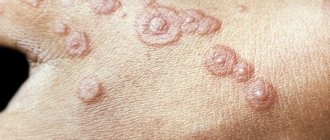
Folliculitis of the scalp is a bacterial inflammation of the hair follicles. The causative agent of the disease in most cases is Staphylococcus aureus. This trouble can take a man, a woman, or a teenager by surprise.
Folliculitis in severe cases leads to hair loss and scarring in the affected areas
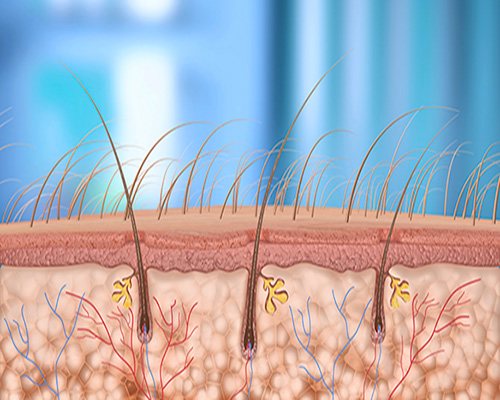
What is a hair follicle
The hair follicle is a pore that is the receptacle of the hair root, where the hair shaft is formed and grows outward from there.
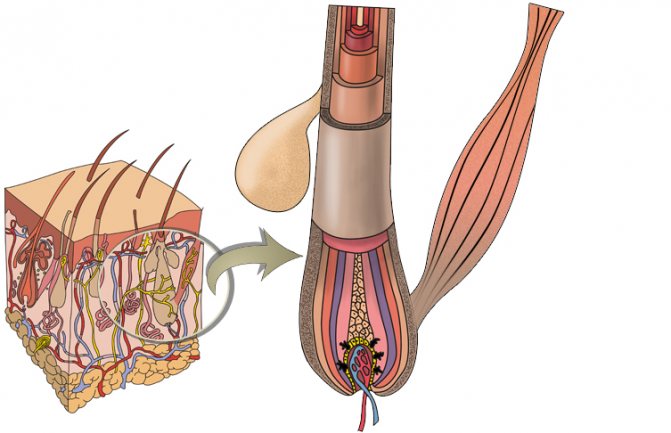
It depends on it what the structure, color and length of the hair will be. The hair follicle is located in the dermal layer. Consists of the following parts:
- hair follicle;
- follicular funnel;
- root sheath;
- holding muscle.
Capillaries, sweat and sebaceous glands also communicate with it. Capillaries are responsible for nutrition, and the sebaceous glands are responsible for lubricating the hair with sebaceous secretion, protecting it from aggressive environmental influences. But in the absence of proper hygiene or excess sebum production, it is the activity of the sebaceous gland that most contributes to the inflammatory process.
Causes
The close location of hair follicles to the surface makes them a target for infections and various fungi, especially when they are damaged during hair removal. Another common cause of inflammation is blockage of the excretory duct of the hair follicle with dirt, particles of dead skin or hardened sebaceous secretions. In this case, sweat and sebaceous secretions cannot find their way out, accumulating in the hair follicle. And as you know, sebum and sweat are a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria, fungi and viruses.
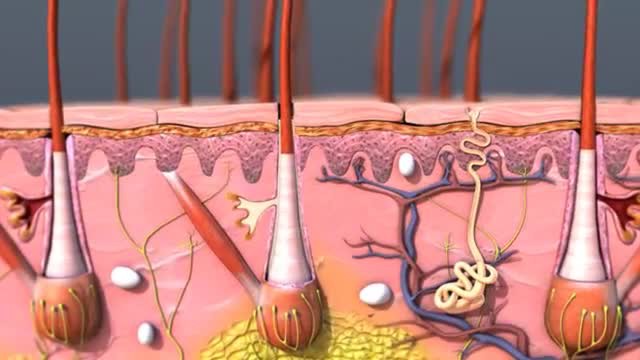
The inflammatory process in the hair follicle is called folliculitis. It is one of the varieties of pyoderma - purulent diseases of the skin layer caused by the activity of microorganisms.
