Squamous cell papilloma is most often found in older people, but sometimes representatives of the younger generation also face a similar problem. This disease does not always lead to life-threatening and health-threatening consequences, but it must be treated in a timely manner.
Squamous cell papilloma of the skin is dangerous because it may not cause discomfort to a person for a long time, but under the influence of provoking factors it turns into a malignant tumor.
This type of skin growths are benign tumors consisting of squamous epithelial cells and stroma. Most often found in the area:
- faces;
- esophagus;
- genitals;
- throat.
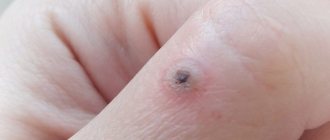
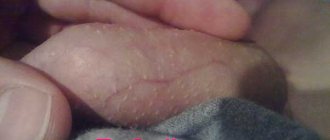
Flat papillomas in intimate places look like rounded tubercles with a diameter of several mm to 3 cm. The formation can have both a soft and hard structure. When injured, the growths can become malignant. The combination of papilloma with hyperkeratosis is considered especially dangerous in this regard.
The growths can be either single or multiple. When merging with each other, they form clusters resembling cauliflower, which can be seen in the photo. Neoplasms appear when pathogens of the papillomavirus group become active. It is HPV that causes pathological changes at the cellular level with subsequent hypertrophy of the epithelium.
What causes papillomas?
The main reasons for the penetration of the infectious agent are considered to be unprotected sexual intercourse (both vaginal and oral). In rare cases, household transmission of the virus is possible. Infection occurs through contact with infected objects, shaking hands, or using common hygiene items. The provoking factor is the presence of wounds and cracks in the skin. The appearance of squamous cell papilloma may result from a visit to a bathhouse or sauna.
The disease in its early stages occurs in a latent form. However, with a decrease in immunity or under the influence of unfavorable factors, the skin begins to become covered with characteristic growths.
Other reasons for the appearance of flat papillomas on the body include:
- advanced age;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- allergic reactions;
- upper respiratory tract infections;
- psycho-emotional shocks;
- alcoholism, smoking and drug addiction;
- metabolic disease;
- taking hormonal contraceptives.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
Most often, squamous cell neoplasms appear in places where there is stratified squamous epithelium: skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx, esophagus, vagina. Doctors believe that such a neoplasm may be a variant of metaplasia - a change in the structures of the epithelium, leading to uncharacteristic manifestations. For example, the appearance of a defect in the esophageal mucosa can provoke keratinization of a wart.
The etiology and pathogenesis of the disease are not fully understood. There are two versions of the appearance and development of the defect, but neither has yet been confirmed.
According to one version, squamous cell papillomas appear in an area that is constantly exposed to mechanical, physical or thermal influences. Acids, alkalis, high temperatures, and friction irritate the epithelium of the skin or mucous membrane. Constant irritation triggers processes in which the designated structures grow. As a result, the formation of papilloma.
According to another version, neoplasms appear as a result of HPV infection. Their growth is detected in carriers of different strains of the human papillomavirus.
Infection can occur during sexual contact with a sick person, through microscopic damage to the skin during a handshake, or when using someone else's towel or washcloth. The risk of infection transmission increases in places of high humidity: swimming pools, gyms, saunas.
Once in the body, the virus is not immediately activated. The incubation period can last from six months to two years. However, even then the development of infection becomes unnecessary. A strong immune system can stop the virus from multiplying. Activation is possible only in the presence of immunodeficiency conditions.
Structure and symptoms of growths
A skin growth of this type has a structure similar to other neoplasms. The main difference is the structure of the outer shell. In papilloma, it has a multilayer coating, while other growths consist of transitional epithelial cells. The inside of the tumor is a collection of connective tissues and blood vessels.
Flat papillomas are classified based on location. Lesions occur:
- larynx;
- penis;
- esophagus;
- cervix.
Characteristic features:
The disease is especially often found in men who abuse alcohol, smoking and fast food. Papillomas most often affect the middle and lower parts of the esophagus. The growths have the appearance of tubercles with uneven edges, slightly protruding above the mucous membranes. The structure of papillomas can be studied in detail using photographs. The size of the tumors does not exceed 2 mm. They can be represented by single or multiple growths.
The main cause of papilomatosis of the digestive system is HPV infection against the background of stomach pathologies. Young people are increasingly facing this problem. The reasons for this are:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- neglect of contraception;
- constant stress;
- bad habits.
Papilloma that appears in the esophagus does not manifest itself for a long time. It is discovered when other diseases are detected.
The following symptoms help to suspect the presence of a benign tumor:
Despite the fact that squamous cell papilloma of the larynx and esophagus is a fairly rare disease, it is considered the most dangerous. It is this form that is most susceptible to malignancy.
Symptomatic manifestations
In addition to their specific appearance, papillomas have a number of other manifestations, depending on the location of the lesion. The following symptoms can be expected from flat papillomas:
- If the digestive system is affected: in the tongue - swelling, unpleasant odor from the mouth, ulcers on the surface of the tongue, deterioration of its mobility, pain while eating; on the lips - swelling, ulcerative manifestations, active growth of formations in the mouth area; inside the oral cavity - swelling, problems with swallowing movements, distortion of diction, excessive salivation, pain when chewing, feeling of a foreign body in the oral cavity.
