Features of the development of the disease
Viruses themselves are microparticles that consist of a genome and protein.
They are unable to divide in any way, so they need cells from another organism to reproduce. Reference! Human papillomavirus belongs to a group of viruses that are particularly tropic for epithelial cells. There are about 100 types, and each of them is characterized by certain clinical manifestations.
When the papilloma virus enters the body, it begins to produce certain enzymes that allow it to penetrate the basal skin cells. Until the genetic information of the virus has penetrated into the nucleus of a human cell, there are no symptoms. But as soon as this happens, the healthy cell begins to change, and not only at the structural level, the genetic code, which is responsible for the growth of the cell, also changes.
As a result of this “reprogramming,” cells begin to actively and uncontrollably divide, which manifests itself on the surface of the skin in the form of skin growths, which are no different in color from the skin. Some strains of the virus divide very quickly, without even having time to mature, and this leads to the formation of a colony of atypical cells.
Symptoms of infection
The virus is capable of exerting a productive, transformative effect on the epithelium. Productive - characterized by thickening of the epithelial layers due to increased cell division, the formation of warts on the skin and mucous membranes. Transforming – due to oncogenic activity, which means provoking malignant degeneration of epithelial cells. HPV genotypes 16 and 18 in women are strains with a high oncogenic risk.
In men
In men, symptoms include the formation of condylomas. HPV types 16 and 18 are associated with the development of Keir's erythroplasia, squamous cell carcinoma of the penis.
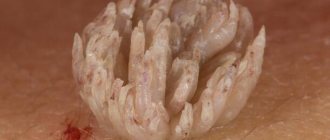
Exophytic condylomas are located on the head of the penis, on the fold of skin covering the head, and in special cases on the surface of the sponges of the external opening of the urethra.
Condylomas have the following characteristics:
- nodules with projections on the surface similar to a cockscomb;
- have a leg;
- the tissue around does not change;
- prone to inflammation, erosion, and ulceration.
There are inverted condylomas with intraepithelial growth - a subclinical form.
Papillomas affect the skin on the pubis and scrotum.
Keir's erythroplasia is a disease induced by the 16th variety of HPV types 16 and 18. It is characterized by the appearance of an irregularly shaped red spot on the head of the penis or the sheet of foreskin adjacent to the head. The surface of the spot is velvety or shiny. Over time, crusts and erosions appear.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis is similar to Keir's erythroplasia, but tissue destruction is more pronounced.
Among women
It manifests itself as condylomatosis of a different location. HPV types 16 and 18 in women can provoke Bowen's disease, the development of dysplasia against the background of cervical erosion.
Exophytic forms of condylomas affect the surface of the labia facing the vestibule of the vagina, the clitoris, the anus and perineum. During oral-genital contact, growths may appear in the throat and mouth.
Cervical papillomas are represented by exophytic and flat condylomas. Their presence can be determined by colposcopic examination.
Giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma in women often occurs during pregnancy. It is a large wart up to 10 cm in diameter. There is papillomatosis and furrows on the surface.
Bowen's disease is characterized by the appearance of a red, infiltrated spot with a weeping surface on any part of the body. Over time, it rises above the skin and foci of hyperkeratosis appear.
Indirect symptoms include:
- feeling of discomfort, pain during sexual intercourse;
- pain;
- burning sensation, itching.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Such an infection in gynecology can manifest itself as follows:
- severe vaginal itching;
- pain in the groin, especially during sexual intercourse;
- neoplasms appear on the female genital organs, mucous membrane, etc.
HPV is a factor that provokes the development of cervical cancer; this dangerous disease can be diagnosed in women of any age, most often during menopause or during menopause.
It can take 10 to 20 years from the moment of infection to the development of pathological changes, but not always this infection can cause oncological problems. Thanks to timely diagnosis of the disease, it is possible to effectively treat formations on the cervix and remove tumors in the groin.
As numerous studies show, the papilloma virus most often appears in a young body, during increased sexual activity and puberty, so you need to carefully monitor the hygiene of the genitals, avoid unprotected contacts and, in case of the slightest disturbance, seek advice from a specialist.
Surgery
If the oncogenic virus is at the stage of forming simple papillomas, then surgery is used to excise the affected areas with a scalpel.
At the initial stage of cancer, the cervix is excised along with the tumor . In the second or third stage, complete extirpation of the uterus and appendages is performed.
To prevent further spread of metastases, the patient requires chemotherapy and radiation. It is not possible to treat an advanced form of the tumor. It is characterized by the spread of metastases not only to nearby but also to distant organs. To improve the quality of life to some extent, maintenance treatment is prescribed.
Main symptoms
The main classification of the virus is based on:
- species;
- degree of oncogenicity.
According to the degree of oncogenicity, viruses are divided into three types:
- Low level. This group of viruses does not provoke the development of cancer, however, HPV 51 can, subject to the presence of provoking factors, cause malignant processes. This group includes HPV 3,6,13,34,42.
- Average level. These are types 52 and 56, which mainly affect the epithelium of the cervix, and under favorable conditions can provoke oncology.
- High level. These are 16,18,31 types. These types of viruses have a special region in their genome that synthesizes E7, a protein that transforms healthy cells into atypical ones.
These are the main types of papillomavirus, but there are also others that, although they affect a woman’s body much less frequently, cause generalized verrucosis - multiple warts covering any part of the body.
Reference! This disease can develop if there is a hereditary predisposition.
