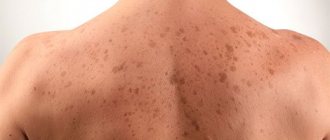
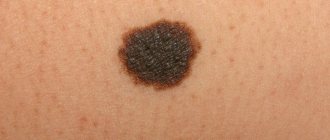
What types of moles are there?
One person may discover very different tumors. Types of moles are classified according to several criteria. This helps in correct diagnosis in case of changes. They differ in:
- origin – congenital, newly acquired;
- structure – pigmented, vascular;
- place of formation - in depth, on the surface, in the boundary layer;
- raised above the skin - flat - even, protruding as a hemisphere, pedunculated, larger birthmarks;
- potential threats - dangerous, degenerating into melanoma, non-dangerous.
According to the risk of developing pathology
Dermatologists classify nevi according to the risk of developing cancer:
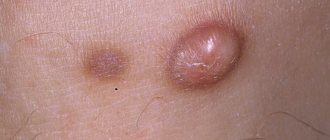
- Non-hazardous. Such moles degenerate into cancerous formations extremely rarely. Such degeneration can only occur with mechanical damage, which can occur during shaving or through irritation with clothing.
- Dangerous. Dangerous moles include Ota moles, blue nevi, borderline moles, pigmented congenital huge nevi, and atypical moles. Such formations often transform into melanoma, which should be removed immediately after degeneration and confirmation of the diagnosis.
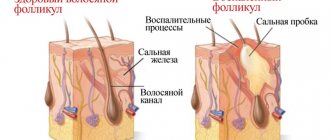
Birthmarks are formed under the influence of several factors: hereditary, intrauterine abnormalities of cellular development, oxygen starvation of the fetus, hormonal imbalances.
Prevention of melanoma development
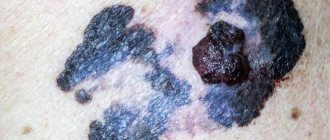
Speaking about how to recognize melanoma and what it is, first of all, it should be said that it is either a nodule or a spot that has a dark color (although there are also non-pigmented types) and an irregular shape.
Risk factors that can accelerate or provoke the development of melanoma include the following:
- the effect of ultraviolet radiation on the skin (this applies to both sunlight and artificial sources - solariums or bactericidal lamps);
- previously existing precedents for the occurrence of melanomas, both in the patient himself and in his close relatives;
- the presence of a large number of moles on the human body (we are talking about fifty or more);
- female;
- old age (although melanomas also occur in young people);
- white skin, red hair and a large number of quickly appearing freckles.
The first sign that a person is developing melanoma at the site of a mole is, as a rule, changes that suddenly begin in it. Take a closer look at your birthmarks.
- Ordinary moles are always symmetrical. If you mentally draw a line through their middle, then both halves of a normal mole will completely match in shape and size. Any violation of this symmetry should raise your suspicions.
- Pay attention to the borders of the mole. If they are uneven, blurry, unclear, then it should be checked.
- A change in the color of your tumor should also alert you. If the mole is colored in more than one color or has several shades, check it.
- Symptoms of melanoma development include an increase in the size of the birthmark. Even if your spot has no other deviations (even color, clear boundaries, symmetrical shape), but its diameter exceeds 6 mm (this is about the same as the eraser on the tip of a pencil), this can be considered alarming symptoms.
From the above, we can draw an unambiguous conclusion regarding how to recognize melanoma at an early stage. But at the same time, you should remember that you don’t need to wait for all the listed symptoms - just one of them is enough for you to have a serious reason to consult a dermatologist.
Melanoma, like any other disease, has a number of preventive measures, following which you can avoid encountering it. Prevention is the most important element to prevent the transformation of a healthy mole into a dangerous neoplasm. To reduce the risk of its occurrence, you must:
- Try to avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight (no more than 4 hours) and reduce visits to the solarium to one session per week (or even better, completely abandon this hobby);
- Avoid injury or injury to birthmarks;
- Avoid being under the sun during the hottest and most dangerous time for your skin – from 11 am to 5 pm.
Knowing the main signs of the degeneration of moles into melanoma, it is possible to timely diagnose an insidious and dangerous malignant tumor. Thanks to this, it is possible to timely prescribe drug therapy that prolongs life or completely rids the patient of a tumor.
Types of melanomas
To understand how melanoma differs from a mole, it is necessary to understand in detail its varieties. Experts divide melanomas into:
- Lentigo. This pathology is often observed in elderly patients. Melanoma of this type can be localized on the neck and face. The formation protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin.
- Knotty. Melanoma of this form is an aggressive oncological formation. Outwardly, it looks like a cluster of nodules of different colors and sizes. The formation may have a purple or black color and can rise high above the surface of the skin.
- Superficial. This form of melanoma is the most insidious type of cancer. Since the tumor does not rise above the skin, it is difficult to distinguish it from a nevus.
- Subungual. Most often, subungual melanoma is located under the nail on the big toe. This formation is found in 1 in 10 patients with melanoma.
The first and main sign of the degeneration of a nevus into melanoma is a significant visual difference from other moles on the body.
Where to check a mole for cancer? This can be done by a specialist either in a municipal medical institution or in a private clinic.
Safe moles
Those who have dark spots on their skin should be wary of their changes. In time, detected signs of degeneration into melanoma contribute to the timely removal of the formation and preservation of health. Safe moles are different:
- the presence of a stalk – it cannot be formed by malignant cells that grow randomly;
- long-term condition without changes.