If only one follicle is inflamed, then we are most likely talking about poor hygiene, but in the case where there are several of them, it can already be classified as a rash. This means that it is not just a matter of poor hygiene. The causes of inflammation of the hair follicle may be the following:
- allergic reaction;
- decreased immunity;
- colds;
- hormonal imbalances;
- fungal infection;
- diabetes;
- avitaminosis;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea and syphilis are also accompanied by folliculitis.
The disease occurs in several stages:
- Inflammation of the hair follicle, slight redness is noticeable around the hair.
- Inflammation of the hair follicle down to the root, a pustule is formed, which begins to fill with pus.
- The inflammation affects the entire follicle and the sweat and sebaceous glands communicating with it; a large amount of pus in the pustule is visible to the naked eye.
- Simple folliculitis ends either with the inflammation subsiding or with an opening.
- In case of an unfavorable outcome, it develops into complicated folliculitis.
But you should not count on the fact that the abscess will open on its own and everything will go away. If this is not done on time and under sterile conditions, folliculitis can be aggravated by complications and scars will remain.
How to cure folliculitis
If you make an accurate diagnosis of folliculitis, you must adhere to the doctor’s prescriptions . They will depend on the nature of the disease:
- bacterial folliculitis is treated with antibacterial ointments - Erythramecin or tablets intended for oral administration - Cephalexin and Dicloxacillin;
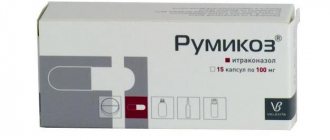
- fungal - antifungal agents, as a rule, such drugs include Flucanazole, Intraconazole and Bifonazole 1%;
- in the case of a gram-negative type of disease, attention should be paid to restoring immunity;
- in the presence of diabetes mellitus, special treatment methods are considered - a therapeutic diet, special medications.
For the treatment of folliculitis, brilliant green, fucarcin, salicylic acid, special lotions and creams from the Klerasil series can be prescribed. In case of severe forms of the disease, antibiotics from the “sulfonamide” group and compresses with ichthyol ointment may be prescribed.
In some cases, the state of health is reflected in a person’s skin, and, despite the fact that folliculitis is infectious in nature, its development can be facilitated by malfunctions of any body systems. Therefore, it is important to promptly consult a doctor if you have suspicious symptoms, which will make it possible to maintain the health and aesthetic appeal of the skin.
Kinds
Folliculitis is classified according to several criteria. According to severity, it is divided into the following:
- easy;
- average;
- heavy.
If it is a mild or moderate type, then after opening the pustules the disease will subside.
Based on the type of microorganisms that cause inflammation, folliculitis is divided into the following types:
- bacterial;
- infectious;
- pseudomonas;
- parasitic;
- fungal;
- viral.
By location on the body:
- genitals;
- scalp;
- cheeks and chin in men;
- eyelashes;
- armpits;
- other parts of the body.
According to the degree of damage, it can be superficial (no more than 5-7 mm) and deep (from 10 mm). It can become deep both in case of a superficial complication, and it can be so initially if caused by a secondary infection. In this case, a painful nodule appears on the outside first. After about 5 days, the abscess itself appears at the site of the nodule.
The nature of the course can be acute or chronic. Untreated acute can develop into chronic. When inflammation affects neighboring follicles again and again. And in the same follicle, inflammation can subside and flare up from time to time.
Folliculitis caused by careless shaving and neglect of disinfection after it is called sycosis.
Features of the diagnosis of folliculitis and its symptoms
Folliculitis is an infectious skin disease that affects the hair follicle. It is characterized by purulent inflammation first of the superficial area of the follicle, and with further development of the process - damage to the deeper layers.
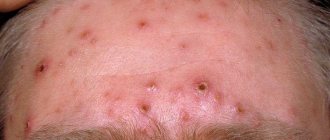
The infection penetrates the skin when it is scratched, through cracks, small wounds, and cuts. This disease manifests itself in the form of one or more purulent pimples, which, when opened, turn into ulcers. Most often they form in places where hair grows on almost any part of the body:
- in the armpits;
- in the groin area;
- on foot;
- on the skin of the face or scalp.
Barley
This is essentially the same folliculitis, but of a more specific localization. Ophthalmologists call it hordeolum. This is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash. Accompanied by hyperemia of the skin of the eyelid and the formation of pustules with pus. A rather painful formation due to its location; often the eyes cannot even be opened due to swelling and pus.
