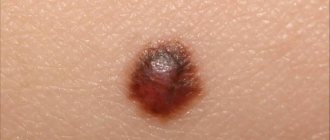
- Coloring. Papillomas have the same color as the skin. Papillomatous moles come in brown, black and other colors.
- Structure. Moles are denser to the touch than papillomas.
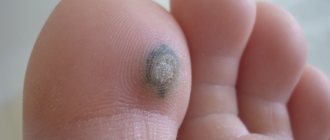
Papillomatous nevus is often darker in color
Types of nevi
The concept of papillomatous nevus includes several types of moles, which differ in qualitative characteristics. Based on their appearance, they can be classified into:
- Pigment type. In this case, the mole is most noticeable, since it is located on an open area of skin without hair, and the color of the growth is dark or even black.
- Hair type. In this case, one or several long dark hairs grow from the neoplasm, which cannot be removed independently, so as not to start the complex process of malignancy, that is, transformation into melanoma.
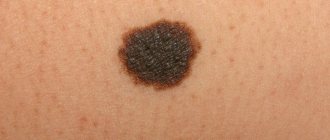
- Verrucous type. Such a nevus, like a pigmented nevus, rises significantly above the surface of the skin, but its shade is lighter. A verrucous mole has a rough surface consisting of individual lobules. The neoplasm is characterized by fairly slow growth, not complicated by bleeding or ulceration.
In addition, papillomatous nevus is also divided by shape, but in this case there are only two varieties. Firstly, there is an organic form, which is the most common and least unpleasant, since in this case the neoplasms are single in nature and they do not rise too much above the surface of the skin.
The shade of such a mole is brown, it is attached to the epithelium on a wide base, and is quite dense to the touch. Secondly, a disseminated form is isolated, which is characterized by multiple formations that are distributed over all parts of the human body.
Such nevi can disappear during life and appear again; they are larger in size and darker in color.
Experts divide this type of mole into two large subgroups:
- Organic papillomatous growth. It looks like a single formation on a wide base, slightly rising above the skin. It may look like several small papillary projections that are covered with a layer of keratinized cells.
- Disseminated papillomatosis appears as many formations located throughout the body. Some of them may disappear over time, while others appear again.
If you have a mixed papillomatous nevus, you should be especially careful, since this form can lead to the development of cancer.
Papillomatous nevi are divided into the following types.
Along its outer surface:
- a pigment type nevus is almost black in color and appears on the body where there is no hair;
- a hair-type nevus often has several long, dark-colored hairs inside;
- a verrucous nevus is similar to a wart, but its surface is more lumpy and uneven, and also has a predominantly dark color;
Depending on the shape:
- organic nevus is most often presented in the singular. It is distinguished by its brown color and wide base. This type of nevus has a dense structure due to the presence of keratinized cells;
- disseminated nevus is represented by many formations resembling plaques. They are usually located throughout the body. These moles can change in size and disappear within a few years.
There are several classifications of moles of this type.
Causes of papillomatous nevus
It is still not known exactly what causes such tumors. Scientists have put forward three theories about the origin of papillomatous moles:
- Excess melanin. The coloring pigment accumulates in one place in large quantities, which leads to the formation of large nevi. This accumulation can be caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- Hereditary predisposition. According to the observations of doctors, in some cases, papillomatous nevus in a person occurs in the same place as in his relative.
- The cause of the development of congenital moles may be disruptions in the body during intrauterine development.
Reasons for education
Doctors say that the main cause is an abnormal accumulation of pigment cells in one area of the skin. Therefore, the nevus is called melanocytic.
Since the predisposition to its occurrence begins during embryonic development, pregnant women should avoid:
- toxic components,
- radiation,
- changes in estrogen in the blood.
Sometimes it also results in infection of the genitourinary system in a pregnant woman. It can also occur in a person if the baby’s body malfunctions.
