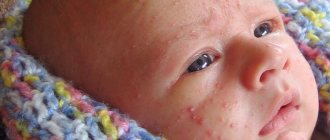
What are acne conglobata?
Conglobate (clumped, spherical) acne is characterized by a chronic, recurrent and severe course. This type has its own characteristics: close proximity to each other and extensive infiltration. The place of their formation is the deep layers of the epidermis. The color of acne formations ranges from bluish-purple to purple.
Inside the spherical acne, ulcers (pustules) mature, which, bursting (breaking through), lead to the release of pus and the spread of the rash to other, healthy areas of the skin.
Acne conglobates are often combined with folliculitis or perifolliculitis, polycystic ovary syndrome in females and lead to the formation of boils and abscesses.
Main locations:
- face;
- chest and abdomen;
- back;
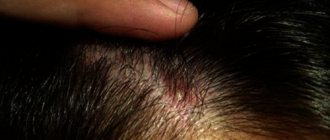
- neck (back);
- head (mainly occipital region).
On this topic
- Pimples
13 ways to prevent acne
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- March 29, 2020
The formation of fistula tracts, the merging of pimples and comedones significantly worsen the condition of the skin. Without the necessary treatment, this pathology leaves behind many scars: keloid, atrophic, hypertrophic.
It is important to remember that contacting specialists in the early stages of the disease will help you quickly and without consequences get rid of the pathology and the associated physical and psychological discomfort.
Causes and symptoms
There are many reasons for the appearance of conglobate acne. Experts consider the following factors to be the main ones:
- Hyperandrogenism (a genetic disease associated with a high level of activity of male hormones in a woman’s body). The etiology of this pathology can be different: disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries (tumors or polycystic disease) and adrenal glands. May be congenital or acquired.
- Increased activity of 5-alpha reductase. This enzyme is involved in the transformation of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone. Dihydrotestosterone is able to stimulate the cells of the sebaceous glands, which is the cause of increased sebum secretion.
- Reproduction opportunistic microorganisms (propionobacteria, fungi, etc.) in favorable conditions. Propionic bacteria provoke the proliferation of keratinocytes, which have a high degree of inflammatory activity, which is why infiltrates and cystic formations develop.
On this topic
- Pimples
5 ways to get rid of acne right now
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- March 29, 2020
In some cases, the following provoking factors become the causes of conglobate acne:
- Unfavorable psycho-emotional state. According to research, stressful situations (conditions) can provoke increased production of neurotransmitters, which, in turn, increase sebum production and disrupt the division and differentiation of keratinocytes.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the glands.
- Diabetes . Elevated blood sugar levels negatively affect the skin. Therefore, if such large-scale rashes as spherical acne occur, you should immediately visit an endocrinologist.
- Taking certain medications : steroid hormones, halogen-containing antiseptics, antidepressants, anti-tuberculosis and anticonvulsant (anti-epileptic) drugs.
- Inadequate and poor quality nutrition. Foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates can increase the level of insulin production, which, in turn, leads to excess secretion of sebum and increased concentrations of male sex hormones.
- Influence of environmental factors . Adverse weather conditions (solar radiation, frost, wind, rain), skin contamination with dust (industrial pollution, mainly associated with professional activities), frequent use of soap, poorly selected or low-quality cosmetics, constant injury - all this can worsen the condition of the skin, including including triggering the occurrence of conglobate acne.
- Tobacco smoking. It has been proven that nicotine has a negative effect on facial skin. It changes color (has a yellowish or grayish tint), wrinkles appear, a feeling of sagging and dryness occurs due to poor circulation, oxygen starvation and slow tissue restoration caused by a bad habit.
- Failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene.
- The presence of foci of chronic in the body.
On this topic
- Pimples
How to quickly get rid of acne on the chin
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2020
To determine the exact cause of conglobate acne, consultation with a specialist (specialists) is necessary.
The main symptoms of the disease include:
- the appearance of defects in certain areas of the body (face, scalp, abdomen, back, chest, neck);
- features of the clinical picture (large rashes in the form of infiltrates and pustules located close to each other, forming fistulas after opening).
