8 steps after melanoma removal - after mole excision
After removal of melanoma, the patient is at risk of recurrence of the disease.
It is also possible for new tumors to form. Melanoma that develops after removal of a mole should be examined and removed as quickly as possible. In some people, melanoma surgery may completely eradicate the tumor. However, there will always be a risk of relapse of the disease.
In other patients, melanoma may be inoperable, in which case you need to be prepared for immunotherapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy and other treatments aimed at curbing tumor growth and increasing life expectancy.
Learning to live with cancer is not easy, as a person is forced to completely change his lifestyle. In this case, it is very important to develop the following plan with your doctor:
- Approximate schedule of necessary examinations and tests.
- A schedule of tests that may be needed, such as screening for other types of tumors and early detection of possible complications.
- List of possible side effects of treatment.
- What you need to pay special attention to and when to see a doctor.
- Individually selected diet and frequency of meals.
- Physical activity regimen and list of possible restrictions.
What to do after radical removal of melanoma?
After therapy is completed, doctors will continue to monitor the patient closely. Along with the risk of recurrence of melanoma, other complications may occur. Postoperative monitoring of the patient's condition will include:
- regular examination of the skin and the condition of the lymph nodes - independently and by a doctor;
- depending on the stage of the disease, control instrumental studies (X-ray, PET, CT, etc.) may be needed;
- in some cases, to prevent recurrence of skin melanoma, techniques using radiation therapy (local irradiation of the tumor defect area), as well as protocols using immune drugs, can be used.
In some cases, after surgical treatment of melanoma, protocols using irradiation of the tumor defect area are used to prevent local tumor recurrence. Although this approach does not guarantee a reduction in the incidence of distant metastasis, according to statistics, it reduces the likelihood of local relapse.
Recently, techniques using intensity-modulated radiotherapy have been actively introduced into practice, which allows for maximum focusing of radiation with minimal damage to healthy tissue.
The use of stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic melanoma makes it possible to directly irradiate the tissue of the secondary tumor, which limits the rate of its malignant growth.
The use of immunodrugs and the use of targeted therapy in the treatment of common tumors in 70% of cases makes it possible to transfer tumor cells to a “switched off” state. At the same time, intoxication is reduced, quality and life expectancy are increased.
Follow-up after melanoma excision
The frequency of follow-up examinations depends on the stage of the tumor process. After excision of early stage melanoma, physical examination is performed every 6 to 12 months for several years. In the absence of alarming symptoms, the periods between visits to the doctor can be extended. Conversely, if the patient has a large number of moles, the frequency of examinations may be increased.
For thicker melanomas or those that have spread beyond the skin, a typical screening schedule may include physical examinations every 3 to 6 months for several years, after which visits to the doctor may become less frequent.
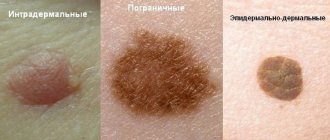
Life after melanoma removal should include careful self-monitoring. For self-examination of the skin, the ABCDE algorithm has been developed:
| A | Asymmetry. Asymmetry | Lack of symmetry of moles is a warning sign. |
| B | Border. Border | A benign birthmark, unlike melanomas, has smooth borders. The edges of melanoma are usually irregular and may be jagged or jagged. |
| C | Color. Color | Most benign formations have a uniform color, usually brown tones. A warning sign is a change in color or shade of a mole. |
| D | Diameter Diameter | Benign moles usually have a smaller diameter than malignant ones. Melanomas typically have a diameter larger than the eraser on the tip of a pencil (¼ inch or 6 mm). |
| E | Evolving. Development | Benign moles look the same over time. Any change (in size, shape, color, height or other characteristic) or the appearance of any new symptoms (bleeding, itching, crusting) is dangerous. |
Is it possible to reduce the risk of progression or recurrence of melanoma?
There are a number of recommendations that will reduce the risk of melanoma recurrence or progression:
- limit exposure to ultraviolet rays (sun, solarium);
- monthly skin examination (ABCDE);
- a complete diet;
- to give up smoking;
- physical education classes;
- maintaining normal weight.
About food supplements
There is still no scientific evidence that taking dietary supplements (BAS), including vitamins, microelements and herbal components, helps reduce the risk of relapse or prevent the appearance of metastases after treatment of melanoma. However, in some cases, these supplements may be recommended as a dietary supplement. In each case, when making a decision on this matter, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
About psychological support
Patients with skin melanoma often have questions after surgery:
- Will a relapse occur after a mole is removed?