Then a large amount of coloring pigment accumulates in one particular area. Over time, under the influence of one’s own hormones and external factors, such formation becomes more noticeable.
Varieties
Papillomatous moles have different sizes, colors, shapes, and locations. Therefore, they are divided into several types. This makes them easier to learn.
Papillomatous growth
They are also called warty growths. A distinctive feature of the growths is their appearance - they are very similar to a wart on a thin stalk. Such moles rise greatly above the surface of the skin and have a rough structure. They can be flesh-colored, black or brown. The size of warty nevi can reach 15 mm. Often several dark, coarse hairs grow from them. If a mole causes inconvenience or is often damaged (rubbed by clothes, underwear, touched while combing), it should be removed in the manner recommended by the doctor.
Noncellular nevus
Such moles are congenital and appear only in infants. They can form immediately after birth or in the first 3 weeks of a child’s life. They have an oval shape, their surface can be either convex or flat. Most often, noncellular nevi are localized on the neck and face. In rare cases, neoplasms occupy the entire anatomical area. If a dermatologist has designated a mole as a cosmetic flaw, it is recommended to remove it as quickly as possible.
Pigmented (melanocytic) growth
Unlike papillomatous nevus, pigmented growths do not rise too much above the skin. They also have smooth edges and rich color. According to experts, such moles never change color. The surface can be either smooth or rough. The size of the growths reaches a maximum of 5 mm. They are usually located in the armpit, groin, neck, and chest. Sometimes melanocytic moles can change their shape.
Papillomatous nevi can also be dangerous and non-dangerous (melanoma-dangerous and melanoma-non-dangerous). Dangerous moles are highly likely to develop into a malignant tumor. Non-dangerous nevi degenerate extremely rarely. Most often, melanocytic growths become malignant, so it is recommended to excise them.
Diagnostics
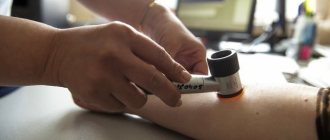
Dermatoscopy is a mandatory research method. It is prescribed for the presence of any moles on the body. This hardware method allows you to study the formation at multiple magnification.
Dermatoscopy makes it possible to differentiate neoplasms from malignant tumors.
Siascopic examination is a spectrophotometric scan that allows you to study the structure of the nevus, its color, and the distribution of melanin cells. Siascopy makes it possible to look at a depth of 2-4 mm, which is very valuable in making an accurate diagnosis.
It is especially important to conduct this study if the formation begins to change its shape or size, since it allows melanoma to be diagnosed at the earliest stages.
If indicated, a biopsy is also performed. Typically, cells are sent for histological examination after the removal process.
The fact is that a biopsy requires excision of the tumor, and therefore is a strong traumatic factor. The method is chosen only in extreme cases.
Features of papillomatous nevi
Papillomatous growths have characteristic features by which they can be distinguished from other neoplasms:
- Clear edges, knobby surface;
- Elevated relative to skin level;
- They have beige, brown, dark brown shades (rarely black);
- May be riddled with thick hairs;
- In most cases, they occur on the scalp, face, and neck;
- There are single and multiple;
- Gradually increase in size.
Diagnosis and treatment
The appearance of neoplasms should prompt a consultation with a doctor, even if this is not associated with discomfort. Early diagnosis will help determine the appropriate treatment and rule out the possibility of developing melanoma.
After examining the nevus, the dermatologist performs dermatoscopy to determine the type of nevus, then the patient undergoes a siascopic examination. At the slightest suspicion of malignancy, a biopsy is prescribed.
The diagnosis can only be made by a doctor and will prevent the formation of melanoma.
The appearance of a feeling of discomfort is the main reason why a papillomatous nevus should be removed, especially if the neoplasms are localized in the head, face or neck, it does not look very aesthetically pleasing. Also subject to removal are formations that are constantly injured due to their inconvenient location or are rapidly growing.
Removal of nevi of the papillomatous variety can be carried out in different ways.