How acne can manifest itself on human skin
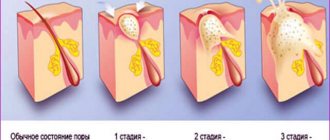
The non-inflammatory form is black and white acne (dots) mainly on the face. In medical terminology - open (black) and closed (white) comedones or milia. Popularly, whiteheads are also called millet.
As a result of inflammatory processes on the skin, the following occur:
- Papular acne.
These are red bumps on the skin, which, unlike pustules (pimples), do not have purulent endings. If papular acne is squeezed, it changes color to a paler color. In most cases, they are formed from closed comedones. - Pustular.
These are the so-called acne, which probably everyone has encountered in one form or another. What does common acne look like? Red, inflamed bumps and at the top of the bump there is a purulent ending, which many want to squeeze out. - Papulopustular type of acne.
This is a type of acne in which, as the name suggests, both papules and pustules are present on the human skin. If the size of pimples and papules is small, then the color of the inflammation will be red, but if the pimples and papules reach large sizes, then the color of the inflammation will become purple or bluish. This form is treatable and in most cases, after effective therapy there are no scars left on the skin.
Photo : papulopustular type of acne.
- Cystic acne.
This is a form of acne in which inflammatory processes affect not only the surface layer of the skin, but penetrate much deeper, under the skin, forming cavities (cysts) filled with pus.
In medical sources you can find another, more complete name, nodular cystic acne. Dermatologists define this type by the presence of a large number of compacted and deep infiltrates. Infiltration is when cells that are uncharacteristic for this part of the body accumulate on organs or on the skin, and at the same time they become denser and enlarged. When deep and hardened infiltrates are found on the skin, they are called indurative acne. - Indurative
This is when pimples thicken and they are no longer on the surface of the skin, but deeper, under the skin, the compactions reach the size of a large pea. If you squeeze out these acne, scars will remain on the skin, which are called post-acne scars. Photos cystic (nodular cystic). - If the disease progresses, another form of it appears, phlegmonous, when the cysts begin to merge with each other into groups, forming mounds on the skin, the size of which increases to a large plum. The color of such formations is purple-red. Phlegmonous acne affects the skin for a long time and the treatment process (extremely difficult) lasts for years.
- Conglobate acne
, also known as spherical acne, is also called heaped (multiple) acne, a form of acne in which large nodules appear on the back, neck, chest and face, they penetrate deep into the skin, the diameter of the nodules is about 2 cm, the nodes are very painful to touch. If the nodes are connected to each other, spherical formations are formed and abscesses may occur. The color of the seals is blue-purple; - Acne fulminans
This is a rare form in which acne very quickly transforms into extremely destructive inflammation, in which the temperature rises, the joints hurt and ache. - Inverse
With this type of acne, the apocrine glands become inflamed. Apocrine glands are sweat glands found under the armpits and in the groin. Inflammation, in the form of red bumps, occurs near the navel, nipples, groin or armpits. Once ripe, they burst and pus comes out.
The most severe forms of acne include necrotic acne and acne tetrad.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, the following actions are necessary: a visual examination by a specialist, taking an anamnesis and prescribing a number of diagnostic measures.
In order to select the correct and effective treatment, the doctor may order the following tests:
- general blood (to determine the severity of the disease);
- hormone analysis (testosterone, FSH, LH);
- biochemical blood test (to exclude the diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome in women);
- examination of the intestines for the presence of dysbacteriosis (problems from the gastrointestinal tract negatively affect the condition of the skin).
On this topic
- Pimples
Everything you need to know about subcutaneous acne
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2020
In addition to the above tests, the attending physician may prescribe the following diagnostic measures:
- Ultrasound of the adrenal glands and pelvis (for women);
- MRI of the cranium;
- analysis to determine the amount of sebum ( sebometry);
- study of the relief of the epidermis;
- checking the level of hydration and hormonal levels.
Histological studies can also be carried out, which confirm the presence of conglobate acne by the following indicators: skin rashes consist predominantly of lymphocytes, exocrine glands and hair follicles are destroyed, and an accumulation of fibroblasts is observed.
You may need to consult the following specialists: endocrinologist, gynecologist, cosmetologist.
What type of acne does Clindovit® help fight?