- What are the chances that melanoma will come back?
- How will I know if the cancer comes back?
- What will I do if he comes back?
- When will he return?
In this regard, treatment after removal of melanoma should include psychological assistance from specialists and support from close relatives. Many of them should be helped to learn to live with uncertainty. Although there are no visible signs of relapse at this time, patients should understand that the disease can recur at any time.
Self-monitoring algorithms after surgery to remove melanoma
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends having your skin examined every month. This is especially true for patients undergoing treatment for melanoma. This approach makes it possible to detect relapse and identify minimal skin changes at the earliest stages, thereby increasing the chances of timely therapy.
For inspection you need a light source, 2 mirrors, a hairdryer, 2 chairs, a body diagram, a pencil.
Stage 1 You need to check the face, especially the nose, lips, mouth and ears (their front and back surfaces). It is recommended to use one or two mirrors to get a clear picture of the nature of the changes. Step 2 Thorough examination of the scalp using a hairdryer and mirror to visualize each area more thoroughly.
Stage 3 Careful inspection of hands: palms and back surfaces, skin between fingers and under nails. Continue the inspection to the wrist to examine the front and back of the forearm. Step 4 Standing in front of a full-length mirror, continue to examine the shoulder area, elbow area and all surfaces of the forearms. Don't forget to check your armpits.
Stage 5 Next, you need to focus on the neck, chest and torso. Women should lift their breasts to examine the skin underneath the breasts. Step 6 With your back to a large mirror, use a hand-held mirror to examine the back of the neck, shoulders, upper back, and parts of the upper extremities that were not visible in the previous steps.
Step 7 Using both mirrors, examine the lower back, buttocks and the back of both legs. Step 8 The examination is carried out in a sitting position: place each leg in turn on another chair or armchair. Use a hand mirror to examine your genitals. Checking the front and sides of both legs, thighs and shins, ankles, backs of the feet, skin between the toes and under the nails.
Careful examination of the soles of the feet and heels.
Such regular examination of the skin will identify pathological changes at the earliest stages.
The development of metastases after removal of melanoma can be detected after examination by an oncologist and special studies (ultrasound, PET-CT, MRI). This is why regular follow-up with a specialist is extremely important after treatment for melanoma.
As the disease progresses and widespread forms appear, the question may arise: how long do they live after removal of melanoma complicated by metastases to other organs? Today, with the advent of new progressive techniques, treatment of metastatic forms of melanoma can significantly increase the duration and quality of life.
Immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma using immune point inhibitors has been successfully used for metastatic melanoma in cases where the tumor cannot be removed surgically.
Sources
https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/melanoma/melanoma-warning-signs-and-images/do-you-know-your-abcdes#panel1-5
After Treatment
https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/early-detection/step-by-step-self-examination
https://www.cancer.org/treatment/survivorship-during-and-after-treatment/be-healthy-after-treatment/life-after-cancer.html
Source: https://melanomaunit.ru/lechenie-melanomy/nablyudenie-posle-udaleniya/
Recurrence of melanoma on a postoperative scar: signs, stages of development, symptoms and prognosis
Malignant melanoma has a reputation for complete unpredictability, however, in comparison with other cancer processes, quite a lot is known about the patterns of its progression.
Why is relapse dangerous?
Relapse in melanoma is not only the appearance of a malignant formation in the scar, but also metastases. They most often affect the lymph nodes, lungs, skin, brain and liver. The possibility of removing a recurrent formation opens up prospects for a long life; if the operation is technically impossible, then the present and future will be occupied by drug therapy.
Survival for multiple organ metastases does not exceed six months; the results of drug therapy leave much to be desired, even with the use of innovative immuno-oncological drugs, which rarely promise more than two years of life.
Forecast
Every year, melanoma is diagnosed in an average of 15 people out of every hundred thousand adults, approximately 3 patients die, and with a fairly stable mortality rate in the last quarter century, men began to die more often. Gender determines a lot in the prognosis of the disease, other things being equal, but young people experience the disease with less difficulty.
The probability of death with a late relapse is many times lower than with an early relapse. Early detection of progression promises better treatment results.
It is extremely difficult to predict the course of melanoma, because even a common process is not considered absolutely fatal; this malignant disease does not often live up to expectations. Don’t guess “to be or not to be”, contact specialists if you have problems, or better yet, before they appear - we will always help.
