What is papilloma?
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm caused by the human papilloma virus. Often the carrier of such a virus does not suspect that he is infected and is a carrier of HPV.
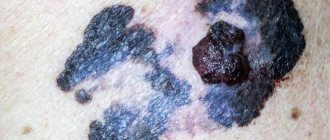
The incubation period lasts on average from 1 to 24 months; during this period the virus may not manifest itself in any way. The virus can be activated by a sharp decrease in the immune system after an illness or severe stress. It is not difficult to distinguish a papilloma from a wart; more often it resembles a “mushroom”, but there are also flat types.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact a specialist; after conducting research, it will be revealed what type of virus the patient is infected with. It can be a carrier of one or several types of papillomas at the same time.
HPV types:
- HPV 1, 2, 3, 5 - viruses that do not pose a danger to humans, in most cases they are cured on their own;
- HPV 6, 11, 42, 43, 44 – patients with these types of virus are at risk of developing cancer;
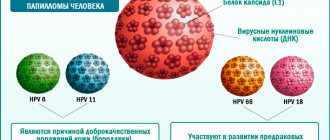
- HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66 and 68 - these types are the most dangerous, often leading to cancer.
What is papilloma on a man's penis?
When the human papillomavirus enters the body, it is impossible to notice, since this disease can only be detected through early diagnosis. Without reason, no one turns to doctors for help, and at this time HPV is activated in cells and damages their original structure.
Penetrating into a man’s body, HPV mutates in cells and reproduces growths of various types on the surface of the epidermis - papillomas, carcinomas, warts, genital warts. Some of them pose a deadly threat.
When the immune system weakens, the virus comes out, forming growths of various types on the skin. Depending on the subtype of HPV introduced into the body, the growths behave differently when they come to the surface. The most dangerous strains of HPV are:
- HPV types 16 and 18, which are transmitted only through sexual contact;
- HPV types 35, 39, 52;
- HPV types 31, 33, 45, 56 and 58;
- HPV types 51, 59 and 68.
Doctors are of particular interest in HPV types 16 and 18. Both strains provoke diseases in the genital area, exceeding the level of cancer development by 50 times compared to a healthy person. They have been fully researched, and recently even a vaccine against HPV types 16 and 18, Gardasil, appeared.
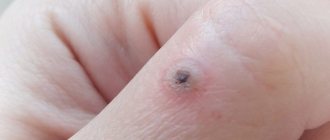
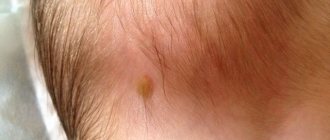
Typically, papilloma takes the form of a growth formed on the surface of the body. The first papilloma can appear on any part of the body and only then form on the genitals. There are differences in appearance that will help you understand a specific type of education:
Types of papillomas on the genital organs in men
- Flat . They look like plaques, rise slightly above the skin, and cause burning or itching. They often cluster together and can grow quite large.
- Genital warts . They rise strongly above the epidermis, looking like protruding threads. Such growths are easy to injure, which is fraught with additional infection.
Before treatment, it is necessary to understand what type of HPV you will have to fight. If the formations begin to actively multiply, then at first the man experiences external discomfort. Papillomas can cover the entire head of the penis, which subsequently leads to phimosis. It is possible for a small papilloma to transform into a malignant tumor.
How to identify papilloma on the penis?
In appearance, papilloma is very similar to a simple wart. There are ways to determine it, and only a qualified doctor has these skills. Sometimes even a doctor’s examination is not able to reveal whether it is a wart, a mole, or a papilloma. In this case, a diagnosis is prescribed that will put everything in its place.
Causes of papilloma on the penis
Papillomas are a response to the activation of the human papillomavirus that has entered the body. Infection can occur in cases such as:
- promiscuity or choosing an unhealthy partner;
- failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene in the foreskin;
- increased sweating;
- contact with a carrier of infection;
- improper shaving.
Only in cases of suppressed immunity can the virus enter the body. If a person is completely healthy, then HPV will not be able to affect the immune system and manifest itself in the form of papillomas. As soon as the body’s natural defenses weaken, papillomas appear on the body.
HPV in men
The course of HPV in men occurs in a milder form, but there are cases when the disease takes a severe course, but this happens much less frequently than in the fairer sex. The appearance of a small rash and its subsequent rapid spread and growth in size indicate the presence of a virus. The size of the rash varies from 1-2 mm to several centimeters .
The largest papilloma was recorded, its size reached 6 cm. The number of neoplasms is also varied. There are cases when a single papilloma appears on the foreskin of the penis, but much more often there are patients who have a significantly larger number of genital warts.
The most susceptible to such rashes are: the scrotum, frenulum, head, coronary groove and inner layer of the foreskin. With single manifestations, the scrotum and penis are most often affected.
As a rule, the presence of papillomas on the penis does not cause pain; many men experience a feeling of discomfort when the papillomas are injured during sexual intercourse. If you ignore the symptoms of HPV, a man risks provoking the formation of purulent wounds and ulcers, which can subsequently lead to inflammation.
Development of disease on the head of the penis
Untimely treatment of a skin tumor that appears can lead to such a terrible diagnosis as cancer. Moreover, this disease has the potential to develop from a benign tumor to a malignant one. A man may greatly regret that he did not consult a doctor with the problem of papilloma appearing on his penis. The photo shows what neoplasms on the body can look like.
Papilloma degeneration occurs in the epithelium of the head or in the inner layer of the foreskin. The tumor develops according to the following pattern:
- Phimosis, which was not diagnosed in time, enters an advanced stage.
- Smegma (a fat-like substance) accumulates under the inner layer of the foreskin.
- Urine that gets on the smegma provokes infection. And this can lead to the formation of tumors.
- The body of the penis and the head become inflamed, and erosion appears.
- In the end, all these processes lead to the appearance of papilloma on the penis in men, which can later develop into cancer.
Methods of infection
There are several ways to become infected with HPV:
- Unprotected sexual contact. One of the most common ways, no matter what type of sex you engage in, the penetration of the virus occurs through the presence of microcracks in the skin and mucous membranes. In other words, you can become infected with the virus not only through classic sexual intercourse, but also through oral or anal sex. Even a small area of mucous membrane or skin can cause infection, so you should not rely on a condom, it is not a 100% guarantee of protection against this type of pathogen. Another sexually transmitted infection is syphilis. Here you can read more about the symptoms of syphilis and the stages of the disease.
- Contact and household path. Scientists have found that the human papillomavirus has the ability to maintain vital functions while outside the human body. Consequently, HPV can be transmitted by personal hygiene items and public places: toilet, razor, toothbrush, bathhouse, swimming pool, gym, etc. Studies have shown that HPV can also spread through a handshake.
- During childbirth. In this case, the baby may develop anogenital warts.
- Autoinfection. Although rare, such cases do occur. For example, after shaving, through a razor. A person can independently transfer an infection from one part of the body to another.
As mentioned earlier, HPV can remain in the latent phase for a long time, but when provoked by various factors, external manifestation begins.
Here are several factors that can cause papillomas to appear:
- Decreased immune system. In people with strong immunity, the papilloma virus may never manifest itself externally, and the person will live his entire life without even knowing that he was a carrier of HPV.
- Presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, taking drugs, intoxication.
- Emotional, physical and psychological exhaustion, leading to depression and stress.
You might be interested! HPV in women: how does it manifest itself and what to do if it is detected?
Reasons for appearance
Papillomas on the penis, like on any other part of the body, are caused by the human papillomavirus. This is a DNA-containing pathogen that has a tropism for the epithelium.
A large number of virus strains are known (more than 100), but strains 6, 11, 42–44, 54 are predominantly responsible for the occurrence of formations on the genital organs.
Features of infection:
- The main routes of infection are sexual and contact. As for contact, it is carried out through the use of shared hygiene items (towel, razor) with a sick person.
- The virus stays in the body for a long time without causing significant clinical manifestations. The first neoplasms may appear long after infection - the duration of this period is individual in each case (from a month to a year).
- The virus is able to integrate into the DNA of the cell, while the shell itself is destroyed. When transitioning to this form, it becomes almost impossible to completely eliminate it from the body (it is extremely difficult to completely cure the patient).
- Immunity after an illness is weak and nonspecific. This means that antibodies are produced only in relation to one specific strain and there is always a risk of infection with other types of virus.
- Since genital warts are caused by certain strains of the virus, it is not possible to become infected by touching warts and papillomas on other parts of the body, since their formation is caused by other strains.
Predisposing factors:
- Visiting public places such as baths, swimming pools. To reduce the risk of infection, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene (changeable shoes, individual towel).
- Reduced immunity. This condition can be caused by taking a number of medications (antibiotics) or by long-term infectious processes.
- Injuries and microtraumas of the skin. In this case, minor microcracks in the skin that occur during sexual intercourse with an infected partner are enough for a growth to appear. In this case, it does not matter whether the partner has specific external manifestations or not, since the virus can persist in the blood without symptoms on the skin.
- Frequent change of sexual partners (of any gender), lack of contraception and earlier onset of sexual activity.
- Chronic diseases of the urinary system, which simultaneously affect the functioning of the immune system and cause traumatic damage to the skin (maceration).
- The negative influence of environmental factors (stress, hypothermia, poor nutrition) have an indirect effect, weakening the immune system.
- As a rule, the manifestation of this disease requires several simultaneously active causes.
Symptoms
Papillomas can be localized on any part of the body, it all depends on the type of HPV. Most often, papillomas appear in intimate places and the anal area. But in practice, there are cases when papillomas appear in the urethra, resulting in problems with emptying the bladder.
When the foreskin is affected, papillomas are often located in a fold of the skin or slightly lower. In the genital area, the color of papillomas can be pale pink, transparent and shiny in places. The papilloma is elastic to the touch, but during the process of reproduction and growth it acquires a denser texture. In some cases, the foreskin may narrow.
Another sign of the presence of the virus in the body is the presence of an unpleasant odor and bleeding from tumors. They appear as a result of damage to the papilloma, which can cause the tumor to degenerate into cancer.
Causes
To understand how to get rid of papillomas, you need to understand the provoking factors of this phenomenon.
There are many reasons why papillomas can be found on any part of the body. In some cases, papillomas appear on the head of the penis or on the flesh of the organ, as well as in the intimate area. This type of papillomas is usually called condylomas. After infection with the virus occurs, a fairly long period of time may pass, for example, a year, two or more, before papillomas appear.
This is due to the fact that the body’s immune system is able to independently suppress the development of the virus and prevent it from manifesting itself. If the body becomes weaker, the immune system is unable to suppress viral agents.
Provoking factors include:
- chronic diseases;
- failure of the hormonal system;
- AIDS disease;
- hypothermia of the body;
- frequent acute respiratory viral infection;
- symptoms of intoxication due to a long course of potent medications;
- regular stress;
- unbalanced diet and any other factors affecting the functioning of the immune system.
What does papilloma look like on the head of the penis?
The virus, which is in its early stages, appears as small pink blisters accompanied by redness and itching.
Papilloma affecting the glans penis can look different. In some cases, papillomas resemble plaques with a rough surface; there are also larger growths that merge and have a surface resembling a cockscomb.
The color of papillomas at different stages remains unchanged and has a pale pink, closer to transparent tint. Papillomas on the penis and scrotum have a more lumpy and firm structure with a wide base.
Photo
Diagnostics
First of all, if you suspect HPV, you should consult a specialist.
The doctor will conduct a visual examination and, if signs of a virus are detected in the body, will prescribe the following tests:
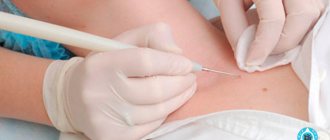
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - perform a scraping, smear or biopsy from the glans penis;
- Tests to determine antibodies to this virus;
- A swab from the urethra;
- Digene - the test with the highest accuracy detects not only the presence of HPV, but also determines its type;
- Anal Pap smears, this type of examination is performed if the patient has had anal intercourse.
How to get rid of papillomas on the head of the penis?
After passing all the tests and confirming the presence of HPV in the body, the patient is prescribed individual treatment depending on the type of virus. At the moment, there is no drug that can affect the virus from the inside, so complex treatment is the most effective.
Here you will find a similar article on the topic of rash on the glans in men.
It includes:
- Medication. Antiviral, immunomodulatory and vitamin complexes are prescribed;
- Surgical. Papillomas are removed using one of the methods: hardware, surgical;
- Additionally, ointments for external use are prescribed.
Conservative treatment
The treatment regimen for each patient is prescribed individually. After the external manifestations of the virus have been removed, it is necessary to begin treatment with medications. You should also refrain from intimacy with your partner.
To date, the following drugs are considered the most effective:
- Salicylic acid . Used as an antiseptic;
- Epigen-intim – has antiviral and immunostimulating effects;
- Isoprinosine is an antiviral agent that enhances the effect of immunomodulators taken;
- Allokin-alpha is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug, characterized by maximum effectiveness in the treatment of HPV strains.
Removal of papillomas on the head of the penis
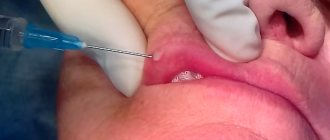
There are several methods for removing papillomas on the head of the penis:
- Laser removal. A beam of light is directed at the papilloma, causing it to evaporate.
- Electrocoagulation. The papilloma is exposed to electric current.
- Radio wave surgery. Due to the use of specialized medications, removal of papillomas is painless.
- Chemical coagulation. Under the influence of the drugs “Podophyllin” or “Vartek”, papillomas are cauterized.
- Cryodestruction. The papilloma is exposed to liquid nitrogen, as a result of which the cells begin to freeze and disintegrate. What distinguishes this method from previous methods is the guaranteed absence of relapses.
Treatment of papillomas on the penis
There are currently no treatments or medications that can completely get rid of the papilloma virus.
However, there are therapeutic methods that can suppress the development of HPV, eliminate its visible signs and reduce subsequent relapses of the disease.
✔ Drug therapy
Drug therapy is prescribed to suppress the activity of the virus.
Includes:
- antiviral drugs to treat affected areas (creams, ointments);
- antiviral drugs in tablets;
- immune stimulants.
Antiviral tablets for the treatment of papillomas on the penis are used as the main therapeutic methods or in addition to antiviral ointments.
As a rule, treatment with tablets takes about two to three weeks.
Medicines and treatment regimen are selected by the doctor depending on the number of tumors.
The most effective results can be achieved with the help of complex treatment - antiviral agents and immunomodulators.
Antiviral agents
- Acyclovir
Acyclovir belongs to the group of antiviral drugs.
It stops the multiplication of a viral infection.
It also has a devastating effect on diseases such as herpes zoster, Epstein virus, cytomegalovirus or varicella zoster virus.
Acyclovir in the body of a sick person takes the form of active acyclovir triphosphate.
It is converted into a molecule of a chemical compound necessary for the synthesis of nucleic acid.
Modified in this way, acyclovir replaces the viral nucleotide in its DNA chain and prevents its synthesis.
The effect of the drug's substance molecules is to inhibit the reproduction of the virus without affecting the cellular metabolism of the infected person.
Side effects are relatively rare.
Sometimes the following may occur: headache, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash.
- Valaciclovir
An antiviral drug that is a prodrug of acyclovir.
Inhibits the reproduction of the virus, almost completely turning into acyclovir in the body.
According to numerous studies, valacyclovir is an effective antiviral therapy, and viruses with reduced sensitivity to it are practically not found.
Regarding side effects, they develop extremely rarely, often when the recommended dose is increased.
- Groprinosin
Groprinosin contains inosine pranobex, therefore, it is a drug with antiviral and immunomodulatory effects.
Prescribed in the complex therapy of viral infections, as well as as a prophylactic drug.
During long-term treatment (3 months or more), patients should regularly monitor serum and uric acid levels, liver function, blood counts and renal function parameters.
✔ Immune stimulants
Immune oral drugs for the treatment and prevention of papillomas on the penis, as a rule, are prescribed without fail.
The activity of such drugs is due to the ability to accelerate the production of interferon in cells and tissues.
For example, the drug Cycloferon activates bone marrow stem cells, creating granulocytes that restore immunity.
Cycloferon, which contains acryonic acetate meglumine, also has radioprotective and antitumor effects.
Immune stimulants are available for oral administration in tablet and injection form.
It is noted that the injection of such drugs is more effective.
✔ Ointments for the treatment of papillomas on the penis
Oral antiviral drugs for the treatment of papillomas on the penis are recommended to be combined with local agents.
Usually these are creams or ointments that help eliminate papilloma.
One of the popular options is Vartek cream based on the substance podophyllotoxin (analogue of Condilin).
Podophyllotoxin is obtained from plants of the Coniferae and Berberidaceae groups (e.g. Juniperus and Podophyllum).
The drug has a strong antimitotic effect and leads to necrosis (death) of epithelial cells.
Thus, papilloma disappears after exposure to the drug.
When treating papilloma on the penis, the drug can be used at home.
To do this, using the attached applicator, carefully apply the drug to the affected areas (papillomas), and then let it dry.
The frequency of use of the product is determined by the doctor.
For large papilloma, the use of the drug often does not bring any effect.
In this case, it is recommended to remove the formation surgically or with other modern methods (laser, cryo, etc.).
Local side effects can provoke: pain, erythema, surface itching.
These symptoms are mainly related to the therapeutic effect and usually occur on the second or third day of treatment, when necrosis of the condyloma begins.
Prevention
The most common route of infection with papillomas is sexual.
Thus, in order to protect yourself from infection, you must adhere to some recommendations:
- Don't have sex with people you don't know.
- Always use a condom during sexual intercourse.
- Do not use other people's hygiene products.
- Avoid swimming pools, gyms and other public places where the administration does not require a certificate of health.
- Carefully monitor the hygiene of the genital organs.
If infection cannot be avoided, it is necessary to monitor the functioning of the immune system. To maintain immunity, you should add fresh vegetables and fruits to your usual diet. Take a complex of immunostimulating drugs.
Why are penile papillomas dangerous?
Back in the 80s, doctors increasingly began to report the danger of HPV to humans. The carrier of this virus was at risk of developing cancer. Decades later, statistics proved these assumptions. The appearance of oncogenic types of papillomas in the anal area most often leads to cancer , since it is quite difficult to identify papilloma in this area at an early stage.
There are many cases where, after removal and complex therapy, papillomas appeared on other parts of the body. In addition to the discomfort that occurs when papillomas appear on the penis, this disease can lead to the development of cancer of the reproductive organ.
Treatment of neoplasms
Treatment is carried out after a medical examination and consultation. If necessary, a biopsy and cytological analysis of their tissues is performed. The main principle of modern treatment of HPV infection is drug immunological therapy in combination with surgery performed by a urological surgeon. Thus, the effect on the virus in the body is not only through immunotherapy, but also through the method of physical damage to papillomas cells by laser or radio wave evaporation during surgery. If there are signs of degeneration of the neoplasm, part of the papilloma tissue must be sent for histology to ensure the absence of oncogenic cells.
To remove papillomas on the penis, innovative surgical techniques are used (including removal using a laser, ultrasound or radio knife). They provide rapid healing, do not cause tissue destruction, and are characterized by the absence of scars and purulent complications after surgery. The advantages of this treatment:
- high efficiency;
- painlessness;
- rapid tissue healing;
- bloodless operation;
- absence of stitches and scab (rough burn surface).