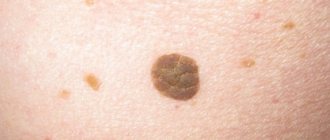
A nevus or mole is a benign neoplasm, the basis of which is made up of pigment particles of the epithelium - melanocytes. If you notice that a papilloma is growing from a mole, this may be the beginning of the process of malignancy.
Melanoma or skin cancer is the most serious cancer. Today there is an increase in melanomas certified by doctors, as well as an increase in the fatal outcome of this disease. There are characteristic features that help distinguish a nevus from melanoma.
In the area of special attention
It's easy to miss melanoma developing from a mole. And pigmented areas of the skin are at risk of epithelial degeneration at the cellular level. The sharp growth of a nevus should be a warning first of all.
Additional evidence of cell transformation into cancer is:
- Blurring boundaries;
- Pain on palpation;
- Color change;
- The appearance of bleeding;
- Leakage of fluid from a mole.
Failure to consult a specialist in a timely manner can cause the progression of cancer and the development of metastases.
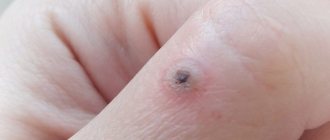
If a papilloma has grown on a mole
The appearance of papillomas is associated with human infection with HPV (human papillomavirus). Additional differentiated studies are recommended if papilloma appears on a mole. The main purpose of such tests is to establish the benignity of the neoplasm, as well as to exclude the development of dysplasia.
Depending on the research results, a treatment or observation program is developed.
It includes three variations:
- Remaining under observation - in the absence of signs of degeneration;
- Mole removal – if dysplasia is detected;
- Fighting melanoma: excision of the tumor, administration of chemotherapy or radiation.
Diagnostics
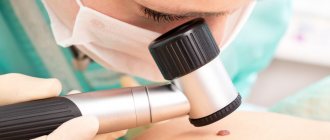
Regardless of the type of formation, you need to visit a dermatologist. It will help prevent the growth from becoming malignant. Particular attention should be paid to papillomas, as they more often transform into cancer. Moles are most often left untouched.
The growth can be removed only after examining the patient. The doctor needs to evaluate the location of the formation, its type and further actions. Decisions regarding papillomas are made depending on the type of formation.
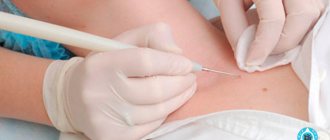
Moles can be examined under special magnification. If the doctor doubts the benignity of the formation, it may be necessary to collect tissue from it for further histological examination.
The doctor must examine the formation to determine its type
Diagnosis of papillomas is a more extensive procedure. Depending on the location and type, the following is carried out:
- inspection;
- colposcopy;
- biospia;
- histological study;
- cytological examination;
- PCR typing;
- determination of the presence of infection using PCR.
Only on the basis of a complex of examinations is a diagnosis made and a decision is made regarding removal of the formation.
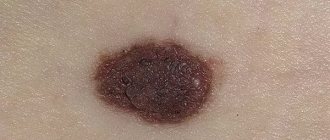
If the mole turns black
In addition to the problem of papillomas growing on a nevus, a change in its color can also be alarming. Many people are frightened by the black or dark brown tint of a mole. Don’t panic, blackening of a nevus does not always indicate the process of degeneration. Here are the signs:
- Color blurring - the appearance of lighter and darker areas;
- Painful sensations in the area of the mole;
- Bleeding and crusts that form on the surface of the mole;
- The appearance of separated particles;
- Swelling of the nevus;
- Fuzzy outline;
- Inflammation and redness.
The presence of at least one of the listed signs is a reason to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Causes of malignancy
All factors that provoke the transformation of mole cells into cancerous ones are conventionally divided into controllable and uncontrollable. Controllable factors include:
- Injury to formations;
- Prolonged exposure to the sun;
- Visit to the solarium.