Make an appointment for a consultation around the clock +78 800 100 14 98
Is melanoma excised or not?
Often, removal of melanoma is the only measure to get rid of the pathology. If malignant pigmentation is not removed in a timely manner, it can lead to serious complications and consequences, including death. Therefore, it is important to understand what methods exist to eliminate formation and which of them are the safest.
Removal of melanoma is at times a justified measure to suppress cancer.
Indications for melanoma removal
Getting rid of the tumor is mandatory, since melanoma is a malignant tumor that can be fatal.
When a person develops tumors on the body that change shape, increase in size, change color or bleed, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
During the consultation, the doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe the required tests, which will show the nature (malignant or benign) of the growth and whether it needs to be removed.
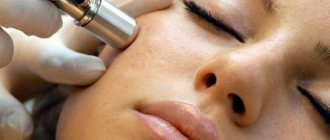
Laser removal
Laser removal of melanoma is sometimes performed, since some people have contraindications for surgery. Thus, the operation is not performed if the patient is elderly or has certain diseases. It is important to note that laser treatment is used to get rid of melanoma only when its size does not exceed 0.5 centimeters.
Advantages of the method
The benefits of having melanoma removed with a laser:
- No scars after melanoma removal. Since cosmetic defects are not observed, they resort to removing the formation even on the face.
- Painless.
- The ability to get rid of a tumor when there are contraindications to surgery.
- Minimal risk of complications.
- Fast wound healing.
After eliminating melanoma with laser therapy, the patient will need to undergo chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
This is done to prevent the re-development of melanoma and to get rid of malignant cells. Sometimes metastases penetrate the human circulatory system, and chemotherapy can reduce this risk.
These methods of therapy have many side effects, however, they must be completed.
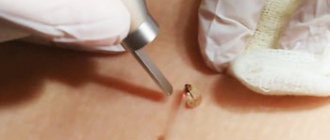
Removal operation
Melanoma surgery can be done under general or local anesthesia.
Excision of melanoma is carried out under local or general anesthesia, depending on the size of the formation.
If the growth is small and penetrates shallowly under the skin, then it is cut out and covered around 2 centimeters of healthy skin in order to prevent relapses.
At the end of the procedure, the doctor applies a suture using special threads that dissolve on their own after a certain amount of time. After surgery, a noticeable scar remains on the skin.
If the neoplasm is large, then it is removed along with a large area of healthy skin.
Sometimes a piece of skin from another part of the patient's body is transplanted into the area being operated on.
If the melanoma is located under the nail, it is often impossible to cut it out; in this case, the entire finger is amputated. When the growth is on the genitals, amputation may be required.
Surgical methods
Melanoma can be operated on in the following ways:
| Name | Description |
| Simple excision | Only small formations can be removed. |
| Wide excision | They resort to get rid of large melanoma. |
| Amputation | Used when melanoma affects certain areas of the body. |
| Lymph node removal | It is used when the tumor grows and affects neighboring lymph nodes. |
Consequences of intervention
Surgery to remove melanoma has a number of consequences and complications:
- bleeding;
- infection;
- injury to nerve endings;
- partial removal of cancer cells;
- the appearance of scars and cicatrices;
- relapse.
Wound care after removal
Until the wounds are completely healed after melanoma removal, daily sanitation is necessary.
The operated wound for melanoma requires special care.
In most cases, the period after removal of the tumor passes quickly and without complications, however, there are situations when the growth hurts, itches or itches. This indicates improper care and requires contacting a doctor.
It is important for the patient to remember the following principles of postoperative wound care:
- maintain hygiene and constantly change bandages;
- discuss with your doctor the possibility of taking a shower and bath and find out what means can be used to wash the affected skin;
- lubricate the wound with an antiseptic prescribed by a healthcare professional;
- use prescribed antibiotics and painkillers;
- During the healing of the operated area, avoid intense physical activity.
Proper nutrition during treatment
Treatment for melanoma requires the patient to maintain proper nutrition. The following foods are prohibited:
- ice cream;
- baked goods;
- salo;
- roast;
- fat;
- cocktails based on milk and coffee.
Reduce your consumption of these foods:
- pistachios;
- Pine nuts;
- butter;
- animal fats;
- vegetable oils;
- pumpkin and sunflower seeds;
- offal.
In the first days after removal of melanoma, you will need to follow a diet.
