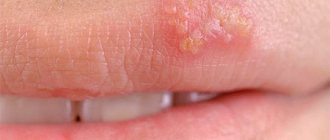
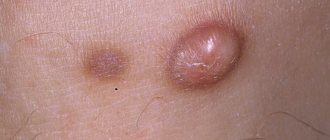
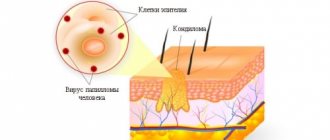
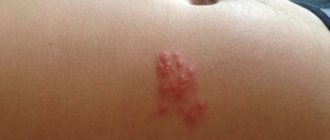
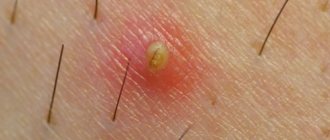
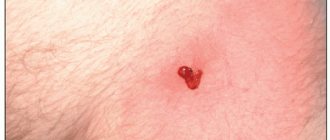
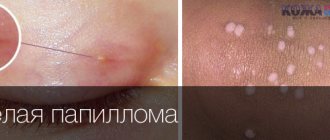
Unpleasant formations in intimate places are something that worries many, but it is not customary to talk about it. According to statistics, every third person is infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Not everyone has it externally; some people are simply carriers. Others experience unsightly growths on their skin. They are called papillomas or condylomas if they are localized in the genital area. These formations are uneven, soft to the touch, and are characterized by high growth rates. Condylomas can grow to noticeable sizes in a few hours.
READERS RECOMMEND!!!
To treat papillomas, our readers actively use the remedy... Read more
What is this?
Similar neoplasms are usually called “hanging moles.” They rise above the body, anchored at the base by a thin leg or a wide platform. This neoplasm is benign, but tends to become inflamed, affecting surrounding tissues.
Condylomas are localized on the skin of the genital organs, pubis, urinary canal, around the anus and inside the rectum. Their structure is lobed, and their color ranges from pinkish-beige to brown.
There are two types of condylomas:
- Wide – has a large base (up to several centimeters) and thickness, is considered a symptom of secondary syphilis;
- Pointed - in appearance they resemble bubbles on a thin stalk.
Usually people have condylomas of the second type. They grow at the opening and inside the vagina and in the anal area. Genital warts look like pearly papules and are not considered a disease. Their difference is that the former have a soft consistency and a thin stem.
Important!
HPV is transmitted through sexual contact (all types). Therefore, this infection is included in the concept of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases).
Pointed
Condylomas acuminata symptomatically appear as small formations on the genitals. The human immune system is able to prevent pathology from developing for a long time, completely hiding it. Several years may pass from the moment the virus enters the body until symptoms appear.
Reference! Condyloma is a reaction of an infected organism to weakened immunity when the virus gets out.
At first, the patient experiences unpleasant sensations: itching, itching, stinging, burning. After a few hours, a small condyloma forms (just a few millimeters) and cannot always be seen with the naked eye.
The formation is similar to cauliflower, lumpy, characterized by the presence of a “leg” of a pinkish or pale tint. They are able to develop, grow and form entire groups of growths.
This is how Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is formed. This is a huge growth that can rot. Zonal sprouts are located within the vagina, at the junction of the labia or near the clitoris. The localization expands over time, and unpleasant neoplasms can affect the intestine.
This consequence is fraught with pain during defecation, the condyloma bleeds. A damaged growth on the labia can cause cosmetic discomfort, but nothing more.
Genital warts differ in:
- syphilitic (wide leg);
- molluscum contagiosum;
- cancer pathologies on the skin and mucous membranes.
Why do they arise?
The virus is transmitted through sexual contact or from mother to child at birth. When the pathogen enters the body, symptoms do not appear immediately. Some people are only carriers of infection, but never get sick themselves. This is due to the active functioning of the immune system. The stronger the body’s defenses, the more effectively the virus multiplies in the body. A small number of pathogens are not capable of causing external symptoms.