Types 6 and 11 can provoke giant condylomas, which are most often diagnosed in the vulva. They grow very quickly and affect both the superficial and internal layers of tissue.
Symptoms of HPV can be obvious, subtle or hidden. In the first case, patients usually seek help from a doctor - they are concerned about pathological neoplasms and other accompanying signs of the disease. With the erased type, condylomas do not yet appear, but the woman begins to feel minor discomfort. The virus is detected only after diagnostic tests. The latent course is characterized by the complete absence of specific symptoms.
When the infection enters the active stage, a woman encounters the following manifestations of HPV:
- discomfort after sexual intercourse;
- pain during sex;
- specific secretions;
- unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- slight traces of blood after sex;
- itching in the genital area.
To prevent the transition of benign tumors to malignant, it is necessary to begin treatment as early as possible. This can only be done if the infection is detected in a timely manner.
With high activity, HPV in gynecology looks like numerous round growths. They are convex and dense, the color is most often flesh-colored. There is no pain during palpation. Genital warts usually appear in the anal and genital areas.
They are usually localized in the rectum, cervix and vagina. The edges of the new growths are uneven and sharp, the color is brownish or flesh-colored. After some time, single condylomas can unite into a continuous infectious focus.
It is because of them that itching and discomfort occur during sexual intercourse. If the formation is damaged, a liquid with a pungent odor or a small amount of blood is released. Serious injuries lead to inflammation and infection.
Where does HPV type 16 come from in women?
According to WHO, up to 80% of the population is infected with HPV.
But only about 10% of those infected have clinical manifestations.
The answer to the question of how HPV 16 is transmitted to women is well known: the main route of infection is sexual contact.
Including anal-genital and oral-genital, with an infected partner.
HPV has a very high prevalence: almost 80% of women by the age of 50 have been infected at least once.
At the same time, the virus has a tendency to self-eliminate.
So it is not possible to establish the probability of infection after a single contact.
This is why it is so important not to neglect preventive measures during casual sexual acts.
Infection of a child by the mother at the time of birth is possible with viruses of types 6 and 11 - the cause of such a disease in children as respiratory papillomatosis.
No other types of virus, including HPV type 16, usually cause problems during pregnancy in either women or newborns.
There are only isolated cases of infection of newborns by mothers with bowenoid papulosis.
Therefore, routine HPV testing is not recommended by any international/national guidelines.
The incubation period varies from three months to several years.
It is possible to become infected with several types of viruses at the same time.
After entering the body, the virus infects the tissue covering the surface of the body and organs - the epithelium, namely its inner part (basal layer).
The virus inside the cell may not affect chromosomes or integrate into the genome.
The last option, the so-called. the malignant form is manifested by the appearance of cells with altered DNA, which multiply and form a tumor.
Thus, if a woman is a carrier of HPV type 16, 18, 6, 11 or others, the following conditions are possible:
- latent course of infection, when the virus does not affect cellular DNA, women have no clinical manifestations, and infection is detected only by PCR
- the appearance of such clinical manifestations as condylomas, warts, papillomas, the virus does not change the cellular genome, but provokes increased cell proliferation (the problem is detected by the presence of symptoms, PAP test, PCR method)
- the development of neoplastic changes (dysplasia), when the virus made a change in the DNA of the cell and caused corresponding changes in the latter (such changes are called koilocytosis), the situation is confirmed by PCR, PAP test, histological and colposcopic examination
- carcinoma, when the pathogen has changed the cellular genome and caused the formation of a large number of altered (“atypical”) cells – invasive cancer (the diagnosis is confirmed by PCR, Pap test, histological and colposcopic studies)
In most situations (up to 90%), the body heals from the virus within about 2 years.
The development of symptoms is observed only in 1-5% of infected people.
With regard to HPV 16, causes of severe clinical symptoms in women include:
- early onset of sexual activity
- having multiple sex partners
- multiple pregnancies/births before age 20
- smoking
- chronic cervicitis
- decreased immune defense, for example, due to concomitant HIV infection (with a normal functioning immune system, cancer in an infected woman can develop in 15-20 years, while in an HIV-infected woman - in 5-10 years, while HIV also increases the likelihood HPV infection)
Factors that can trigger the development of cancer
Women are considered vulnerable due to certain factors:
- weak immune system;
- indiscriminate change of sexual partners;
- the appearance of tumors in the genital area;
- period of bearing a baby;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, long-term treatment of the influenza virus.
HPV manifests itself on a woman’s genitals in the form of genital warts; in gynecology, the virus is capable of transforming and spreading throughout the body, forming new outbreaks.
The locations of papillomas in women are under the breasts, on the neck, on the genitals, in the groin, on the cervix, as well as in places where the disease does not cause physical discomfort, which especially increases the risk of developing cancer.
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women. Developed countries provide all women with the opportunity to undergo screening, which can help detect the disease at an early stage; in 80% of cases, this helps prevent the progression of the disease and save the woman from death.
Factors that may influence the development of cervical cancer:
- the first sexual experience was gained at an early age;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- smoking;
- significant suppression of the immune system (HIV infection).
Local immunomodulators
Among the “universal” drugs that can be prescribed for various viral infections - from common respiratory infections to herpes and human papillomavirus - are interferons. In particular, preparations of human recombinant interferon alpha-2b.
Interferon alpha-2b has antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative properties. It suppresses the replication of RNA and DNA viruses, enhances the activity of macrophages, and increases the cytotoxicity of lymphocytes to target cells. The use of drugs containing interferon alpha-2b is accompanied by an increase in the level of immunoglobulins type A and normalization of IgE [5]. However, these therapeutic effects are fully manifested when the drug is administered systemically.
when its high concentration in the blood is reached. It should be noted that quite powerful side effects can develop, including fever, loss of appetite, headaches, muscle pain, joint pain and many other adverse reactions.
Due to the specific safety profile, injectable interferon preparations are prescribed only in very serious cases, when the risk of side effects is justified - for example, in the treatment of hepatitis, a number of oncological diseases, etc. HSV and HPV infections do not apply to such situations and are not indications for systemic interferon administration. At the same time, the Russian Federation has registered a very impressive list of local forms of interferon alpha-2b, including ointments/creams for treating mucous membranes with genital herpes.
Theoretically, local interferon preparations should have all the advantages of injectable ones and not have their side effects, since local forms are either very slightly absorbed into the systemic circulation or do not penetrate into the blood at all. However, today there is no sufficiently reliable evidence of the effectiveness of interferons when applied topically. However, in domestic practice they are quite often prescribed as part of the complex treatment of recurrent genital herpetic infections.
Along with local forms containing only interferon alpha-2b, several combination drugs are also registered in the Russian Federation:
- Interferon alpha-2b + acyclovir + lidocaine, ointment. Indications: HSV.
- Interferon alpha-2b + taurine + benzocaine, vaginal and rectal suppositories, prescription. Indications: HSV, HPV. Taurine, according to the instructions, acts in combination as a reparative, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory component.
+
High safety profile.
!
The feasibility of using local forms of acyclovir for genital herpes is subject to serious doubts due to insufficient activity, which is confirmed in Western recommendations [3]. Interferon alpha-2b preparations, both mono- and combined, are available with or without a prescription, depending on the indications of the dispensing rules in the instructions for a particular drug. It is important to draw the visitor’s attention to the fact that the first-line treatment for HPV - oral forms of acyclovir and valacyclovir - must be prescribed by a doctor, so you should be advised to immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of papillomatosis
In the female half of humanity, the papilloma virus has the following clinical picture:
- Genital warts look like formations with a wide base and uneven edges. These formations, as a rule, are not accompanied by any symptoms, although in some cases itching in the genitals during urination and some discomfort during intimacy are possible. Genital warts can appear not only on the genitals, but also in the anus. As for the cervix, formations are localized mainly in its canal.
- Flat condyloma of the cervix is the most dangerous manifestation of a viral infection, which means that the virus has been present in the body for a long time and all this time provokes cellular changes in the epithelium of the cervix.
- Cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition that is provoked by highly oncogenic viruses. This disease cannot be diagnosed during a gynecological examination; in this case, histological and cytological studies are necessary.
- Oncology of the cervical region - provoked by types 16 and 18 of viruses.
In addition, women may experience:
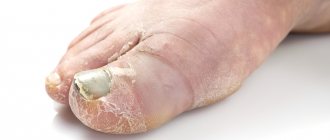
- Plantar wart - occurs in the area of strong compression of the skin by shoes. They are accompanied by painful sensations and cause discomfort when walking. These are solid formations of a benign nature.
- Keratopapilloma. It can be observed on the face, armpits and neck. The color of the neoplasm can be flesh-colored, brown or burgundy.
- Fibropapilloma is a nodular formation that protrudes above the skin surface. Most often found on the body or head. The color and shape of these formations are different.
- A seborrheic wart is a brown formation that may become covered with cracks.
- Flat papilloma is flesh-colored lumps that can bother a person with itching, redness and inflammation.
Prevention
The disease caused by viruses types 16 and 18 is easier to prevent than to carry out long-term treatment and fear the cancerous degeneration of cells. To this end, you should follow these tips:
- Sexual intercourse with a casual partner should be carried out only using barrier contraception.
- Use protection during sex to prevent abortions.
- Do not use other people's or shared household hygiene products.
- Maintain a daily routine, do exercises, and recharge yourself with positive emotions.
- Eat nutritiously, eating only fresh and high-quality foods.
- Eliminate bad habits.
- Treat chronic infections and STDs promptly.
- If the slightest signs of HPV appear, immediately visit a gynecologist and undergo the necessary tests.
- If an infection is detected, follow the advice of your doctor.
The appearance of a virus affecting the genital organs is not a reason to panic. Doctors do not give a guaranteed probability of developing cancer, especially if you start competent and complete treatment in a timely manner and follow the rules for preventing re-infection.
How to treat HPV in women
To identify the papilloma virus, modern gynecological methods offer several examination options:
- PCR diagnostics is an accurate method for detecting the disease.
- General examination by a specialist - the doctor will be able to visually identify condylomas on the genitals and in the groin area.
- Cytological analysis - smear from the cervix.
- Digene-test is a modern method for diagnosing HPV.
As well as other laboratory methods that can confirm the presence of the virus in the body. Even if such tests are positive, this does not mean a death sentence.
It is important not to panic, but to normalize your lifestyle, follow the prescribed course of treatment from a specialist and hope for a speedy recovery!
The currently available treatment methods for the papilloma virus cannot be called perfect, since it is impossible to completely get rid of the virus. However, it can be deactivated, and the effectiveness of therapy is almost 90%.
When choosing therapy, doctors rely on the genotype of the virus. Therefore, it is very important to undergo diagnostic tests.
Specialists prescribe drugs that significantly strengthen the immune system and destroy virus cells. These could be the following:
- Allokin-alpha. This is a drug for intravenous administration, which is prescribed in the presence of a highly oncogenic strain of the virus.
- Groprinosin. The tablet form of the antiviral drug quickly eliminates the external manifestations of the virus.
- Viferon is available in the form of ointment, spray and suppositories. Eliminates external manifestations and is a drug that is part of the complex treatment of human papillomavirus infection.
- Isoprinosine. This drug is used both for the treatment of viral infections and for prevention. Enhances the effect of Allokin alpha.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in combination with drug treatment.
Surgical treatment
A significant disadvantage of surgical treatment is the high probability of relapse, which is 50%. Therefore, together with surgical treatment, it is necessary to take medications that reduce the activation of the virus.
The papilloma virus in some cases responds to folk remedies, however, their use is advisable only in the initial stages of development. Castor oil, herbal infusions, and chicken proteins are used.
For now
, which could completely eliminate the virus from the body.
Treatment regimens used for this disease boil down to the use of antiviral drugs and procedures to eliminate papillomas on the skin or mucous membranes.
This virus can be driven into a latent or dormant state, when it cannot harm the body.
It is especially important to carry out treatment if HPV of a high oncogenic type is detected.
The most dangerous genotypes for women are the following genotypes of the virus: 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52. They most often cause cervical dysplasia and cancer.
After treatment for high-oncogenic HPV, a woman should regularly visit a gynecologist and carry out the recommended examinations to eliminate the risk of malignant tumors.
Treatment regimen
Competent care for this disease consists of complex therapy and an individual approach to each patient. Treatment of HPV 16, 18 in women with certain drugs usually gives a positive result. But if drug therapy is ineffective, the doctor raises the question of surgery.
They try to cure the virus using the following means and techniques:
- Immunostimulating drugs that strengthen the defenses and prevent further activation of the virus in the body. Transfer Factor, Cordyceps helps. Interferon is used in all patients, including children. Derinat is also used in pediatrics. In addition, the patient is recommended to use vitamin complexes and a number of homeopathic remedies to improve immunity.
- Vaccination. Vaccination should prevent the progression of a viral infection into a malignant tumor. At the moment, Cervix and Gardasil are widely used.
- For skin growths, chemical and herbal remedies are used for local cauterization (Supercleaner, Solcoderm, Verrukacid oil). For freezing at home, there is a Cryopharma spray.
- The inflammatory process, which often accompanies such pathological changes, is stopped by NSAIDs.
- Other destruction methods (radio-knife, scraping, electrocoagulation, nitrogen cryotherapy, laser removal).
- Cytostatic drugs are used.
How does HPV infection occur?
HPV is transmitted from person to person by:
- contact with skin and mucous membranes;
- use of common objects;
- wearing shoes or clothing of an infected person;
- visiting public places - sports showers, saunas, baths.
However, the main route of infection is sexual intercourse. Infection occurs during any sexual contact - anal, oral, vaginal. In this case, viral agents enter the human body through microscopic damage to the mucous membranes.
Oncogenic viruses in most cases are transmitted through intimate intimacy, therefore, people who constantly change sexual partners and are promiscuous are at particular risk.
Reference! Most often, men infect women; the reverse route of transmission of the virus is much less common.
In addition, the virus can be transmitted from an infected mother to the fetus when the child passes through the genital tract during childbirth. Breastfeeding also does not exclude transmission of the virus.
Etiology of the disease
The HPV-18 genotyping virus has a high degree of contact, so out of 3 cases, 2 are infected through sexual contact.
After getting inside, the infection waits for favorable conditions, after which it begins to actively progress. The formation of growths similar to tumors is observed. The disease can manifest itself for the following reasons:
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- activation of chronic diseases;
- discharge from the genitals;
- spontaneous abortions, miscarriages;
- poor vaginal hygiene.
The risk group is that group of girls who have a huge number of sexual partners and began early sexual activity. Often pregnancy also causes the activation of papillomavirus due to changes in hormonal levels.
Diagnostic methods
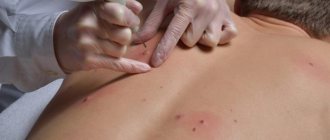
One of the most accurate diagnostic methods is PCR blood test. What it is? Polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory test of a blood sample or mucosal swab. The medical test is highly reliable and is aimed at searching for the DNA of the virus. Thus, the papilloma virus will be detected even in the absence of symptoms or rednecks on the part of the patient.
Diagnosis of a smear or scraping from the mucous surface is one of the most accurate studies. You can take a test (smear) in a gynecologist’s office. The resulting biological sample will be sent by the doctor to the laboratory for detailed examination. A smear can also be taken in the laboratory upon referral from the attending physician.
Laboratory procedures and tests often frighten patients almost more than the disease itself. How are samples taken for testing for papillomavirus? Blood is drawn from the ulnar vein by a doctor or laboratory assistant. The doctor can determine HPV of the cervix by visual examination of the patient. In this case, a sample (smear) is taken from the lesion and sent for examination.
Only a gynecologist can carry out treatment and prescribe medications; only he can choose the correct method for removing tumors, according to the woman’s health condition.
Today, the following methods are used to remove growths on the genitals and other intimate places:
- laser beam exposure;
- surgical removal, in which the infected area of tissue is cut out from a woman;
- cryodestruction – for external formations;
- electrocoagulation – complete removal of problematic tissues.
In some cases, cytotoxic exposure or chemical irradiation may be required. For this, specialists use drugs such as Feresol or Solcoderm.
During the treatment of HPV in women, doctors individually select a course of antiviral therapy, prescribe medications such as Kipferon, Reaferon, Vikferon, Alpirazin, Panavir, etc.
Diagnosis of HPV infection
Anogenital warts, caused by viruses type 6 and 11, are easily detected during a gynecological examination.
Identification of such formations is an indication for additional examination of the uterine cervix, and, if necessary, the urethra (urethroscopy).
The main method for detecting neoplastic changes caused by HPV is the Pap test.
It is a cytological study of smears from the uterine cervix.
In general, oncocytology is a method for detecting cancer cells in the cervix and vagina.
Samples of material for study are taken during a gynecological examination using special cyto-brushes and are absolutely painless.
A distinction is made between simple oncocytology, when the cells under study are immediately applied to slides for microscopy.
And liquid, when the cells are pre-treated with a special solution and dye.
The latter type is the PAP test.
After processing the material with two types of dyes, changes in the cell nuclei and cytoplasm are easily detected in the sample using microscopy.
The type of pathological process is preliminarily determined: inflammatory, malignant, or other.
Then, based on the severity and nature of the changes, a differential diagnosis of possible conditions is carried out.
The PAP test is included in the screening system for detecting cervical cancer in all developed countries.
Its annual holding is recommended for all females who have reached the age of 20 years.
Cytological signs of HPV infection include:
- koilocytosis - the appearance of characteristic koilocyte cells with voluminous uneven nuclei, vacuoles (absent normally) and clearing zones near the nuclei
- dyskeratocytosis - the appearance of keracite cells with dark nucleoli and characteristically altered cytoplasm
If the PAP test reveals a change in cellular structures, the following is carried out:
- colposcopic examination with acetic acid examination and test with Lugol's solution
- histological examination – small fragments of tissue are studied under a microscope (the latter are obtained by targeted biopsy)
Colposcopic signs of infection:
- lightening of areas treated with acetic acid
- uneven staining with Lugol's solution
- the presence of characteristic outgrowths (for low-oncogenic types of the virus)
According to international recommendations, diagnostic tactics for detecting disorders using the PAP test include:
- The first option is to repeat the examination after three months, in case of normality, repeat after six months and a year, in case of abnormality - colposcopic examination
- The second option is to immediately conduct a colposcopic examination; if no abnormal abnormalities are detected, cytology is repeated six months later (for oncogenic types of the virus). If necessary, a biopsy and canal curettage are performed. In a situation with insufficient reliability of colposcopic data, anti-inflammatory, estrogen therapy is recommended, followed by repeating the study
- The third option is to determine the type of virus using the hybrid capture method (the so-called Daijin test, Digene) or PCR (polymerase chain reaction). Detection of HPV type 16 or another oncogenic virus in women (the norm is the complete absence of the pathogen) is an indication for colposcopy
Typing of papillomaviruses by PCR has a high diagnostic value in terms of determining the type of virus and its belonging to a high-risk group of oncology.
Also to predict the likelihood of developing cancer against the background of existing neoplastic changes in the cervical epithelium.
Qualitative analysis produces a result in the format “there is a virus of this type / not.”
The quantitative method (real-time PCR) allows you to detect viral DNA even in very low concentrations from 10 to 100 copies in a sample.
Can be used to track the dynamics of infection.
Due to the fact that young women have a high rate of self-healing from HPV, PCR is recommended to determine the type of virus only after the age of 30.
A blood test to determine antibodies to HPV has no diagnostic value and is carried out only for research purposes.
As for the problem of preferring the Digene test or PCR, it is important to consider that the first method determines the number of HPV type 16 and other types in women from 5000 copies.
Whereas PCR “senses” a significantly lower content.
This point is significant from the point of view that this is the number that is clinically significant.
Those. More than 5,000 copies were detected against the background of neoplastic conditions - a high risk of oncology.
And detection of a smaller amount does not allow predicting the risk of developing cancer against the background of dysplasia.
In general, the analysis data allows the doctor to decide whether to start treatment or limit himself to observation.
The diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a gynecologist, in some cases a consultation with a proctologist and oncologist is carried out.
Diagnosis comes down to:
- examination in mirrors;
- conducting genetic research (DNA methods);
- cytological and histological examination.
The examination involves the doctor identifying condylomas. Colposcopy is performed in women. When pathology associated with HPV types 16 and 18 appears, acetowhite zones are detected - under the influence of acetic acid, the affected areas become paler. Condylomas have the appearance of point formations. A smear is taken from the area of pathological changes and a biopsy is performed.
The norm for research is considered to be a pale pink mucosa with a smooth, shiny surface.
PCR and Digene tests are common DNA methods that detect viral DNA fragments in the material being tested.
Normally, the results are negative. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detects the type of virus. Digene tests are aimed at identifying only 8 strains of oncovirus. As a result of decoding the test, quantitative indicators will be provided. There is no special preparation for women to take this test for HPV types 16 and 18.
Scrapings for PCR are not taken during menstruation.
As a result of a cytological examination, they try to detect koilocytes characteristic of moderate dysplasia. Pathologically altered cells are formed as a result of the action of the papillomavirus. Normally, such cells should not exist.
Factors that can trigger the development of cancer
It must be said that papillomavirus is not considered a highly contagious virus. For infection to occur, a number of provoking factors are necessary:
- violation of the barrier function of mucous membranes;
- decreased immunity;
- changes in vaginal and intestinal microflora;
- the presence of sexually transmitted diseases in the body;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- prolonged stressful situations;
- harmful working conditions.
Reference! 90% of the world's population has papillomavirus, however, in most of them it is in an inactive form.
Many people do not even suspect that they are carriers of the virus; this latent period can last up to several decades. In order for the activity of the virus to increase, the following factors are necessary:
- long-term diseases of an infectious nature;
- pregnancy;
- chronic diseases in acute form;
- taking medications that can negatively affect the functioning of the immune system.
Infection options
The main feature of HPV genotype 18 is that it is highly likely to become infected.
This infection occurs in various ways:
- household option;
- during sexual intercourse (no matter whether it was protected or not);
- during childbirth (transmitted from mother to child during the passage of the birth canal);
- through microtraumas on the body.
As soon as HPV DNA enters the skin or mucous membrane, it immediately integrates into the nuclei of cells, changing them. If a person’s immunity is strong, then he is able to fight the problem; the virus remains in a “dormant” state. If the protective functions are reduced, HPV will begin to multiply, which leads to precancerous and then malignant tumors.
There are a number of provoking factors for the development of HPV type 18 in women:
- presence of STDs;
- promiscuity;
- early or late onset of sexual activity;
- frequent inflammation in the body;
- decreased immunity;
- a history of miscarriages or abortions.
4 stages of infection
There are 4 stages of development of genome 18 disease:
- The latent phase is when HPV is present in the body but does not cause mutations.
- Symptomatic stage. During this period, signs of the disease begin to appear. The papilloma virus type 18 begins to multiply and is very active. The damaged surface is covered with ugly growths.
- Dysplasia. At this stage, the DNA of the virus interacts with healthy cells, transforming them. The cellular structure changes to abnormal.
- Cancer. The last stage, when cells degenerate into malignant formations, oncology develops.
How to protect yourself from developing HPV disease
It is necessary to carry out regular preventive maintenance:
- strengthen the immune system, both folk and medicinal means;
- completely give up bad habits;
- switch to a healthy diet, create a special menu with a nutritionist;
- actively engage in sports, keep the body in good shape;
- control weight gain, which may increase with HPV infection;
- avoid casual sexual contacts;
- Regularly check with your local gynecologist.
For girls who have not yet begun to be sexually active, it is recommended to get vaccinated, the Gardasil vaccine, which will help build immunity and protect the body from the most common strains of HPV.
Features of immunomodulators
Immunomodulators are groups of drugs that enhance the body's protective function. They are used to treat infectious and viral diseases that are potentially dangerous with the risk of complications.
Immunomodulators for HPV are necessary only in cases where the concentration of the virus in the body is so high that after removal of papillomas there is a high risk of their formation at home. In this case, taking special medications will allow the body to contain the virus, and over time, completely suppress its activity.
HPV develops only against the background of decreased immunity. When a virus enters the body, protective functions are activated, which are aimed at suppressing HPV. If the immune system is compromised due to hypothermia, recent illness or severe stress, the body cannot cope with the virus. This leads to the formation of growths. Timely removal of papillomas and condylomas and a course of immunomodulatory therapy makes it possible to again activate protective functions in the fight against HPV.
With strong immunity, the papillomavirus remains in a passive state
The body can completely heal itself, but this takes time. Complete suppression of HPV takes about two years. Immunomodulators are designed to support immunity during this period and prevent the development of other infectious diseases.
Treatment prognosis and recommendations
At an older age, after 35-40 years, if an infection is detected, it will not be possible to completely get rid of HPV, but it is quite possible to stop the process of reproduction of pathogenic cells, and you need to undergo regular examinations with the treating gynecologist and take PCR tests.
For women with papilloma infection in the genitourinary system, it is important to follow all the doctor’s instructions, monitor your well-being, and if tumors appear in intimate places, immediately seek qualified help.
Medical practice notes a negative trend in the uncontrolled development of diseases that are associated with HPV and gynecological disorders. When patients seek help, it turns out that the virus has been raging in the body for a long time, and the symptoms are already in a severe stage; formations in intimate places and other parts of the body interfere with full movement and cause severe pain.
Tests such as colposcopy, biopsy, and cytological examination will help to accurately determine changes in a woman’s body that are characteristic of HPV infection.
Take care of your health, do not engage in promiscuity and do not self-medicate! Health comes first!
After 35 years, it is impossible to eliminate the virus from the body; you can only stop the process of cell division. But for this you need to undergo preventive examinations with a doctor, do a PCR test and strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations.
Doctors note an alarming trend of women seeking help in advanced stages of the disease caused by HPV. However, with timely medical intervention, the prognosis is quite favorable.
Knowing the insidiousness of the papilloma virus, every woman should closely monitor her health, and if there is the slightest disturbance, immediately contact a competent specialist. Girls who have not yet had sexual intercourse are recommended to get vaccinated, as this can protect them from highly oncogenic strains of the papilloma virus entering the body.
How to live with HPV type 18?
There is no need to panic if papillomavirus genotype 18 has been detected. It's not lethal. True, you will have to change your lifestyle a little. The process of increasing immunity will now become important for the patient. If the body's defense mechanisms are normal, then the likelihood of developing cancer is minimized.
You will have to constantly undergo examination for oncological pathologies. And in order not to provoke the proliferation of atypical cells and their mutation, you need to avoid any stressful situations and overwork.
Papillomavirus type 18 and pregnancy
If HPV type 18 is detected in a woman during pregnancy, regular biopsy and colposcopy are prescribed.
If HPV is detected before pregnancy, then you need to undergo a course of treatment. Only after this can you plan the birth of a child. If the infection is detected during pregnancy, then there is a possibility that the baby will become infected as it passes through the birth canal. It is better to make sure that the virus is not in the body and then get pregnant.
If, nevertheless, HPV was diagnosed during pregnancy, the doctor will prescribe treatment. It is carried out for a period of 28 weeks, during this period the fetus completes the formation of all systems and internal organs. The reason for this is the forced use of special medications that adversely affect the development of the baby.
Popular drugs
The most popular topical antiviral agent used for HPV is Oxolinic ointment. Its effectiveness against papilloma has not been officially proven, but many patients have noted its positive effects.
Oxolinic ointment is used to remove warts only as part of complex treatment. It needs to be applied to the growths several times a day, waiting for complete absorption. At night you can make a compress with this remedy.
Panavir gel also has a delicate effect on the problem. This is an antiviral drug with an immunomodulatory effect, made on the basis of plant components. Panavir can be used to treat warts of any type and location. They need to treat the growths several times a day throughout the course of treatment.
Interferon-based Viferon ointment can also be used as an additional therapy. It can be used safely by almost any person; the product should not be used only by children under one year of age and those who are allergic to the components of the drug.
There are also antiviral drugs for HPV in the form of tablets. They allow you to return immunity to its previous form, help restore the body’s own defenses, acting from the inside.
The most commonly prescribed tablet from this group is Isoprinosine, a broad-spectrum antiviral and immunomodulatory agent. For the treatment of warts, adults are recommended to take 2 tablets of Isoprinosine three times a day; the child’s treatment regimen is determined individually by the doctor.
In addition, Groprinosin tablets are sometimes prescribed. This is another immunostimulating drug with an antiviral effect that is used in the treatment of many infectious diseases. Groprinosin should be taken 2 tablets 3-4 times a day, the dosage for children is determined by the doctor.
Before using any local or internal antiviral drug, you should consult your doctor. Also, before starting the treatment course, you need to read the instructions, paying special attention to contraindications and side effects.
In complex treatment for HPV, in addition to antiviral and immunostimulating drugs for papillomas, vitamin and mineral complexes play an important role. Thanks to them, the body receives the missing biologically active substances to improve the metabolism of cells and tissues. And strengthening the body means preventing diseases.
Skin diseases caused by papillomavirus are often accompanied by inflammation and itching, which causes a lot of discomfort for the patient. When scratched, papillomas become injured and bleed.
Cauterizing papilloma is an effective method. Indeed, in this case, the death of the affected tissues is ensured, which eliminates the further development of the disease. You can buy products to remove papillomas at the pharmacy, or you can also find them among home remedies or even kitchen seasonings.
lapis pencil
Preparations for papillomas based on silver nitrate have been used for several decades. They are effective, but outdated, because after using the lapis pencil, a dark spot remains on the skin.
How to use:
- moisten the tip of the pencil with water;
- apply to papilloma without affecting healthy skin;
- cover the treated area with a plaster (preferably a bactericidal one).
Repeat the procedure 1-2 times daily for a week. Treatment can be extended up to a month.
Kondilin
The mummifying effect of the drug is ensured by the content of podophyllotoxin. Its concentration is 0.5%, this is enough to treat those papillomas that appear in the genital area and on mucous membranes. The product is applied using a loop applicator, which is included in the package with the drug.
It is unacceptable to process more than 50 growths at a time. The frequency of application is twice a day for 3 days. The break between courses should be at least 4 days. Do not use the product during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as in children under 12 years of age.
Mountain celandine
Cauterizing balm with celandine juice as an active ingredient. A cheap product of domestic production, supplied in bottles of 1.2 and 15 ml. The disadvantage is the strong smell, as well as the need to keep the product on the skin for 5-15 minutes.
To apply Mountain Celandine, you can use a plastic applicator or a cotton swab. Before treatment, steam the formation and remove the keratinized layer of cells. Lubricate the skin around the growth with cream or Vaseline.
Super clean
Cauterizing solution based on hydroxide, bicarbonate and sodium chloride. The combination of these three components provides a powerful cauterizing effect, eliminating papilloma in 5-14 days, depending on the size and location of the formation.
Sometimes, after using Super Clean, burns remain, so it is not recommended to use it on the face and genital area. Before using the medicine for papillomas, it is necessary to wash and steam the growth, and treat the skin around it with a rich cream.
Vartek
Cream based on podophyllotoxin - a substance of plant origin with a necrotizing and local antiviral effect. The cream can be used on any part of the body. But before you get rid of papillomas with its help, you should prepare the skin.
After using the cream, you must wait for the treated areas to dry completely and wash your hands thoroughly with soap to prevent the product from getting on the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth.
Solcoderm
A necrotizing agent based on four acids - acetic, nitric, oxalic and lactic. This is the most effective remedy for large papillomas and plantar growths. The drug is packaged in ampoules, one is enough to treat 5-7 growths. The kit includes an applicator - liquid is applied to the wart with its help.
Working with this product requires caution, because contact with healthy skin results in burns. Before using Solcoderm, lubricate the area around the papilloma with a thick cream or oil.