After removal of melanoma, you are allowed to eat the following foods:
- fiber;
- greenery;
- spices;
- lean fish;
- lean meats;
- fresh juices;
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- peanut;
- shrimps;
- chicken;
- turkey;
- cereals;
- bran bread;
- Brown rice;
- seaweed;
- wasabi;
- dairy products.
Features of proper nutrition for melanoma
After getting rid of the tumor, the patient’s diet should be healthy and balanced. The approximate menu is determined by the doctor, and the patient must follow it unconditionally. In addition, it is important to follow the following diet principles:
- Reduce fat intake to a minimum.
- Cook food by steaming, in the oven, boiling or stewing. Frying is prohibited.
- Fill your diet with foods rich in vitamins C and D.
- When a patient experiences complications in the form of nausea and vomiting, they resort to split meals in small portions 5 times a day.
- You need to eat without being distracted by reading or watching TV; food should be chewed thoroughly.
Prevention
Considering that melanoma is a serious pathology, it is better to prevent its development than to get rid of it later.
Doctors recommend monitoring the condition of moles, birthmarks and age spots and warts and if they change, for example, if they increase in size, change color, shape and bleed, immediately contact a medical facility to undergo a histological analysis and identify malignancy in the early stages education.
How to prevent a relapse?
According to statistics, melanoma relapse occurs in 10% of patients 10 years after melanoma removal. After 15 years - in 8% and after 25 years - in 12% of patients. After eliminating melanoma, a person will have to undergo a course of chemotherapy, which has a number of negative consequences, but is very important in the fight against cancer cells.
In addition, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, include physical activity and a healthy diet in your schedule. You need to eat more fresh vegetables and fruits, eliminate fatty and fried foods from your diet. Do not snack on the go and do not visit fast food establishments. Doctors recommend sticking to a sleep and rest schedule.
All these measures will help prevent recurrence of melanoma.
Prognosis for cancer
The outcome is directly related to the stage at which the formation was diagnosed. The sooner a patient with melanoma sees a doctor, the more positive the prognosis will be.
Doctors often receive a question: how many years can you live after removing melanoma? Health workers agree that if the tumor has not metastasized, and it was disposed of correctly, and subsequent therapy was carried out, then patients continue to live their normal lives, without remembering the insidious disease.
But at the initial stage, diagnosing melanoma is not easy. Most often, people who have been living with a tumor for a long period of time turn to a medical institution. The prognosis in this case is unfavorable.
When melanoma is removed at a late stage, only 1 in 3 patients lives more than 5 years. If the formation has metastasized or affected the lymph nodes, then the prognosis is even more unfavorable.
Even when the lymph nodes have been removed, there is a risk of relapse; the cancer appears in other areas of the body or on organs.
Source: https://StopRodinkam.ru/obrazovaniya/melanomy/udalenie.html
Complications
Unfortunately, complications are possible during and after the operation. After excision of the tumor there may be:
- bleeding;
- postoperative wound infection and inflammation;
- damage to nerve endings and other structures;
- formation of a rough colloidal scar;
- progression of the disease and spread of malignant cells.
To minimize the risk of undesirable consequences, any oncological operations should be performed by oncologists.
Removal of melanoma: consequences
One of the most pressing questions of modern dermatology is how to remove melanoma? The search for new methods is associated with a constant increase in the incidence of oncological pathology, a tendency to relapse with poor quality treatment, and an unfavorable prognosis for the patient. In this article we will look at the main methods for removing melanoma, the advantages and pitfalls of each of them.
Preparing for surgery
Before removal of melanoma, the patient must undergo a standard set of laboratory and instrumental tests. It includes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- analysis for tumor markers;
- electrocardiogram;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- X-ray examination of the lungs;
- dermatoscopy;
- collection of anesthetic history.
These studies will make it possible to determine the boundaries of the tumor, diagnose the presence or absence of metastases, eliminate possible contraindications for surgery, and avoid adverse reactions to antibacterial drugs.
It is worth noting that preliminary puncture of melanoma is not performed. This can injure the tumor and cause its development to progress.
Histological examination is done after excision of pathologically changed tissues. There is no special preparation before surgery.
Using a laser
In patients with stage 1 melanoma, the tumor can be removed using a laser. This technique has a number of advantages. Among them:
- There is no pain, and therefore no need for general anesthesia.
- Contactless.
- Minimal likelihood of complications.
- No risk of infection.
- Short duration of the procedure.
- Almost complete absence of contraindications.
- Stage 1 melanoma is removed from the skin with a laser almost without a trace, so this manipulation can be used on the skin of the face.