Spots that appear shortly after birth are not considered dangerous. It is important that they are small in size. Good – non-dangerous – signs of neoplasms include:
- flesh tone;
- unchanged pattern of the skin of the nevus and adjacent tissues;
- soft consistency;
- hair on the surface of the neoplasm - growing from the skin, indicates the absence of pathologies;
- diameter no more than 5 mm;
- symmetry;
- nevus in the form of a spot.
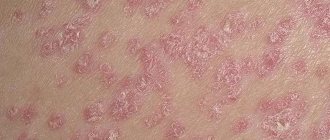
Types of skin cancer
Along with melanoma, there are other malignant tumors that affect the skin , including basal cell carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma) and squamous cell carcinoma. They occur in 88% of cases of all types of skin cancer.
Why is melanoma not cancer?
It should be remembered that skin cancer and melanoma are not the same thing. Cancer is formed from epithelial cells (skin), while melanoma is formed from pigment cells (melanocytes).
The answers are in the video from Bookimed.
To get a consultation
| Types of skin cancer | Basalioma, basal cell carcinoma | Squamous cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma | Melanoma |
| Peculiarities |
|
|
|
| Frequency | Very common. | Less common. | It is the least common, but among types of skin cancer it is the most dangerous. |
| Appearance (signs) | A nodule similar to a boil that does not mature for a long time; Over time, it ulcerates, destroying the area of skin. | A tumor that can go deep or rise above the skin; ulcerates and becomes painful. | It looks like an asymmetrical mole with an uneven contour, larger in size than usual; painful, may itch, swell, bleed. |
| Photos | «> |
To get a consultation
Melanoma and mole - what's the difference?
«>
According to various oncology communities, in 30-40% of cases, melanoma develops from moles, nevi and age spots already existing on the body.
Moles and nevi are clusters of pigment cells that every person has. We are not born with them: they appear in early childhood and may disappear in later life. Often, new moles form on the body before the age of 40. Normal moles do not change throughout life; they are clear and uniform. Melanoma is characterized by dynamics: if a mole grows and changes, it is most likely malignant.
Symptoms of the disease
Additional signs that will tell you how to recognize melanoma will be changes that occur with the mole. If the nevus thickens, rises above the skin, increases in size and at the same time changes pigmentation, then it should be shown to a dermatologist.
Particularly obvious signs of a dangerous situation are redness of the tissues around the nevus, the appearance of cracks, crusty ulcers, and bleeding. In such cases, the mole causes concern - it itches or burns. In this case, the patient's lymph nodes may become enlarged.
As a rule, skin melanoma has the appearance of a mole with an asymmetrical shape, exceeding 1 centimeter in diameter. How to distinguish a mole from melanoma? Signs of melanoma (malignant moles):
- uneven color of the birthmark on the skin;
- sometimes the mole becomes very dark, almost black;
- redness appears around the change;
- itching may occur;
- the surface of the change may be uneven;
- Bleeding and ulcers may occur.
If any of these symptoms occur, you should contact your doctor immediately.
When melanoma metastases to the lymph nodes, they increase in size. Organ metastases manifest differently depending on location. Melanoma causes metastases to soft tissues, lungs, brain and liver.
Melanoma can be recognized by examining it magnified or using a dermatoscope. If melanoma is suspected, a biopsy of the changed tissue should be performed. But this can lead to the spread of cancer cells.
Therefore, suspicious moles are always removed completely and only then a histological examination of the removed tissue is carried out.
If ulcers exist, a smear can be taken for examination. Enlarged lymph nodes are examined using a biopsy. A chest x-ray is performed to rule out lung metastases.
The degree of development of melanoma is assessed by measuring the thickness of the changed skin in millimeters. An unfavorable factor is the occurrence of ulcers. The condition of the lymph nodes and the presence of distant metastases are assessed.
Melanoma occurs where melanocytes are found. Most often it is the skin (90% of cases), especially open areas exposed to solar radiation.
Quite less often:
- eyeball;
- nail;
- oral mucosa;
- mucous membrane of the genitals and anus.
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of malignant tumor.
And although, according to statistics, this disease makes up no more than 10% of other cancers, it tends to affect younger and younger people.
Melanoma most often develops on the lower leg (in women) or the back (in men), but can even form on the palm of the hand. It can occur for no apparent reason or be the result of degeneration of nevus cells.
How to determine that a mole is no longer benign?
Let's look at the signs of melanoma moles.
Types of nevi
In medicine, several classifications are accepted.
So, based on the structure of the neoplasm, the following are distinguished:
- vascular. Consist of overgrown vessels;
- non-vascular. Formed by a cluster of melanocytes.
According to the location they are distinguished:
- epidermal nevi - formed in the epidermis;
- intradermal - in the deep layers of the dermis;
- borderline - can affect both of these layers of skin.
Depending on the existing risk of degeneration into melanoma, there are:
- melanoma-free. In the absence of adverse effects, degeneration into a malignant tumor does not occur;
- melanoma-hazardous. High risk of developing melanoma from a nevus.
Risk factors
It should be noted that the exact reasons for the degeneration of a nevus into melanoma are still unknown. However, experts identify factors that can provoke the transformation of a mole. These factors include:
- Age from 30 years.
- Long stays in a solarium, under the sun.
- Sunburns that were received in childhood and made the skin unstable to melanoma.
- The presence of a large number of moles on the body.
- Increased tendency to develop freckles.
It is important to remember that melanoma can develop on a clear area of skin, and not just degenerate from a nevus.
But in any case, if there is the slightest doubt, it is better to remove it.
