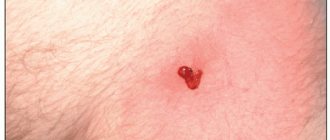
White papilloma is a small growth on the human body of different shapes and colors. Their appearance on the skin is a consequence of infection of their carrier with the human papillomavirus (HPV). New growths on the body, as a rule, are considered benign and do not threaten the health of their carrier, but there remains a possibility that the tumor can develop into a malignant one. But with a timely and, most importantly, correct approach to your health, you can get rid of existing growths and prevent the appearance of new ones.
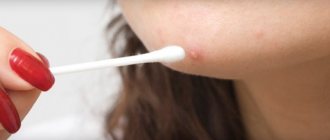
White papillomas can differ from each other, both in the shape of the growth and in color. The color of warts can vary from pale flesh to dark burgundy.
Reasons why papilloma color changes
There are many other reasons why the color of growths may change, these include:
- growth of papilloma under the hairline, in such a case repeated damage to the neoplasm becomes inevitable;
- the formation of a growth in the armpits and in the groin area, places where the papilloma can be damaged due to shaving, after which you can notice not only a change in color, but also the formation of a blood rim around it;
- infection;
- activation of the body’s protective functions, in the process of the body’s fight against the virus, the color of the papilloma may change due to the death of its cells;
- the use of medications, a natural growth reaction to its burning.
There is also a possibility that the color of the warts will not darken, but rather lighten. The reason that the papilloma has turned white is mainly its death; this can be caused either by the use of medications or by the body’s own fight against the disease.
Human papillomavirus in women
The female papillomavirus belongs to a large group of viruses. To date, about 120 genotypes of the virus have been identified, but not all diseases caused by the papilloma virus in women have been studied. All types of virus are divided into three groups:
- serotypes associated with low cancer risk (3, 6, 11, 43, 44, 72, 73);
- viruses with an average degree of risk (type 31, 33,36);
- highly carcinogenic (types 16 and 18).
Papilloma virus in women - symptoms
Since human papillomavirus infection does not appear in women immediately after entering the body, in some cases it is difficult to establish when the infection occurred. Symptoms of the papilloma virus in women are varied and depend on the type of virus, ranging from a latent (hidden) course to dangerous oncological diseases. The fact is that the virus infects the basal cells of epithelial tissues and causes their active division, which subsequently leads to the appearance of tumors. Long-term exposure to viruses changes the function and structure of epithelial cells, even changing the structure of the cell’s genetic apparatus. This is precisely what is associated with the appearance of neoplasms.
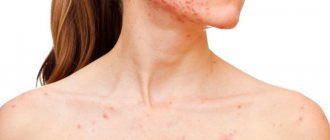
The main symptoms may be:
- genital warts, located not only on the external genitalia and on the skin near the anus, but also often on the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system (on the cervix, vaginal walls) that are hidden from view;
- warts on various areas of the skin;
- flat papillomas;
- dysplasia of the cervical epithelium, which implies structural changes in cells;
- cervical cancer.
Most often, asymptomatic carriage is characteristic, with the virus being diagnosed accidentally or manifesting itself in conditions of decreased reactivity of the immune system. It has been proven that the risk of developing cancer increases with smoking, since the substances contained in tobacco activate the dormant virus.
Routes of transmission of human papillomavirus
Infection with the human papillomavirus occurs during sexual intercourse, and unlike other sexually transmitted infections, a condom does not provide adequate protection, since the virus can concentrate in condylomas located in the external genital area. Much less common is another method of infection that is more typical for warts - this is the contact-household route.
Papilloma virus in women - treatment
There are no specific treatment regimens for human papillomavirus in women. Unfortunately, today there are not even specific drugs that can eliminate the virus. Therefore, therapeutic tactics regarding how to treat papillomas in women consist of combating the consequences caused by the virus and normalizing the functioning of the immune system. In order to maintain the immune system, injections of interferon drugs (Cycloferon, Reaferon) are prescribed. Independent removal of any papillomas and warts on the skin is contraindicated, since the cause of these formations may be the papilloma virus, and such manipulation will lead to the spread of viral particles throughout the body.
