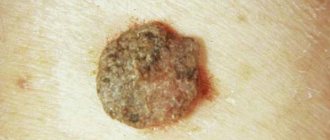
A specialist uses a special device - a dermatoscope - to determine the structure of the formation.
1. What is melanoma and for what reasons does it begin to develop?
Sofya Knalyan, oncologist of the Amur Regional Dispensary, Candidate of Medical Sciences:
— Melanoma is one of the most dangerous types of skin cancer, which, even with a small tumor size, is very aggressive - it develops quickly and metastasizes to different organs. The disease occurs against the background of ordinary moles (nevi) under the influence of various factors, the main of which are solar radiation and injury. In addition, so-called immune defects that arise due to electromagnetic pollution, increased stress, unhealthy eating behavior, uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives and hormonal changes during pregnancy and breastfeeding can provoke tumor growth.
2. What symptoms can be used to suspect the development of melanoma?
— The first signs that you need to pay attention to are changes in the color and structure of the mole: from light brown to dark brown, from soft to denser, the surface has changed from rough to glossy. You should be alarmed if the hair component predominated in the structure, and suddenly it began to fall out. In such cases, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist. The same is true if the mole has been injured. The specialist will examine the formation using a special device - a dermatoscope, which allows you to evaluate its structure. If signs of melanoma are detected, surgery to remove the tumor is prescribed. It is strictly forbidden to take material for a biopsy - a procedure where a piece of tissue is pinched off from a mole and analyzed - just as it is absolutely impossible to remove a tumor with a laser. Otherwise, you can provoke its growth.
1-2
An episode of sunburn to the point of redness, that is, getting burns, increases the risk of melanoma in the future by 10-20%
Melanoma can appear not only on the skin, although it is most often localized there. In second place in terms of frequency of diagnosis is melanoma of the mucous membranes - eyes, rectum, meninges. The disease also occurs without a primary focus, when the disease develops against the background of a mole, and then the tumor disappears on its own. The skin in this place looks healthy and without pigments, but metastases appear in the body. Making a diagnosis in such cases is extremely difficult even for experienced specialists.
3. How often do doctors diagnose melanoma to residents of the Amur region?
Elena Filippova, deputy chief physician for the medical department of the regional dispensary:
— Every year in the Amur region, melanoma is diagnosed in 40-60 patients, and recently the number of cases has been increasing. And if we used to consider melanoma a disease of older people, today it has become much younger. Due to its geographical location, the Amur Region, along with Primorye and the Khabarovsk Territory, is one of the three regions of Russia with the highest insolation - that is, exposure of the earth's surface to solar radiation. This means that the risk of skin cancer is higher here. Every year we see the same picture: as soon as the beach season arrives, people begin to actively sunbathe, getting burns. Also, our citizens, having worked the whole year in offices, go to the seas, where in a short period of time they receive a large dose of solar radiation, wanting to tan faster, although their skin is completely unprepared for this. Last August, specialists from the Moscow Blokhin Clinic, which has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating melanoma, conducted master classes for doctors at our oncology clinic. We invited Amur residents with modified moles to the classes to assess their condition. In many of them, melanoma was confirmed and operated on. Our oncologist colleagues shared their experience with us. After their arrival, the Amur Regional Oncology Center introduced new solutions for diagnosing melanoma and choosing tactics for its treatment, which increases our patients’ chances of recovery. But still, the disease is better to prevent, that is, its timely prevention is necessary.
4. What is the prevention of melanoma?
Tatyana Korobkova, head of the clinic of the Amur Regional Oncology Center:
“We cannot completely give up the sun, because the body requires vitamin D produced during tanning and so-called “sun training,” but sunbathing must be approached in doses and thoughtfully, limiting the time spent in the sun. We remember the postulates from Soviet times that you can sunbathe from 8 to 11 o'clock and after 16 o'clock, but from 11 to 16 o'clock you cannot - there is a large ultraviolet load. All this is still relevant today. It is safer to sunbathe not under direct sunlight, but under diffused sunlight, for example, under an umbrella or in the shade of trees, when the rays are reflected from the ground. Under no circumstances should the skin be allowed to become red or burnt. It is believed that if a person has had at least 1-2 episodes of sunburn to the point of redness (that is, getting burns) during his life, then his risk of developing melanoma in the future increases by 10-20%. Often patients aged 40-45 years come to us with advanced stages of melanoma, who have injured a mole and tried to treat themselves, listening to the advice of friends, using folk recipes. No need to experiment on yourself! You must go to the doctor immediately. As they say, in such cases, overdiagnosis is better.
40-60
Doctors diagnose cases of melanoma every year.
Prevention of melanoma also includes medical examinations, which must be completed at a local clinic once a year. You can ask questions on this topic to therapists, dermatologists, and oncologists. Only an experienced specialist is able to adequately evaluate all formations on the skin and mucous membranes suspicious for melanoma. In addition, our dispensary holds an open day every quarter, aimed at informing patients for the purpose of early detection of neoplasms, where Amur residents can come for examination without a referral. For the convenience of patients, appointments are carried out by appointment, announced on our official website (18+) and on Instagram. Due to the coronavirus situation, the event scheduled for May 17 has been postponed. The date will be determined after restrictive measures are lifted.
5. How do you feel about the stories that one woman went to the doctor, removed a mole and died, but could still live if she had not touched it?
“Such stories, perhaps, are born from ignorance,” Tatyana Korobkova is convinced. “The fact is that many patients come to the appointment already with the fourth, most complex stage of the disease, when the melanoma has metastasized. During treatment, the primary tumor itself may not grow, but distant metastases grow rapidly. Hence the high mortality rate. But patients die not because we removed the melanoma, but because they came in at advanced stages, and our capabilities are limited compared to those when the disease was detected at the first stage. Nevertheless, modern treatment solutions allow us, in some cases, to stabilize such tumors, that is, to control and restrain the process of their growth and metastasis. If ten years ago patients with the fourth stage of the disease died within a year, modern drugs can prolong their life, they are reintegrated into the family, and can work.
Since the drugs are quite new, there are no long-term results of treatment yet, but we are already seeing their effectiveness: patients live for five years or more, and we believe that this is not the limit.
Our doctors can tell you other stories: a patient comes and says that he removed an ordinary-looking mole in some salon, and now something is wrong. During the examination, we detect melanoma and distant metastases. It turns out that the removed tumor was not sent for histology - a study that allows determining pathology at the tissue level. As a result, time was lost, the time frame for making a diagnosis and starting to fight the disease that developed was extended, and we do not know either the depth of germination of the removed tumor or its size, which is of great importance in management tactics. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you undergo mole removal procedures from qualified specialists. If the doctor does not have enough experience to recognize melanoma and it is removed non-radically with a laser or using cryodestruction, this can have fatal consequences. Unfortunately, we are increasingly seeing such examples in practice. Take care of yourself and your loved ones!
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, SPECIALIST CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED
As an advertisement
Age category of materials: 18+
- Valentina Petrova
- Amurskaya Pravda from 05/14/2020
Melanoma in adults
Melanoma in men
The likelihood of melanoma in a man is 7-8 cases per 100 thousand population, which is less than in women. However, most often it is located on the back and lower legs - and these are those areas of the skin that men rarely closely examine.
Melanoma in women
Melanoma in women develops with a frequency of 12-13 per 100 thousand population, so female gender can be considered an additional risk factor for this disease. However, they respond better to radiation and chemotherapy, so their prognosis for life is slightly higher than for men.
What causes it: reasons
Scientists have not determined the exact causes of melanoma. Many of them adhere to the theory that the main mechanism of skin cancer is a disorder at the molecular and genetic level. In epithelial cells, DNA is damaged and chromosomal changes begin. Melanoma on the face can begin to develop if you accidentally pick off a nevus or expose it to constant exposure to sunlight. When such pathological cells appear in the human body, they can easily degenerate into a tumor and begin to multiply rapidly and affect more and more tissues.
According to many studies, it was found that in 70% of patients, pigmented melanoma developed from a nevus or other birthmarks that are located on any part of the body. Predisposing factors that contribute to the degeneration of a neoplasm into a cancerous tumor increase the risk of melanoma. These include:
- solar ionizing radiation and radiation;
- ultra-violet rays;
- psychosomatics (constant irritation and state of excitement);
- sunburn;
- nevus injury;
- genetic predisposition;
- giant nevi;
- bright skin;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- hormonal imbalances;
- human papillomavirus;
- decreased immunity;
- chronic inflammation of the skin.
Melanoma can grow in any part of the body and penetrate the layers of the skin to varying degrees.
What is skin melanoma
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm that forms from pigment cells. A synonym for this disease is melanoblastoma, which, along with basal cell and squamous cell, is one of the most common types of skin cancer.
In addition to skin melanoma itself, other localizations of this neoplasm are possible: the eyes, the mucous surface of various internal hollow organs. It is one of the most unfavorable types of cancer, because the human immune system is practically unable to prevent its progression. In addition, melanoma metastases spread quite quickly through the bloodstream to various distant organs, which makes the prognosis for this disease very serious.
The main causes of melanoma
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
The main risk factor for the appearance of melanoma of the skin or other localizations is unfavorable heredity for this disease. Back in the middle of the last century, scientists identified special genes that are located on chromosomes 9 and 12. Mutations in their structure lead to a decrease in the specific antitumor response, which significantly increases the risk of the appearance of signs of melanoma. However, not all people with such genetic abnormalities will develop this terrible disease; for its occurrence, the presence of other risk factors is necessary.
- Excessive ultraviolet radiation. This is the most important provoking factor, and it does not matter whether it is artificial sun rays or active tanning in a solarium.
- Certain external signs: fair skin and hair, gray or blue eyes, the presence of freckles. Skin phototypes I and II significantly increase the risk of developing this neoplasm.
- The presence of a large number of nevi (more than 50 throughout the body). A mole and melanoma can be very similar and sometimes only a specialist can tell them apart.
- Over 55 years of age, this disease occurs somewhat more often in women than in men.
- The presence of skin melanoma in the past, even after a long time (10 or more years) after undergoing combined treatment.
Melanoma prevalence
Skin melanoma is common among the population of the entire globe, but residents of European countries are more susceptible to this disease and, to a lesser extent, people in African countries. Hundreds of thousands of new cases of this disease are registered every year. Tens of thousands of patients die every year, because melanoma metastases spread throughout the body rapidly and quickly lead to a sad ending. Unfortunately, about a third of people with newly diagnosed melanoma die within the first year, and only a third of the remaining survive the five-year period.
In Russia, 6-8 thousand new cases of this disease are registered annually, and most of them develop in the older age group (after 60 years). In recent years, melanoma, the symptoms of which are recorded every year 10-20% more often, has become one of the most common types of malignant neoplasms, along with lung, cervical and breast cancer. It accounts for 1-1.5% of all cancer diseases.
Despite the fact that this disease has been known for a very long time, during the period from 1950-2000. According to American experts, the number of annual primary cases has increased 60 times. However, most likely the incidence is increasing not only due to its true growth, but due to better and more effective diagnosis of melanoma, which can increasingly be identified at an early stage.
Treatment of melanoma: how to treat melanoma? Symptoms, immunotherapy for melanoma, targeted therapy
How to recognize melanoma and who to turn to for help? If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a dermatologist or oncologist. In most cases, therapy for the corresponding disease is carried out in specialized hospitals.
A family doctor or local therapist who has recorded the development of signs of melanoma refers the patient to an oncology clinic.
Melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer. Of course, ultraviolet radiation actively contributes to its appearance, but it can also occur in areas where the sun's rays did not reach.
Despite the fact that it progresses more actively than other types of skin cancer, there are specific drugs that help treat and cope with melanoma.
And in the early stages, the number of finally recovered people approaches 100 percent.
Stage 0 (in situ): Melanoma is only in the upper layers of the skin. Full recovery occurs in almost 100 percent of cases. After excision of the melanoma and a small amount of healthy skin around it, your doctor may recommend visiting a dermatologist annually and performing a monthly self-examination for suspicious moles and enlarged lymph nodes.
Why are further checks needed? To catch melanoma that has returned around a scar, that has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body, or new melanoma in a completely different location.
How to conduct a monthly self-examination?
- Undress and stand in front of a large mirror in a well-lit room. Take a smaller mirror in your hand and examine your face, as well as your mouth and ears.
- Using a small and large mirror, inspect the back of your head, ears and neck. Examine your hands from all sides, the skin between your fingers and under your nails, and your armpits.
- Using both mirrors, examine your shoulders, upper back and arms, lower back, buttocks, the skin between them, and the backs of both legs.
- Sit and examine your legs, ankles, feet, the skin between your toes and under your nails. Use a mirror to examine your genitals.
Melanoma stage 1 or 2A: tumor thickness less than 4 mm, without ulceration, or thickness less than 2 mm, but with ulceration. Surgery alone is curative in 70–90 percent of cases.
In stage IA, a person should visit the doctor 2 to 4 times during the first year, after which the doctor may recommend an annual checkup. The patient should also conduct a self-examination every month. If melanoma is detected at stage IB, then you need to visit a dermatologist every 3 months for 3 years.
Then every six months for 2 years. Self-examination is also necessary. If the doctor deems it necessary, he will change these recommendations.
Stage 2B or 2C: Tumor thickness 2.1–4 mm with ulceration, or thickness greater than 4 mm but no ulceration. After tumor removal, recurrence occurs in 40 to 70 percent of patients.
For those at high risk of such consequences, treatment of stage 2 melanoma with interferon alfa-2b is usually recommended, but the recommendation is not strict, since the effectiveness of this drug is somewhat questionable and side effects are common.
After surgery or completion of treatment for stage 2 melanoma, you need to see your doctor every 3–6 months for 2 years, then every 3–12 months for 2 years, then annually. Self-examination is also necessary. The doctor, among other things, may prescribe regular CT scans.
Stage 3: Cancer cells are present in the lymphatic ducts surrounding the tumor or adjacent lymph nodes. Additional therapy is highly recommended, as melanoma returns in more than half of cases. Immunotherapy with interferon alfa-2b reduces the risk of relapse.
It can boost the immune response so that the body can better fight tumor cells. Treatment for stage 3 melanoma lasts up to 12 months (subcutaneous injections are given).
However, not all guidelines contain such a recommendation due to the fact that interferon often provokes flu-like symptoms (fever, pain in muscles and joints, fatigue, loss of appetite), depression, etc.
After stage 3 melanoma cancer cells are removed, you need to see a doctor every three months for three years, then every six months for 2 years. If the doctor has any suspicions, he will ask for a blood test, a CT scan or an ultrasound.
Stage 4: metastases are present in more distant parts of the body (usually distant lymph nodes, lungs, liver, brain; melanoma metastases in the bones are also common).
This may include immunotherapy, targeted drugs, surgery, radiation or chemotherapy.
At stage 4, there are no clear recommendations for the treatment of malignant melanoma, since all methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, besides, the manifestations of the disease and wishes of each patient are different and when choosing therapy it is necessary to build on this.
Chemotherapy kills cancer cells or suppresses their growth. However, it is less effective than immunotherapy and targeted therapy and is therefore used less frequently (usually for small tumors).
The drugs mainly used are dacarbazine, temozolomide, cisplatin, vinblastine and carmustine. For example, one chemotherapy regimen for melanoma includes cisplatin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine.
The other is cisplatin, dacarbazine, carmustine and tamoxifen (according to some reports, the latter drug may not be included in this regimen).
There is also reason to believe that the drugs carboplatin and paclitaxel in combination with sorafenib have a good effect, and they are less toxic than dacarbazine.
Chemotherapy usually causes blood tests to worsen, diarrhea, mouth pain, fatigue, and hair loss. If the primary tumor is on an arm or leg, then the doctor may suggest regional (local) chemotherapy - when the drug does not circulate throughout the body, but only reaches the limb.
The surgeon places a tube into a vessel that carries blood to and from the arm/leg. The tubes are connected to a machine that injects the necessary drugs along with warmed blood, and after a short time the blood flow is restored. You can also add oxygen to this mixture and then the procedure will take about an hour.
If pain appears in an unusual place in a limb, you must immediately tell the doctor: it may be a blood clot.
Surgery is sometimes necessary if melanoma has spread to a limited area, and the tumor or metastases can be excised. This often allows not only to extend life by months and years, but also to reduce pain due to a tumor, for example, if it is in the lung or brain.
Surgical treatment options for melanoma:
- Simple and wide excision of the tumor. Typically used for small melanomas. The surgeon removes the cancer and a small amount of tissue around it.
- Mohs surgery is now rarely used, usually if the melanoma is on the face. The tumor is removed layer by layer, each removed layer is examined under a microscope. When tumor cells are no longer detectable in the sample, the melanoma is considered to be completely removed.
- Amputation. They resort to it if the melanoma is on the finger and has managed to grow deep into the tissue.
- Lymph node dissection is the removal of nearby lymph nodes into which tumor cells have spread.
- For melanoma metastases in internal organs, surgery is ineffective.
Melanoma: symptoms of the disease
If a person has melanoma, the signs of which do not immediately become apparent, he may well mistake it for an ordinary mole. The latter are present on the bodies of the vast majority of people; many have several dozen of them. During their lives, their numbers increase and they change in size. Therefore, if melanoma appears among them, the symptoms of which do not manifest themselves in any way at the initial stage, not everyone pays special attention to it.
Melanoma is a malignant tumor of pigment cells that are found in the skin, eyes or lining of hollow internal organs. After a period when there is only a primary focus, malignant cells gradually spread beyond its boundaries, to regional lymph nodes; with melanoma, metastasis occurs rapidly.
What does melanoma look like?
Many people who have a large number of moles or nevi on their skin are concerned about the answer to the question of what melanoma looks like. Indeed, this is a real chameleon, so it is impossible to give a definite answer. Considering that this neoplasm develops from pigment cells, it usually has a very dark or even black color. However, this sign of melanoma is unreliable, because sometimes it has a blue, brown, purple, gray, pink color, and in rare cases, pigmentation does not occur at all and the neoplasm does not differ in color from the patient’s normal skin. Most often, the color of the tumor is not uniform, but mottled, spotted, and varies greatly in its different parts.
Patients often ask an oncologist or dermatologist what does melanoma look like in the initial stage, what size should a person be alerted to? It is believed that the size of this neoplasm ranges from 3 mm to 3 cm, and its irregular shape is characteristic. The consistency of this formation is usually denser than skin, sometimes even hard. If you touch melanoma carelessly, a symptom that is very important in terms of diagnosing the disease is possible - increased bleeding. Often this formation has areas of ulceration and weeping on the surface; a distinctive feature is the absence of a skin pattern on the surface of the tumor and hair loss.
Usually, if a person develops melanoma, the initial stage of the disease does not manifest itself clinically, but sometimes itching and discomfort may appear in the area of the tumor (but this symptom is not necessary). The tumor first grows in width, usually reaching a small size (no more than 3 cm), and then it begins to grow in depth, affecting the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. In this case, its surface rises sharply above the rest of the skin, it becomes bumpy, dense, and then the likelihood of suspecting it increases.
Mole and melanoma: commonalities and differences
More than 60% of people around the world have at least one nevus on their skin, and most of them have more than ten such formations. Many people know that a mole and melanoma can be very similar in appearance. However, it is extremely important to timely identify the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one, because the patient’s life depends on how quickly therapy is started. Anyone should know the distinguishing signs of a mole and melanoma, including the following:
- Dimensions. Moles can vary in size, while melanoma usually does not exceed 3 cm in diameter. Unlike nevus, the latter is characterized by rapid growth.
- Form. Moles have a round, oval shape with clear edges. Melanoma is characterized by uneven contours, the shape can be varied, but most often irregular.
- The surface of the mole is smooth and even, while melanoma is lumpy, dense, and heterogeneous. A skin pattern can often be found on the surface of the nevus, which is not typical for melanoma.
- In the thickness of the nevus there may be a hair follicle and small hairs sometimes grow from it, but a distinctive feature of melanoma is that hair never grows from it.
- The surface of melanoma may bleed, ulcers and weeping appear on it, while this is not typical for a mole.
- Nevi are painless, but melanoma can cause slight pain and itching.
Thus, sometimes a mole and melanoma can be very similar, but this series of symptoms allows you to suspect the malignancy of the nevus in time and consult a doctor in a timely manner. If a person doubts the nature of a skin tumor, he should definitely see a dermatologist or oncologist, because reinsurance in this case can save his life. In the case when a specialist has confirmed that the neoplasm on his skin is benign and the patient is not in danger, he must find out from him what melanoma looks like.
How to determine that a mole is degenerating into melanoma
Currently, the most common melanomas that develop from nevi, or moles.
Suspicion should be raised by those moles that grow quickly and form uneven edges. Sometimes patients notice that several different shades . In some cases, a small lump forms in the center of the tumor.
The traditional ABCD diagnostic method is often used in practice. Doctors teach it to all patients, especially those at risk for developing melanoma.
- “ A ” is “asymmetry”: if you mentally fold a mole in half, the edges will not match.
- “ B ” stands for “borders”: in a malignant tumor they are uneven, jagged or blurred.
- “ C ” is “color”: several different colors are present in one neoplasm.
- “ D ” is diameter: large moles should be especially suspicious.
Recently, the letter “E” has been added to this formula. The importance of this parameter must be emphasized. “E” stands for “change” and is what primarily indicates malignancy. If a mole itches and turns red from time to time, this means that pathological changes are occurring inside: an initially benign mole turns into melanoma. In addition, there are pink melanomas - that is, almost flesh-colored.
In a word, if you have any suspicious growth on your skin, you should immediately contact a dermatologist.
Get a treatment program for free
Melanoma: signs of the disease
Diagnosis of melanomas is usually difficult due to the variety of their external signs. Often, even a specialist without special additional examination methods finds it difficult to say for sure whether this skin tumor is malignant or not. The difficulty lies in the fact that there are several forms of this formation, among which there are superficial widespread, nodular melanoma and lentigo melanoma, each of them has its own distinctive features. In addition, this education is dynamically changing. The stage of melanoma changes its external manifestations.
Certain forms of melanoma
During this disease, there are 2 main periods: the phase of horizontal and vertical growth. The stage of melanoma, at which it increases in width, lasts for a fairly long period of time. The neoplasm does not cause any special symptoms, except for immediate local manifestations. This phase is not characterized by metastasis and it is during this period that treatment of melanoma leads to a favorable outcome.
However, this is replaced by a period of vertical growth: this stage of skin melanoma is characterized by the tumor growing into the deep layers of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It proceeds rapidly, malignant cells spread to regional lymph nodes, and with melanoma, metastasis quickly occurs to distant organs. Treatment of the disease at this stage rarely leads to recovery without consequences.
If a person is diagnosed with melanoma, the prognosis for the patient depends primarily on at what stage of the disease (horizontal or vertical growth) he went to the doctor and whether there are metastases to the lymph nodes and organs.
Superficial spreading melanoma
The most common form of this disease is superficial spreading melanoma, accounting for about 60% of all cases of this disease. It has a favorable course, because the first phase of the disease, in which the formation grows horizontally, takes from 5 to 7 years. In this variant, melanoma, the symptoms of which are extremely scarce, has the appearance of an ordinary pigment spot that does not rise above the surface of the skin. However, when it enters the vertical growth phase, it quickly penetrates into the deep layers, the surface becomes dense, convex and lumpy. At this stage of skin melanoma, it metastasizes in a short time.
Nodular melanoma
Nodular melanoma develops in every fifth patient with this disease. Externally, this form of the disease differs from the superficial spreading form, because in this case the neoplasm has the appearance of a rounded node, a mushroom cap or a polyp on a short stalk. Previously, it was believed that nodular melanoma did not have a horizontal growth stage, but now it has been proven that it does exist, but it is much shorter than in the first version of the course of this disease. This tumor initially rises sharply above the surface, but it is easier to suspect its appearance than in the case when it imitates a pigment spot (as happens with the superficially spreading form). In addition, it usually has a bright color - black or burgundy, which also facilitates the diagnosis of nodular melanoma.
Lentigo melanoma
Lentigo-melanoma is the most favorable variant of the course of this disease, because the horizontal growth phase lasts from 10 to 20 years. The likelihood that during this period of time the patient will consult a doctor is quite high, but it is its slow growth that is the factor that worries people to a lesser extent. Symptoms of lentiginous melanoma are extremely scarce; for many years it resembles an ordinary pigment spot; it usually appears on the skin of the face and neck. Women suffer from this disease in most cases. After the transition of the first stage of skin melanoma to the deep growth phase, its surface becomes dense, bumpy, and bleeds when touched.
Melanoma of the eye
There are pigment cells on the retina, conjunctiva, iris, eyelids, as well as on the surface of the skin, so eye melanoma is one of the variants of tumor localization. It occurs in approximately 5% of all patients with this disease. This is an extremely unfavorable course of this disease, because very often eye melanoma is completely asymptomatic. The first sign of damage is often a unilateral decrease in vision, which cannot be corrected by any optical devices. High-risk groups include older patients (over 60 years), but this disease can appear at any period of life. The following types of eye melanoma are possible:
- melanoma of the eyelid (lower or upper),
- melanoma of the conjunctiva,
- choroidal melanoma,
- iris melanoma,
- orbital melanoma,
- melanoma of the ciliary body.
Experts distinguish two main forms of ocular melanoma: nodular and planar, and in the vast majority of cases the second occurs. The course of the disease is particularly malignant, because it is often diagnosed already at the last stage of melanoma, when it has already managed to give distant metastases. Treatment of this form is difficult and requires caution and precision, but such patients are not always able to preserve their organ of vision.
Stages of melanoma
What are the stages of skin melanoma?
After this malignant neoplasm appears, the tumor begins to grow in width. This is the so-called horizontal stage of skin melanoma. Depending on the form of the disease, it lasts from several months to tens of years; this parameter is very individual. Unfortunately, during this period, the neoplasm is very similar to an ordinary pigment spot and a large number of sick people do not pay due attention to it. This is especially sad due to the fact that it is here that treatment of the disease is most effective and sometimes leads to complete recovery. The only exception is, perhaps, the nodular form, in which the tumor from the very beginning differs from ordinary moles and quickly attracts a person’s attention.
After a period of horizontal growth, the next stage in the progression of this malignant neoplasm begins. This is the vertical growth phase of melanoma. It is characterized by rapid tumor growth into the deep layers of the skin (dermis, subcutaneous tissue), muscles and penetration of malignant cells into the blood and lymphatic vessels. At this stage, metastasis begins rapidly, significantly worsening the prognosis for melanoma.
In 1997, a unified classification of this neoplasm according to the TMN system was adopted. It allows you to determine the specific clinical picture of the patient, the presence of lymph node damage and the presence of metastases.
T - determined visually and by the result of dermatoscopy, also by the result of histology in case the melanoma was surgically removed.
N – nature of damage to lymph nodes:
- Nx – there is no reliable information about the presence or absence of metastases in the lymph nodes,
- N0 – no metastases to lymph nodes,
- N1 – metastases to lymph nodes up to 3 cm,
- N2 – metastases to lymph nodes larger than 3 cm.
M – presence or absence of distant metastases:
- Mx - there is no reliable information about the presence or absence of distant metastases,
- M0 – no distant metastases,
- M1 – presence of distant metastases.
Thus, after examination, each melanoma patient receives an individual code reflecting the main aspects of the course of his disease. As a result, all doctors who are related to him can quickly navigate the nature of the pathological process without lengthy familiarization with the medical history or outpatient card of this patient.
Melanoma early stage
If a patient has melanoma, the initial stage of the disease may take a different time interval. Its duration primarily depends on the form of the disease, for example, with superficial spreading or lentigo melanoma it lasts up to 20 years. However, for the nodular form or when the eyes are affected, it is much shorter. There are also a number of factors that influence how quickly the initial stage of melanoma becomes advanced. These include:
- Active insolation.
Under the influence of ultraviolet rays (both from the sun and those received in a solarium), melanoma progresses faster.
- Injury to the tumor.
If the tumor is located in a place where it is constantly exposed to mechanical damage (feet, hands, bra area, etc.), the likelihood that it will quickly enter the vertical growth phase is higher.
- Biopsy.
In diagnosing melanoma, a biopsy to collect material for histological examination is strictly excluded, because in this case the tumor can begin to rapidly grow in depth and metastasize. If for some reason this happened (for example, the doctor was initially unsure of the diagnosis), then the likelihood of complications becomes higher.
Damage to lymph nodes in melanoma
As the tumor begins to grow vertically, it quickly begins to metastasize through the lymphatic vessels. The first places where malignant cells enter are the lymph nodes; with melanoma, not only they are usually affected, but also nearby healthy areas of the skin. This complication consists of foci of pigmentation of skin areas or characteristic nodes located at a short distance from the primary focus. In addition, there are two types of metastasis through the lymph nodes in melanoma:
- Erysipelas-like type. It is characterized by the appearance of foci resembling erysipelas, not far from the primary focus.
- Thrombophlebitic type. Reddened areas of skin and thickened and painful veins appear around the melanoma.
Main metastases of melanoma
Distant metastases of melanoma usually appear when the tumor begins to grow in depth, that is, it enters the vertical growth phase. It is characteristic that the primary focus can be completely insignificant in size, but give an abundance of metastatic complications in various organs. Most often, melanoma metastases have the following localization:
- lungs,
- bones, including the spine,
- liver,
- central nervous system,
- kidneys and adrenal glands.
The spread of malignant cells occurs after they enter the bloodstream, so distant metastases can appear in any organ.
Diagnosis of melanoma
The most reliable way to find out whether a mole is malignant is a biopsy. The doctor removes the tumor and sends it to the laboratory for examination under a microscope. If cancer cells are found in the sample, the diagnosis is certain.
As a screening test, dermatoscopy is used - a study during which the doctor examines the patient's skin under magnification using a special instrument. Modern equipment allows you to enter the resulting images into a computer and draw up a “map of moles” and compare the picture over time. If suspicious neoplasms are detected during dermatoscopy, they are biopsied.
If there is a suspicion of metastases in other organs, additional studies are prescribed:
- Chest X-ray.
- Computed tomography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- PET scan.
- Biopsy of organs in which suspicious lesions are found.
Diagnosis of melanomas
At the slightest suspicion of melanoma, you should consult an oncologist or dermatologist. There is nothing shameful in the fact that this assumption is not confirmed. It is much worse to miss that stage of the disease that may still be treatable.
Diagnosis of melanoma consists of the following main points.
- Assessment of the appearance of the tumor, examination, palpation.
- Medical history described by the patient himself: his story about the presence of unfavorable heredity, frequent visits to exotic countries, bad habits.
- Dermatoscopy. This method involves examining a suspicious area of skin or tumor using a special device - a dermatoscope. This is an excellent assistant for a specialist who doubts the diagnosis.
- Cytological examination of a smear-imprint from the surface of the tumor. It is used because a biopsy for diagnosing melanoma is strictly contraindicated. The presence of malignant cells in the material confirms the diagnosis.
- Close examination and examination for the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes and internal organs. For this, all necessary diagnostic methods are used.
An accurate diagnosis can only be made by histological examination, which is carried out after complete removal of the melanoma with the inclusion of healthy tissue.
Melanoma Treatment Methods
An oncologist directly treats this disease and further monitors the patient.