Laser radiation
Most often, this procedure is prescribed to patients whose nevi are localized on the face or neck. To achieve a cosmetic effect, the patient should strictly follow all the specialist’s recommendations for caring for the wound after the procedure. Laser treatment cannot be prescribed if there is any doubt about the diagnosis, since in this case subsequent histology is not provided.
Cryodestruction
If the papillomatous nevus is located in hidden areas of the body or in areas covered with hair, removal occurs using the cryodestruction method. The operation must be performed by a specialist with sufficient experience and qualifications. This method is based on the removal of tumors with liquid nitrogen, and subsequent histological examination is also not provided for.
Electrocoagulation
This technique involves analyzing the material for histology. Among the disadvantages, the main one is the likelihood of scars appearing at the site of removal of the nevus, and therefore this method is not used very widely.
Radio wave method
This method is very effective and leaves virtually no scars after removal.
Surgical method
If the tumors are large enough, a technique based on surgical removal is most often prescribed. This method allows you to make stitches and scars not very noticeable on the skin.
There are also so-called traditional methods for removing such tumors, but they should be used with extreme caution, and consultation with a specialist is necessary.
The diagnosis is made in most cases based on the results of a visual examination by a dermatologist. Sometimes dermatoscopy is performed for clearer visualization.
If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, a biopsy may be performed.
Signs of degeneration into skin cancer
Papillomatous growths rarely degenerate into a malignant tumor. But since there is still a possibility, you need to treat neoplasms very carefully. Here are a few signs that may indicate malignancy:
- Excessive elevation above the surface of the skin;
- Blurry boundaries;
- Hair loss from a mole;
- Rapid increase in size;
- Change in color (lightening or darkening);
- Bloody discharge from the growth;
- The appearance of small spots and dots on the mole;
- Inflammation of the edges of the growth;
- Burning, pain, itching, tingling in the nevus;
- The formation of new small moles, cracks, and ulcers on the nevus.
You should go to the doctor when at least one of these signs appears. Melanoma is considered one of the most aggressive types of cancer; it progresses very quickly and almost immediately gives multiple metastases throughout the body. To recover and survive, you need to start treatment immediately after diagnosis.
Existing features
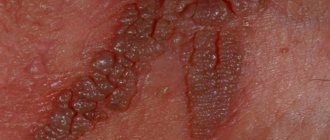
Papilloma is a completely different type of formation than papillomatous nevus. Unlike the often congenital mole, papilloma is an acquired growth due to infection by the human papilloma virus. It is transmitted through contact or sexual intercourse.
The papilloma formation is externally a growth on a stalk and is localized:
- on human mucous membranes;
- on the neck;
- centuries;
- armpits;
- on the genitals.
Nevi are located under the scalp or other areas of the skin and may have a wide, low stalk. Papilloma is always the color of the skin and is never colored. The edges of the nevus are clearly defined, it itself is slightly more elastic than the rest of the skin, the color ranges from brownish-beige to almost black, and the surface is granular. Papilloma may not have clear outlines and reach up to 20 mm in diameter. Moles are not normally painful; a change in their sensitivity should be a mandatory reason to visit a doctor!
Papillomas often grow under the arms
Reasons for appearance
The main cause is uncontrolled proliferation of skin cells. Their dark color is given by the skin pigment melanin, which is supposed to protect from ultraviolet radiation and is produced by special cells - melanocytes. The brown color of moles is given by pigment produced by melanocytes. Some other body systems also take part in the coloring of nevi - the pituitary gland and melanotropic hormone.
The difference between moles and malignant skin growths is their relatively slow growth.
As a rule, by the age of 25 of a person’s life, all hidden formations appear and their growth stops.
There are several reasons for the appearance of papillomatous nevi, including:
- heredity;
- injuries of various types:
- hormonal reasons;
- some developmental defects;
- excessive ultraviolet radiation;
- viral infection.