Uncontrollable causes of malignancy include:
- Sunburn received in childhood;
- Freckles;
- A large number of benign nevi;
- Genetic predisposition - having relatives suffering from melanoma.
Therapy for papilloma that has grown on a mole
The treatment protocol for a growth on a nevus is a set of measures:
- Taking a biopsy using local anesthesia (the size of the tissue for examination is two millimeters or more);
- If the benignity of the nevus and growth is confirmed by histology, the patient remains under observation;
- If dysplasia (superficial melanoma) is detected, the neoplasm must be removed immediately.
Characteristic signs of melanoma
The first signs of the process of degeneration of nevus cells into an oncological tumor were indicated above. As for the classification of melanomas, sometimes even a specialist can establish a diagnosis without additional clinical studies. The following basic types of skin cancer are distinguished:
- Dysplasia or superficial melanoma is the most common cancer;
- Nodular melanoma is an aggressive type that appears as a lump on the skin;
- Lentigo is a cancerous formation located on the head and neck of elderly people;
- The subungual variety attacks the epithelial tissue under the nail plate.
Timely seeking medical help will allow you to diagnose the pathological process in the early stages and stop its development. Without active therapeutic measures, melanoma quickly metastasizes.
Prevention of melanoma
Doctors give the following recommendations to prevent the process of malignancy:
- Reduce and, if possible, prevent injury to the neoplasm;
- Avoid exposure to the sun during periods of increased activity;
- Use a cream with a sun protection factor of more than 20;
- Wear T-shirts or shirts with sleeves;
- Protect your head with a Panama hat, cap, hat;
- Undergo an annual preventive examination.
The location of melanomas differs in men and women. In women, the lower legs become the danger zone. The cause is hair removal on the legs. For men, the problem area is the back. This is due to exposure to direct sunlight. Men often go without shirts or T-shirts. Regular preventive examination ensures diagnosis of the early stages of the disease.
Be healthy and remember: your health is in your hands. Attentive attitude to your body, preventive examinations and compliance with doctors’ recommendations will help prevent the development of serious pathology.
Papilloma on a mole is an ambiguous phenomenon that requires study and diagnosis. A mole is a benign tumor that is not capable of causing harm to the body on its own. A nevus consists of a cluster of special cells - melanocytes, which are arranged in layers. Inside the mole there are sebaceous, sweat glands, hair follicles, but there are no cells of the basal layer of the skin epithelium from which papilloma develops.
Differences between papilloma and mole
Papilloma, like a nevus, is a benign formation, but the nature of its origin is different - it develops as a result of human infection with HPV. Comparative characteristics will help to distinguish formations from each other:
| Index | Mole | Papilloma |
| Color | It has shades of brown, but some species can be black, blue, pink and red. | Flesh, light pink. |
| Form | Symmetrical oval, flat or convex. | Rising above the surrounding tissues, it looks like a papilla on a stalk. Increases in length. |
| Structure | Dense, smooth surface, consisting of skin cells. | Soft, loose, contains blood vessels. |
| Size | 1-5 mm is a benign element, more than 6 mm is suspicious. | 2-15 mm. Trauma can cause active growth. |
| Appearance period | In the first months and years of life after birth, after exposure to the sun, during hormonal changes, etc. | 1-4 months after HPV enters the body. |
| Localization | Open areas of the body, mucous membranes. | Areas subject to the most friction. |
A dermatologist can accurately determine the type of formation after examining the structure under a dermatoscope.
Exposure to an irritant can cause dangerous changes and provoke degeneration into skin cancer - melanoma. It is important to monitor changes in education throughout your life and undergo timely examinations by a dermatovenerologist.
Differences in the treatment of formations on the body
The main difference between the treatment of birthmarks and condylomas is the treatment method. When treating nevi, doctors prescribe only complete removal of the tumor without additional treatment. When diagnosing a wart, therapy to improve the body's immune defense and take antiviral drugs are mandatory.