Before using the laser, the skin is treated with an anesthetic. The device is then precisely positioned over the melanoma and turned on. In this case, the cancer cells are completely destroyed.
The duration of exposure is determined by the size of the neoplasm. As a rule, it does not exceed several minutes.
After the procedure is completed, the surgical site is covered with an adhesive plaster to prevent water and sun rays from coming into contact with it.
However, this technique has disadvantages. The main one is that the removed tumor is not amenable to histological examination.
Surgical intervention
More traditional surgical excision of the tumor is still widely used in the treatment of oncological pathology. It is performed at almost any stage of the disease, except for cases with active metastasis.
In addition, its advantages are:
- The ability to remove not only the tumor, but also regional lymph nodes.
- The obtained biological material after resection is submitted for histological examination.
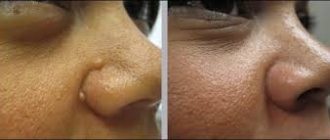
One of the consequences of surgical removal of melanoma is the formation of a postoperative scar. This problem is partially or completely solved with the help of special creams that act on the resulting connective tissue.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia, so not all patients can undergo it. Liver and kidney failure and other severe conditions are contraindications for surgery.
Not only the neoplasm is subjected to resection, but also nearby healthy tissue, as well as regional lymph nodes.
Along the way, an emergency histological examination of the obtained biological material is carried out. If no malignant cells are found within healthy tissue, then the wound is sutured.
In cases where the histological picture is unfavorable, the surface of the removed tissue is increased.
At the end of the operation, the wound is sutured, leaving a drainage tube in it. It is covered from above with aseptic material to prevent secondary infection of the resection site. Hygienic treatment of the wound is carried out daily. For this purpose, the patient is left in the hospital.
Possible complications
Using a laser to remove melanoma almost completely eliminates the likelihood of complications. The method is low-traumatic; the most common complication is a burn at the surgical site. Most often it is grade 1 or 2.
Traditional surgical removal of melanoma is more traumatic, so the risk of complications is higher. Most often they are associated with non-compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis:
- development of purulent inflammation at the site of primary leakage;
- the occurrence of an abscess;
- a common purulent process in the form of phlegmon or sepsis.
Incomplete removal of malignant cells leads to recurrence of the disease.
The choice of treatment method for melanoma is determined by a specialist in each specific case. When preparing for surgery, the doctor takes into account the potential risks, the patient's condition and the stage of the disease.
Laser removal of melanoma is an effective technique used in modern cancer centers. Having a minimum of contraindications and restrictions, it allows you to quickly get rid of tumors in the initial stages.
If the disease is detected late, the cancerous tumor is removed surgically. In any case, melanoma cannot be left without treatment, as it progresses rapidly, affecting more and more organs and tissues.
This is one of the most dangerous cancer pathologies known to medicine.
Source: https://MoyaKoja.ru/onkologiya/rak/udalenie-melanomy.html
Melanoma prevalence
The prevalence of melanoma has increased substantially over the past 35 years and now stands at approximately 1 in 70 Americans, mostly white.
Approximately 62,000 patients are diagnosed with melanoma each year, and over 7,000 die from the tumor each year. It is necessary to establish whether the increase in incidence is real or due to improved diagnostics. Although the incidence doubles every 10 years, the overall mortality rate from melanoma has increased only slightly. This trend indicates that a significant proportion of melanoma cases are diagnosed when the tumor is thin and can be successfully treated by radical surgical removal.
Surgical treatment of primary infiltrating melanoma has become more individualized, based on information obtained from microstaging of primary melanoma and determination of sentinel lymph node status.
How to remove melanoma: consequences
Melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer. It arises from pigment cells - melanocytes. Most often, the neoplasm affects the skin, but can also be localized under the nails, on the mucous membranes or in the structures of the eye. The tumor is very dangerous due to its rapid growth and tendency to form metastases in the lymph nodes, internal organs and skeletal bones.
The only effective way to get rid of melanoma at the initial stage is to perform surgery. Neoplasms that are small in thickness are cut off, capturing intact surrounding tissue.
Typically, excision is performed under local anesthesia; general anesthesia is used when the formation has a large area or is located in a hard-to-reach place.
We will tell you in this article how to remove melanoma and what consequences await the patient.
New growths with developing metastases cannot be excised. The exception is when the tumor causes pain or discomfort to the patient.
Melanoma is the most aggressive malignant tumor; only timely treatment can save it.
Melanoma removal methods
Surgical excision of the tumor can be done in four ways:
- Simple removal method. This method is used to operate on small melanoma. After excision of the neoplasm and adjacent tissues, the wound is sutured. As a rule, after such an intervention a scar remains.
- Wide excision method. It is used when it is necessary to cut off a significant amount of tissue around the lesion. This is done to excise all cells affected by cancer. The incision is sutured or healthy skin grafted.
- Amputation. This method is used when the tumor is located on the finger, in which case complete amputation of the organ is required.
- Removal of lymph nodes. In cases where melanoma has metastasized to the lymphatic system, they are removed surgically. After the operation, I remove the stitches in 10-14 days.
Removal of melanoma is performed in two ways: surgery and laser removal.
Surgical removal
When the malignant neoplasm is at an early stage, it is removed along with adjacent intact tissues, capturing them a couple of centimeters - this helps to avoid relapse of the disease.
Although the procedure to excise melanoma has been performed for more than 100 years, doctors still debate about the area of excision.
According to statistics, cutting healthy skin even at a distance of up to 5 centimeters does not provide a 100% guarantee that the disease will not return again.
The advantage of surgical excision of the formation is that the removed tissue can be sent to the laboratory for histological analysis, as well as the possibility of removing metastases in the lymph nodes. Complications often develop after melanoma has been removed. The consequences of the intervention are as follows:
- the likelihood of wound infection;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- a noticeable scar on the skin after healing;
- if cancer cells remain, relapse may occur;
- long recovery period after surgery.
If dangerous consequences of melanoma appear - metastases, then surgical removal is not advisable. In this case, a course of chemotherapy is administered, although the prognosis in this case is extremely unfavorable.
Surgical removal of melanoma is performed under local anesthesia
Laser removal
Laser removal of melanoma is used in cases where surgical excision is not possible for certain reasons. For example, when the patient has concomitant diseases.
The laser removal method also has contraindications; it is performed only for melanoma, which is no more than 0.5 centimeters in size.
The advantages of removing tumors with laser radiation include:
- the patient does not experience pain;
- the possibility of performing the procedure when surgical excision is prohibited;
- almost complete absence of complications after removal;
- absence of noticeable scars and cicatrices.
Also, without fail, the patient is prescribed treatment after removal of the melanoma. If you follow all the doctors’ recommendations, the rehabilitation period will be faster and easier.
Melanomas no larger than 5 mm in size are subject to laser removal.
Treatment after surgery
Despite the fact that the current statistics are disappointing, with proper treatment there is every chance of getting rid of such an aggressive disease as skin melanoma. Treatment after surgery is prescribed depending on the stage of development of the tumor:
- radiation therapy (to exclude the appearance of metastases after tumor removal);
- immunomodulatory therapy (to help the body fight cancer cells);
- chemotherapy (the use of drugs that can kill cancer cells).
In addition to traditional treatment, medicinal herbs with antitumor effects are often used.
Finding melanoma early can save your life. Carry out regular self-examination of moles and age spots; if you have the slightest suspicion, immediately contact a specialist.
Source: https://lechimkozhy.ru/novoobrazovaniya/melanomy/kak-udalit-melanomu-posledstviya.html
Melanoma: metastases and how to operate
Have you been fighting PAPILLOMAS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of papillomas by taking every day...
Read more "
More than half of all skin melanoma metastases penetrate the lymph nodes, and metastases are detected due to their thickness, as in the photo.
Thickness less than 0.7 mm is extremely rare, mostly sizes up to 4 mm, and with such indicators the risk of its constant spread increases significantly.
In addition, metastases penetrate not only into the skin tissue and lymph nodes, but also into the brain, in which case the prognosis for life is unfavorable.
If skin melanoma is thin, the potential for growth is quite low, and the incubation period can reach 20 years, and from the moment of diagnosis.
Once skin melanoma is identified, it develops extremely slowly and there is time to begin treatment and protect both the brain and bones and lymph nodes.
As is known, metastases of skin cancer spread with the bloodstream and can affect any organs, including bones and the brain, but there is a certain pattern that allows us to identify organs that are more likely to undergo degeneration than others:
- Leather;
- lymph nodes;
- Lungs;
- Liver.
- Brain.
Types of melanoma metastases
- Skin metastases in melanoma. Indicative are the forms of metastases, which appear in the form of satellites and nodes;
- Skin metastases of melanoma to lymph nodes. The primary manifestation is observed on the surface of the skin of the legs. Once in the lymph nodes, melanoma metastases grow and the skin located above them becomes blue and black;
- Visceral, organ. These metastases affect the brain, kidneys, and lungs.