The main cause of occurrence is the entry of Staphylococcus aureus into the hair follicle with reduced immunity.
It is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist urgently – and not to a dermatologist. If an autopsy is indicated, it will be performed exclusively in a hospital setting. How to treat inflammation of the hair follicle on the eye at home? In serious cases, such an idea is extremely unreasonable and can even lead to loss of vision.
What you need to know about the course of the disease
Ulcers burst five to six days after their appearance. The places where they were will become crusty. Hair from follicles weakened by the disease falls out (in most cases). It is worth noting that folliculitis on the head can leave behind such depressing “memos” as scars. It is also possible that boils and inflammation of the lymph nodes may occur after this disease.
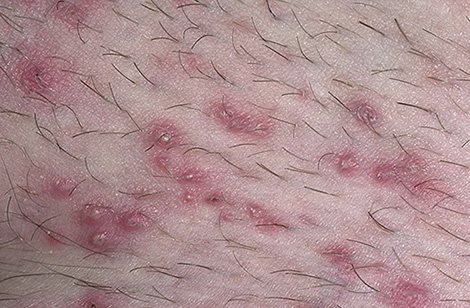
Purulent contents collect inside the hair follicle
Inflammation on the head
As in the case of barley, the main cause of inflammation of the hair follicle on the head is considered to be the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. But about 20% of the total population of the globe is a carrier of it, and not all of them suffer from folliculitis. Because something must provoke folliculitis. Usually this is a decrease in immunity or neglect of hygiene. Folliculitis of the scalp caused by staphylococcus is called ostiofolliculitis.
But it can also occur in older people suffering from cerebral atherosclerosis. They are tormented by unbearable itching of the scalp, and they introduce infection into hair follicles damaged by scratching.
In men, Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis occurs on the head. It is characterized by hair loss on the affected part and the separation of pus from the open fistula.
Inflammation of the hair follicle on the head is especially unpleasant because it is accompanied by partial alopecia. The affected area is difficult to treat with topical ointments unless the hair is shaved. And this is quite tragic for many. In particularly advanced cases, folliculitis leaves behind scars, in the place of which hair will never grow again. Therefore, it is better to treat it completely without causing complications.
Preventive measures against the occurrence of the disease
- Compliance with the rules for caring for the body and face.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Treatment of chronic diseases.
- In bedridden patients, control the condition of the skin.
- Choosing the right shampoo and washing your hair regularly.
- Careful selection of sexual partners.
- Treating the skin with special aftershave lotions.
- Limit contact with chemicals.
Folliculitis is an infectious disease that, with timely treatment, has a positive prognosis and reduces the risk of complications. In most cases, patients are left with age spots, and in severe cases, scars. After a certain time, the skin becomes uniform in color.
Folliculitis - symptoms, causes and treatments
Pyoderma accounts for half of the cases of temporary disability due to skin diseases. A considerable proportion of them belong to folliculitis. They can occur in different people, but most often they affect representatives of certain professions - miners, builders, metallurgists, and transport workers. In this regard, pyodermatitis and folliculitis in particular are socially significant diseases, in the fight against which both the state and employers in the most dangerous industries from the point of view of dermatological morbidity should participate.
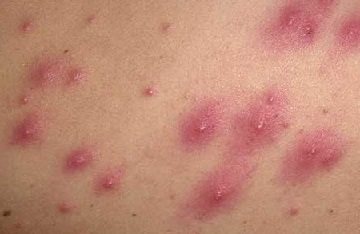
Ingrown hair
Due to frequent hair removal and poor-quality exfoliation of the body in front of it, the hair may not find a way out due to overgrowth of the hair follicle. In this case, it changes its direction and begins to grow inward. Like any foreign body, it thereby causes inflammation. If the hair has not grown far, and the folliculitis has not developed into a severe stage, sometimes it is enough to simply carry out high-quality exfoliation of the body. Then the hair will become accessible so that it can be picked up with tweezers and pulled to the surface. It is advisable to carry out this procedure by a cosmetologist and always under sterile conditions. Since in this case it will no longer grow, the inflammation should disappear. If folliculitis has developed quite severely, then you still need to consult a dermatologist. He will open the inflamed follicle, drain the cavity and prescribe standard treatment for such a case.