- In the esophagus - signs of nausea, excessive salivation, temporary pain, belching, vomiting with blood, bad breath; in the intestines or stomach - foul-smelling discharge, temporary pain, vomiting with traces of blood, diarrhea with blood, itching in the anus, periodic problems with the passage of food.
- When the lesion is located in the respiratory system: damage to the nasal cavity - bleeding from the nose, an enlarged nostril on one side, constant nasal congestion, slight pain, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the nasal cavity; in the larynx - speech impairment, breathing difficulty, problems with swallowing movements, frequent hiccups, hoarseness of voice.
- Papillomas in the genitourinary system are most dangerous when they grow on the cervix, since they often provoke malignant formations. Characteristic symptoms: discharge in the form of leucorrhoea, pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal itching, uterine bleeding. In other localizations, problems with urination, traces of blood in the urine, and pain in the genital area appear.
- Skin papillomas grow relatively slowly. Areas with delicate skin are most often affected. The main symptom is an external manifestation in the form of a growth or flat ulcer.
How are squamous cell papillomas diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with a dermatological examination. In this case, the doctor analyzes the patient’s external signs of the disease. To confirm the diagnosis, scrapings and smears are analyzed. If malignant degeneration of the growth is suspected, a biopsy is indicated.
Treatment of oral papillomas is prescribed by an otolaryngologist.
In the presence of tumors in the larynx, a number of diagnostic procedures are performed: laryngotracheoscopy, biopsy followed by histological examination, CT.
If papilloma is detected on the gum, you should contact your dentist.
To identify papillomas on the mucous membranes of the esophagus, the gastroenterologist uses the following methods: FGDS, radiography with the introduction of a contrast agent, biopsy followed by histological examination, CT and MRI. A specialist will tell you how to get rid of growths during your appointment.
Description and structural features
Squamous cell papilloma is a benign small growth that grows in the squamous epithelium of the skin, on the lining of the esophagus, mouth, larynx or vagina. Such a wart has its own connecting stroma with thin blood vessels.
This type of papilloma often grows on the facial and cervical skin, as well as in the esophagus, mouth, uterine cervix and other human organs. In appearance, such a tumor is a round wart with a diameter of up to 30 mm. Its color is flesh or dark brown.
To the touch, squamous cell papillomas can be soft or hard, depending on the type of stroma (base). When injured, such a tumor often becomes oncogenic - a person develops cancer. More often this happens if, in the presence of papilloma, the patient develops hyperkeratosis (thickening of several layers in the epidermis).
A squamous wart contains several thin vessels, a stroma of various connective tissues, and sometimes small nerves.
When cancer-like tumors appear, their appearance changes slightly. Then pearlescent gray balls (cancer pearls) form on the papilloma, and small ulcers appear.
Therapeutic techniques
Flat papillomas of the cervix, mouth and skin bring a lot of discomfort to a person. That is why most patients have a question: how to get rid of unattractive growths? The most commonly prescribed surgical treatment, the main types of which are:
- low temperature exposure;
- laser destruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- removal of papilloma with a scalpel.
The second method is considered the safest. Using a targeted beam, you can remove skin tags on any part of the body, including lips and eyelids.
It is often possible to remove large papillomas on the body only with the help of classical surgery. For these purposes, medical scissors or a loop-shaped instrument are used. Treatment of laryngeal papilloma can be carried out in two ways: open surgery and endoscopic intervention. The use of the second method shortens the recovery period and reduces the risk of complications. Growths present on the mucous membranes of the esophagus can be removed in the same way. The material removed during the operation is sent for histological analysis.
If there are papillomas in the area of the eyelids and lips, the attending physician may recommend radio wave destruction. The main advantage of this therapeutic technique is the low risk of injury to the skin and mucous membranes, as well as the penetration of pathogenic microflora. Tissue healing occurs without scarring. Various chemicals are also used:
- trichloroacetic acid;
- potassium permanganate;
- silver or lead salts;
- hydrogen peroxide solution.
After surgery, treatment of papillomatosis continues. The doctor prescribes antiviral drugs, vitamins and immunostimulants. It is recommended to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, harden the body, and eat right. Is it possible to display flat ones, what means are used for this?
Locations
Squamous cell papillomas are very common and can occur in many areas.
Face
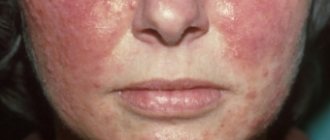
It is the skin of the face that most often suffers from the presence of viral tumors. They usually affect the eyelids, neck, or area behind the ear. These areas have delicate skin that is prone to increased trauma, which can aggravate the progression of the disease.
If PP appears in the eyelid area, the eyes may be at risk. This entails potential loss of vision, so the growths must be removed. In this area, papillomas are usually small in size and grow slowly.
Esophagus
Squamous cell papillomas in the esophagus are usually rare. If they are present, the patient experiences symptoms such as:
- belching;
- nausea;
- intense salivation;
- stomach pain.
Neoplasms in the esophagus are considered a rare type of growth that practically never occurs.
Cervix
PP on the mucous membranes of the cervix is difficult to diagnose without examination by a gynecologist. For a long time, the disease in this area can be asymptomatic.