All neoplasms caused by the human papillomavirus in women, including areas of cervical dysplasia, are removed using the following methods:
- Cryotherapy.
- Laser removal.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Chemical and cytotoxic drugs.
It is possible that over time the virus may spontaneously disappear from the body, which indicates the presence of an active immune system response to the virus. If elimination of the virus does not occur within a year, this means that the epithelium is susceptible to the virus due to the presence of hereditary defects in antiviral and antitumor defense.
The best prevention of human papillomavirus infection is vaccination. Today, there are two vaccines on the pharmacological market: Gardasil and Cervarix. Data periodically appear in the literature about the need to include vaccination against human papillomavirus in the national vaccination calendar.
Activation of HPV, what is the reason?
A person may not even suspect that he is infected with the HPV virus, because quite a long period of time may pass from the moment of infection to the moment warts appear. As a disease, papilloma does not make itself felt, causing absolutely no ailments.
After infection with the HPV virus, it can manifest itself in the form of growths on the body several years later.
The reasons for the activation of the virus in the body can be:
- the slightest weakening of the immune system;
- infection through an unhealthy lifestyle: smoking, drinking alcohol, having promiscuous sex life;
- flu, gastrointestinal diseases, etc.
Classification
Viral papilloma in women in gynecology can be localized in various areas:
ATTENTION!
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the new method, based on natural ingredients, discovered by Elena Malysheva. At the Research Institute of Mammology, based on a study of a group of volunteers, they confirmed the fact of recovery from mastopathy and the disappearance of tumors in the breast.
Read about Malysheva’s new technique...
- Cervix . In this case we are talking about dysplasia - a precancerous condition and malignancy. Among the main signs of human papillomavirus in women in gynecology are bloody discharge that has an unpleasant odor. You should also highlight pain in the lower back and lower part of the peritoneum, symptoms of intoxication (sharp loss of body weight, weakness and fatigue, headaches).
- Labia . It is characterized by the appearance of genital warts, which in appearance resemble a hanging bag. In this case, a bacterial infection occurs, which is accompanied by characteristic itching and requires the use of antibacterial drugs.
Papilloma on the tongue
On the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, genitals, growths appear less frequently than on other parts of the body. However, when it appears, it can cause great discomfort. White papillomas on the tongue can cause a lot of discomfort when eating and even when talking. There is a possibility that its appearance on the tongue is a consequence of infection during a kiss.
HPV: features of the virus
Papillomavirus is a purely cutaneous parasitic microorganism, which, when penetrating inside a cell, causes a violation of its genetic code and provokes the uncontrolled division of modified dermatocytes. This is how various new growths – warts – form on the skin.
The virus has the following features:
loading…
- If it does not have the opportunity to penetrate inside the cell, it is firmly attached to the outer surface - episomes - and waits in the wings.
- When the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes is damaged, the microorganism is activated and causes the development of skin defects.
- The most favorable environment for it is the external (and, under certain circumstances, internal) mucous membranes: a moist environment is optimal for preserving the viability of the harmful agent, and mucosal tissue is more prone to damage.
- Local immunity can defeat the virus and expel it from the body, while the carrier of the infection often has no idea what an intense struggle is going on in his body.
- Different strains of the virus cause completely different forms of the disease; not everyone is capable of causing cancer.
- The harmful agent does not enter the bloodstream and is not spread throughout the body; it manifests itself exclusively at the site of its initial contact with the skin.
- The virus is easily transmitted sexually.
It is the forms associated with transmission of infection during sex that have the highest oncogenic risk. These include genital warts (anogenital warts), which are caused by strains of serotypes 16, 18, 6 and 11. Whereas ordinary and filamentous warts rarely degenerate and, in general, do not pose a threat, but rather are cosmetic defects.
We told you about the main types of HPV manifestations and the risk levels of papillomatosis in the article “Human papillomavirus: how it is transmitted”, where we looked at the most common forms of the disease. Today we will focus your attention on the most dangerous types of HPV for women.