Symptoms
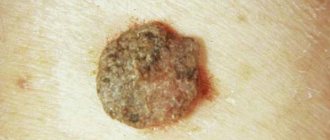
The most striking symptom of inflammation of the hair follicle is the formation of a bubble of pus around the hair. The area around it will be painful, especially when pressed, and prone to hyperemia. But other symptoms may vary for different types of folliculitis.
When bacterial, those areas that are exposed to razors or friction are most often affected. It is multiple in nature and is accompanied by unbearable itching.
The infection may be accompanied by alopecia, which is difficult to treat externally, since the problem is inside the body.
With Hoffmann's folliculitis, a rounded area is formed, which changes its color to icteric-blue with fluctuating contents inside. Hair stops growing on it, and when pressed, pus is released.
Pseudomonas is characterized by the fact that symptoms appear after taking water procedures, including at home. The main reason is infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in ponds and swimming pools. Contact with Pseudomonas aeruginosa itself will not necessarily lead to pseudomonas folliculitis. But after swimming in public places, it is still better to wash your body with antibacterial soap. Most often found in children.
Epidemiological information
Folliculitis is mainly observed in hot countries. Additionally, it is observed in socially disadvantaged sections of society, and this is facilitated by unsanitary living conditions. The pathology is often of a professional nature and is recorded in people whose work activity is associated with the constant influence of aggressive factors - fuels and lubricants. Accurate statistical data is not provided, since in most cases such patients rarely seek medical help and self-medicate. Those patients who, as a result of folliculitis, have developed complications in the form of phlegmon, abscess or lymphadenitis are becoming known.
Complications
In most cases, folliculitis is not serious. But if the disease is advanced, the root cause is not eliminated or the immune system is weakened, then serious complications may appear, such as an abscess, boil, scars, carbuncle and alopecia of the scalp.
An abscess is an inflammation in the deep layers of the dermis that does not allow pus to escape. Gradually, normal tissues are replaced by purulent cavities. It has quite serious consequences and requires urgent opening and drainage of the cavity.
A carbuncle is an inflammation of the hair follicles, but in an acute form, accompanied by partial necrosis of the affected tissues. With a carbuncle, inflammation spreads to the deepest layers of the dermis. The spectacle is not for the faint of heart and threatens inflammation of the soft tissues located under the dermis. Accompanied by intoxication of the body. From the Latin carbunculus translates as “coal”. It got its name because of its external resemblance to a burn.
Furunculosis or boil formation is also a complication of folliculitis. This is an inflammatory process that spreads from the follicle to the connective tissue and is accompanied by necrotic lesions. It is very difficult to cure completely, and it constantly appears again and again, in especially severe cases it does not go away at all. Advanced furunculosis can damage the hair rhizome irrevocably. This means that even after the boil goes away, hair in this place will never grow again. It can also leave a pretty serious scar. These complications are purely cosmetic and do not pose a threat to health.
Purulent skin disease - folliculitis
Folliculitis in dermatology is classified as one of the severe purulent skin diseases called pyoderma. Among the population, this disease occurs quite often - according to statistics, in 40 people out of 100. The disease is most common in countries with hot climates, where conditions contribute to the development of pathogens on the skin, their reproduction, and infection. In particular, if a person lives in unsanitary conditions and does not maintain hygiene, then inflammatory processes on the skin are a natural phenomenon.
Diagnostics
Externally, the cause of folliculitis is not always easy to identify. The absence of infiltration around the hair follicle usually indicates a staphylococcal nature, but this is not enough for a full diagnosis. Sometimes it is quite difficult for a specialist to determine what type of inflammation of the hair follicle it is (including from the photo). For a full diagnosis, a blood test or the contents of the pustule itself, a careful examination and clarification of all accompanying symptoms are required.
To make a diagnosis, a dermatologist may ask about the following points:
- eating habits;
- holidays in exotic countries;
- sexual activity and the possibility of contracting sexually transmitted diseases;
- how long does the disease last?
- how exactly hygiene is maintained;
- are there any diseases of the hormonal system;
- does the patient visit a fitness club, swimming pool and other establishments of a similar nature.