Condylomatosis is provoked by the following factors:
- Decreased immunity due to previous illness;
- The presence of a focus of chronic inflammation in the body;
- Insufficient hygienic treatment of the genitals;
- Regular unprotected sexual intercourse with different partners;
- Microtraumas of the mucous membrane and skin;
- Having bad habits;
- Lack of sleep and rest;
- Prolonged mental stress;
- Hormonal disorders or changes in the body;
- Hypothermia or overheating.
Preventive measures
Even after effective removal and treatment of the tumor, there is a risk of its secondary attachment, because the virus continues to be in the body and can mutate at any time.
To avoid complications you must:
- strengthen the immune system in various ways (drug and folk therapy);
- normalize your diet, add more vitamins and microelements;
- it is important to get rid of bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- devote time to sports activities;
- avoid promiscuous sexual intercourse, use protective barrier means;
- undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist in a timely manner.
The stronger a person’s immune system, the lower the risk of secondary tumors. Precautionary measures will help identify the problem at an early stage and effectively eliminate the violation.
How do they manifest themselves?
Condylomas are located in places of greatest friction against clothing and underwear, as well as during sexual intercourse. Several localizations are typical for them:
- On the outer and inner labia;
- At the entrance to the vagina;
- In the cervical area;
- On the vulva;
- In the crotch;
- On the walls of the vagina;
- In the area around the anus.
In the absence of adequate treatment, neoplasms tend to merge into masses, in the photo resembling a rooster's comb or cauliflower. This growth is called confluent genital wart.
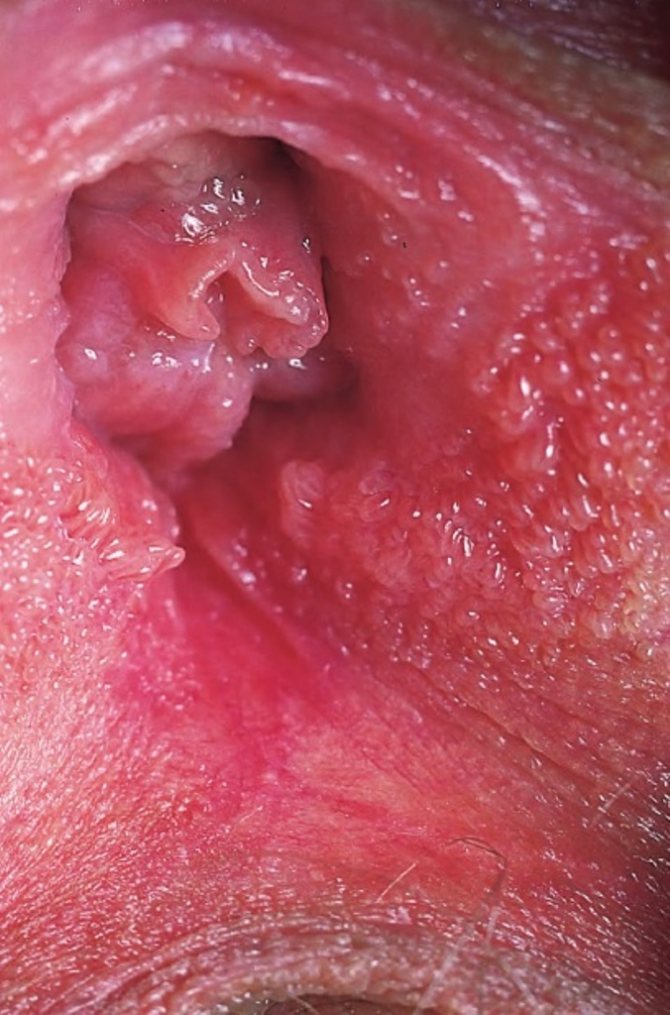
Signs that a woman has condylomatosis include:
- Formations of a characteristic appearance on the external and internal genital organs and the area around them;
- Decreased level of differentiation of epithelial cells (3 stages, the last of which is precancer);
- Oncological lesion of the cervical epithelium.
Genital condylomas reach a length of 2 mm to 10 cm. The apex of the formation is usually wider than the stalk. Condylomas appear 2-3 months after infection with a low level of immunity, concomitant sexually transmitted diseases and high sexual activity. In the absence of predisposing factors, symptoms appear many years later, when favorable conditions are created for the development of the virus.
The danger of tumors on the genitals
Studies have shown that many HPV genotypes manifest themselves in the form of growths in the genital area. Independent removal of condylomas can lead to the development of an inflammatory process, suppuration and the appearance of a secondary relapse.
In the absence of professional intervention, growths can spread throughout the body and damage the mucous membrane of the genitals. Increasing in size, they can completely block the passage to the vagina and rectum.
Warts, papillomas and condylomas on the labia pose a serious danger to a woman’s health. The effect of the virus can provoke:
- cervical oncology;
- pathological changes in the reproductive organ.
All this indicates that the disease must be eliminated in a timely manner, without causing the clinical picture to progress and not self-medicate, so as not to worsen the situation.
Complications
If vaginal condylomas are not treated, they can develop into ectopia, dysplasia and cervical tumors. The severity of the condition depends on the severity of the infection. Ectopias can heal on their own, dysplasia is considered a precancer, and oncological neoplasms lead to complete removal of the organ.
To avoid consequences, women need to visit a gynecologist once a year. A standard analysis for atypical cells will help to notice changes in the epithelium in time, and an examination will show the presence of condylomas even on the vaginal walls. If the patient knows that she is a carrier of HPV, she needs a gynecological examination every six months.
Prevention
A special vaccine has been developed to prevent infection with particularly dangerous strains of HPV.
Photo: HPV vaccination
It helps prevent the development of cervical cancer or penile cancer - the main dangers of oncogenic strains.
But other measures are also important:
- having a permanent sexual partner;
- using condoms when in doubt about a partner's health;
- annual visit to the gynecologist for a preventive examination;
- taking care of your own health and immune system.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment, a woman needs to go through several diagnostic stages. Without this, it is impossible to prescribe adequate therapy.
- A visit to a dermatovenerologist - an examination by a specialist is required to determine the type of neoplasm, assess symptomatic manifestations and conduct a test using acetic acid;
- If there are suspicions and uncertainties, the doctor performs a dermatoscopy. This method allows, without injuring the skin, to evaluate the parameters of the neoplasm, its structure and texture. This will help to correctly determine the type of growth;
- Laboratory diagnostics is carried out using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, with the help of which the number of pathogens is assessed and the type of HPV is determined. Analysis is required for all partners of the carrier. If the result is positive, even in the absence of condylomas, it is worth undergoing a course of treatment. This will help suppress the activity of the virus and avoid the appearance of tumors;
- Urethroscopy - used to determine the condition of the mucous membrane of the urinary canal. For this purpose, an endourethral endoscope is used. The study is carried out on patients of both sexes;
- Extended colposcopy - the cervix is examined using a colposcope. The patient undergoes Schiller tests and a reaction to acetic acid;
- Immunogram – evaluates the functioning of the body’s immune system.
Growths near the vagina
Existing growths in the vagina are a common sight in gynecology. Often these are benign formations of flesh-colored or pink color. They indicate the presence of HPV in the body or diseases of internal organs.
Located in or around the vagina. The formation of growths can be asymptomatic, or can provoke itching and burning in the perineum with bloody discharge.
Maintaining personal hygiene and protected sexual intercourse are the best ways to protect yourself from contracting the human papillomavirus.
The presence of growths in the vagina in women can become an obstacle to intimate life and pregnancy.
Types of growths
A growth that appears inside the vagina is medically called condyloma. Appears due to invasion by the human papillomavirus. They can appear at any age and have a different nature of occurrence. The following condylomas are classified:
- by size into small, medium, large;
- according to the structure: loose, hard;
- according to form.
Condylomas on the vagina are distinguished by color and density. Such nodules can be either benign or malignant. But besides condylomas, other types of neoplasms can be observed: lipoma, cyst and others.
A white growth in the vagina may indicate a genital wart. Hemorrhoids (coming out) or a polyp can also appear in the form of a nodule.
If a growth appears, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis.
Condylomas in the vagina grow near the perineum and on the labia.
Location of condylomas
HPV tumors are localized at the entrance to the perineum, inside or outside the labia. The vaginal mucosa is a frequent area of distribution of formations in the form of pink papillae, which can be either single or multiple. They may increase near the anus, on the thighs or pubis.
The human papillomavirus is located inside the body, and when it matures, it appears outside in the form of pink or flesh-colored lumps. Depending on the strain (science knows of 100 types of HPV), the formation in the vagina has a specific localization zone. Growths such as hemorrhoids appear between the anus and the entrance to the vagina.
The walls are often affected by lipomas or cystic structures. Internal growths are papillomas.
Causes of formations
Depending on the state of the immune system, HPV may not appear in the form of condylomas for up to 3 months, but there are cases when a growth appears 2 weeks after infection. The main reasons for this process:
- decreased human immune system;
- promiscuous sex life;
- unprotected sex;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases (vulvovaginitis, chlamydia, gonorrhea and others).
Weak immunity, infections, poor hygiene, and unsafe sex can cause the formation of condylomas in the vagina.
The exact reason why condylomas appeared cannot be reliably established. Since the virus can stay in a woman’s body for a long time and not manifest itself, and with high immune function it may not arise at all.
HPV easily penetrates the genital mucosa, so sex is a common cause of infection. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, a woman’s body is more susceptible to viral invasion, so the risk of contracting HPV is higher.
Problems with the nervous system, when exposed to shock and stress, can also play a negative role in the development of condylomas, provoking the activity of the strain.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of the disease and the period of their occurrence depend on the functionality of the body’s defense system. The incubation period lasts from approximately 2 weeks to 3 months. In this case, the virus waits for a favorable moment to manifest itself. When a growth appears in the vagina, the patient experiences itching, burning, and pain.
The mucous membrane swells and redness appears. Often the nodules have white tops and emit an unpleasant sour odor. Ignoring such manifestations leads to serious complications: cervical erosion, dysplasia, and subsequently to oncology.
When bleeding appears, the gynecologist checks the surface of the condylomas for the presence of injured areas.
Treatment of vaginal growths and diagnosis
It is impossible to delay the treatment of formations in the vagina. The earlier removal techniques are applied, the greater the likelihood of avoiding developmental pathologies.
Fixing the problem yourself is fraught with negative consequences. The method of curing the disease is prescribed only by a gynecologist who has a clear clinical picture. To establish it, diagnostics are prescribed.
The table describes the main methods for diagnosing the disease.
MethodDescription
| Visual inspection | Conducted by a gynecologist along with an oral survey of the patient for symptomatic manifestations. The walls of the vagina and uterus (colposcopy) and the anus area (anoscopy) are examined. |
| PCR diagnostics | The type of HPV, quantity and effect on the body is determined, which can be done by scraping from the affected area of skin |
| ELISA | The presence and reaction of antibodies to the virus are checked |
| Cytological and histological | Cells and tissues of nodular formations are examined using a microscope |
| Oncocytology | The presence of cancer cells is determined using a smear from the cervical area and the cervical canal area |
Having complete information about the type and type of growth around the vagina or on its walls, the treatment method is determined.
To treat condylomas, you cannot do without antiviral tablets.
Hardware treatment
Gynecologists recommend using hardware methods for getting rid of vaginal condylomas.
Such treatment is not as long as medication, not as traumatic as a conventional operation, which is performed by a surgeon with complete excision of the condyloma, and, if necessary, with nearby tissues.
Hardware techniques reduce the risk of relapse and leave no scars. It is carried out in combination with immune therapy under the supervision of a physician. The table provides descriptions of hardware methods.
Hardware treatment methodDescription
| Laser therapy | Drying and removing the growth using a laser. Used for large diameter build-up |
| Cryodestruction | Freezing with liquid nitrogen. The procedure takes place in several stages |
| Radio wave destruction | Removes using radio waves, leaves no scars |
| Electrocoagulation | Getting rid of condylomas using elevated temperature. Skin restoration course - 14 days |
It is rational to treat extensive or aggressive neoplasms in the vagina using hardware methods.
The choice of hardware treatment technique is based on the wishes of the patient and the doctor’s recommendations. Only specialized clinics perform such procedures.
You should not go to a cosmetology salon because of the risk of encountering unprofessionals. The rehabilitation course does not last long; during this period you should abstain from sexual activity.
Recurrence of condylomas in the vagina means that HPV remains in the woman’s body and repeated intervention is required.
Source: https://StopRodinkam.ru/obrazovaniya/dopolnitelno/narosty-vo-vlagalishhe.html
Conservative treatment
If condylomas are localized in the vagina or the presence of micropapillomatosis, it is better to start treatment with conservative methods. They do not injure the mucous membrane when used correctly, they are convenient to use at home, which solves the problem of lack of time to visit hospitals and is perfect for overly shy people. But you cannot prescribe medications yourself; before use, you need a face-to-face consultation with a specialist.
Important!
Genital warts in the vagina cannot be treated with most pharmaceutical products due to their localization. Drugs with a strong cauterizing effect can damage the mucous membrane and increase the number of health problems.
An infusion of celandine is well suited for douching. This plant is found in high concentrations in most known medicines for benign tumors. In small quantities, it is not capable of causing burns, but it effectively and gently removes condylomas from the mucous membrane.
Imiquimod 5% cream can remove warts even inside the vagina. They need to lubricate problem areas for 7 days at night. In the morning, the treated areas are washed. It is not recommended to use the cream for longer than 16 weeks.
Interferon preparations taken orally increase overall immunity, thereby speeding up recovery and preventing repeated relapses of the disease. There are ointments with this component that are used externally. They are also highly effective.
Panavir suppositories based on herbal components have an antiviral effect and also improve local immunity. Under the influence of the active substances of the drug, the body begins to intensively produce its own interferon.
If conservative treatment has no effect, the doctor prescribes special procedures.
Papillomas in the vagina: causes, symptoms and treatment
Proper care of intimate areas of the body involves not only hygiene procedures. Caring for the female genital organs means a correct lifestyle, since it is this part of the body that suffers the greatest number of various diseases. Most often, pathogens enter the female organs through sexual intercourse, so caring for intimate areas is also a protected intimate act.
A person can be a carrier of the papilloma virus for years and still not be aware of this fact. But one of the quite common problems is papillomas in intimate places, especially in the vagina.
Externally, such growths resemble small formations in the shape of a cockscomb or genital warts. Most often, the appearance of papillomas is caused by the papilloma virus. A healthy human body is capable of overcoming such formations on its own, if we exclude the influence of a number of provoking factors.
What is papilloma?
Often, papillomas look like small nodules that form in the vaginal area. They can acquire pigmentation from flesh to pink. There are both single specimens and several formations in one area. By merging with each other, they can form quite large clusters. If such a process develops, then we can talk about papillomatosis.
The emergence of such formations occurs under the influence of the human papillomavirus on the body. This pathogen is sexually transmitted and is quite common among the sexually active population.
In this article, we have already covered in detail the issue of human papillomavirus in women.
Photo
To understand the location and external signs of condylomas, use the photographic material provided below.
Treatment of vaginal papilloma
Therapy for curing papillomas can be carried out in several approaches:
- Conservative treatment methods. Necessary to prevent the tumor from degenerating into a malignant formation. Includes purpose:
- Immunomodulators. They are used after testing the sensitivity of the papilloma virus to a specific medication. These include Viferon, Reaferon, Kipferon.