Methods for removing papilloma
Since HPV tends to grow, cause discomfort, and there is a danger of a malignant tumor, it is best to remove the papilloma. However, doing this at home is extremely unsafe; the best solution in this situation is to contact a specialist.
There are several methods for removing papilloma:
- surgical , used quite rarely if there is a suspicion of a tumor and if the size of the growth is large. When surgically removing papilloma, local anesthesia is used, the operation lasts relatively short. But the disadvantage is that when a tumor is removed, a healthy area of skin is also removed, and subsequently scars and cicatrices may remain.
- cryodestructive , involves the use of liquid nitrogen to remove papillomas. Removal of warts using the cryodestructive method can occur both in a medical facility and at home. The method is absolutely painless and leaves no scars. The use of this method if a malignant tumor is suspected is strictly prohibited.
- laser removal involves removing growths by burning it with laser beams for 60 seconds; redness may form around the growth, which will disappear in a few days; the wart itself will disappear within a week. Before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a tumor.
- electrocoagulation , cauterization of growths using electrical discharges, does not provide for age restrictions. Removal of papillomas occurs quite quickly, and damaged skin is restored within a week. However, there are also disadvantages: depending on the sensitivity of the person, the procedure can be quite painful, and if the method is chosen incorrectly, there is a risk of scarring.
- radio wave , getting rid of growths through removal using high-frequency radio wave radiation. The radio wave removal method is absolutely non-contact, so it can be used to remove one or several papillomas. The advantage of non-contact removal is that it can be used to remove tumors in all areas of the body. Currently, the most effective and painless way to remove papillomas.
What methods are used to remove papillomas?
Removal of growths is carried out only after a thorough examination of them and determination of where the papilloma virus comes from in a woman or man who has addressed this problem.
View gallery
The removal procedure is carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Today, several methods are used for this purpose:
- Cryodestruction. It involves removing papules using liquid nitrogen.
- Electrocoagulation. Allows you to destroy tumors with short-term electrical influence.
- Surgical. The papule is excised, which is the most painful and traumatic procedure.
- Laser. The growth is destroyed under the influence of a laser beam.
View gallery
The latter method is considered the most popular, as it allows you to completely remove the tumor without consequences in the form of scars. This technique does not require patient preparation and does not imply rehabilitation after the procedure.
How to prevent recurrence of papillomas?
Papillomas that appear as a result of infection with a virus can be removed, but it is impossible to get rid of the virus completely. And even when the growths are removed, there is always a risk that they will appear again. However, if you take certain preventive measures, you can avoid the reappearance of growths on the body.
To do this, you need to: observe the rules of personal hygiene, immediately treat all diseases, eat right, get rid of bad habits, strengthen the immune system, get proper and timely rest and exercise.
Treatment methods for papillomas
The only way to treat the resulting growths is surgery. Papules are removed and sent for cytological analysis. Examination of papillomas tissue gives the most accurate results. Not only the cells are analyzed, but also the correct location of them on the skin.
The results obtained allow specialists to draw conclusions about the degree of changes in the body and the likelihood of growths transitioning from benign to malignant. Timely and correct diagnosis is very important, since sluggish and untreated viruses more often lead to the formation of cancerous tumors.
Types of papillomas
The human papillomavirus has more than a hundred varieties, and papillomas themselves also come in several types:
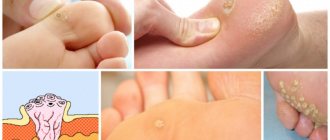
- simple , the most common type, appear most often on the palms, soles, armpits, etc., most often, the color of warts is almost the same as the color of the skin. It has a fairly small size, but over time it tends to grow, while changing color;
- flat , more often appear in childhood and adolescence, tend to rapidly increase in size, and may leave scars after removal;
- filamentous , the very name of this species speaks of the thin structure of either the papilloma itself or its legs. Appears on areas of the body with thin skin: eyelids, armpits, neck. Most often it predominates in elderly people 45-50 years old. It can be removed quickly and painlessly;
- genital condylomas are located mainly on the genitals or inside them. In most cases it is transmitted sexually. At first they appear in the form of a small growth, but later they grow. shaped like cauliflower. They are dangerous because even after removal, there is always a risk of relapse;
- laryngeal papillomatosis , rare, mainly transmitted from mother to child during childbirth, can partially disrupt the function of the respiratory system, even leading to suffocation. If you detect the slightest signs, you should immediately undergo examination by a doctor;
- papillomas of the bladder , a rather rare disease, more often in men, can only be treated surgically, outwardly completely invisible, but causes discomfort, pain, and problems with urination;
- plantar , appear on the feet, most often in childhood or adolescence. The cause may be sweating, wearing tight shoes, decreased immunity and poor personal hygiene. The main problem with this type of growth is that they grow not on the skin, but inside the skin, causing discomfort and pain. It is also very difficult to remove, and most often leaves scars afterwards.