The hereditary factor in the occurrence of nevi is determined by gene regions in DNA and is inherited in the chromosome set. Since DNA is the body’s development program, at a certain stage a section of the chain is activated and the growth of the nevus begins. Such formations are always benign and are passed on to every second descendant. The presence of the same type of moles is a “quick” test to confirm family ties.
Traumatic injuries to the skin due to insect bites or cuts can cause inflammation and uncontrolled growth of skin cells, leading to growths. Nevi that appear as a result of injury are not inherited.
Excessive ultraviolet irradiation often leads to rapid, uncontrolled growth of skin cells. The body, in defense, produces an excess amount of melanin, which stimulates the development of melanocytes. Women over 40 years of age are sensitive to this influence.
It has been noticed that during the period of hormonal maturation or withering, various growths or formations appear on human skin, which is associated with the activity of the pituitary gland. Melanotropic hormone in this case is responsible for the appearance or sharp coloring of nevi.
Some defects in fetal development in late pregnancy lead to the growth of skin areas and the appearance of such moles.
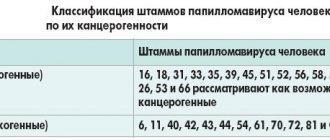
Now some scientists are putting forward a theory of the bacterial or viral origin of such marks on the skin, which, according to the principle of action, resembles traumatic causes. But papillomas that arise from the introduction of a virus into the human body should be distinguished from papillomatous nevus.
Abuse of ultraviolet radiation provokes nevi, especially after 40 years
Indications for removal
Papillomatous moles do not bother their owners physiologically.
Doctors see them mainly for cosmetic reasons - large, colored growths attract attention and do not decorate. Nevi on the scalp and on the body under clothing are often injured and lead to inflammation of the skin.
Medical indications for removal are only their sudden changes (increase, pain, appearance of spots, change in edges) or traumatic nature. As a rule, nevi very rarely degenerate.
There are several possibilities for their destruction:
- surgical excision;
- laser;
- cauterization;
- destruction with a radio knife;
- freezing.
The removal method is selected by the doctor depending on the type and size of the mole, in some cases after consultation with a neurologist (systemic type), or an oncologist based on histological examination. The following methods are currently used to remove papillomatous growths.
- Operational (surgical) removal is quite traditional. Used for large formations on the head.
- Using a radio knife is a very modern and bloodless method. Using this method, large moles can be removed, the mark after it is almost invisible.
- The laser method is indicated for eliminating small formations on exposed parts of the skin, which is removed layer by layer until the growth completely disappears.
- Freezing using liquid nitrogen, which kills nevus cells.
- The use of this method is effective, but requires a very experienced doctor, as skin damage and post-operative scars are possible.
- Cauterization using electric current, somewhat reminiscent of freezing, can also leave scars, but is less traumatic and bloodless.
If there are noticeable changes in the nevus, the removal method should allow one to leave a sample for histological examination to determine whether the growth is benign. This is an operative method, the radioknife method. All other methods destroy cellular tissue.
The laser method is used to remove growths on open areas of the skin.
Is it necessary to remove papillomatous nevus?
The nevus should be removed for the following indications:
- Frequent trauma;
- Risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor;
- Inflammatory process in the growth;
- Emotional discomfort.
There are many ways to remove nevi:
- Laser removal. If the mole is localized on an open area of skin (neck, face), this method is the most suitable. This is a painless procedure, after which there is never any bleeding and the nevus disappears forever. 7-10 days after removal, the wound heals without leaving any marks. But this technique also has a significant disadvantage - the impossibility of histological examination of the mole.
- Surgical excision. The operation is performed by a surgeon. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The disadvantage of this method is that after the operation you cannot wet the operated area for 10 days. But there is also a big plus - the possibility of conducting histological examination. For this reason, most dermatologists recommend the surgical method.
- Electrocoagulation. The method is used extremely rarely, since after the procedure a noticeable scar forms at the site of the nevus. Also, electrocoagulation is always performed under local anesthesia.