What dangerous moles look like
Why do people with nevi on their bodies need to monitor their changes? There is always a threat of degeneration of non-dangerous tumors into a cancerous tumor. What moles are dangerous to health? Key signs you need to know:
- change in shades towards the dark side, the appearance of multi-color;
- rapid increase in size - exceeds two millimeters per year;
- occurrence of cracks;
- the formation of asymmetry due to uneven growth;
- lack of elasticity;
- the appearance of itching, burning;
- presence of discomfort.
The appearance of dangerous moles requires an immediate visit to a specialist to clarify the nature of the changes and the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Pathological transformations provoke:
- injury to the nevus due to negligence;
- self-removal;
- abuse of exposure to the sun, use of a solarium;
- location of the formation in places of frequent contact with clothing - on the neck, head, genitals, legs;
- placement in the hair, on the face, palms - where there is a high probability of injury;
- previously removed melanoma.
Not a single person is protected from the sudden proliferation of cells of a harmless mole. Melanoma is an extremely serious disease. Changes not detected at the initial stage can result in death. The provoking factor is unsuccessful independent removal of tumors. Moles are dangerous because of their ability to:
- transform into an atypical – precancerous form;
- grow to large sizes;
- turn into cancerous;
- with minor external changes, metastases actively spread throughout the body through the circulatory and lymphatic channels.
What do nevi that are subject to pathological changes look like? Only a doctor can correctly distinguish between non-dangerous tumors. Dangerous formations look like this:
- blue – seals under the skin with clear boundaries, with dimensions no more than 10 mm;
- nodal – round, flat in shape, color – brown, black;
- skin – often pale, convex;
- halo nevus - pigment surrounded by a light or white rim;
- Spitz - looks like a dome-shaped tumor of pink shades, with the possible presence of a hole through which blood and fluid leaks;
- connective - connect individual formations into a whole.
One of the signs of a non-hazardous formation turning into a dangerous one is a change in contours. It often has blurred edges and scalloped borders. There are non-dangerous types of nevi - dysplastic. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis. A mole with uneven edges can be dangerous if there are additional signs of melanoma:
- accelerated changes in size;
- the presence of clearly defined asymmetry;
- the appearance of highly indented boundaries.
Rough mole
Such a neoplasm is harmless if its diameter is no more than 5 mm and remains constant in size. Often its appearance signals a lack of vitamins and nutritional disorders. Doctors advise coming for a consultation if it is discovered that:
- the smooth nevus turned into a rough one;
- bothered by burning, itching, tingling;
- irregularities and compactions appeared in the middle;
- areas with different shades formed;
- diameter has increased significantly.
A dangerous rough mole requires immediate examination if:
- the appearance of bleeding;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- rapid change in size;
- formation of asymmetry;
- formation of purulent discharge;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when touched;
- the emergence of an irregular shape, blurred boundaries, along the edges of the neoplasm.
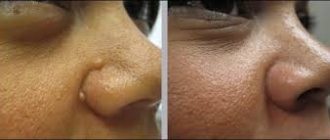
Large moles
Large formations on the skin are pigment spots. When they remain unchanged and do not cause inconvenience, this is not a dangerous phenomenon. It is important to constantly monitor their appearance, color, and size. To eliminate worries, you need to consult a dermatologist. During the visit, the specialist will conduct a diagnosis and give a forecast of the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm. Large moles become dangerous if they:
- injured;
- thickened;
- started to itch;
- were unsuccessfully removed independently;
- changed in size, shape;
- are bleeding.
Types of melanoma
Skin cancer is divided into types according to shape and position. Laboratory studies have identified melanoma varieties, some of which are especially difficult to distinguish from traditional moles and freckles:
- Superficial formations are the most common type of melanoma when its surface coincides with the top layer of skin. The danger of this type is its relationship with an ordinary mole. Therefore, it is difficult to determine in the initial stages. A person does not perceive melanoma as a skin disease.
- Nodular formation is an aggressive type of melanoma when the nevus takes the form of a nodule. The surface of melanoma is raised compared to the top layer of skin. This species in most cases has a dark brown color. Due to its ugly appearance, darkened color and unpleasant sensations when you catch the nodule with your hands or a household object, nodular melanoma soon becomes the subject of examination by a doctor. A cosmetic defect affects the patient’s consciousness and forces him to consult a dermatologist.
- Nail formation is rare, but the signs are the same. The location of melanoma is the big toes; a pigment spot of a malignant tumor forms under their nail cover.
- Lentigo is a formation in the form of a flat spot, which also looks like a mole. This pigmented nevus slightly exceeds the surface of the skin and has a diameter of up to 3 cm. It most often forms on the cervical area or on the head. It does not cause pain, so it is not always diagnosed on time.
Lentigo is a flat spot on the skin
How does melanoma grow?
Most often, melanoma develops on the lower extremities, torso and arms; in only 10% of patients it can occur on the head or neck.
The described tumor, as a rule, grows in three directions - into the deep layers of the skin, along its surface, or through the skin into nearby tissues. By the way, the deeper the tumor spreads, the worse the prognosis of specialists.
Answering questions about how to recognize melanoma and how it manifests itself, oncologists note its rapid metastasis and damage to nearby lymph nodes. It spreads not only through the skin, but also by hematogenous or, as already mentioned, lymphogenous route. By the way, hematogenous metastases have the ability to penetrate any organ, but most often they affect the kidneys, adrenal glands, liver, brain and lungs.
Metastases on the skin look like peculiar small rashes that rise slightly above it and are brown or black in color.
All of the above signs of the development of the disease will probably make you look at your body with fear. But we also want to warn you that when thinking about how to recognize melanoma and not miss its symptoms, do not immediately start sounding the alarm as soon as you notice that the mole has enlarged. After all, an ordinary nevus can change, just as we change with age.
By the way, the presence of hairs on a mole confirms that it is healthy!