The most dangerous form of HPV is papillomatosis. With papillomatosis, a large number of warts appear on the body, damage to which can be life-threatening.
Almost every person is faced with the problem of the appearance of papillomas; if this happens, you should not self-medicate, it is better to consult a specialist in time.
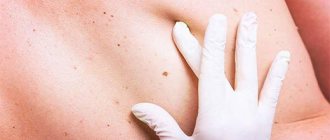
What are papillomas and why do they occur?
In medical practice, papillomas are considered to be benign neoplasms that are formed from epithelial cells. They are located above the epidermis and are small droplets of various shapes. Papillomas can appear both on the skin and on the mucous membranes, genitals and ligaments.
View gallery
Where do papillomas come from? The main cause of their occurrence is the human papillomavirus (HPV). According to statistics, it is present in the body of 9 out of 10 examined patients. It can be inherited or acquired during life.
If a person has a strong immune system, the pathogen does not manifest itself for a long time. However, when certain circumstances arise, the skin begins to become covered with small growths.
Types of papillomaviruses and features of negative effects on the body
All HPV strains can be divided into 3 groups: non-oncogenic (do not cause degeneration into a malignant tumor), low-oncogenic (the risk of degeneration is minimal) and highly oncogenic (the risk of developing cancer is very high). Another name for the last group of strains is HPV-HCR (high carcinogenic risk human papillomavirus).
REFERENCE! Viruses of types 16, 18, 31, 33, 51, , 56 have the highest risk of degeneration of formations into malignant tumors. They can provoke the development of such terrible diseases as cancer of the cervix, external genitalia, vagina, and anus.
Diagnostic methods
Komarovsky says that before starting treatment for papillomas, a diagnosis of the pathology is required. That is, it is necessary to carry out appropriate examination methods to establish the type of neoplasm, stage and nature of its development.
Diagnosis of this pathology does not consist of complex procedures. A doctor can determine the type of papilloma by visually examining the tumor; in some cases, a screening PRC test may be required. In order to make a diagnosis of laryngeal papillomatosis, direct laryngotracheoscopy is performed.
Symptoms
The main clinical manifestation indicating the development of gynecological papilloma is the formation of growths in the female genital area. The location of the growths will depend on their type.
In this case, papillomas will be represented by small neoplasms, usually up to five millimeters.
The manifestation of the clinical picture will largely depend on the location of the lesion.
Labia minora and labia majora
The formation of neoplasms is accompanied by certain difficulties during intimate hygiene procedures. In addition, this area is subject to inflammatory processes, which can be facilitated by wearing tight underwear. Also, during intimacy, a woman begins to experience unpleasant sensations.
Clitoris
There is a pronounced pain syndrome, which also interferes with a full sexual life. Urination is impaired, since it is in this place that there is increased sensitivity.
Pubis
The appearance of papillomas is accompanied by itching. If there is damage in this area, the risk of infection increases several times.
Vaginal and cervical mucosa
Warts cause pain during gynecological procedures and during sexual intercourse. There is inflammation of the affected area.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
In addition, the following clinical signs will indicate the development of papillomas inside the genital organs:
- deterioration in general health;
- purulent or bloody discharge due to injury to growths located inside the cavity of the reproductive system;
- discomfort when walking.
If the above symptoms appear, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist.