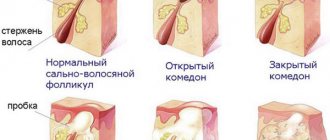
Types of hyperpigmentation
In everyday understanding, hyperpigmentation is a cluster of freckles. However, this is just one type of this skin defect. Depending on the causes, severity and nature of pigmentation, several more varieties can be distinguished.
- Melasma - brown symmetrical spots localized on the neck, shoulders, and sometimes the face
- Chloasma – dark brown spots of irregular shape, most often appearing on the face
- Secondary hyperpigmentation - dark or light brown spots that arise as a result of previous skin diseases: neurodermatitis, eczema, etc.
The most common hypermelanoses, their correction
The list of hypermelanoses is quite extensive, but most often we encounter the following: melasma (chloasma), freckles, age-related lentigo, post-inflammatory and post-traumatic hyperpigmentation.
Melasma
Melasma (Fig. 1) is brown or light brown spots that appear on the face in most cases during pregnancy (“pregnancy mask”), when taking hormonal contraceptives, or due to other reasons. The appearance of melasma is explained by the congenital increased sensitivity of melanocytes to stimulating influences - UV radiation, estrogens, etc. Melasma, of course, is a clear cosmetic problem, but it does not always require treatment. Thus, hyperpigmentation that occurs during pregnancy usually goes away some time after childbirth, and to eliminate hyperpigmentation that occurs while taking hormonal contraceptives, it is enough to switch to other methods of contraception. Melasma often occurs in people with genetically dark skin, whose melanocytes have increased sensitivity to various influences. Eliminating melasma in dark-skinned people is a difficult task even for a dermatologist.
To eliminate melasma, use:
• 2-4% hydroquinone;
• 2-4% hydroquinone in combination with glycolic acid or retinoids;
• kojic acid in combination with glycolic acid;
• 20% azelaic acid in combination with glycolic acid or tretinoin;
• glycolic acid at a concentration of 50% or higher;
• dermabrasion, laser resurfacing.
Whitening procedures should be combined with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapy. The darker the skin, the more carefully you need to handle it, trying not to damage it or provoke inflammatory reactions.
Freckles
Freckles (Fig. 2) are more often observed in fair-haired people and are especially numerous in people with red hair and blue eyes. Clinically manifested as small pigmented spots of light brown color. In the spring-summer period, after insolation, the ephelides darken and their number increases. Freckles first appear at 3-5 years of age and are especially numerous during puberty. Their favorite localization is exposed areas of the body, especially the skin of the nose, cheeks, temples, forearms and hands. However, freckles are often located on closed areas of the body. The cause of freckles is congenital changes in the structure of melanocytes caused by an autosomal dominant gene. Such melanocytes have enlarged, elongated melanosomes, which produce melanin faster and more intensely after exposure to sunlight, compared to normal melanocytes. The number of melanocytes in pigmented areas of the skin is not increased.
To eliminate freckles use:
- arbutin;
- bearberry extract and other plant extracts;
- ascorbic acid derivatives;
- AHA (glycolic, milk, etc.);
- home remedies (whey, kefir, lemon and cucumber juice, etc.).
Freckles cannot be eliminated once and for all, since their appearance is due to the genetic characteristics of melanogenesis. Therefore, an important condition for successfully combating freckles is the early use of UV filters, wide-brimmed hats, and reducing exposure to the sun.
Lentigo
Lentigines (Fig. 3) are brown or light brown spots that rise slightly above the surface of the skin. In the area of lentigo, a combination of hyperpigmentation and keratosis (thickening of the stratum corneum) is observed. There are solar lentigo, which is one of the signs of skin damage by UV radiation, and senile lentigo, which usually appears in old age.
To eliminate lentigo, use:
• skin exfoliation - peeling with concentrated ANA solutions (up to 70%),
• laser grinding (erbium laser), phenol, trichloroacetic acid,
• dermabrasion;
• hydroquinone from 2 to 4%;
• kojic acid;
• retinoids;
• preparations containing hydroquinone, glycolic acid and retinoids in various combinations.
Post-inflammatory and post-traumatic hyperpigmentation
Post-inflammatory and post-traumatic hyperpigmentation is residual hyperpigmentation at the site of the inflammatory process. It is a common consequence of acne, as well as one of the possible complications after cosmetic procedures (laser skin resurfacing, dermabrasion, peelings, etc.)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is a real scourge of plastic surgery, since, despite the warnings of doctors, not all patients use sunscreen and avoid the sun. Pigmentation at the site of the inflammatory process can resolve spontaneously, but more often additional intervention is required. Since the appearance of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation indicates an increased sensitivity of melanocytes to stress factors, bleaching should not create additional stress.
To eliminate post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, use:
- ANA;
- ascorbic acid derivatives;
- azelaic acid;
- retinoids;
- bearberry preparations and other herbal preparations.
- antioxidants, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory agents.
In some cases, when the risk of hyperpigmentation after plastic surgery is very high, the use of bleaching agents in the pre- and postoperative period is recommended.
- Hyperpigmentation: problems and solutions
Medical cosmetology
- Rehabilitation of patients after chemical peeling, microdermabrasion, laser skin resurfacing, mesotherapy
- Mesotherapy
- Injection contour plastic surgery
Causes of hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is caused by the deposition of melanin pigment under the skin. Depending on its amount, the skin can take on different shades - from flesh to dark brown. This process plays a protective role for the body: melanin is able to absorb ultraviolet rays, protecting the skin from excessive solar activity. This is why pigmentation increases in the warm season. If the process of melanin synthesis is normal, then, as a rule, there are no special problems with the appearance of the skin. When certain functions of the body are disrupted, hyperpigmentation appears. It can intensify during periods of hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, menopause), with metabolic disorders in the body, hormonal imbalance, as well as with some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Some medications, such as antibiotics, can also provoke hyperpigmentation. Heredity and skin type play a big role in this process: the lighter it is, the more susceptible it is to hyperpigmentation. Prolonged exposure to the sun without using protective creams can also cause excessive freckles.
Causes
Among the most likely causes of hyperpigmentation are the following:
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- skin injury or inflammation;
- endocrine diseases;
- metabolic disorders (for example, due to a lack of vitamins);
- some liver or gallbladder diseases;
- pregnancy;
- menopause period;
- elderly age;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- intoxication of the body;
- inflammatory or post-inflammatory reaction (for example, due to sun exposure to skin damaged by peeling);
- hereditary predisposition.
Methods to combat hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation does not pose a danger to human health, but it is a cosmetic defect that spoils the lives of many representatives of the fair sex and causes serious psychological discomfort. Home remedies (peelings, scrubs and other cosmetics) may not only not bring the desired result, but also aggravate the defect. There is no point in experimenting on your own - after all, today there are many effective professional means of combating skin hyperpigmentation. The following treatment methods are used at the Ego Estetic clinic.
- Phototherapy is one of the safest and most effective methods in the fight against hyperpigmentation. The skin is treated with special light waves with the exception of ultraviolet rays. Depending on the nature of pigmentation, the cosmetologist selects the optimal length and power of the light wave, which contributes to the destruction of melanin. As a result, the skin color is evened out. Skin whitening is possible immediately after the first procedure. With severe hyperpigmentation, several sessions may be required: on average from 4 to 6. After a year, the course of procedures can be repeated to consolidate the result. It is not recommended to carry out procedures in the summer.
- Chemical peels. The effectiveness of chemical peels in the fight against hyperpigmentation is due to the body’s response to microdamage to the skin. Peeling activates regenerative processes in skin cells, as a result of which metabolic processes accelerate. This allows you to eliminate shallow skin pigmentation, and at the same time renew the upper layer of the epidermis, restore a healthy complexion, and enhance the effect of nourishing and moisturizing cosmetics. The Ego Aesthetic clinic uses glycolic and yellow peeling, as well as Kojicol Gel, to combat hyperpigmentation. This effective remedy for restoring the appearance of the skin has a beneficial effect not only on its color, but also on its overall tone.
- Mesotherapy with whitening cocktails. The method allows you to deliver active substances directly to the cells of the epidermis, affecting pigment spots from the inside. Performed by experienced cosmetologists using the finest needles, the injection procedure is effective, safe and painless.
In the fight against hyperpigmentation, a lasting effect can only be achieved with a comprehensive and professional approach to treatment. That’s why you shouldn’t try to cope with this problem on your own; contact our specialists.
Methods for correcting and treating age spots
Methods for correction and treatment of hyperpigmentation are selected individually in each case, depending on the medical history, severity, and stage.
According to the mechanism of influence on the body, preventive and therapeutic measures are divided into several types:
- correction of melanin production (mesotherapy, depigmenting agents);
- exfoliating hardware and cosmetic procedures (laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, chemical peeling, cryotherapy, cosmetic masks with medicinal preparations);
- selective photothermolysis (laser exposure to target cells and damage to certain subcutaneous and intradermal areas without invasive effects on the outer skin), pulsed light therapy;
- regulation of melanogenesis.
Treatment with dipigmenting drugs
Depigmenting drugs are divided into tyrosinase inhibitors (ascorbic and kojic acid, arbutin) and inhibitors of melanin synthesis and function (azelaic acid, hydroquinone).
- Kojic acid is an antioxidant that binds Fe II ions involved in melanin synthesis. Has a brightening and exfoliating effect. The melamine pigment reproduction blocker gives a lasting effect, allows you to mask cosmetic defects and whiten the skin. Kojic acid is used externally in the form of creams and ointments. When applied to the skin, may cause irritation similar to a mild burn.
- Ascorbic acid is a blocker of the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into dioxyphenylalanine and DOPA-chromium; it destroys the catalyst enzyme tyrosinase. Ascorbic acid brightens the skin well, whitens age spots and freckles.
- Azelaic (nonandioic) acid was previously widely known only as an active bactericidal agent that reduces the production of fatty acids. It was used mainly to reduce the formation of comedones and acne. Recently, nonandic acid has been used to inhibit the activity and growth of abnormal melanocytes. The mechanism of action of the acid is similar to the mechanism of hydroquinone - it interferes with the synthesis of RNA and DNA in melanocytes, disrupting their rhythm of work. Treatment of hyperpigmentation with azelaic acid is long-term, usually prescribed in courses of 3 or more months with repetitions for prevention and enhancement of the effect.
Mesotherapy
Mesotherapy is a popular injection cosmetology method that uses microdoses of medication. Epidermal, superficial dermal, deep dermal and mixed mesotherapy are used to treat age spots The drug for injection is selected individually, depending on the type and degree of skin hyperpigmentation. This can be linoleic, glycolic or ascorbic acid, placental and vitamin-mineral complexes, emoxypine, etc.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is the effect of liquid nitrogen on the skin. Cryodestruction is used mainly for secondary hyperpigmentation to exfoliate the upper layer of the epidermis, in which a large amount of melanin accumulates.
Laser therapy
With the development of laser therapy, it became possible to influence cells and deep layers of tissue without damaging the surface epidermis. The penetration depth of the rays depends on the wavelength. For surface exposure, waves of 300-400 nm are used, which are intensely scattered. Longer wavelengths are used to penetrate deep subcutaneous structures. The laser device acts on endogenous chromoforms - target molecules, among which is melamine. Also, using a laser, you can destroy exogenous chromoforms, for example, tattoo dyes.
Various laser devices are used to treat hyperpigmentation. With laser dermabrasion, layer-by-layer removal of surface layers occurs with a defocused laser beam on carbon dioxide.
Selective photothermolysis method
The most widely used method for correcting hyperpigmentation is selective photothermolysis. The pigmented target structure absorbs the pulse, as a result, the process of photothermolysis occurs in the chromoform - the conversion of radiation energy into thermal energy. In this case, melamine is destroyed or provided. It is important to correctly select the wavelength, duration and frequency of the pulse, and the density of the emitted energy, so that the selective effect is directed exclusively at the target, which should absorb the rays. There should be no absorption outside the target structures so as not to overheat and injure healthy tissues in which there is no accumulation of melamine.
Read also
All articles Quality and skin problems
Forehead
- Forehead wrinkles
- Eyebrow wrinkles and folds
- Replenishment of the volume of the temporal region
Face
- Wrinkles around the eyes
- Hernias of the eyelids
- Drooping eyelid skin
- Dry eyelid skin
- Correction of the nasolacrimal trough
- Dark circles under the eyes
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Correction of the nasal bridge
- Enlargement and reshaping of cheekbones
- Age-related volume deficit on the face
- Nasolabial folds
- Rabbit wrinkles
Lips
- Lip augmentation and reshaping
- Correction of drooping corners of the lips
- Elimination of dry lips
- Purse-string wrinkles around the lips
- Marionette wrinkles