How to distinguish a mole from melanoma?
Melanoma is a cancerous tumor that arises from melanocytes—pigmented dermal cells—that begin to grow uncontrollably.
The reason for the development of this type of malignant formation is not fully known to specialists. Melanoma accounts for only 1% of all cases of malignant tumors. Despite such a low prevalence rate, this pathology has a high mortality rate - up to 80%. This feature is due to rapid metastasis to the liver, lymphatic system, lungs, bones, and brain.
As a rule, the tumor is localized on the skin, but there is a possibility of its appearance in the eye, on the mucous membranes of the rectum, vagina, mouth, and nose.
How quickly does melanoma develop from a mole?
The transformation of a nevus into a cancerous formation can occur in different ways. The process depends on the stage of the disease and the type of tumor. Instant metastases are dangerous. Begins:
- growth of cancer (oncological) cells in the deep layers of the epidermis;
- their entry into the blood and lymph;
- penetration into the lungs, liver, kidneys;
- growth in these organs;
- complete damage to the body;
- death.
The growth phases of pigment cells are observed, along which melanoma develops from a mole. There are varieties:
- horizontal - damage to the upper layers of the skin occurs, lasting up to 10 years, but metastases do not appear;
- vertical – accompanied by the spread of cancer cells throughout the organs, can last two years, has an unfavorable prognosis;
- nodular - especially dangerous - characterized by deep spread within two months.
Features of melanoma
Melanoma can develop from epithelial melanocytes or degenerate from a mole. It can occur anywhere, but most often it is detected on open areas of the body (limbs, neck, face). Its insidiousness lies in the fact that the tumor can very quickly metastasize and affect the lymph nodes, liver, brain and other vital organs.
Risk factors that result in the degeneration of melanoma from a mole include:
- frequent exposure to ultraviolet radiation (visiting a solarium or staying in the open sun);
- Skin type I or II;
- the formation of large numbers of freckles or moles (over 50) on the body;
- presence of atypical moles;
- hereditary predisposition;
- sunburn, especially in childhood;
- development of benign tumors;
- radioactive radiation;
- frequent contact with toxic chemicals;
- skin injuries (scars, burn scars);
- age (over 30 years old).
Melanoma may appear after mole removal.
There are several types of melanoma:
- Superficial. It is most often diagnosed and is found in the upper layers of the skin.
- Lentigo is a formation that develops on the skin of the neck or head and protrudes slightly above its surface. Elderly patients are mainly susceptible to its development.
- Nodular melanoma. Its distinguishing features are dark nodules of different sizes. This type of tumor is the most aggressive and develops very quickly.
- Subungual – occurs in every tenth patient diagnosed with melanoma. It occurs under the nail plate of the lower extremities.
There are 4 stages of development of a malignant tumor:
- Epithelial or nevus cells degenerate and look like a spot with jagged edges or a bright nodule that is clearly visible above the surface of the skin.
- The thickness of the neoplasm exceeds 2 mm and may bleed.
- The thickness and area of melanoma spread unevenly, gradually affecting healthy cells and nearby lymph nodes.
- Melanoma has a negative effect on all lymph nodes and internal organs, disrupting their functioning.
Diagnosis of the disease
And yet, if you have doubts about the condition of your mole, do not guess about how to recognize melanoma yourself, but consult a doctor. He will clarify the symptoms, find out all the risk factors, and conduct an examination.
Due to the fact that, as already mentioned earlier, melanoma is very aggressive, and its development can be triggered by even a minor injury, an invasive method of examining it is highly undesirable (by this we mean scraping or histology, when not the entire formation is taken for analysis, but a small part of it) ). Therefore, most often the doctor performs an external examination of the nevus.
He will definitely check the condition of the lymph nodes under the arms, neck and groin, and will also conduct a radioisotope study, which uses phosphorus. Its increased accumulation in the tumor is used to determine the presence of melanoma.
A cytological examination is also used, in which, if there are ulcerations on the suspected melanoma, an imprint is taken from the surface of the tumor and then sent for analysis.
To determine the presence of metastases, ultrasound of internal organs, x-rays and tomography are also performed.
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. Every person (especially those with a large number of birthmarks) should know the difference between a mole and melanoma. After all, by identifying small changes and contacting a specialist about them, you can significantly increase your chances of recovery and survival.
- Size – even a slight increase in size requires immediate contact with an oncologist;
- Color - a change or uneven shade may indicate the beginning of transformation into a malignant tumor;
- Edges – uneven, blurred or jagged edges indicate the presence of an oncological process;
- Asymmetry - uneven distribution of spots is also a good reason to start worrying about your own health;
- Surface - the presence of any bulge indicates the need to visit an oncologist.
What are they?
In order to understand what the main differences between a mole and melanoma are, you should study the types of nevus.
Experts divide moles into:
- Vascular.
- White.
- Birthmarks.
Many people are interested in which moles are dangerous and cause melanoma.
They are classified taking into account the depth of origin, color, size, and the degree of danger of transformation into cancer.
Birthmarks are often inherited, like eye color and nose shape. The cause of moles on the body is a large accumulation of abnormal cells rich in melanin in one place. It is melanin that determines the color of human skin and moles. The most common moles are brown in various shades. The intensity of the brown color of the nevus directly depends on the genotype.
Warm blue nevi are much less common than brown moles. The blue color is due to the content of white or pink melanocytes in the epidermal cells.
It is important not to confuse spots in the form of plaques that are brown in color with moles, as this is a seborrheic dermatome. Red spots are hemangiomas, and hanging moles are called acrochordomas.
What moles can be removed
Often nevi cause trouble for women when they are in a visible place - the face, neck. Even if they do not bother you, using removal will be the right decision - the appearance will improve significantly. After the procedure, the doctor must send the tissue for histological analysis to decide whether the mole is malignant or not. If the neoplasm is not dangerous, does not bother you, and does not change in size, surgery is not required. What moles cannot be removed? Experts believe:
- there are no contraindications;
- It is important to choose the right excision technique.
You should be careful about skin growths; it is unacceptable to remove them yourself. Only the doctor will determine whether a nevus is dangerous or not and decide what to do with it. You can delete it if:
- injured from clothing - on the neck, in the groin area, under the armpits;
- cause pain when touched;
- are located under the hair on the head and can be damaged when combing or cutting;
- change color, shape, outline;
- significantly increase in size;
- characterized by the presence of burning, itching;
- accompanied by inflammation and bleeding.
Signs of unsafe moles
1. Asymmetrical shape
A normal mole that does not threaten your life should be symmetrical, that is, round or oval, its parts should be equal to each other. Its edges are clear, smooth and bright. A dangerous mole has an arbitrary shape, torn, unclear, blurred edges. If you have such a birthmark on your body, consult a specialist immediately. Only he can accurately determine whether it is a mole or melanoma.
2. Color
A harmless mole has an even brown or dark brown color, it is evenly colored, and does not have spots or impurities of other colors. A potentially cancerous mole is uneven in color and has spots and impurities of different colors. Check the color of moles on your body, and also ask your family to examine pigmented formations that are in places inaccessible to your eyes.
Size 3
All pigmented formations on the skin that exceed 6 mm should be examined by a doctor. Moles larger than a pencil eraser may be cancerous.
4. Transformation of moles
Pay attention to whether changes occur to your mole. A sharp change in color, shape, or increase is evidence of potential danger.
5. Unprotected skin
If you frequently visit the beach or tanning salon without using sunscreen, you are putting your health at risk. It has been proven that ultraviolet rays increase the likelihood of a healthy mole degenerating into a malignant one by 74%.
How is melanoma treated?
If the patient managed to contact an oncologist in time, then at an early stage of development the melanoma is simply excised. Depending on how deep it penetrates, a small amount of healthy skin is also removed. The doctor may also prescribe additional therapy in the form of medications that will help reduce the likelihood of relapse.
If damage to the lymph nodes is suspected, then after a biopsy of one of them and a positive result, they are supposed to be removed.
Immunotherapy has proven to be of significant benefit in the treatment of melanoma. This is a relatively new treatment method that is performed immediately after surgery to remove the tumor.
In the later stages of the development of the disease, they resort to radiation and chemotherapy, which, by the way, at the fourth stage of the development of a cancerous tumor turn out to be ineffective, allowing only to reduce it to some extent.
Who is at risk for the appearance and development of melanoma?
Even the most experienced doctor cannot say exactly what determines the choice of fate: to get sick or not to get skin cancer. It is also definitely unknown what factor progresses the development of a malignant mole. One thing is known: everyone needs to be checked at least once every six months.
After a series of studies on melanoma, it was found that the following categories of people are at risk of this disease:
- natural blondes, as well as people with red hair;
- a person who had cancer patients in his family (namely skin cancer);
- a girl or guy whose skin is strewn with moles or freckles;
- working in the open sun during the hot season (rescuers on the beach, construction workers, etc.), because their body is exposed for a long time, receiving direct burns from the rays of the daylight.
It is difficult to say at what age people are susceptible to melanoma. Both young and old get sick. The main source of the disease is the sun. Depending on how sensitive the skin is to solar radiation, infection and tumor development will occur.
Doctors warn tanning bed lovers: ultraviolet radiation causes great harm to health; it is on the list of the most common ways of causing melanoma. Think about it: isn't it better to keep your distance from them?
People with freckles are at risk
The degree of danger of a mole to health
Melanomic moles - their degeneration into a malignant form is considered an extremely rare phenomenon, and basically they do not pose any threat to the body.
They are dangerous if they risk being damaged by shaving, rubbing or scratching. In this case, there is a possibility of developing a malignant form from a benign one.
Melanoma-dangerous moles are a form of precancerous pathology, and more often degenerate into an oncological tumor, and they must be removed immediately after detection. These include:
- nevus of Ota;
- blue nevus;
- border nevus;
- dysplastic nevus;
- congenital giant pigmented nevus.
How important is it to check moles?
Despite the fact that some people are more susceptible to melanoma than others, any of us can develop this terrible disease. To identify melanoma or a mole on the body, you need to visit a dermatologist at least once a year and conduct a self-examination using the above methods. Timely diagnosis of melanoma can save your life. It is important to know how to distinguish melanoma from a regular mole in order to take all necessary measures and prevent the development of the disease.
What is melanoma?
Melanoma is the name given to malignant formations that appear on the skin from various age spots or, in common parlance, moles. At the moment, this type of cancer is not fully studied, and the exact causes of its occurrence have not been established.
A tumor can form almost anywhere on the body, both from the cells of birthmarks and from cells of ordinary skin. Melanoma grows in all directions, growing above the skin, along its surface and inward through the layers of the skin. At later stages, which makes the disease very dangerous, bad cells can move through the circulatory system to vital organs of the body, such as the heart, brain and others, thereby forming metastases, which ultimately leads to death. Despite the seemingly harmless name, compared to other types of cancer, melanoma is very dangerous, develops quickly and forms secondary tumors.
The main place of occurrence of malignant formations are moles or, as doctors call them, nevi. One way or another, nevi are present on the body of almost all people, and it is believed that by the age of 25-30, most moles have already appeared. However, in practice, there may be cases where new birthmarks are formed at a later age. In addition, over time, nevi may change color or disappear altogether. There are a great many different types of moles. They can be flat, convex, and have different colors - from light flesh to black. Dimensions are also varied over a wide range - from a small point to several centimeters in diameter. This variety of shapes and sizes is normal and depends on the genotype of a particular person. More details about skin cancer with photos.
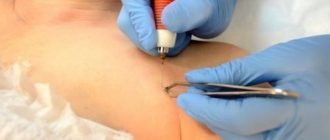
Melanoma removal
Malignant melanoma is removed surgically, removing healthy tissue around it. In some cases, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are additionally used. After removal, studies are carried out to determine the type of tumor.
The following methods are used to remove moles:
- Surgical method. We use it most when removing dangerous forms of moles and on areas of the skin hidden from view. In this case, nearby areas of skin are excised, and scars may form.
- Laser removal. Moles in the surface layer of the skin are evaporated using a laser. The procedure is quick and leaves no traces.
- Cryodestruction. Moles are removed with liquid nitrogen. Its low temperature can lead to scars.
- Electrocoagulation. Moles are destroyed by “cauterization” - high frequency current.
- Radiosurgery. The mole is affected by a beam of radio rays. The method's results are similar to surgical ones, but less traumatic.
Signs of degeneration according to the ACORD test
If you notice signs of changes in yourself, refer to the ACORD algorithm proposed by the American Cancer Society. Checking with the ACORD test will help you understand how to distinguish a mole from melanoma; it will not require special skills and will not take much time.
- A – Asymmetry. We examine the pigment formation, mentally drawing a line through the center. Normally, both halves will be identical, usually semi-circular or semi-oval. In melanoma, the shape of the halves of the nevus will be asymmetrical in relation to each other.
- K – Edges. An ordinary mole has even and smooth borders. When degenerated, the edges of the nevus become jagged, blurred, and have an irregular shape.
- O – Color . A benign nevus has a uniform color over its entire surface, from light brown to dark. The appearance of different shades on one mole is an alarming sign. In such cases, a whole range of shades from red to blue or black may appear.
- R – Development . Notice the mole that suddenly begins to change. If the nevus began to protrude above the surface of the skin, its size increased, the edges became fuzzy, and the color changed - this indicates degeneration. You should also be alert to the appearance of new symptoms, such as: bleeding, itching, burning, peeling, cracks or crusts.
- D – Diameter. When a mole degenerates, its diameter, as a rule, becomes larger than 6 millimeters, although at the initial stage the size of melanoma is smaller. Measuring the diameter is quite easy; apply the back of the pencil (with the eraser) to the mole, the diameter of the eraser is just 6 millimeters; if the nevus goes beyond the limits, this is a reason to contact an oncologist.
Timely diagnosis of a mole can save lives
What does melanoma look like and how to identify it at an early stage?
At an early stage, melanoma is difficult to distinguish from an ordinary mole. It appears as a spot or nodule on the skin, mucous membrane or iris of the eye. If you notice a mole larger than 6 mm and it causes discomfort (it grows, changes color, hurts or itches), you should consult a doctor to determine whether the formation is malignant. At a later stage, nearby lymph nodes are involved in the oncological process.
General health with metastatic melanoma worsens. The patient notices weight loss and weakness, which indicates a disruption in the normal functioning of all body systems. It must be remembered that the earlier the diagnosis is made, the higher the curability of this disease.
Causes of melanoma
Today, melanoma is considered one of the most dangerous types of cancer in the world, and the number of patients with this diagnosis is growing rapidly. To date, it has not yet been possible to definitively determine the specific cause of development, but the factors that significantly increase the risk are definitely known. By being aware of such factors, you can limit them and thus reduce your risk.
Risk factors in the development of melanoma:
- Genetic predisposition
If anyone in your family has been diagnosed with melanoma, you are more likely to have melanoma. It is necessary to regularly examine the skin and, at the slightest suspicion of melanoma, consult a doctor.
- Ultraviolet radiation (sun, solar lamps, solarium)
Uncontrolled exposure to the sun and frequent visits to the solarium lead to excessive insolation (UV irradiation) of the body and burns. The latter are especially dangerous in childhood, as they can lead to the development of melanoma in adulthood.
- Multiple and/or atypical moles
The more moles on the body, the higher the likelihood that they can degenerate into malignant formations. Timely monitoring will allow you to identify suspicious elements on the skin and provide timely treatment.
- Light skin phototype
The skin of people with blond or red hair is poorly protected from ultraviolet radiation. They are more prone to sunburn and statistically have a higher incidence of melanoma.
- Decreased immunity
The immune system protects us not only from viruses and bacteria, but also from the formation of malignant cells in the body. Immune activity may decrease with chronic infections, as well as while taking certain medications.
- Xeroderma pigmentosum
This is a fairly rare hereditary disease in which the skin is unable to recover after exposure to sunlight. She burns easily, which increases her risk of melanoma and other skin cancers.
To get a consultation
Prevention of melanoma
A healthy lifestyle and timely treatment of infections are the first step in the prevention of cancer pathologies. These factors cannot completely protect against cancer, but they reduce the risk of getting sick. For prevention, it is necessary to dose out sun exposure, use sunscreens with a high degree of protection and undergo periodic examinations with a dermatologist.
«>
In order to identify melanoma, it is very important to notice any changes in the skin through examination. You should examine your body in front of a full-length mirror; you can use a mirror to examine areas of your back. You can also ask a loved one to help examine hard-to-reach areas of the skin.
Using a special algorithm, you can promptly notice suspicious formations on the skin at home.