Metastases exhibit cyclical growth and spread. In this case, the first case may completely regress, and will not even be detected after repeated examination. Also read: What causes red moles?
Dimensions and relapses
If the thickness of each metastasis of skin melanoma does not exceed 0.7 mm, then we can say that the metastases will not progress further, and there will be no penetration into the brain, bones and lymph nodes.
This, however, does not guarantee that the disease will not progress at all, so the prognosis for life with metastases still remains unknown and the question of removing metastases is open.
The thickness of skin melanoma metastases up to 1.5 mm indicates that the patient is at risk and the prognosis for life is unfavorable, as in the photo.
The likelihood of recurrence and damage increases if the thickness of the metastases is more than 1.5 mm, in which case the brain may be affected. Relapse in this case manifests itself in the first 36 months; it is these data that determine the need for constant examinations by an oncologist in the first three years after diagnosing melanoma metastases.
On this basis, the prognosis for further therapy is considered and treatment is selected.
Forecasts
In more than half of the cases with grade 4 melanoma, metastases affect the skin and subcutaneous tissue; the symptoms are pronounced and cannot be missed.
With such damage and development of the disease, life expectancy in only a quarter of patients reaches one year, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable, and treatment only relieves pain, but is not able to save the patient.
In second place in terms of damage are the liver, brain, and lungs. The life expectancy of such patients is 2-6 months, and only one tenth lives with such lesions for about a year, that is, treatment practically does not help, and the prognosis is unfavorable.
Melanoma removal
If the melanoma is small in thickness, it can be completely removed by excision and removal of a small amount of healthy tissue around the edges of the tumor. This treatment is quite common and gives a positive prognosis.
The amount of melanoma tissue that will be excised depends on the thickness of the tumor; in surgery it is from 0.5 cm to 2 cm. The operation is quite simple and is performed under local anesthesia.
Symptoms make it possible to quickly identify melanoma and carry out surgical treatment, after which the patient can be almost 100% calm.
Operation Mohs
In this surgery, the melanoma tumor is excised in layers, with each layer examined immediately for the presence of melanoma cells to confirm signs and symptoms of cancer.
The operation is stopped only when no danger is detected in the layer and there are no signs and symptoms of cancer. Thus, infected tissue is not simply removed, but more healthy tissue is preserved, which simplifies the rehabilitation period after surgery.
Amputation
If the melanoma is located on the finger, then doctors may recommend partial or complete removal of the finger, this can be considered as a radical treatment.
A folk recipe will get rid of papillomas. Take the simplest...
This is what our grandmothers did. The warts will go away in 10 days. Just take...
Lymph dissection
If melanoma is located in a lymph node, then complete excision of both the damaged area and all nodes that are located next to the lesion is performed.
If a biopsy reveals melanoma cells in a sentinel lymph node, the remaining nodes are excised.
Surgeries for metastatic melanoma
This type of surgery may be performed not so much to remove the melanoma, but to control its development and continue treatment with other means. It is this kind of treatment and this kind of surgery that is the most controversial decision in the fight against melanoma.
As always, in conclusion, it is worth noting that even if such a misfortune as melanoma has happened to you, you should not give up. We need to fight it, fight metastases, and the one who doesn’t give up will definitely win.
Melanoma metastases are a very serious disease, but there are cases where people recover and go on to live healthy lives.
How is melanoma removed and what are the consequences of the operation?
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm of pigment cells that are designed to protect the body from ultraviolet rays. At some point, degeneration of pigment cells occurs, and they turn from defenders into aggressors. The exact cause of malignant degeneration of melanocytes is unknown.
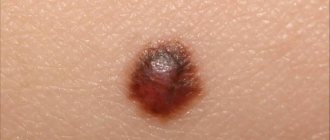
Photo 1. Melanoma is the fastest growing type of cancer. Under no circumstances should you postpone a visit to the doctor. Source: Flickr (wildmeadow).
Indications for melanoma removal
Since the neoplasm is malignant, its very appearance is already an indication for surgical intervention. Removal of a malignant tumor is a mandatory procedure .
Melanoma is a very aggressive neoplasm that quickly begins to metastasize . If you do not remove it in time, it quickly spreads throughout the body. The presence of cancer screening foci in the internal organs indicates the transition of the disease to the fourth stage and a very unfavorable prognosis.