Removal of warts is recommended even in cases of low oncogenic risk. Therefore, education is eliminated in almost all cases. Removal of a nevus is necessary only if it is actively growing or if there is a negative cosmetic effect. The best way to get rid of any growth is laser therapy. This technique for removing tumors allows you to quickly destroy tumor tissue, but at the same time avoid the appearance of scars and other complications.
The difference between a papilloma and a mole is difficult to understand on your own. Removal of moles and papillomas is carried out when they cause a health hazard, cosmetic defect, or discomfort. The pathological nature of the formations is determined by the oncologist, based on the results of tests, visual examination, the nature of the formations, causes, rates of growth and changes.
Papillomas and moles are somewhat similar, but the nature of their occurrence is completely different, as is the therapy.
Is it possible for papilloma to appear on a mole?
Papillomas have appeared on a mole - a cause for concern. Both formations separately from each other are harmless, although they grow for different reasons and have different etiologies of origin. A mole is a congenital element consisting of melanocyte cells, a papilloma is a sign of infection with papillomavirus and consists of basal cells of the skin.
The appearance of a new wart on the surface of a mole is dangerous. May indicate the development of cell dysplasia.
Therapy and further observation are carried out after studying the results of tests and diagnostic procedures.
Three scenarios:
- The doctor takes the patient under observation and conducts regular preventive examinations. The scenario is justified if no signs of malignancy are detected.
- Removal of nevus and papilloma is prescribed if degeneration has begun.
- Treatment of melanoma. The tumor is surgically excised, and the patient undergoes chemotherapy.
Papillomavirus causes proliferation of basal cells of the skin. Under its influence, the skin cell changes at the genetic level.
Treatment options
Warts and papillomas can go away on their own within 2 years. Self-resolution is observed when the immune system is restored; systemic treatment of concomitant diseases may be required. If the patient wishes, the growths are removed using a laser, chemicals, cryodestruction, or electrocoagulation. Papillomas can also be treated using pharmaceutical creams and ointments.
How to remove moles on the face? Surgical treatment of nevi is indicated when the growths are frequently injured by clothing items. Moles can also be removed if they cause aesthetic discomfort or grow on the face or eyelids. The treatment methods are the same as for eliminating papillomas and warts.
(nevi) – benign neoplasms that appear at any age in different parts of the face and body
. Their formation occurs due to the concentration of pigment cells - melanocytes, located between both layers of the skin - the epidermis (outer) and dermis (inner).
Nevi are: flat, convex, hanging, with a smooth and bumpy surface. Depending on the location and level of pigment, they differ in colors and shades (from flesh-colored, red to dark).
The diameter of nevi varies from 0.5 to 10 cm, sometimes they exceed these parameters. If flat pigmentation cannot be confused with anything, then convex or hanging pigmentation is often similar to other types of skin formations. Therefore, the question often arises: how to distinguish a mole from a papilloma, wart, or melanoma?
What changes on a mole are dangerous?
For nevi, any mechanical impact is dangerous. Pregnancy, sunburn, injury or the papilloma virus can cause dangerous cell degeneration. The rebirth process takes about 5 years. If you regularly visit a doctor, you can prevent the development of dysplasia, maintain health and life. In the absence of preventive measures, suspicion should be caused by the following symptoms:
- The color on the surface of the growth has become blurred, uneven, darker or lighter areas and inclusions have appeared.
- The surrounding skin is inflamed, reddened, and a halo has formed.
- When touching or pressing on a mole, a sharp, throbbing pain occurs.
- There is a blurring of the boundaries and the appearance of jagged edges.
- Crusts form on the surface, blood, pus or ichor are released.
- The element changes appearance from flat to convex.
- The shape loses symmetry.
The main reason for the transformation of cells into oncology is trauma. The papilloma virus disrupts the integrity of the growth and thins it. As a result, it begins to bleed from accidental friction, contact with clothing, hand or other parts of the body.
Melanoma develops on the skin with weak protection and a tendency to develop various pathologies.