Examination of moles at home
| 1. Determine for yourself a time for regular inspection : this can be done once a season. But if you have any of these risk factors, check your skin more often. |
| 2. Keep a diary and make notes about the date of the examination, moles that have recently appeared and are suspicious. |
| 3. To visually record the changes that have occurred, take photos of moles . |
| 4. Find a place for inspection - it should be a bright room with a large mirror; Use a small hand mirror to inspect hard-to-reach areas. A loved one can also help you with the examination. |
| 5. Examine the entire surface of the skin, including the face, ears, neck, armpits, chest, sides, palms, fingers, front and back of the legs, genitals. Pay attention to the nails and interdigital areas; Visually examine the reflections of your eyes and skin in places that come into contact with clothing and shoes (for example, underwear, glasses, belt). Women should examine the skin under their breasts. |
| 6. Examine the scalp - use a comb, hair dryer and mirror to remove strands of hair and check for moles. |
| 7. Record the size of the moles by measuring their size with a ruler and recording it in a diary, or use a camera. |
| 8. Carefully touch moles that differ from others in color, shape, texture to determine whether they cause discomfort, whether they itch, and to understand how much they rise above the skin. |
| 9. If you find suspicious moles or lumps on the skin, record their size, position on the body in a diary and undergo diagnostics. |
Source: bookimed.com
Prevention
Prevention significantly reduces the risk of developing skin cancer.
It includes simple and accessible actions for everyone:
- Annual examinations by oncologists (dermatologists) if new spots appear or changes in the appearance of previous ones.
- Minimizing traumatic moments: do not try to get rid of moles without the help of a specialist.
- If sun exposure is necessary, use creams with UV filters to reduce the effect of sunlight on the dermis. It is undesirable to be outside on a sunny day from 10 a.m. to 5 p.m.
- After visiting exotic countries, be examined by a doctor.
- Avoid solariums, where artificial irradiation is much stronger than natural irradiation.
The rules are simple and achievable, but health is the same and it can be difficult to restore it. Therefore, take sunbathing in the morning, check the condition of your birthmarks and enjoy life, the right attitude towards which will give you many positive moments.
Cancer is a serious, fatal disease that was not defeated in the 20th century, but the fight continues in the 21st century. There are many varieties of this disease; this article discusses skin cancer
Precancerous types of neoplasms
Degeneration of a mole into melanoma is common. How to determine visually: “A mole or melanoma has appeared on the skin?” There are types of neoplasms that, due to their characteristics and external manifestations, are similar to melanoma, harbingers of melanoma are moles or nevi:
- nevus of Ota;
- Dubreuil's melanosis;
- Setton's nevus;
- pigmented border nevus;
- giant pigmented nevus.
Let us characterize in more detail all the presented types of neoplasms, for the purpose of correct diagnosis, when difficulties arise in determining the diagnosis visually: “Nevus or melanoma?”
Nevus Ota
This neoplasm has characterological features:
- located on the facial area;
- gray or brown;
- has layers of white skin;
- creates the appearance of “dusty” skin.
Nevus of Ota is usually located on the face
Dubreuil's melanosis
The neoplasm is a precancerous skin pathology and has a number of characteristic features:
- single spot;
- brown tint;
- has blurred boundaries;
- changes color (from light brown to black);
- localization on the facial area;
- size – 19–28 mm.
Nevus of Setton
The neoplasm is represented by a nodule with a brown tint. Setton's nevus has a number of characteristic features:
- nevus size 3-6 mm;
- raised above the skin;
- oval shape;
- there is a depigmented area around the nevus;
- localization: arms, torso.
Pigmented border nevus
The neoplasm is visually represented by a black node with a flat shape. Nevus is characterized by a number of features:
- lack of hair on the surface;
- smooth and dry surface;
- size 9 mm;
- localization: skin of the palms, genitals, feet.
Pigmented borderline nevus has a flat, smooth surface
Giant pigmented nevus
The neoplasm is gray-black in color and has a number of characteristic features:
- has a bumpy surface;
- has cracks;
- there may be a “leg” at the base of the nevus;
- The nevus grows in size along with a person’s height.
Classification of neoplasms on the skin
Neoplasms form at birth or throughout life; the acquisition of spots is often associated with the teenage maturation of the body and the period of pregnancy. The spots can transform, changes are reflected in:
- form of neoplasm;
- shade (darkening).
The spots have a unique structure and color. The surface structure of neoplasms has certain indicators:
- smoothness;
- tuberosity;
- roughness.
Types of neoplasms:
- lentigo;
- epidermal-dermal neoplasms;
- complex neoplasms;
- intradermal neoplasms;
- dysplastic nevi;
- blue nevi;
- large pigmented nevi.
Let us consider in more detail the characterological features of each neoplasm, with the aim of better studying and the possibility of conducting comparative diagnostics with melanoma.
Lentigo occurs due to excess melanocytes
Lentigo
A pigment spot that is brown or brown in color is lentigo. The neoplasm appears due to the presence of the following indicators:
- a large number of melanocytes;
- a sharp increase in the production of melanocytes.
Melanocyte cells are carriers of the pigment responsible for skin color; their number is limited by the physiological characteristics of the body.
It is important to remember that lentigo has a dark shade, and freckles have a light shade. Ultraviolet radiation does not affect lentigo, changing its shape and color.
Epidemo-dermal formation
A flat, yellow-colored neoplasm is an epidermal-dermal neoplasm that has the following characteristic features:
- the size of the mole is less than one centimeter;
- localization: palms, soles, genital skin.
Complex mole
Complex moles are dark-colored neoplasms in which melanocytes are located in the deep layer of the skin, so these moles have a convex shape.