The only treatment method is removal. Prevention
Ultraviolet rays with moderate and proper tanning have a beneficial effect on the skin - they activate the synthesis of vitamin D, increase immunity, and have a beneficial effect on blood circulation in general; their effect is beneficial for such skin pathologies as eczema, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, etc. However, the fashion for a beautiful suntan and beach holidays goes against the views of doctors on this problem. Therefore, patients traveling to the sea in the summer can be given the following recommendations on behavior during their stay on the sunny coast:
- appear on the beach during safe hours - before 11.00 in the morning and after 15-16.00 in the afternoon, when the sun is not so active;
- use photoprotective creams with a high degree of SPF (30-50);
- use high-quality sunglasses, as well as clothing made of fabric with a high UV protection factor - linen, silk, denim; colors – dark blue, deep red, black. There are special brands of sun protective clothing – Parasol, Mott50, Cover.
- Products that protect the skin from the effects of insolation are currants, kiwi, bell peppers, orange, lemon, and others containing ascorbic acid, which is destroyed under the influence of solar radiation. Also important are vitamin A (foods containing it - carrots, apricots, pumpkin, melon, mango, watermelon) and vitamin E (which is found in large quantities in unrefined vegetable oil, almonds, avocados, dried apricots, hazelnuts). Tomatoes containing lycopene, a substance that accelerates the production of melanin, are useful.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Melanoma: treatment of the disease
If a patient is diagnosed with melanoma, the treatment the doctor chooses depends on many parameters. These include both those that characterize the malignant process itself (type of tumor, growth pattern, presence of metastases in lymph nodes and distant organs, location, size), and those that depend on the patient himself. The latter include gender, age, the presence of concomitant diseases, contraindications for surgery under general anesthesia.
Melanoma: surgery or non-surgical methods?
After diagnosis and examination, the oncologist must decide one fundamental question: whether to surgically remove the melanoma or give preference to other methods of therapy. The answer to this is ambiguous, but in most cases the following rule is followed:
- If the patient has a tumor with horizontal growth and no distant metastases or damage to the lymph nodes, then surgery is performed and the melanoma is removed along with the surrounding healthy tissue.
- If the growth of the tumor has become vertical, then the risk of surgical treatment outweighs the potential benefit. If melanoma is excised, surgery can give rise to active metastasis, which significantly worsens the prognosis. In this case, preference is given to conservative methods: immunotherapy, radiation and chemotherapy.
However, if there are contraindications for surgical treatment under general anesthesia (high risk of cardiovascular complications, bleeding, etc.), sometimes a patient with the initial stage of the disease may be denied surgery. If a patient is diagnosed with melanoma, treatment should be carried out exclusively by specialists in a specialized oncology hospital: no self-medication, the use of traditional medicine, healing and other alternative methods is unacceptable, because this could cost him his life.
How is melanoma removed?
Cryodestruction (cauterization with liquid nitrogen), electrocoagulation, laser therapy and other methods that are used to remove various skin formations are not used to remove melanoma, since they can give impetus to the active growth of the tumor in depth and metastasis. In addition, these methods do not make it possible to reliably verify that the entire tumor has been removed.
The only way melanoma can be removed is through surgery under general anesthesia. In this case, the tumor is excised along with the surrounding healthy tissue (up to 2-3 cm wide), subcutaneous tissue and deep muscle fascia. Only such a volume of surgical care can guarantee that the tumor will be completely removed and this will reduce the risk of relapse. If you leave even a small area of malignant tissue, there is a high chance that it will begin to grow very quickly, metastasize, and the entire melanoma treatment will need to be repeated.
If metastatic lesions of the lymph nodes appear in melanoma, the operation will also include their mandatory removal. Surgical treatment in the presence of distant metastases is a controversial issue; sometimes it is performed to temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition, but it does not improve the prognosis, and sometimes even vice versa.
What other types of therapy are used?
In addition to surgical treatment of melanoma, there are other non-invasive methods. They can be effective in addition to surgery and sometimes allow the patient to completely forget that this diagnosis took place in his life. In some cases, they are performed in the absence of the possibility of radical treatment of the tumor (deep invasion, the presence of distant metastases and contraindications for general anesthesia). These include:
- Irradiation of the tumor.
It is carried out by radiologists. The total focal dose is calculated individually depending on the volume of the tumor, the presence of metastases and the patient’s health status.
- Chemotherapy.
This is the use of various drugs that stop the growth of the tumor, and sometimes help to reduce its size. These include decarbazine, carmustine, lomustine, cisplatin, cyclophosphamide, etc.
- Immunotherapy.
This is the most progressive branch of cancer therapy, which has been actively developing recently. Monoclonal antibodies (the drugs ipilimumab and nivolumab) are used, which in half of the cases make it possible to achieve a significant reduction in tumor size, which makes it possible for oncological surgeons to subsequently carry out radical treatment. In addition, interferon-alpha, interleukin-2, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor are used.
Treatment
Treatment of melanoma is selected individually and begins with a thorough examination of the patient. Typically it includes:
- surgical intervention to excise formations, as well as affected lymph nodes, etc.;
- chemotherapy. Approaches and programs are different and depend on the task and condition of the patient;
- immune support.
Prognosis largely depends on the extent of the lesion. Superficial types of cutaneous melanoma suggest that with timely treatment, the five-year survival rate of patients is 95%, which is an excellent indicator. If damage to the lymph nodes is already observed, this figure decreases by more than 2 times.
Prevention of melanoma recurrence
What does melanoma look like after removal?
If the patient has undergone surgical treatment of melanoma, after removal, as a rule, a significant cosmetic defect remains. To prevent relapse, surgeons try to excise not only the tumor itself, but also fairly decent volumes of nearby healthy tissue, along with subcutaneous tissue and muscle fascia. If the patient is dissatisfied with the way the part of the skin where the melanoma was previously located looks, after removal and undergoing the rest of the necessary treatment (radiation, chemotherapy, use of immune drugs), he can seek help from a plastic surgeon. However, as a rule, specialists do not seek to actively intervene during the postoperative state of the wound, as this increases the risk of relapse.
How to avoid recurrence of melanoma
If a patient has had melanoma, after removal of the tumor he should always remember the likelihood of relapse. Whether this will happen or not is a complex question, and the quality of the surgical treatment performed and the amount of conservative care play an important role. Prevention of recurrence of melanoma after removal plays an important role, because compliance with a number of measures will enable such a person to significantly prolong his life.
- Avoid excessive sun exposure.
It is difficult to say how many minutes under the scorching sun can be considered acceptable and how many cannot. Therefore, it is better for patients who have undergone treatment for melanoma to generally avoid being under direct ultraviolet light and visit southern countries (if they really want to) in the spring and autumn.
- It is necessary to undergo regular examinations with a dermatologist so that he can evaluate the condition of the most alarming nevi.
- A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, elimination of bad habits and regular rest complement the first two types of melanoma prevention.
Types and classification
Classification allows you to more accurately determine the causes and factors that influenced the occurrence of the pathology and, if necessary, eliminate them. All types of melanoma have an optimal treatment method and precise characteristics. In most cases, the main background is a pigmented nevus, but sometimes it develops as an independent neoplasm, usually dark in color or completely unpigmented.
Melanoma can affect the dermis and internal organs and systems to varying degrees.
| Melanoma classification | ||
| Clinical form | Description | Who is affected? |
| Super official | Has a long period of benign progression. It grows deep inside for years. | Diagnosed in 65% of all cases, women are more susceptible. |
| Nodular or nodular | Grows quickly deep into the skin. It looks like a round bump. Has black or other dark color. Sometimes there is no pigmentation. As a rule, it is localized on the skin of the body (on the stomach, on the shoulder) or on the leg. | Diagnosed in older people. |
| Acrolentiginous | First it affects the top layer of the skin, penetrating deeper and deeper. Localized on the hands (usually on the palms or under the nails), in the foot area. | People from Asian and African countries are susceptible. |
| Lentiginous | Melanocytes accumulate in the epithelium and grow deep into the skin. Localized on the skin of the face (often on the temple), neck, and limbs. In especially dangerous cases - on the tongue, the membranes of the eyes. | Often found in women over 70 years of age. |
| Pigmentless (achromatic) | New growths are flesh-colored or pink. The cells that secrete pigment lose their function. Sometimes a tumor without pigmentation is considered to be a nodular variety. | The most rare. Of all the types of melanomas, this type is diagnosed only in 5% of cases. |
The reasons for the development of skin melanoma lie in a genetic malfunction in the body or a negative effect on moles.
Stages of melanoma
There are 4 stages of skin melanoma. Remember, the sooner the disease is diagnosed and the necessary measures are taken, the higher the chances of a further healthy life.
| Stages of development | |
| Stage | What's happening? |
| First | The disease is not very dangerous. If removed, the chance of recurrence is small. It is also recommended to remove the lymph nodes close to the affected area. The thickness of the lesion reaches 1 millimeter. The integrity of the surface is compromised. |
| Second | Melanoma affects the lymph nodes. The neoplasm is about 2 millimeters thick with a loose surface. During treatment they are cut out. During the period of complex treatment, immunological drugs are used that act directly on the immune system. |
| Third | The tumor continues to grow into the deeper layers of the skin. Treatment consists of immunotherapy, which makes it possible to avoid relapses. The inguinal lymph nodes become inflamed. If there are several affected areas, all are removed. |
| Fourth | Melanoma reaches large sizes. It is removed surgically. If possible, metastases are removed along with the tumor. At this time, the effect of therapy is very weak. |
Skin melanoma manifests itself as changes in moles in color, size, and shape.
How is the diagnosis done?
The main task of the doctor when making a diagnosis is to correctly differentiate a specific pathology from other skin manifestations (carcinoma looks like a cancerous tumor). To confirm a preliminary diagnosis, a number of techniques are used to determine the specific type and stage of the disease. The main ways to determine melanoma include:
Skin melanoma is confirmed or refuted by the results of laboratory tests and hardware examination.
- histological examination;
- X-ray examination;
- cytological examination;
- tissue biopsy;
- lab tests.
Prevention and prognosis
The main prevention is the timely removal of tumors that are constantly exposed to injury. Do not expose your skin to sunlight. Not only your skin, but also your eyes should be protected from sunburn with sunglasses. The prognosis for recovery depends on the time the tumor is diagnosed. Stages 1 and 2 of pathology are treatable and have a favorable prognosis. At grade 3, there is already a 50% survival rate for patients. At grade 4, there is a characteristic extremely unfavorable prognosis.