Dermavit
Therapeutic gel with a cauterizing effect based on sodium tetraborate. It is used for 7-10 days, during which time the treated papilloma darkens. This indicates the wart is drying out. In a few days it will fall off on its own.
The drug is sold in the form of a dropper bottle, which makes it easy to measure drops. To avoid burns, it is necessary to seal the skin around the papilloma with a plaster or lubricate it with a rich cream.
Therapeutic plasters
An example of such a patch is Salipod. A solution of salicylic acid is applied to the non-adhesive part. With regular wearing of such a patch, the wart gradually peels off.
This remedy for removing papillomas is suitable for removing growths on the feet. In this case, the patch additionally protects the formation from friction of clothing and shoes, preventing its damage.
These products have not only a cauterizing, but also a disinfecting effect. Regular use reduces the growth of warts. The main advantages compared to other drugs are availability at any time, as well as a lower risk of burning the skin around the growths.
This cheap remedy for papillomas has a pronounced cauterizing effect, but does not allow you to get rid of formations in 1-2 sessions. To achieve the effect, you will need to use acetic acid 5 times a day for 1-2 weeks.
Essential oils
What is the reason for the appearance of papillomas on the body
The papillomavirus enters the human body through contact: when visiting public places, using shared hygiene items, kissing or sexual contact with an infected person. If the body was weakened and did not have enough strength to overcome the virus, papillomas appear in the area affected by the infection.
The localization of growths can be different: on the skin of the arms, legs, face and neck, in the armpits, on the mucous membranes of the mouth and nasopharynx, the external and internal parts of the genitourinary system.
Benign skin growths occur as a result of human infection with human papillomavirus. It is the most common and affects a huge number of people. When bacteria enter the human body in childhood or adolescence, they live there permanently and may not manifest themselves in any way.
Subsequently, when the body’s protective reaction decreases, the virus is activated and various formations appear on the surface of the skin in the form of warts of various shapes. They are mostly benign and do not pose a threat to human health.
Certain types of papillomavirus are oncogenic. They contribute to the emergence of cancer cells and the destruction of human DNA. In total, medicine can currently recognize more than 600 different forms of HPV.
The appearance of a viral formation on the surface of the skin indicates a decrease in human immunity. The body stops producing substances that prevent bacteria from multiplying, the virus becomes more active and comes out in the form of papillomas. Decreased immunity is observed in people who:
- have suffered any infectious disease;
- took antibiotics for a long time;
- underwent surgery;
- lead an unhealthy lifestyle and have bad habits;
- often experience stressful situations.
Papillomavirus spreads in the upper layers of the epidermis. Warts typically appear in places such as the hands, feet, neck, scalp, chest, and genitals. They can also be located on mucous membranes, for example, the tongue, respiratory tract, etc.
In some cases, skin tags go away on their own after some time. This period can range from 3 months to one and a half years. However, if papillomas are detected, it is better to immediately consult a doctor to diagnose them.
Condyloma of the cervix
This is the name given to a type of viral warts localized on the mucous membrane of the female reproductive organ. The virus can also spread to the anus, perineum, and labia. The appearance of growths in any area of the body is a nuisance, and even more so in an intimate area. Let's learn in detail about cervical condyloma.
Clinical picture of the disease
It appears in the form of papillary growths. By merging, they can form an entire colony, the shape of which resembles seaweed.
Representatives of the fairer sex should be aware that such formations can cause infertility. That is why, when identifying signs of cervical condyloma, you need to rush to a specialist, do all the procedures prescribed for diagnosis, and complete the treatment to avoid relapses.
Doctors state that there are more than a hundred types of HPV - human papillomavirus. Some of them provoke the development of cancer. That is why genital growths must be subjected to histological examination. Of these, the most common are anogenital. Less common are flat internal or endophytic. They are localized inside the cervix, under the mucous membranes. They cannot be detected during a routine gynecological examination. Such growths are detected only during colposcopy. The presence of endophytic condylomas is practically asymptomatic. In rare cases, itching in the genital area may occur.
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis are flat red or pink papules. Another type of growth - giant condylomas - can occur in expectant mothers when the body's defenses are greatly reduced.
Condylomas are only a consequence of the activation of HPV, which finds itself in ideal conditions, which occurs with a sharp decrease in immunity.
Localized growths in patients cause burning and itching. They may produce a liquid with an unpleasant odor. If such formations are damaged during sex, irritation, pain, and burning are felt.
Clinical picture
In the female body, this pathological process is accompanied by the appearance of:
- Wart. This is a type of benign tumor that rises above the surface of the skin. Most often it has a round shape, and its growth is facilitated by the proliferation of skin epithelial cells.
Their location can be observed in the armpits, shoulders, arms, and chest area. Sometimes the virus affects the plantar area. This happens when a woman wears uncomfortable and tight shoes. In this case, there is pain in the places where pathological growths appear, especially when walking.
- Condylomas. Pointed projections with jagged edges. In rare cases (damage to intimate places), when they appear, skin itching occurs.
If the target of the lesion is the cervix, then there is a high risk of degeneration of this growth into a malignant tumor.
- Seborrheic wart. It develops over a long time, its size can reach 6 cm in diameter. It has a dark brown color, and over time its surface becomes covered with cracks. Most often it affects the skin of the face or neck.
- Flat papilloma is flesh-colored. Most often, their appearance is accompanied by hyperemia and itching.
- Fibropapilloma . Nodular growth of benign nature. Localized on the head or in different parts of the body.