A complex mole protrudes noticeably above the skin
Mole intradermal
Moles raised above the skin are called intradermal neoplasms (nevi). Intradermal nevi can have different colors:
- light (beige);
- dark beige;
- dark brown;
- black.
Intradermal spots have a smooth or hairy surface.
Dysplatic nevus
Neoplasms of various shapes, red in color, with unclear contours are dysplastic nevi. They have characteristic features:
- dimensions greater than one centimeter;
- smooth or bumpy surface;
- localized on the skin of the chest and buttocks.
Nevus blue
Neoplasms of blue color, hemispherical shape - blue nevi, the following indicators are characteristic of them:
- size less than 2 cm;
- the surface is smooth;
- location: skin of the facial area and buttocks.
Congenital neoplasms, gray and black in color, increasing depending on the growth of the body - large pigmented nevi. These tumors cover a significant part of the skin.
Blue nevus often occurs on the skin of the face
Characteristics of melanomas
Melanoma is one of the types of skin cancer. It is she who is called by oncologists “the queen of cancer” for her rapid growth rate and the rate of formation of metastases. It grows under the skin and on its surface in different directions and planes. Once in the inner layers of the dermis, melanoma cells are able to penetrate the bloodstream or lymph, spreading with the bloodstream throughout the body and becoming established in certain organs. This is how metastases (clumps of diseased cells) form and the disease progresses rapidly. Due to the rapid development, the percentage of deaths is quite high.
Among skin cancers, melanoma is the youngest, occurring even in infants and children. The female gender is more susceptible to its manifestation. A birthmark or age spots serve as a base platform, a source for degeneration into melanoma.
UV rays are considered to be the culprit of skin cancer.
Their influence increases:
- due to the thin ozone layer, the formation of “ozone holes”;
- as a result of people’s high sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation;
- with prolonged exposure to the sun and regular sunbathing;
- with frequent visits to the solarium or hot exotic countries.
Sun exposure and solariums are especially dangerous for people who have many birthmarks on their bodies or a high tendency to pigmentation. You cannot avoid the consequences by covering moles with a band-aid or covering them with a towel: the “greenhouse effect” is harmful, increasing the risk of melanoma.
Sometimes cancer cells form “out of nowhere” for various reasons. On clean, disease-free skin, a dark-colored asymmetrical spot appears, which grows and becomes potentially dangerous. This is usually due to genetic factors and can be traced through the family tree.
What is the difference between a mole and melanoma?
Most often, a person does not monitor the condition of pigmentation or moles that are familiar.
Meanwhile, when a birthmark degenerates, characteristic signs are noticeable:
- changing color to darker;
- lack of uniform color, peeling and loss of clear boundaries of the birthmark;
- redness along the contour of the mole as a result of its inflammation;
- surface growth and compaction;
- formation of dense nodules with signs of necrosis at the base of the nevus;
- irritation of the mole: it itches or there is a burning sensation;
- the formation of cracks and small ulcers, which may result in bleeding.
It is not so difficult to distinguish a nevus from a melanoma if you monitor the condition of the skin. If “metamorphoses” with birthmarks occur, consultation with an oncologist or dermatologist is required. It should be carried out as soon as possible, since the rapid development of melanoma leaves low chances of success.
It is not necessary to look for differences in all of the indicators mentioned. One change, for example, color or shape, is enough for it to become a signal to go to the doctor. An examination is required after visiting hot countries, if the nevus is injured or has significantly darkened.
Types of melanomas
Usually melanoma is a mole in the stage of degeneration.
There are different types of melanomas:
- Lentigo is usually seen in older people on the face or neck, protruding slightly above the surface of the skin.
- Nodular is the most aggressive manifestation of cancer. It is formed by small intertwined nodules that differ in color and volume. Raised above the epidermis and distinguished by shades of dark or purple color.
- Superficial is not much different from a regular birthmark. And since it is difficult to distinguish this type of melanoma, it is the most dangerous because it develops undetected.
- The nail is formed under the nail plate of the big toe. Every 10th melanoma patient has this type of pathology.
In detecting melanoma, the “black sheep” principle applies when one of the moles becomes different from the others in color, shape or other indicators. If an unusual spot is detected, you should undergo a medical examination.
Symptoms and signs of melanoma
How to distinguish malignant growth of cell mass from benign?
Why do moles appear?
One type of moles is congenital (genetic). These moles or birthmarks are large in size and are repeated in subsequent generations. There are also acquired nevi that appear on the body throughout human life due to external factors or as a result of changes occurring in the body.
New moles arise mainly due to:
- Hormonal factor. The occurrence is due to the hormone melantropin. This occurs when hormonal levels jump during puberty, menopause, and pregnancy. This is also facilitated by taking hormonal medications.
- Ultraviolet radiation. Long exposure to the sun or solarium contributes to the increase in pigment spots.
- Skin damage (thermal, mechanical, radiation, chemical).
ABCD International Melanoma Diagnostic System
- Asymmetry (asymmetry). Melanoma is not symmetrical along the axes; one half of the tumor is not similar to the other.
- Border irregularity (disorderly borders) - jagged outlines. The borders can be elongated in the form of a false stalk (a regular mole almost always has even, smooth edges).
- Color variegation – color variations from black to white. Black color indicates the accumulation of melanin pigment in the upper layers of the skin, black and blue - the pigment has accumulated in the middle layer of the skin. Redness and peeling of the surface indicates inflammation.
- Diameter (diameter greater than 6mm) should be measured along the longest axis. Very rarely, melanomas with a diameter of less than 6 mm are found. Melanoma usually has a diameter of more than 10 mm.