It is important to identify the nature of the disease first of all in order to select adequate treatment. Indeed, depending on what microorganisms caused folliculitis, different medications will be needed.
Classification
Folliculitis can be caused by various infectious agents, so the following types of disease are distinguished:
The main signs are characteristic of all types of disease:
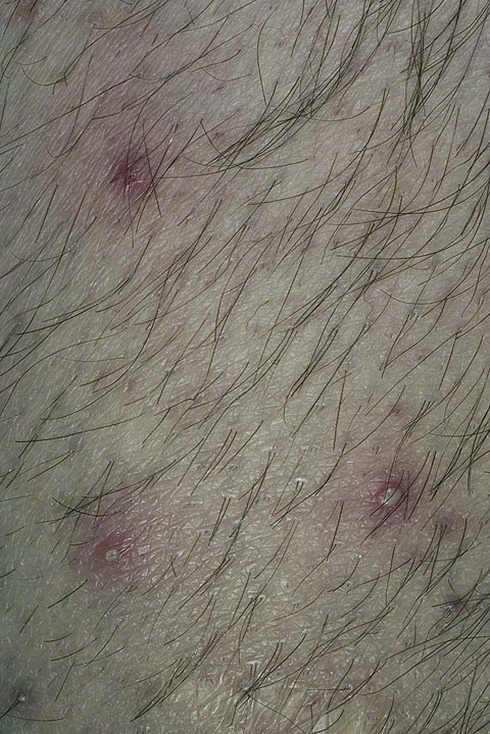
There are several types of folliculitis depending on the area affected. The disease can manifest itself in the following areas:
- on the body;
- on the face;
- on the neck;
- on the scalp;
- on the lower and upper extremities;
- in the intimate area (pubic area, genitals);
- on the back;
- on the buttocks;
- armpits.
The most common are bacterial types of folliculitis. They are diagnosed in almost 60% of all cases of the disease. There are several varieties of it:
Types of folliculitis mainly depend on the shape, location and causative agent of the disease:
- According to the shape of the flow they are divided into:
- By location:
- Superficial - when the crusts fall off, the skin has a light or dark shade than other areas of the skin.
- Deep – formation of boils.
- By pathogen:
- Staphylococcal: ostiofolliculitis and sycosis.
- Pseudomonas (“hot bath”) - develops after a bath where the water is poorly chlorinated.
- Gram negative – formation of abscesses.
- Dermatophytic: scalp, mustache, beard, Majocchi granuloma.
- Pityrosporum.
- Candidiasis - treatment with occlusive dressings and corticosteroids.
Taking into account the etiology of the infection, experts have identified the following groups of the disease:
- fungal;
- bacterial;
- syphilitic;
- parasitic;
- viral.
Treatment
If you open the abscess in time, disinfect it and cover it with a band-aid during the scarring, most often additional treatment for inflammation of the hair follicle will not be needed. The main thing is not to touch the formed pustules and ulcers with dirty hands.
But often inflammation is noticed at stages 2 or 3, when it is better not to interfere. Especially if it comes to tissue necrosis. In this case, you need to contact a dermatologist. He will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis, after which, if necessary, he will refer you to the purulent surgery department so that the surgeon will perform an autopsy and subsequent drainage of the purulent cavity in a hospital setting. You can leave the hospital the same day and go home. After the pustule empties, the symptoms gradually regress.
Next, the specialist will make instructions on how to further treat inflammation of the hair follicle at home. Conservative therapy in the form of antibiotics is usually followed. The type of antibiotics depends on what microorganisms caused the folliculitis. Therefore, they should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, based on this and other individual factors.
Subsequently, you will have to visit the surgeon several times so that he can wash the wound and bandage it. This will be necessary until the wound heals and the risk of infection has passed. If it is not possible to visit the surgery department every day, then the dressing can be done at home, but be sure to follow all the surgeon’s instructions.
If an autopsy is not required, then the affected area is treated with alcohol and local ointments until the inflammation subsides. If it is a stye on the eye, ointments are placed directly under the eyelid. Sometimes it is adequate to use physical therapy, such as irradiation with a quartz lamp or UHF therapy. But in case of acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, this may be contraindicated.
It is prohibited to use any compresses or dry heat at home without consulting a doctor, as unknowingly you can provoke aggravation of the situation.
Folliculitis in the groin: what is it and why does it occur. – Venereologist
Skin diseases can cause many problems.
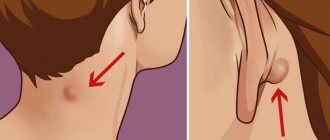
For example, inflammation of the hair follicle under the armpit, in addition to painful sensations, will make it impossible to maintain personal hygiene and wear open clothes. For quality treatment, it is necessary to recognize the disease in time and use the right means. Inflammation of the follicle under the arm is a common occurrence.
A small abscess is a big danger
A disease in which the hair follicle becomes inflamed is called folliculitis. As a rule, it can occur due to infection with Staphylococcus aureus/white, fungus, etc.
Folliculitis is one of several forms of pyoderma. This inflammation is infectious in nature.
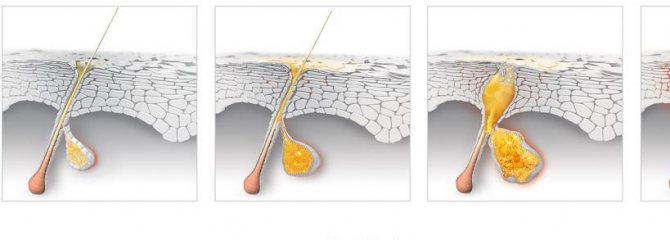
Inflammation of the hair follicle occurs according to the following scheme.
- A red or pinkish papule forms . The surrounding skin may remain untouched or may also become red.
- In the central part of the papule, an abscess (pustule) gradually matures . In its center there is a hair, which sometimes may not be visible.
- Gradually the pustule resolves or opens . A crust forms in its place.
Note! Superficial folliculitis leaves virtually no traces behind.
If it is deep, a boil may form.
The whole process takes several days. In severe cases, it may take at least a week to get rid of folliculitis. Boils take much longer to resolve and may sometimes require surgery.
Comparison of healthy and infected hair follicles
What causes folliculitis?
If the root cause is eliminated, the disease will disappear. However, if the infection remains in the body, folliculitis can recur.
As a rule, new inflammation is provoked by certain factors:
- Mechanical injuries to the skin caused by shaving, depilation, plucking;
Inflammation can occur after shaving
- Diaper rash that occurs in folds (for example, under the breasts or in the armpits). This problem becomes especially relevant in the hot season;
- Taking medications (for example, antibiotics, immunosuppressants) that reduce the body's barrier functions;
- Some diseases (for example, diabetes, anemia).
For example, the follicle may become inflamed after waxing
The disease has a “habit” of manifesting itself in certain places of the body. The parts most often affected are those covered with so-called “vellus hair.”
In this regard, inflammation can be observed:
- on the scalp;
- in the armpits;
- on the pubis;
- in the groin;
- on the lower parts of the arms and legs.
How to identify folliculitis
In the initial stage of folliculitis, it is easy to confuse it with a regular pimple. The main difference in this case: the presence of incipient inflammation of the hair in the center. The number of folliculitis can vary and range from 1-3 to entire colonies.
The disease is often also characterized by:
- itching in the affected area;
- soreness when touched;
- close location of pustules with their massive nature.
Squeezing can lead to serious infection
It should be noted that under no circumstances should you open folliculitis yourself. This can lead to serious spread of the disease and deeper infection. Proper treatment of inflammation of the hair follicle will help protect yourself from an unpleasant and unaesthetic infection.
Advice! If you suspect the initial stage of folliculitis, consult a dermatologist.
He will prescribe a special examination that will help determine the type of disease and prescribe the correct treatment.
Possible complications
Most often, the inflammatory process goes away on its own. In ordinary cases, a person’s life is safe.
However, if not:
- treatment;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- immune response
Unpleasant complications may develop.
These include:
- formation of boils and carbuncles;
- abscess (tissue inflammation followed by decay);
- formation of unsightly scars.
Photo of a boil - complications of folliculitis
If the first two types of complications are the result of improper or insufficient treatment, the latter appears due to aggressive mechanical action. Most often, unsightly scars are obtained by regularly “squeezing out” pus with your own hands and tearing off the crusts during the healing process.