Any skin formation that has signs of melanoma should be carefully examined and, if malignant cells are present, removed as soon as possible.
It is important! The only contraindication to surgery in this case is the fourth stage of cancer and the high risk of postoperative complications. If tumor foci have begun to grow in internal organs, then removal of the primary lesion is a palliative operation that may not be performed.
Types of operations to remove melanoma
During tumor resection, the main thing is to comply with the ablastic rule. This means that all atypical cells must be removed from the lesion.
Considering that melanoma is a superficial neoplasm, it can be removed in two ways: using a laser or classical surgery .
Preparation
Before the operation, it is necessary to undergo all examinations in order to accurately establish the diagnosis and stage of the disease . To do this, they take general and biochemical blood tests, perform a biopsy of the tumor and histological examination of the material taken, do an ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs, and an x-ray of the lungs.
special preparation is required for the operation itself . It is recommended not to sunbathe for at least a week before the procedure. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia.
How does the procedure work?
The skin around the tumor is injected with an anesthetic , and after its action begins, the procedure itself is carried out.
The manipulator is placed over the melanoma and turned on. Laser beams precisely target tumor cells without damaging healthy tissue.
After a few minutes, the atypical cells are destroyed and the procedure is considered complete.
How to care for your skin after surgery
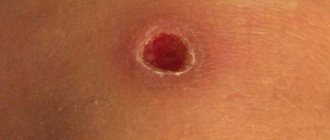
After the operation a small tissue defect remains , the size of which does not exceed the size of the removed tumor. The intervention site should not be exposed to water or ultraviolet rays for a month. It is recommended to cover it with adhesive tape.
Surgical excision
This is a classic type of removal of malignant tumors, which is used in the resection of oncological tumors. Has a number of advantages:
- Possibility of performing surgery at any stage (except for cases with growing metastases);
- Possibility of conducting a full range of studies of remote material;
- The affected lymph nodes can be removed along with the tumor.
This method is a full-fledged surgical operation, after which a fairly large scar remains . In addition, complications are more likely to occur after conventional removal.
Rehabilitation period after melanoma removal
The rehabilitation period after laser removal is approximately 4 weeks , after surgical excision - several months until the tissue is completely healed. After the classic treatment, antibiotics are required.
If the stage of the disease is higher than the first, after surgery it is necessary to undergo a course of additional treatment . For this purpose, radiation, biological or chemotherapy are used. In each specific case, subsequent treatment is prescribed by the doctor. Such therapy can last a year or even more.
After complete completion of treatment, the patient must visit the oncologist at least once every six months . This is necessary to monitor the occurrence of relapse.
Photo 2. After traditional surgery, a large scar usually remains on the skin. Source: Flickr (Samantha Tavares)
Nutrition in the postoperative period
There is no special diet after this operation. The patient is allowed to eat any food . It is necessary to ensure that the number of calories consumed covers the body's energy expenditure. Particular emphasis should be placed on protein foods.
In addition, it is important to monitor sufficient levels of iron, magnesium, potassium and vitamins in the body. However, they should not be used as supplements. It is better to eat fresh fruits and vegetables, foods rich in vitamins and microelements.
It is important! Cancer patients should not take any biological supplements. If at least one altered cell remains in the body, dietary supplements will stimulate its reproduction and provoke the growth of a malignant tumor.
Surgical treatment of stage III melanoma with lymph node involvement
When regional lymph nodes are involved in the tumor process, 5-year survival varies from 30% to 60%, depending on the volume of tumor tissue in the lymph nodes and the number of lymph nodes involved.
Survival rates drop to just a few percent when metastases are found outside the regional lymph nodes, especially in internal organs. In the past, the only way to diagnose regional lymph node metastases was to perform a complete or radical lymphadenectomy, which may be associated with an increased incidence of complications such as lymphedema.
The most important advance since 1992 is the demonstration that selective removal of SLNs is probably the best method for assessing regional lymph node status, since they are the first nodes to receive tumor cells from the primary tumor.
Thus, the provisional diagnosis of primary melanoma relies entirely on evaluation of the regional lymph nodes by selectively removing one or more sentinel lymph nodes to determine the presence of metastases, as described above.
If there are no metastases in them, then the probability of the presence of tumor cells in other lymph nodes is less than 5%. This eliminates the need for a more extensive and more complication-prone radical lymphadenectomy after a negative SLN study in more than 80% of patients.