Only after a few years does HPV lead to the development of cervical dysplasia. At the same time, a few symptoms in the form of itching, changes in the abundance of discharge do not directly indicate this pathology.
The gynecologist determines the presence of a problem during a visual examination. In some cases, colposcopy is used for diagnosis.
Larynx
You can notice the presence of a growth in the larynx area by the following signs:
- the appearance of hoarseness;
- labored breathing;
- problems with swallowing food.
Typically, this type of neoplasm is typical for children. The presence of multiple growths indicates laryngeal papillomatosis.
Asian with his right foot inflamed due to gout.
This type of papillomas has a leg that can tear away from its place and end up in the respiratory tract. This puts the patient at risk of suffocation. Therefore, such growths must be removed without waiting for them to grow.
Alternative Treatments
Some folk recipes are quite effective in removing squamous skin growths, but they must be used in combination with traditional therapeutic methods:
- Fresh potatoes are peeled and grated on a fine grater. The resulting mass is filtered through cheesecloth, the juice is taken 2 times a day, 0.5 cups before meals. Treatment lasts 60 days.
- Celandine leaves are finely chopped, and then the juice is squeezed out of them. The liquid is boiled until its volume is significantly reduced. The concentrate is used to treat the affected areas 3 times a day. The death of papillomas begins a month after the start of treatment.
- Garlic is grated or cut into thin slices and attached to the affected areas of the skin using a patch. The procedure is carried out 2 times a day, it should not last more than 3 hours.
It must be remembered that any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. You can avoid infection by observing the rules of personal hygiene, avoiding casual intimate relationships, and using barrier methods of contraception.
If papillomas do appear, it is necessary to protect the skin and mucous membranes from direct sunlight, lead a healthy lifestyle, and introduce vitamin-rich foods into the diet. All chronic diseases must be eliminated in a timely manner.
Squamous cell papilloma is a benign formation arising from the growing squamous epithelium, stroma and vessel at the base. It often occurs in elderly people in places exposed to constant traumatic effects.
Benign tumors of the skin of the face, head and neck: Squamous cell papilloma
Squamous cell papilloma
- a benign tumor originating from the squamous epithelium of the integumentary tissue.
Occurs more often in older people. It grows slowly. In young people, squamous cell papilloma occurs in areas subject to constant trauma. The clinical picture is very diverse and depends on the duration and severity of keratinization processes, papillary growths, and the presence or absence of a stalk. Clinic
.
Papillomas appear in the form of single warty formations, although there are also multiple papillomas localized in one place - papillomatosis. The papilloma rises above the skin level and is located on a thin stalk or wide base. Most often mobile, with the exception of long-existing papillomas. The color of papillomas varies: from the color of normal skin or whitish to gray or dark brown, with a diameter of 0.3-1.5 cm, maybe more. The shape is round or polygonal, similar to “cauliflower” or “raspberry”. Depending on the severity of the stroma, it can be soft or dense. The surface is villous or covered with easily detachable horny masses. When injured, they are easily destroyed and inflamed. With chronic injury, it may degenerate into a malignant tumor - squamous cell carcinoma. Histological picture
.
Papilloma is built from cells of a growing epithelium, keratinization is unevenly expressed. A pronounced intrinsic membrane is noted. Tissue atypia is represented by uneven development of the epithelium and stroma, as well as excessive formation of small blood vessels. Differential diagnosis
is carried out:
- with fibropapilloma, which, unlike papilloma, is located on a thin stalk, and the surface is represented by wrinkled, slightly pigmented, hairless skin;
- Papilloma differs from wart vulgaris in its localization, more often on the face and torso, and in middle-aged and elderly patients. Also, these diseases differ in the number of elements and the duration of their existence. Papillomas are single and exist for decades, while warts are multiple and capable of self-resolution. The histological structure is also different;
- Seborrheic keratosis is distinguished by its dark color, significant size of elements and the fact that it is often localized in closed areas of the body. Quite often, with seborrheic keratosis, powerful hyperkeratotic growths develop. With seborrheic keratosis, a waxy sheen is noted on the surface, which does not happen with papilloma;
- with senile keratoma, the lesions are localized in open areas of the body and are covered with dense crusts, after removal of which a compacted bleeding base is exposed;
- with a cutaneous horn, which is characterized by massive hyperkeratosis and tightly packed scales, whereas with papilloma they are easily rejected. On palpation, the cutaneous horn is dense and motionless;
- The difference between fibroma and papilloma is given when describing fibroma.
Treatment
is surgical. Tumor excision, cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation, laser destruction. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, often using modern anesthetics: lidocaine, ultracaine, mepivacaine. Advantage should be given to the surgical method, since it allows for histological examination and the cosmetic effect is much higher. A schematic representation of the operations used in the excision of not only papillomas, but also other benign tumors is presented in the figures. It should be noted that when removing benign formations on the lower eyelid with small tumors up to 0.5 cm, a horizontal incision is used. If the formation is more than 0.5 cm, then it is better to use a vertical incision. This technique is used to prevent cicatricial eversion of the eyelid. It must be remembered that all excised material is subject to mandatory histological examination.