- Cryodestruction. The method is used when the nevus is located on areas of the body hidden under clothing or on the scalp. This procedure should only be performed by an experienced specialist, as improper use of liquid nitrogen can lead to tissue damage and scar formation. This technique excludes histological examination of the biomaterial.
- Radio wave method. The radio wave method helps to get rid of the growth and examine it for malignancy. Another undeniable advantage of the technique is healing without scarring.
Removing a nevus with a laser
However, there are several contraindications to removing nevi:
- Exacerbation of a chronic disease;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Allergy to lidocaine (with surgical excision);
- Inflammation of the operated skin area;
- Pregnancy;
- Diabetes;
- Having a cold;
- HIV AIDS;
- Malignant tumors of the blood and internal organs.
The concept of papillomatous nevus of the skin
The formation can be single or located in different parts of the body, but most often it grows on the head and neck.
Since it almost never develops into cancer, it is classified as a non-dangerous type. However, experts recommend protecting the nevus from various damages.
The tuberous nodule consists of papillary growths that are attached to the epithelium by a stalk. Although it can appear at any age, it is of the congenital type, like most other moles.
Care after nevus removal
During surgical excision, it is recommended to seal the wound with a bactericidal plaster. The bandage needs to be changed 2-3 times a day. Also, before gluing, the mole site should be treated with alcohol. It is important to remember that during recovery not a drop of water should get on the wound.
If any other method was used, the wound should not be wetted for 5 days. Under no circumstances should you lubricate the wound with lotion or other cosmetic product.
After the crust falls off, young, pale pink skin will remain in its place. Try to protect it from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Until the skin color at the mole removal site becomes normal, you should apply a high-level sunscreen to this area in the morning, afternoon and evening.
With improper care, multiple pigment spots appear at the site of the nevus.
Diagnosis and treatment
If you find damage to the nevus, blood on it, redness around the mole, feel discomfort, or notice that the mole is growing, then this may be the basis for its removal. In addition, nevi of this type have an unaesthetic appearance and this is also a reason for their removal.
Possible treatments for papillomatous nevi include the following:
- laser treatment or surgery
- radio wave method
- cryodestruction
- electrocoagulation
The doctor chooses the treatment method depending on the location on the body, size and characteristics of the human body.
Let's take a closer look at each treatment method.
Removing a nevus using a laser has many advantages. But you should know that this method is used when the diagnosis is made accurately and it is unambiguous. It is used to remove nevi located on the face or neck. After the operation, strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations for caring for the wound so that no trace remains of it.
One of the most popular is the radio wave method of removing nevi. Electromagnetic vibrations do not leave marks on the skin, scars or scars. And the histology can be checked.
The cryodestruction method means that the nevus will be exposed to very low temperatures. It is used if the mole is located in the hair growth area or in hidden areas of the body. It is worth finding an experienced specialist, otherwise you may end up with a scar or scar. As in the previous method, histological examination is impossible after surgery.
Electrosurgery or electrocoagulation is also used to remove skin lesions. But it is not very common, since it is possible to get a scar at the site of the nevus. That is, from an aesthetic point of view, this is not always acceptable. But you can conduct a histology examination.
A simple surgical procedure can remove particularly large nevi.
There are, of course, traditional methods of treating moles, but still, it would not be superfluous to first undergo a full examination by a specialist.
Papillomatous nevus
Constant trauma to the nevus, psychological discomfort and the appearance of inflammatory changes are indications for its removal. In cases where the diagnosis failed to 100% exclude melanoma, dermatology recommends removal of the nevus with mandatory histological examination of the removed formation.
Removal of papillomatous nevus can be carried out by laser, cryodestruction, radio wave method, electrocoagulation or surgical excision. The use of any of these methods is usually performed under local anesthesia.
For papillomatous nevi located on the face and neck, laser mole removal is often used. This method, with proper care of the wound after removal, has the best cosmetic effect. However, it is not suitable for diagnostically questionable cases, since it usually does not leave the opportunity for histological examination of the removed tissue.