How to cure folliculitis
You can get rid of inflammation using several methods, used individually or in combination.
These include:
- local treatment with a special solution;
- opening;
- antibiotic therapy;
- compresses.
Self-treatment can lead to irreversible processes. Take medications only as prescribed by a cosmetologist or dermatologist
What to process
Treatment of folliculitis is effective if the disease is “caught” at the very beginning.
As a rule, widespread, over-the-counter products are used:
- brilliant green;
- camphor/salicylic alcohol (only 1-2%);
- fucorcin;
- methylene blue.
Salicylic ointment will also help with this problem in the first stages of its manifestation.
These solutions can be found at any pharmacy. The average price of funds is 30-60 rubles. Any of these solutions must be kept in your home medicine cabinet.
Autopsy of an abscess
An autopsy is performed in particularly acute cases, when there is a large accumulation of purulent masses. Very often, this procedure is performed if there is inflammation of ingrown hair on the pubic area, head, buttocks, etc. This process is quite difficult to stop and cure exclusively with external use.
Zelenka is a well-known antiseptic
The autopsy must be performed in a medical facility. The doctor will carefully cut the abscess with a scalpel and remove the accumulated pus. You will then be given detailed instructions for care at home.
After opening, the wound must be regularly treated with drying solutions (for example, fucorcin or brilliant green). The formed crusts cannot be peeled off. Sometimes a doctor can prescribe a course of antibiotics that will help “kill” the infection in the body and prevent blood poisoning.
Compresses according to traditional recipes
Traditional recipes are often safe, and their effectiveness is time-tested. That is why treatment of inflammation of the hair follicle can begin with the creation of special compresses based on herbal decoctions. (See also the article Cream: slowing hair growth: how to use.)
The decoction will help cope with folliculitis without incisions.
One of the best remedies is a decoction of rose hips and viburnum.
For it you will need:
- viburnum and rosehip berries (200 g each);
- green nut shells (10 g);
- dried nettle (100 g);
- fresh cottage cheese (50 g);
- water (2 glasses);
- honey (50 g).
Rinse all berries with clean water. Place the nutshells and nettles in a saucepan and cover with hot water. Bring to a boil, simmer for 10-15 minutes over low heat. Leave to infuse for a day in a warm, dark place, and then strain.
For a compress, mix honey and cottage cheese. Add 2 large spoons of the strained mixture to them. Wrap the resulting product in gauze/bandage and apply to the inflamed follicle for at least 15-20 minutes. The procedure must be repeated 3-4 times a day.
Chamomile solution also has excellent soothing and antibacterial properties. (See also the article Chamomile decoction for hair: how to use.)
To prepare a useful product, use:
- chamomile (unpackaged dried flowers);
- boiling water.
Chamomile compresses will help relieve inflammation
Pour two large spoons of crushed chamomile into a glass of water. Bring to a boil over low heat and simmer for about 10-20 minutes. Cool and leave overnight.
Use the decoction as a topical disinfectant. Rub it over the damaged areas two to three times a day. The follicles will dry out, swelling will decrease, and the skin condition will quickly return to normal.
Summary
Folliculitis is an unpleasant but harmless disease
However, incorrect or late treatment can lead to serious complications. To prevent this, find out more information on this topic from the video presented in this article.
Source: https://antiaids41.ru/prochee/follikulit-v-pahu-chto-eto-i-pochemu-voznikaet.html
Prevention
The main type of prevention is personal hygiene and the use of antibacterial soap.

But here are some more useful tips to avoid this disease:
- After hair removal, you should not neglect the scrub and disinfecting lotion.
- Mascara can only be used by one person and for no longer than three months.
- The towel must be washed in water at least 90°C and at least twice a week.
- Take a fresh face towel every day.
- Always wash thoroughly after visiting public bathing areas.
- Avoid unprotected casual sex.
- Thoroughly treat all personal hygiene items with an antiseptic.
- Do not scratch the itchy areas with your nails or at least trim them.
- Wear underwear and clothes made of cotton, as synthetics promote the growth of bacteria.

Maintaining a healthy lifestyle in general will boost your immunity and protect you from such skin diseases.