Schematic representation of operations used in excision of papillomas and benign tumors
: a - diagram of excision of the formation of the lower eyelid and suture line;
b - diagram of excision of a forehead formation and suture line. Scheme of operations for excision of formations in the buccal region, intradermal suture. Postoperative management is the same as for conventional elective operations. A regular aseptic dressing or dressings such as Op Sait Postop, Primapore are applied to the wound - these are modern dressings with antibacterial and hypoallergenic properties () or similar dressings. If interrupted sutures are used, then the first suture is placed in the middle of the wound and all subsequent sutures follow the principle of dividing in half. Interrupted sutures are removed one at a time on the 6-7th day, provided that the healing process proceeds without complications, the remaining sutures are removed the next day. If the wound is sutured with an intradermal suture, it is removed simultaneously on the 7th-8th day. “Diseases, injuries and tumors of the maxillofacial region,” ed. A.K. Iordanishvili
Features of papillomas
Places where squamous cell papillomas can occur:
- skin: face, collar part of the neck, lower back, arm area;
- mucous membranes: oral cavity, larynx, esophagus, rectum.
Such formations grow slowly, do not cause any inconvenience and do not pose any particular danger to health. But if you are not careful, they can be injured, which can lead to the risk of papilloma transforming into a malignant tumor.
The main cause of papillomas is papillomavirus (lat. Papillomavirus). You can become infected with the virus in several ways:
From the histological side, papilloma is an overgrown squamous epithelium and stroma, with uneven tissue atypia. It has a developed circulatory system in its structure. Papillomas do not appear immediately. The virus can remain in the human body for a long time, and manifests itself only in the presence of certain factors:
- weakening of the immune system;
- elderly age;
- dermatoses;
- allergies;
- infectious diseases;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- harmful environment;
- stressful situations;
- genetic predisposition.
Squamous cell papillomas are classified according to their location on the body:
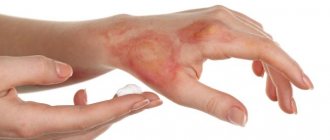
- Squamous cell papilloma of the skin. Such warts appear in places of increased trauma: the skin of the face, neck, hands. Often it does not cause health problems. The question is more about aesthetic appearance.
- Papilloma of the mucous membranes. The problem here is more significant. The mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx, esophagus, and rectum are often irritated. This can lead to their traumatization and subsequent malignancy. In addition, they cause inconvenience, causing sensations of a foreign object, the inability to perform certain functions, and simply cause discomfort.
Where are flat papillomas located?
Squamous cell papilloma occurs on the human skin. Often this is the back of the hand, lower legs, shoulders or forearms. A flat papilloma on the face can appear like a papilloma on the body. Such formations are also localized on the genitals.
It is necessary to concentrate on papillomas that appear on a person’s neck. This occurs due to a malfunction in the functioning and production of hormones.
When changing clothes, carriers of this formation experience pain and discomfort. A papilloma in such a place makes a person feel discomfort and can have a bad effect on his psychological state.
This type of human papillomavirus can occur either singly or as a group of formations that are close to each other. Group warts strongly resemble an allergic rash.
Very often, such formations go away on their own, without outside intervention.
The body reacts to squamous cell papillomas in different ways.
It depends on the age category of the infected:
- In children and adolescents, flat papilloma can appear on different areas of the skin. It is very rare to observe a formation at the site of injury. Due to stress and improper daily routine, the growths grow and occupy a significant area of the skin.
- In middle-aged people, papillomas arise at the site of contact with the source of viral infection.
- The adult generation suffers from a large number of widespread infections throughout the body. This happens because the immune system is weakened. It does not protect the body from viral infection.
Flat papillomas can cause great discomfort when wearing clothes. The cloth rubs the infected area. Due to such mechanical damage, warts become inflamed, which in some cases leads to changes in formation.
From a benign papilloma, when damaged, growths develop into malignant ones.
Diagnostics and treatment methods
The main methods for diagnosing and differentiating warts are:
- external examination and assessment of education;
- biopsy;
- taking smears from surrounding tissues.
The examination of papilloma is carried out by a certain doctor, depending on its location. If it is present in the larynx, the check is carried out by an ENT specialist. If in the esophagus or stomach - a gastroenterologist. In the rectum - by a proctologist.
Additional research methods include blood tests, ultrasound, MRI or CT, and endoscopy. They are used if papilloma is located in hard-to-reach places or if there are complications.
Often, a visual examination is sufficient to make the correct diagnosis. Diagnostics are carried out to confirm or refute the onset of transformation into a malignant tumor.
The doctor decides how to get rid of papilloma. He can assign deletions using one of the following methods:
Traditional methods
You can use home recipes to remove warts, but experts do not recommend resorting to this without their consultation. The fact is that when carrying out the removal procedure at home, a person cannot know about the condition and shape of the papilloma. If the papilloma has become malignant, treating it with traditional medicine can seriously worsen your condition.
If the doctor approves of this method of treatment, you can use one of the following methods of removing papillomas using folk remedies:
- You can get celandine juice yourself or buy it at any pharmacy. Celandine extract allows you to remove the problem on the skin after 3 weeks of use. You need to apply it to the wart 2-3 times a day. You need to be careful. Accidental contact of celandine extract with healthy skin can cause a chemical burn.
- You need to crush a clove of garlic into a paste and apply it to the papilloma, securing it with an adhesive plaster. You need to do the procedure 2 times a day, leaving the product on the growth for about 3 hours.