People at risk are those who:
- pale skin;
- Blue eyes;
- red or brown hair;
- a scattering of freckles;
- increased susceptibility to sunburn.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the type of formation. And even within the same group, the signs of a nevus will differ from the symptoms of a hemangioma, and a plantar wart will differ from a condyloma.
Moles
General signs of a nevus are uniform color, the presence of symmetrical and unblurred edges, and lack of growth.
The following types of birthmarks with individual symptoms are distinguished:
- Dysplastic mole - may be asymmetrical, slightly raised above the surface of the skin. Brown color.
- Borderline nevus – up to 10 mm in size and brown in color. The edges are smooth and symmetrical. There is no hair.
- A blue mole is formed by an accumulation of melanocytes in the deep layers of the skin. Dimensions – no more than 5 mm.
- The papillomatous form is a nevus with a bumpy surface. Favorite location on the head.
- An intradermal mole is a formation that occurs in all people.
- Hemangioma is a congenital form, the color is red, strawberry.
- An anemic nevus is a colorless area of the skin with underdeveloped blood vessels.
- A halonevus is a birthmark surrounded by an area of skin with loss of pigment.
- Nevus of Ota is a blue mole. It appears as a large area with a cluster of small nevi. Formed on the face, on the sclera of the eye. The defeat is always one-sided.
- Giant nevus is a congenital form. It is distinguished by its large dimensions - up to 200 mm in diameter.
Papillomas
The symptoms of papillomatosis depend on the strain of HPV that causes the disease. General signs are the appearance of soft formations on the body, neck, under the armpit, on the reproductive organs, in the perianal fold. Benign vegetations can be hanging, have a wide base, or a stalk. The difference is visible visually.
- Warts, papillomas are soft growths of skin color. They rise above the surface of the skin and have a vascular network. The surface is rough, bumpy. The appearance is painless, itching may be present.
- Spines - located on the soles and palms. Similar in appearance to dry calluses. Painful when pressed, pain is felt when walking.
- Condylomas are growths of the mucous membrane of the genital organs in the perianal area. Cause pain, itching, inflammation.
- Flat condylomas - appear on the cervix. Their appearance is caused by oncogenic types of HPV. There are no symptoms. They are detected during a gynecological examination in the speculum.
Possible complications and precautions
Papillomatosis develops quickly. Often the patient does not notice the first signs. It is difficult to prevent infection; the carrier of the virus may not have growths on visible parts of the body. If a papilloma grows on one of the moles, take the following precautions:
- protect the growth site from injury. You can seal it with an adhesive plaster with a pad or apply a gauze bandage;
- do not expose to direct sunlight;
- do not burn it yourself, do not cut it;
- Do not treat with antiviral drugs without consulting a doctor.
- undergo preventive examination and diagnostics.
Papillomavirus often covers areas of the body that are subject to mechanical stress. The birthmark cannot be injured. Do not pull hair out of it during epilation, do not apply lightening creams, and do not allow cosmetologists to carry out aggressive procedures in the area where it is located. The most susceptible to changes are balloon cell nevi, which are susceptible to HPV infection. If such a formation becomes inflamed, a papilloma may appear on it, which is dangerous for the development of melanoma.
Pigment spots can appear on a person’s body throughout life; the process is not always associated with a risk to health and life. Those with a scattering of freckles and large growths should take careful care of their skin; it is susceptible to various pathological processes. It is dangerous if warts and nodules begin to grow on the body of the nevus. Indicates the occurrence of harmful processes inside the body and the need for prompt treatment.
Throughout life, a person can detect various neoplasms on his body. They can be either benign or malignant. To protect your health and life, a person must clearly understand how to distinguish a papilloma from a mole.
What are the differences between condyloma and nevi
There are many signs of how a mole differs from a papilloma
and
a photo
can be an excellent clue to identifying a tumor on the body.
- Size. Typically, genital and flat warts do not exceed one centimeter in diameter. At the same time, birthmarks can reach large sizes and occupy large areas of the skin, creating a negative cosmetic effect.
- Structure. To the touch, condyloma is quite soft and even loose. It is noted that such a neoplasm is quite easily injured. A nevus, on the contrary, has a denser and harder structure and is more difficult to damage.
- Color. Usually warts are flesh-colored, but under some factors the color of the neoplasm can change. Birthmarks are most often darker than the skin itself, but in any circumstances they do not change their original color during the growth of the neoplasm.
- Outlines. Condyloma is an uneven formation. Its edges are always discontinuous and may even be jagged. The edges of the birthmark, on the contrary, are always clearly defined and smooth. Nevi always have a smooth surface, unlike the rough surface of a wart.
- Secondary symptoms. During the appearance and growth of condyloma, many people notice itching, burning and other unpleasant sensations. Throughout its existence, a birthmark does not bring any symptoms to a person.
- Appearance. The appearance of warts is associated with the action of HPV. This virus is active during weakened immunity. Nevi most often appear in early childhood and are present on the human body throughout his life.
Types of skin neoplasms
Before you understand how to distinguish a mole from a papilloma, you should understand what types of skin tumors there are. Papillomas are divided into the following types based on appearance and location:
- Wart. A benign skin neoplasm, predominantly of viral origin, in the form of a nodule or papilla. In addition, they are divided into pointed, flat, simple or plantar.
- Condyloma. Warty formations on the skin and mucous membranes caused by the human papillomavirus. Externally, genital warts resemble a cauliflower inflorescence and are located mainly in the genital area or near the rectal sphincter.
- Acrochordon. This skin neoplasm is a soft, pedunculated polyp. Most often they can be found in the groin folds or axillary area, on the eyelids or neck.
- Horny keratoma. A dense formation of a spinous layer of skin, resembling a small horn in appearance.
Papillomas can be flat or hanging in shape and range in size from 2 to 15 mm in diameter.
Moles can also be very diverse:
- border;
- intradermal;
- intradermal;
- basal;
- linear;
- blue;
- Seton's nevus;
- Ota moles.
Many patients attribute any new growth on the skin to moles, but in reality this is far from the case. Only a dermatologist can determine for sure what growths on the skin are.
Are formations dangerous?
Moles can develop into melanoma. Although this happens infrequently, you should consult a doctor if:
- growth of education;
- change in shade;
- the appearance of pain, itching, bleeding;
- inflammatory process;
- increasing density;
- changes in skin pattern.
Papillomas and warts are dangerous depending on the type of virus that caused their appearance. Thus, patients with HPV 16, 18, 35 and other types of the virus need to monitor the condition of the skin and prevent injury to the formations. It is best to remove them immediately using progressive methods.
Moles and papillomas have similarities and differences. It remains important to control their condition and growth, as well as timely contact with a dermatologist.
Moles and papillomas are benign neoplasms, but have different etiologies. The former are a pigmented area of skin that appears in a person immediately after birth or is formed during life under the influence of various factors. The second type of growths is formed as a result of infection with human papillomavirus and has characteristic external signs. How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma on the body?
At a certain point, a large amount of melanin pigment accumulates in skin cells, melanocytes are formed, which, in turn, form moles, nevi or birthmarks. Every person over 10 years of age has such neoplasms; most often they are localized on the face. In infants, moles are not visible because the pigmented areas are too small; as they grow older, they become noticeable.
How does a mole differ from a papilloma, what anatomical features does it have? A nevus can be formed from different layers of the skin (epidermis or dermis); it can be single or multiple elements appear, differing in size and color. Melanocytes give it its characteristic color; shades can vary from flesh-colored, dark brown to black and blue.
Acquired moles appear in a person throughout life, most often they form during the period of hormonal changes. These are puberty in adolescents, pregnancy and menopause in women, diseases of the endocrine system.
Over time, nevi can increase in size, change shape and color, but should not hurt or ulcerate.
In medicine, all moles are divided into melanoma-hazardous and melanoma-safe. Neoplasms of the first type can degenerate into a cancerous tumor, but not of the second. Nevi are also classified into vascular and non-vascular.
Types of moles:
- Convex ones have a rough surface, brown color, rise above the surrounding tissues, and often contain hairs.
- Dysplastic moles are irregular in shape with no clear boundaries, can reach 5–12 mm in diameter, and are localized on the scalp, chest or buttocks. The growths persist for life and have a genetic predisposition.
- A flat nevus grows on the hands, feet, soles, its size usually does not exceed 1 cm, the surface is smooth. The mole does not stand out above the surrounding dermis; its color can range from light brown to black.
- The blue nevus is large in size, up to 2 cm, has clear edges, and rises above the rest of the skin. A growth of dense consistency with a smooth surface, dark blue in color, its appearance is noted on the face, buttocks, upper or lower extremities. Blue nevi sometimes turn into cancerous tumors.
- Lentigo looks like freckles. This is an accumulation of multiple small pigment spots in a limited area of the skin. There is a brown or black color; it does not change throughout life.
- Sutton's nevus is a pigmented area surrounded by a halo of light skin. The growth may disappear spontaneously.
- A giant nevus is a flat, pigmented spot that can increase in size with age. The neoplasm can be brown, black, or gray in color; the spot can spread to the entire limb.
Moles, which are often injured by clothing, lentigines, nevi growing from subcutaneous fatty tissue, can turn into a malignant tumor. The greatest danger is posed by convex growths on the fingers, soles, and scalp, where they can be easily damaged by clothing or shoes.
What is papilloma
A benign tumor that occurs under the influence of the human papillomavirus (HPV) has a common name - papilloma. It is formed from connective tissue papillae, inside of which there is a vascular network, and on top they are covered with epithelium.
Growths arising from papillomavirus can have different locations on the skin, mucous membranes or internal organs. Certain types of human papillomavirus have increased oncogenicity and can therefore cause cancer.
Hanging and large papillomas are most prone to degeneration.
Features of moles
Benign formations on the human skin, which are formed by pigment cells, are called moles or nevi. Moles most often appear in infants and continue to form throughout life. The intensity of their manifestations can have varying degrees.
Nevi themselves are not dangerous, but sometimes in the event of injury, moles have a strong relationship with the subsequent development of the oncological process. Active growth of nevi is often observed during puberty and pregnancy, since at this time hormonal levels change greatly.
Moles and papillomas do not always remain benign tumors and can lead to serious complications, so it is necessary to constantly monitor such neoplasms to prevent their degeneration.
What is a mole?
A mole is a benign tumor that does not pose a danger to the body. Despite their harmlessness, formations can degenerate into malignant melanomas.
Even a child can develop a mole. Doctors call these types of formations nevi. They also include birthmarks.
Under the influence of various factors, an accumulation of pigment is observed in the skin. After some time, it transforms into a melanocyte. With a significant increase in the amount of the substance in the skin, the appearance of nevi is observed.
The formation of moles can be observed in children after reaching one year of age. A birthmark is formed before birth.
Moles appear in people of all ages due to an excessive accumulation of melanocytes
There are several types of moles that appear on human skin:
- borderline, which rise slightly above the surface;
- intradermal, representing tubercles;
- intradermal, which are often mistaken for papillomas;
- papillomatous, resembling broccoli;
- basal, having a flesh-colored tint;
- linear in the form of a chain structure;
- blue with a characteristic tint and the likelihood of degeneration into cancer.
Moles are not dangerous, but under the influence of ultraviolet radiation they can become melanomas. You need to pay attention to formations if the mole:
- grew by more than a centimeter;
- changed its shape;
- It began to itch and hurt, and turned red.
The lack of hair growth on a mole should also alert you. Such changes may indicate dangerous malignant processes.
Differences
There are several criteria that will help even a person without specialized education to understand the difference between a mole and a papilloma. But at the same time, it is advisable to show all skin pathologies and neoplasms to a specialist as soon as possible and undergo preventive examinations.
Main Difference
The main difference between papillomas and moles is their source of origin. The former are a manifestation of HPV, and the latter are a collection of pigment cells under the epidermis. Papillomatous formations are always acquired, and nevi are congenital pathologies inherited from parents to children.
Appearance
When a papilloma or mole appears, a dermatologist knows very well how to distinguish these neoplasms from each other. These skin growths externally differ in the following parameters:
- Size. Moles can be quite large, to the point that they can take up half of the face. And growths of viral origin usually do not exceed 1.5 cm.
- Structure. When you feel the nevi, the skin in the lesion remains smooth and has pores. Papillomatous formations have a loose structure or a pronounced increase in skin lines.
- Shape and color. Formations of a viral nature do not have a clear shape, they are asymmetrical, their color is pinkish or flesh-colored. Nevi can have different colors, are always symmetrical and have a circle shape.
Papillomatous neoplasms have vessels, and moles consist only of dermal cells.
Locations
Viral tumors are most often found in the groin, armpits, feet or neck. They are localized in areas of increased friction and severe hyperhidrosis. Moles can be located anywhere. Their appearance is not affected by humidity, temperature or other factors.
Causes and time of appearance
A mole is an individual feature of the body. The spot forms while the baby is in the womb. Babies are born with nevi, which remain with them throughout their lives. Various types of papillomas appear after the introduction of papillomavirus into the body during contact with a carrier of the infection.
These growths have the following distinctive features:
- rapid appearance;
- rapid (in a few weeks) generalization of the process;
- merging of individual growths into one large one.
If multiple growths appear on the skin, then this is a reason for a full examination to identify strains of papillomavirus and provide the correct therapeutic effect.
Should I delete it?
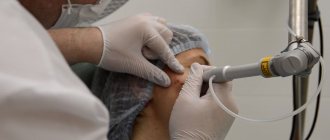
If a mole does not cause cosmetic or physical discomfort, then doctors do not recommend touching the areas of pigmentation. If there are objective reasons for getting rid of nevi, then it is under no circumstances recommended to remove a dangerous mole at home. A dermatologist-oncologist is well versed in the methods of removing moles, and after examining the patient, he will select the most optimal option.
The same is true with papillomas. Only a specialist can determine which papillomatous formations can be removed and by what method. To remove papillomas, there are the following methods:
- Chemical method. The use of special medicinal solutions that dry out the papillomatous formation and it disappears over time.
- Laser method. This method is preferred because after removing the growth, no traces remain and the patient quickly recovers after such manipulation.
- Cryodestructive method. Freezing tumors with liquid nitrogen. The disadvantages of this method are the high probability of relapse.
- Electrocoagulation method. Burning out build-up using high-frequency current.
- Radio wave method. To eliminate the tumor, the affected area of skin is dissected using radio waves.
- Surgical method. This method is used in cases where there is a suspicion that the growth has degenerated into a malignant form. In this case, the formation is cut off with a scalpel.
If the papilloma is small in size, then they try to resort to conservative treatment using specific antiviral agents.
Degree of cancer risk
Although papillomatous formations and nevi have quite a lot of differences, for the most part they do not pose a serious threat and are harmless neoplasms. Their cancer risk is not high. But if the growths are often injured and they are not given proper assistance, then the risk of cell degeneration increases significantly.
Skin lesions are very diverse and have many nuances. Sometimes a patient may confuse the initial stage of melanoma with papillomas. If he starts specific antiviral therapy without a doctor’s prescription, he can only aggravate the course of the pathological process.
It is always advisable to consult a dermatologist before starting therapy.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
Removal
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medications to remove papillomas
Moles and papillomas can be removed in the same way. Doctors use:
- surgical method;
- laser therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation.
At home, patients with papillomas, unlike moles, can cope with the help of creams, ointments, and sprays. You cannot prescribe them for yourself. The medications prescribed by the doctor are applied to the formation several times a day.
You can remove formations in several minimally invasive ways