- Inducers of interferon production. Prescribed after determining the effect of such drugs on the affected areas. Representatives of drugs: Tamerit, Neovir, Larifan.
- Specific drugs that have an antiviral effect. Most often prescribed: alpirazine.
- Surgical techniques for the treatment of papillomas. Several types of formation removal are used:
- Chemical coagulation. Carry out under the influence of drugs: solkovagin, podophyllin.
- Cryodestruction. The procedure is effective for small affected areas.
- Electrocoagulation. It is carried out using a laser.
- Radio knife or excision with a scalpel. Prescribed only for extensive lesions.
Drug treatment
Very often, treatment of papilloma virus occurs under the influence of a whole range of medications.
They have the following properties:
- cauterizing;
- bactericidal;
- oppressive.
At the same time, their spectrum of action contains a component, the influence of which prevents the neoplasm from developing. The virus may be resistant to some antibiotics, so before prescribing treatment, it is advisable to identify the most effective ones.
The main means of fighting infection include:
- lapis pencil;
- drops;
- pills;
- ointments.
If removal of papillomas is not practical, then you can get rid of the growths in 2-3 weeks with the help of medications.
The following have a detrimental effect:
- Feresol.
- Phenol in glycerin solution.
- Super clean.
- Salicylic acid.
- Cryopharma.
In addition to the direct effect of solutions on papilloma, general-effect drugs are also used that increase the immunological status of the body.
The danger of self-removal of papillomas in the vagina
Papillomas can provoke the development of diseases:
- Erosion of the cervix.
- Dysplasia.
- Go to malignant formations.
If the formation is injured by:
- squeezing;
- friction;
- integrity violations;
- unprofessional or self-removal of papillomas.
Possible consequences include the degeneration of a benign formation into an inflammatory process with a high oncogenic risk. Therefore, self-treatment or removal of papillomas from the vagina is simply unacceptable.
Removal methods
Cauterization of condylomas is carried out in several ways. The choice of method is often left to the patient, who is guided by his financial capabilities and wishes.
- Cryodestruction – cauterization of tumors with liquid nitrogen. It is performed without anesthesia, as it is not considered painful. It does not leave scars, so it is very popular among doctors and patients. If there are a large number of tumors, the procedure is performed in several stages. The time between two treatments is at least 7 days;
- Radio wave coagulation - performed with a radio wave knife. The treatment site is anesthetized;
- Electrocoagulation - carried out with a special loop with current, requires local anesthesia;
- Laser cauterization is performed under local anesthesia. To cauterize tumors with a laser, the doctor must be able to handle the device well and feel the depth of the effect. Otherwise, there is a risk of complications and scarring.
Reviews
— I was treated in more than one clinic. Doctors simply removed the consequences of the disease, the condylomas themselves. But they returned again because the cause had not been eliminated. There were condylomas outside and inside, they came out due to prolonged stress. They tried to cure it using the radio wave method. The procedure and recovery after it turned out to be extremely painful. I went to look for a doctor who would recommend something else. I took a bunch of tests, went through all the necessary examinations, and we finally found the reason! It was inflammation of the uterus, ovaries and bladder. We were able to cure it, I was given a course of Allokin alpha, and the disease did not return. So the main thing is to find the cause and cure it.
Olga, Astrakhan
— These warts grew at the vestibule of the vagina, I went to the doctor, and she also found them inside! She advised me to douche with celandine. I did the baths several times, the external ones stopped itching, but I still feel the internal ones. It turns out that you need to spray the solution inside, like an enema. Somehow I didn’t want to use celandine on the mucous membrane, even if it was diluted. I went to another doctor and recommended Panavir suppositories. The gynecologist promises that they will reduce the number of warts and less cauterization will be needed. But I read the ingredients, there is some kind of potato extract in it, but I didn’t find any reviews on it. Is this even effective? For such a price, I don’t want to buy nonsense that again won’t help. I don’t know what to do with these warts anymore.
Alexandra Mitrofanova, Odessa