- You need to squeeze the juice out of clean potatoes and strain it through several layers of gauze. The resulting juice should be taken 100 ml 2-3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Duration of the course is 2 months. While using the removal method, you need to take immunostimulants. This will increase the speed of treatment and improve skin regeneration.
In most cases, the wart is removed completely and without health consequences. The only reminder may be a small scar, which is removed by cosmetologists or plastic surgeons. If you carry out removal procedures at home without first examining a doctor and his recommendations, problems may arise in the form of skin burns or digestive disorders. In the worst case, injury to the wart and its malignancy.
Feedback from our reader - Marina Evstratieva
I recently read an article that talks about the NATURAL effective remedy Papilight for warts and papillomas. With the help of this drug you can PERMANENTLY get rid of papillomas and warts both INSIDE and OUTSIDE
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered a package. I noticed changes within a month: my papillomas disappeared. My husband got rid of warts on his hands in two weeks. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
Squamous cell papilloma is not a big problem for human health, and therefore does not require urgent removal. Before you decide to eliminate such a problem, you must consult a doctor. This will avoid complications and protect yourself from negative consequences.
Are you sure that you are not infected with the PAPILLOMA virus?
According to the latest WHO data, 7 out of 10 people are infected with the papilloma virus. Many live and suffer for years, not even suspecting diseases that destroy internal organs.
- fatigue, drowsiness...
- lack of interest in life, depression...
- headaches, as well as various pains and spasms in the internal organs...
- frequent rashes of WARTS and PAPILLOMAS...
These are all possible signs of the presence of the papilloma virus in your body. Many people live for years and do not know that there are time bombs on their body. If measures are not taken in time, then in the future this may result in cancer, an increase in the number of papillomas and other problems.
Perhaps it is worth starting treatment now? We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the new method of Elena Malysheva, which has already helped many people cleanse their bodies of the papilloma virus and get rid of warts and papillomas...
Many people develop small oblong formations on the skin of the body - papillomas, as a result of infection with papillomavirus. In some cases, these formations become dense, with a rough surface due to the growth and compaction of the stratum corneum of the skin, which contains the dense protein keratin. These are keratopapillomas.
What is keratopapilloma? This is a benign neoplasm that does not pose a threat to health. However, it is also not an adornment for the skin, especially if it is located on the face, neck, or in the eyelid area, but the point is not only about beauty. Keratopapillomas of the skin growing on the scalp, in the collar area, on the lower back are often subject to injury - with a comb, collar, belt, and if they are located near the mouth - exposed to food.
Important! Systematic trauma to the neoplasm leads to its inflammation, growth, and sometimes to malignant transformation into skin cancer. Therefore, treatment of keratopapilloma is necessary.
Symptoms
The symptoms of each type of squamous cell papilloma are directly related to the place of its formation.
The following signs are characteristic of external such growths:
- the wart has a diameter of up to 3 cm;
- such tumors become horny;
- they have small sores;
- The outer growths turn red, swell, and then swell a little.
When such warts appear on the skin, a person experiences slight pain, itching and burning, and the patient also develops various problems with the lymph nodes.
When 1 or several squamous cell papillomas form in the throat, a person experiences the following symptoms of HPV:
- it becomes difficult for the patient to swallow;
- difficulty breathing through the throat;
- diction and speech are impaired;
- the presence of a foreign tumor is felt in the throat.
The size of the laryngeal HPV tumor sometimes reaches 3 mm.
When squamous cell growths appear in the mouth, the patient has the following problems:
- difficult to swallow;
- pain occurs when swallowing food, food, saliva;
- diction is impaired.
When such a tumor occurs on the tongue, a person suffers from the following HPV symptoms:
- tongue swelling;
- bad breath;
- the presence of small wounds that also bleed;
- the appearance of pain when chewing and swallowing food;
- limitations of language movements.
If warts grow in the lip area, the patient develops the following signs of papillomavirus:
- lip swells;
- papilloma gradually increases in size;
- pain appears when touching a wart.
When 1 or several buccal papillomas appear, a person suffers from the following HPV symptoms:
- swelling of the cheeks;
- increased salivation;
- speech distortions;
- having difficulty chewing food.
When such warts form on the genitals, the patient experiences the following symptoms of papillomavirus:
- unpleasant white discharge;
- menstrual bleeding (in women);
- pain in the lower abdomen.
If such symptoms appear, a person should immediately contact their doctor.
Skin neoplasms
Squamous cell papillomas most often grow on thin skin areas. For example, on the eyelids, in the neck and chest area.
If such a growth appears on the eyelid, then the person’s conjunctiva (transparent, thin tissue that covers the eye cornea) is destroyed. Then, the patient's vision quickly declines.
If a squamous cell papilloma grows on the skin, it then no longer grows. Its diameter is 0.3−1.5 cm.
If such a new growth grows for too long, it becomes like a blackberry. Such a wart becomes flesh-colored or purple.
A squamous wart grows not only on the skin, but also on the uterine cervix.
Under no circumstances should the patient touch the papilloma.
Otherwise, then redness appears around such a tumor, and when an infection gets into it, such a growth often becomes oncogenic.
After the appearance of a malignant neoplasm, the attending physician refers the patient to an oncologist.
Respiratory system
Larynx
When 1 or several squamous cell papillomas form in the larynx, a person has problems swallowing food and saliva, and normal breathing is disrupted. In addition, the patient also experiences hoarseness.