It is not enough to know what a pimple looks like to determine the severity of acne or its shape. This should be done by a doctor. At the first manifestations of acne, you should consult a dermatologist who will prescribe adequate treatment.
Clindovit® – clindamycin gel. This topical antibiotic helps fight acne vulgaris6. When applied to the skin, the phosphate contained in the clindamycin drug is hydrolyzed to form clindamycin, which quickly accumulates in comedones, exhibiting antibacterial activity against Propionibacterium acnes6. The drug helps reduce the concentration of free fatty acids6.
*acne
Treatment
When treating spherical acne, both topical (local) and systemic treatment are used.
Systemic treatment consists of the use of the following medications:
- Roaccutane (prescribed to reduce the activity of the exocrine glands);
- antibiotics (most often they use tetracycline and other drugs according to schemes, intravenously and intramuscularly);
- retinoids (used after antibiotic therapy for a course of 3 to 6 months);
- hormonal medications (prescribed to women in cases where the cause of conglobate acne is a hormonal imbalance);
- combined oral contraceptives;
- vitamin complexes;
- immunomodulators.
Topical medications include: ointments, gels, emulsions with antibiotics (erythromycin, tetracycline), as well as retinoids in the form of ointments, gels or creams.
Some local drugs are used to relieve inflammation, these include: adapalene, boric and azelaic acids, isotretinoin, and drugs based on sulfur and salicylic acid.
Non-drug treatment (physiotherapy) is very popular today, including:
- light or laser therapy (destroys protoporphyrins and other anaerobic microorganisms);
- zinc electrophoresis or iodine electrophoresis;
- applications (mud or paraffin);
- darsonvalization (the procedure reduces the amount of sebum secretion, reduces the number of bacteria, restores tissue nutrition, relieves swelling);
- chemical peeling (this procedure helps stimulate the synthesis of fibrillar protein and elastin);
- cryotherapy (indicated for scars).
Only a specialist can select a treatment regimen, taking into account many important and serious factors (the patient’s age, individual indications and contraindications, financial capabilities).
Nutrition for problem skin
Proper nutrition is the basis of health. If you consume healthy foods filled with vitamins and minerals, your body will thank you for clean and healthy skin, beautiful hair and strong nails.
For many diseases, proper nutrition is the best preventive measure, and the relationship between the gastrointestinal tract and the condition of facial skin is a long-proven fact.
Therefore, in order to have clean and blemish-free skin, it is important to remember the principles of nutrition:
- include foods rich in vitamins A, E and B in your diet (vitamin A contains: carrots, red peppers, persimmons, apricots, cottage cheese; vitamin E: banana, oatmeal, beef, buckwheat; vitamin B: potatoes, cereals, meat, fish , eggs, milk, etc.);
- eat foods containing zinc: herring, veal liver and oysters;
- fish at least once a week (or buy red fat at the pharmacy).
On this topic
- Pimples
All about internal acne on the chin
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2020
If you have problem skin, you should avoid the following foods: sweets, flour products, fatty foods, fast food, chips, crackers.
Drinking alcoholic, carbonated and coffee drinks also has a negative effect on the skin. They should be replaced with green tea, purified (mineral) water and juices.
Prevention and possible complications
Preventing the occurrence of conglobate acne in the case of genetic predisposition or other factors beyond the control of the patient is difficult and almost impossible.
But sometimes, by following simple rules and advice, a person can easily avoid the appearance of this unpleasant cosmetic defect:
- do not sunbathe (there is an opinion that you should be in the sun more often, since acne “dries out” in this way, but the sun’s rays also increase the secretion of sebum, so if you cannot avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, you should consult a doctor and choose a high-quality moisturizing sunscreen cream);
- wash only twice a day (hard water and soap can dry out the skin and make it more vulnerable to infection);
- Under no circumstances should you squeeze out the rash (infection is possible);
- do not apply cosmetics containing: various oils, petroleum jelly, lanolin (they can clog pores);
- Healthy food;
- choose cosmetics that suit your skin type;
- seek qualified help in a timely manner.
If left untreated, complications such as scarring, redness and pigmentation may occur.
Acne conglobata is a serious problem that requires increased attention. Treatment at the initial stage gives positive results after approximately 3 months; a severe form can be treated for years and periodically recur.
Only timely contact with specialists will help determine the main cause of this defect, as well as effectively and quickly eliminate it.
Conservative treatment
If multiple conglobate acne with a pronounced purulent-inflammatory process is observed, accompanied by the appearance of massive nodular-cystic formations, combination therapy with the use of systemic and external medications is indicated. As a rule, the therapeutic course of severe acne includes the use of:
- Antibacterial drugs.
- Retinoids (for example, Isotretinoin).
- Benzoyl peroxide, salicylic and glycolic acid.
- Oral contraceptives.
- Glucocorticosteroids.
Antibiotic therapy
The leading role in the treatment of conglobate acne (blackheads) is given to antibacterial therapy. It has been established that anaerobic microorganisms propionibacterium acne (P. acne), which promote inflammation of the sebaceous glands, are sensitive to various types of antibiotics. The following types of antibacterial drugs are usually used:
- Erythromycin.
- Tetracycline.
- Clindamycin.
- Doxycycline.
The optimal dosage of medications is determined by the attending physician. To achieve stable remission, it is recommended to prescribe antibacterial agents in intermittent courses over a sufficiently long period of time. When carrying out antibiotic therapy, the occurrence of various types of side effects cannot be ruled out. The most frequently recorded:
- Headache.
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the abdomen and other dyspeptic disorders.
- Allergies (rashes, itching, burning, redness, etc.).
- Pigment spots on the body.
- Problems with liver function, etc.
- Candidiasis.
- Pseudomembranous colitis (inflammation of the intestines).
Penicillins are ineffective in the treatment of acne. If you are allergic to macrolides, you can use the latest generation of cephalosporins (for example, Cefotaxime). It should be noted that independent use of antibacterial drugs without the supervision of a physician is strictly not recommended.
Traditional methods of treating conglobate acne often do not bring positive effects and only aggravate the patient’s current condition.
Systemic therapy
In case of very severe acne, which is often typical for conglobate acne, the drug of choice is Isotretinoin (Roaccutane), which belongs to the group of synthetic retinoids. The duration of treatment can reach from 4 to 12 months. Roaccutane successfully copes with various types of acne and provides a lasting therapeutic effect. The presence of conglobate abscessed acne is a direct indication for its use.
The optimal dosage is calculated by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s weight. Roaccutane is not prescribed to women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Combination use with vitamin A preparations and antibiotics from the tetracycline group is also contraindicated. In addition, it cannot be used to treat patients with diabetes, serious kidney and liver problems, or high blood lipid levels.
It is recommended to plan pregnancy 2 months after finishing taking Isotretinoin (Roaccutane). It should be noted that during therapy with synthetic retinoids, it is necessary to monitor the levels of liver enzymes, alkaline phosphatase, triglycerides, and cholesterol every three months. Some patients experience the following side effects:
- Headaches.
- Nosebleeds.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Dry skin and mucous membranes.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Pain in muscles and joints.
If adverse reactions occur, adjust the dosage of the drug or discontinue treatment. At the same time, it is recommended to use moisturizing cosmetics. The combined use of drugs such as external synthetic retinoids, benzoyl peroxide and systemic antibiotics is allowed.
In case of severe acne, girls and women are advised to prescribe combined oral contraceptives containing antiandrogens. The clinical effect is observed 60-90 days after the start of use. To achieve stable remission, the therapeutic course can last for several years. If there is a pronounced inflammatory process and severe skin lesions, glucocorticosteroid medications are used. They can be prescribed in the form of injections, ointments and local injections (needling of the affected areas).
If necessary, the treatment of multiple conglobate acne is adjusted every 2-3 months.
External therapy
In addition to systemic antibiotic therapy, antibacterial ointments are actively used (for example, Erythromycin, Clindamycin, etc.). They are usually used for several months to suppress pathogenic microflora on the skin. If a severe course of the disease is observed, which is accompanied by a pronounced purulent-inflammatory process on the face, combined ointments containing antibacterial drugs and glucocorticosteroids can be used.
Upon completion of the main therapeutic course, maintenance treatment is prescribed for a year, which includes:
- External synthetic retinoids (for example, Retin ointment).
- Benzoyl peroxide.
- Azelaic acid.
- Salicylic acid, etc.