The use of cryodestruction of papillomatous nevus is justified when it is located on the scalp or parts of the body hidden by clothing. This removal method can only be used by an experienced doctor, since too deep exposure to liquid nitrogen leads to cold tissue burns and scar formation. Histological examination of the removed formation is impossible.
Removal of papillomatous nevus using the radio wave method gives good results. After surgery, the tissues heal through scarless epithelialization, which guarantees an excellent cosmetic result. In this case, the removed material can be sent for histology without any problems.
Electrocoagulation of a nevus, although it makes it possible to accurately histologically verify it, is rarely used due to the formation of a noticeable scar at the site of removal. Large papillomatous nevus is an indication for surgical excision. The application of cosmetic sutures after surgery guarantees minimal cosmetic defects.
The only treatment option for formations of this type is their removal.
Indications for removal:
- location of the mole in traumatic places (neck, palms, soles, lower back);
- presence of a cosmetic defect;
- human desire.
Important. Before removal, you must consult a dermatologist and oncologist.
There are several ways to remove benign papillomatous nevi:
- Surgical - involves excision of a mole within healthy tissue. The disadvantage of this method is the risk of scar formation, this is especially important when removing a growth on the face.
- Laser is the most modern method. Allows you to carefully remove nevus without leaving a trace. The disadvantage is the complete destruction of tissue, which makes subsequent histological examination impossible.
Prevention of the appearance and recurrence of papillomatous nevi
It is impossible to avoid the occurrence of congenital moles. But if you follow the recommendations of doctors, you can prevent the appearance of new growths:
- Stay in the sun for no more than 40-60 minutes;
- Avoid visiting the solarium;
- If you plan to spend time in the sun all day, use sunscreen, wear a hat or take an umbrella;
- Try not to injure already formed moles.
To reduce the likelihood of dangerous moles appearing in a newborn, the expectant mother should adhere to the following rules:
- During pregnancy, stop using household chemicals. Give preference to cleaning products with natural composition;
- Refrain from using paints, poisons;
- Avoid alcohol. Alcohol leads not only to the formation of nevi in the baby, but also to the development of other pathologies;
- If you live near hazardous industrial enterprises or in a region with high background radiation, try to move to an environmentally friendly place for a while.
Remember that although papillomatous growths are not dangerous, they need to be examined regularly to prevent serious consequences. If you notice a change in the color or shape of a mole, don't panic. In this situation, the main thing is to see a doctor as quickly as possible.
Nevus papilloma - what is it and is it worth removing?
Papillomatous nevus is a benign formation that rises above the surface of the skin and has a lumpy structure. Quite often, such moles are located on the scalp. Often such formations are diagnosed in newborns. They may also appear later, reaching their final size by the age of 30.
Papillomatous nevus is a tuberous nodule, the structure of which includes papillary growths of a warty nature.
Causes
To this day, doctors cannot clearly establish the cause of papillomatous nevus. However, the following reasons for the formation of education are adhered to:
- prolonged action of ultraviolet rays on the skin;
- pregnancy (changes in hormonal levels in the body);
- menopause;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- inflammatory and allergic skin diseases (acne, dermatitis, various types of rashes).
Video: “Removing a nevus (mole)”
Brown papillomas are one of the types of benign neoplasms on the human body, caused by the activity of the pathogen - HPV. Normally, the hue of these soft, painless growths ranges from flesh-colored and pink to dirty gray and brown. Such papillomas can appear on any part of the body - skin, mucous membranes.
Symptoms of the disease
Papillomatous nevus on the head
- rapid growth of age spots;
- modification of the color of the pigment spot (darkening or lightening of the mole);
- the appearance of a red rim around the mole;
- visible changes (the appearance of cracks, growths);
- rapid hair loss from the surface of the mole;
- noticeable changes (itching, burning, pain and tingling).