A similar wart often grows in the larynx in children. Squamous laryngeal papilloma is considered a small neoplasm with a thin stalk. It often comes off on its own.
Moreover, if such a wart gets into the respiratory tract, the baby quickly dies. However, the squamous cell growth goes away on its own - the child outgrows it.
Squamous laryngeal papillomas sometimes appear in older people. However, if they are not cured in time, then such growths become oncogenic.
Nasal lesion
Squamous cell warts also grow on the nose. Then the person infected with HPV suffers from nasal congestion, as well as from the appearance of unpleasant sensations, itching and burning in this organ.
Sometimes the patient's breathing becomes partially difficult or stops completely. Most often, such a tumor grows on the nasal septum, but sometimes papilloma also forms in the nasal sinuses.
Digestive system
In addition to the tongue, lips, mouth and nose, papillomavirus enters the body and then squamous cell papilloma also appears in various organs of the digestive system (for example, in the esophagus).
Then a person develops the following symptoms of HPV:
- nausea occurs;
- salivation increases;
- belching appears;
- short painful attacks occur;
- discomfort occurs in the stomach.
Genital organs (cervix)
Squamous cell papillomas also grow in the genitourinary organs (for example, on the cervix). However, such growths instantly become oncogenic. This happens when the patient has various genital warts in the genital area (in particular, on the uterus) and erosion appears.
At first, the woman does not feel any discomfort. Later, unpleasant itching and a slight burning sensation form on the external female genitalia.
With this disease in women, the nature of menstrual flow changes. A gynecologist can easily and quickly detect cancer or common HPV growths in the cervical area during a routine medical examination.
What are the causes of keratopapillomas?
The main reasons for the appearance of keratopapillomas on the skin are:
- papillomavirus infection;
- hereditary predisposition;
- pathological skin condition (seborrhea, hyperkeratosis);
- digestive system disorder;
- age-related skin changes - loss of moisture, decreased regenerative processes.
In people aged 30-40 years, ordinary skin papillomas first appear, which, under the influence of sunlight, thicken and become keratinized. Against the background of dry seborrhea, when dry skin is pronounced, areas of growth of the stratum corneum also appear. In elderly people, due to a decrease in the function of the sebaceous glands of the skin, hormonal function and metabolic processes, the phenomenon of hyperkeratosis develops quite often.
Types of keratopapillomas
Depending on the cause, the following types of keratopapillomas are distinguished:
- viral etiology, which become keratinized under the influence of sunlight;
- seborrheic, developing against the background.
Seborrheic keratosis of the skin
Age-related dryness of the skin (dry seborrhea), disruption of its blood circulation and metabolic processes leads to thickening of the outer stratum corneum and disruption of stratum corneum detachment. As a result, areas of thickening gradually form - seborrheic, or senile, keratomas.
Their appearance is provoked by excess solar radiation, so such keratomas are quite common among elderly sunbathers.
The formation of seborrheic keratomas occurs in several stages:
- Stage of age spots
, when the tan fades, and many brown spots remain on the skin. They usually do not cause much concern to their elderly owners.
- Stage of papules
, when areas of pigmentation rise above the level of the skin, its surface ceases to be smooth.
- Stage of keratosis
: pigmented papules begin to peel off and become covered with horny scales; these are seborrheic keratomas.
- Cutaneous horn stage
: individual keratomas become denser and rise above the skin in the form of a cone resembling a horn.
This process occurs gradually, subject to repeated exposure to sunlight. Sunbathers often suffer from back skin, and all older people suffer from exposed areas of the body exposed to the sun: face, neck, hands.
Important! If age spots appear on the skin, older people should stop exposure to the sun to avoid the development of seborrheic keratosis.
How to get rid of keratopapillomas on the skin?
Treatment of keratopapilloma is carried out not only for aesthetic reasons. No one can guarantee that the formation will not transform into skin cancer, although this happens infrequently
. But it is in old age that the incidence of skin cancer is highest, and hyperkeratosis plays an important role in this.
Various methods of treating keratopapillomas are used:
- surgical excision;
- electrocoagulation;
- radiosurgical removal;
- cryodestruction;
- laser coagulation;
- traditional medicine.
About
Reasons for appearance
Squamous cell papilloma is of viral origin, since it is the entry of papillomavirus (HPV) into the body that provokes the occurrence of rashes. The virus can remain in the body for a long time without showing itself. The main reason for the virus’s action is weakened immunity and the presence of provoking factors.
Routes of infection:
- Sexual intercourse with a carrier of the virus. Moreover, you can become infected through any contact, during vaginal, oral or anal sex.
- Household contact.
- In places with high humidity.
- From mother to child during childbirth.
Provoking factors:
- elderly age;
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- various skin diseases;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- allergic reactions;
- hormonal imbalance;
- heredity;
- pregnancy;
- work in hazardous working conditions and in production with chemicals;
- unhealthy lifestyle and bad habits.
Causes
After HPV enters the body, a person often develops 1 or more squamous cell papillomas.
This most often occurs in the following situations:
- with decreased immunity;
- due to frequent skin injuries;
- when a viral infection enters the body;
- in the presence of various endocrine ailments;
- under the influence of a genetic factor (heredity);
- during human aging;
- after undergoing chemotherapy;
- damage to the mucous membrane of specific organs;
- due to various skin ailments;
- after exposure of the skin to solar or other irradiation - radiation, etc.;
- due to various chronic diseases (bronchitis, ulcers, etc.);
- with constant stress;
- during hormonal imbalance;
- due to various harmful habits (abuse of alcoholic beverages, smoking);
- in case of non-compliance with hygiene standards and rules;
- due to polluted environment.
However, whatever the reason for the formation of such papilloma, it can be cured in any case.
Symptoms of occurrence
The main symptoms of papillomas:
- manifestation of rashes;
- keratinization of the skin in the affected areas;
- swelling/swelling and redness of nearby skin;
- the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the form of itching or burning in the area where the rash appears.
Symptoms of the presence of squamous cell papilloma depend on the type and location of its location.
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus
The appearance of squamous cell papillomas in the esophagus is very common, which can trigger the development of esophageal cancer. From the medical side, there is no definite answer why papillomas appear on the walls of the esophagus. However, first of all, papillomas are the most common type of diagnosed tumors.
Of course, the main cause of the disease is the human papillomavirus. One of the main reasons for the appearance of squamous cell papillomas in the esophagus is the presence of damage in this organ.
If you have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, heartburn or pain in the epigastric region, contact a gastroenterologist. The main danger is that over time this pathology can turn into a cancerous form.
The main reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the esophageal mucosa:
- advanced form of gastritis;
- constant heartburn;
- eating spicy food;
- alcohol abuse.
Papillomas on other parts of the body
When a rash occurs in the larynx, difficulty swallowing occurs, difficulty breathing and impaired diction are observed, and there is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the throat.
With a tumor in the stomach, nausea, increased salivation, belching, and pain in the abdominal area are observed.
On the tongue
Squamous cell papilloma on the tongue can cause a swollen appearance of the tongue. In this case, there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, pain when chewing food, and restrictions in the movement of the tongue.
On the lips
The appearance of papilloma on the lips reflects not very pleasant symptoms. As a rule, the tumor formation in the lip area gradually increases in size, and swelling or swelling of the lips is often observed. There are frequent cases of bleeding of the neoplasm, and pain when touching the papilloma.
In intimate places
Papillomavirus in women in the intimate area can cause the development of serious diseases. Many who have been diagnosed with papillomas subsequently encounter hyperkeratosis, or in another way, the disease is called cervical leukoplakia.
As a rule, a person does not suspect the presence of papilloma in his body, and especially in the esophagus, and symptoms appear already in advanced forms. Or they are diagnosed together with other diseases during diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Detection of the rash is carried out by the patient himself or the doctor during a medical examination. Depending on the location of the rash, the presence of pathology is detected by a dermatologist, gynecologist or gastroenterologist.
To identify papilloma, determine its type and distinguish it from other types of tumor neoplasms, diagnostic procedures will be needed. It is necessary to take blood tests, do a biopsy and undergo histological and cystological examination.
It is important to exclude the presence of cancer due to papilloma.
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus – Gastrology
The most important are papillomas
Squamous cell papillomas of the stomach are benign tumors. They reproduce from epithelium and connective tissue.
The epithelial cells are actively separated, which increases the layer, visually resembling growth. It has a developed stroma - a complex of blood vessels and connective tissue components.
It is often detected during the diagnosis of other organs and systems, since the disease progresses slowly and asymptomatically.
What is and ICD 10 code for squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus is a dangerous and insidious disease. Rarely does a patient consult a doctor about symptoms associated with this organ.
It is represented by the growth of multilayered, flat, non-emerging epithelium, occupying the surface layers of the organ wall (up to submucosal). The disease is typical for older people. Men suffer more often.
If the tumor is small, a person does not feel any symptoms, when it reaches 2-3 cm, serious symptoms occur.
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), the disease is coded D13 - benign tumors of other, ill-defined digestive organs.
Causes and symptoms of papilloma in the gastrointestinal tract
The occurrence of squamous cell papillomas in the intestine can be caused by several factors:
- hereditary disorders;
- viral infection (HPV);
- system damage.
Congenital disorders of cell coordination lead to the growth of walls.
There is no consensus on the root cause. Squamous cell papillomas are rare in the intestine. It is assumed that the disease is caused by human infection with a virus due to damage to the mucous membrane or chronic inflammation.
The human papillomavirus is widespread. It is resistant to environmental influences and is easily transmitted through contact (handshake, use of ordinary utensils, things). Dangerous masses of people in high humidity.
Humans are not affected by the pathogen squamous cell papillomavirus due to active immunity. Decreased local defense promotes infection.
Reason for reducing local protection:
- chronic inflammation due to esophagitis, frequent reflux of stomach contents;
- secondary and primary immune defects;
- damage due to ionizing radiation;
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane;
- age;
- consumption of strong alcohol, spicy or spicy foods;
- smoking;
- endocrine disorders.
Immunodeficiency develops as a result of the harmful effects of the environment and internal factors on the body. Main reasons:
- heavy metal poisoning, drug poisoning;
- nutritional malnutrition (hunger);
- long-term use of certain drugs (eg, immunosuppressants);
- fatigue;
- constant pressure;
- helminthiasis;
- bacterial infections;
- oncology;
- congenital defects in the interaction and differentiation of cells of the immune system.
When moving to the stage of clinical symptoms, the disease is manifested by the appearance of flat cellular papillomas, warts on the skin of the hands, feet, face, and genital warts on the genitals (depending on the load). If there is insufficient cleaning, the virus remains in the body. In the presence of factors, this can lead to the formation of a neoplasm in the wall of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of the disease have specific features depending on the location.
Features of localization and diagnostics
Diagnosis of squamous cell papillomas is made by endoscopic radiography methods from a gastroenterologist.
The clinic is observed when the size reaches 2-3 cm. Symptoms of localization:
- The lumen of the stomach is blocked, the act of eating is damaged;
- after swallowing there is a feeling of heaviness and pain;
- foreign body sensation;
- bleeding with damage to raw food;
- vomiting while eating;
- salivation.
The patient is usually unaware of the disease. Education can be asymptomatic for a long period of time.
With an endoscopic examination, you can visually evaluate squamous cell papilloma: It does not differ in color from the healthy mucous membrane, can be smooth or have several growths, sit on a thin or wide stalk and have a shape similar to a fungus or cauliflower. It can be removed during the examination, and the resulting material can be sent for histology. The procedure is diagnostic and therapeutic.
Individual growths form in the stomach. But there are also multiple ones, in this case we are talking about papillomatosis.
Rectal papilloma shows the following symptoms:
- with discomfort during bowel movements;
- with difficult bowel movements;
- if there is blood or mucus in the stool;
- when you feel itching, burning in the anus;
- flatulence;
- stomach ache.
Formations in the digestive tract reach large sizes - up to 5 cm. The examination is carried out using endoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Appearance of the localization of squamous cell papillomas in the stomach:
- pain in the front of the abdomen while eating;
- bloating due to fermentation of food;
- vomiting during or after eating;
- nausea;
- salivation;
- stomach bleeding.
Endoscopic examination, contrast radiography, ultrasound are used for diagnosis.
Do you need advice from an experienced doctor? Ask your question right now.
Ask your free question
Other parts of the stomach are less common. Symptoms of papillomas in the intestines are similar to other locations. In case of massive growth, obstruction develops with acute pain and severe deterioration of the patient's condition.
The provoking factor is chronic inflammation (colitis). The disease is easily confused with intestinal polyps, which develop as a result of the inflammatory process. Men over 50 years of age are especially affected.
No viral etiology.
Treatment methods for squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus
Treatment is difficult due to the specific location. The program includes medical and surgical methods for the treatment of squamous cell papillomas. The doctor selects treatment options individually, focusing on the course of the patient’s illness and related health problems.
Drug treatment
The drugs are used for general effects on the body, restoring defenses. For this purpose, antiviral drugs are prescribed - immunomodulators (interferons). Drugs are prescribed to inhibit the synthesis of hydrochloric acid to reduce the destructive effect of reflux. When the papilloma reaches a medium size, the squamous cell papilloma can be removed with equipment.
There are traditional medicine methods that allow you to remove squamous cell papilloma at home.
Recipes with these ingredients are widely used:
- propolis;
- soda;
- nettle;
- currant;
- liquorice. Traditional medicine is useful as an additional condition for strengthening the immune system and relieving inflammation
.
It is useful to make broth from currants, nettles, and licorice, drink 1 glass a day. It is advisable to use when collecting.
self-medication can be harmful to health
Surgical removal
Hardware methods are widely used in surgery. They are completed by cutting the squamous cell papilloma from the mucosal surface and dissecting into healthy tissue. The first option is performed using endoscopic instruments. Electrocoagulation is used as a removal method; it prevents bleeding and complications.
The operation is well tolerated and the rehabilitation period is short.
Complete dissection of squamous cell papilloma in healthy tissue is performed at the birth of a malignant tumor or in case of a large volume of formation. A classic surgical approach is performed—imaging. The operation is difficult to perform and there is a long recovery time. If oncology is confirmed, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are continued.
You might be interested in: Is it possible to do a colonoscopy for hemorrhoids?
The need for diet and balanced nutrition
After removal or during treatment of squamous cell papilloma, it is necessary to ensure free passage of food and minimal irritating effect. Excluded:
- hard;
- fried;
- acidic;
- hot;
- hot and cold foods, drinks;
- alcoholic;
- smokers
A diet of well-cooked, steamed foods is recommended. Eat small portions, well chewed. Number of meals - 5-6. A balanced diet is necessary to maintain immunity and prevent vitamin deficiency.
It is forbidden to eat during your stay in the hospital from the evening before the operation and in the first days after.
Possible complications and treatment prognosis
The treatment prognosis is favorable with complex therapy and timely detection of squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus. Otherwise, it will cause discomfort and increase the risk of cancer. It is likely that the papilloma will be damaged by rough food, which will lead to bleeding. This will be detected by hemoptia, blood in the stool.
Incomplete removal can lead to relapse, which can be prevented with the help of instrumental tests, tests, and complex therapy.
If such neoplasms are localized in other areas, there is a risk of consequences:
- ulcer formation;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- infection connection.
- Prevention consists of regular examinations by a specialist.
- The article was reviewed by the site's editorsLink to the main publication
- No suitable advice found?
- doctor or look at all the questions...
- doctor
- Article rating
- ( 1