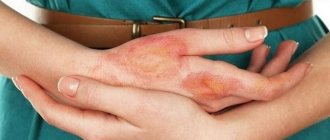
Features of injury
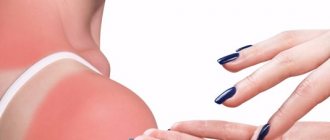
Speaking about the characteristics of a radiation burn, one cannot fail to mention that in many respects it has the same manifestations as a sunburn.
The extent of skin damage and the depth of the burn are related to how long the person was exposed to radiation. However, you should be able to distinguish between a sunburn and a radiation burn, based on some of the features of a radiation burn presented below:
- symptoms appear only over time;
- with a radiation burn, the skin turns red and swells in several places;
- Radiation therapy is an increased risk for people with weakened immune systems, sensitive skin or lack of insulin.
Another unpleasant feature of such skin damage is that it is difficult to treat traditionally and is painful for the patient, and from this we can draw the following conclusion: treatment of a radiation burn is necessary.
Let's move on directly to the classification by severity. It is customary to differentiate four stages, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms.
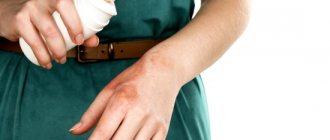
The first stage of a radiation burn is considered to be a time period several hours or days after irradiation. At this stage, there is pronounced redness of the skin at the site of irradiation.
The second stage is longer than the first, it is also called hidden. When it comes to determining the degree of severity, you should pay special attention to the symptoms that arise at this stage - the more pronounced they are, the worse the situation is.
At the fourth stage, inflammatory processes subside and the body regains strength.
There is a high risk of burns if a person quickly burns in the sun. In such cases, even low-intensity exposure leads to injury to the skin. The procedure is especially difficult for people with diabetes or low immunity.
A radiation burn differs from a traditional thermal burn in the late onset of external manifestations. This means that after radiotherapy there must be a short period of time for such a side effect to appear. Injury occurs in several areas of the skin at once.
Burns after radiation therapy (photo)
A radiation burn occurs under the influence of radiation therapy and is very similar in symptoms to a sunburn. The severity and extent of the lesion is influenced by the strength of the ion radiation, how often such procedures are performed and the patient’s condition.
The danger of getting deep burns is especially great with neutron, x-ray and gamma radiation. The first two forms of radiation burn are usually caused by low-energy beta particles, since they are not able to penetrate deeply into tissue. Today we will consider first aid for radiation skin burns, treatment after them, therapy in a hospital setting, and will also give useful recommendations.
A characteristic feature is the presence of a latent period of development. We are talking about late onset of external manifestations: symptoms of radiation exposure make themselves felt after a short period of time. Most often, injury is found in several areas of the skin.
Radiation burns are caused by the following forms of radiation:
- ultraviolet (sun);
- ionizing (alpha, beta and neutron);
- electromagnetic – photons (beta and x-rays).
Alpha radionuclides are safe for humans. They can only affect the upper layers of the skin and mucous membranes (you need to protect your eyes, mouth, throat, and esophagus from them). Beta radiation penetrates 2-3 cm deep into the body. The body is most affected by X-rays, neutrons and gamma rays. They damage all internal organs and tissues.
Depending on the source (cause) of the injury, there are several types of radiation burns:
- As a result of exposure to sunlight (ultraviolet radiation). This type is the most common: after prolonged exposure to the sun, a person burns. If it is prone to increased reaction to ultraviolet light, burning may occur due to low intensity exposure. People with weakened immune systems and people with diabetes do not tolerate the sun well.
- Caused by ground and air nuclear explosions and laser weapons. Such powerful sources instantly affect all parts of the body. Often accompanied by damage to the eyeballs.
- From ionizing radiation. They do not affect internal organs, affecting only the superficial layers of the skin. With radiation sickness, burns heal slowly and the regeneration process is suspended. The vessels become brittle and poorly nourish the damaged surfaces.
- Burns after radiation therapy. May occur as a result of radiotherapy (various types of radiation) in order to cure a disease, most often of a tumor oncological nature (breast cancer, esophagus, larynx, cervix, etc.)
There are different types of burns depending on the affected area:
- skin;
- mucous membrane (eye during welding);
- internal organs.
Each type requires a separate treatment method, taking into account the nature, area of damage, and degree of damage.
Radiation burns: causes, types of dangerous radiation, degrees, symptoms, first aid and treatment
Radiation burns are damage to the skin or mucous membranes as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation.
Peculiarities
Radiation is not perceived by the human senses; after exposure, time passes before the first signs of damage appear. The condition is characterized by a mild inflammatory reaction.
The combination of local symptoms with the body’s systemic response to the action of a negative factor signals the development of radiation sickness.
Classification
Various types of radiation cause radiation burns:
- Ultraviolet (sun, solarium).
- Alpha particles of ionizing radiation have little penetrating power, but when they enter the body they accumulate, causing cell mutation . Alpha isotopes are only dangerous if they come into direct contact with a radiation source.
- Beta isotopes are a stream of electrons produced by the decay of nuclei. Compared to alpha rays, they penetrate much deeper into the tissues of the body.
- Gamma radiation is energy quanta, which are electromagnetic vibrations. In medicine they are used to treat malignant tumors. Dosed directed rays suppress the activity of cancer cells.
- X-ray is electromagnetic energy released in the form of photons. The physical effect on the body is similar to gamma radiation, but with less penetrating power.
Burns after radiation therapy do not occur immediately, and the skin reaction is determined by its type and intensity of radiation.
Causes
The most common type of radiation burn occurs from the action of solar energy, when after prolonged exposure to the sun, a person burns. Such injuries are easily sustained by people with light skin tones, diabetes mellitus, and weakened immunity.
Radiation burns also occur as a result of man-made disasters at installations and structures equipped with sources of ionizing radiation: nuclear power plants, submarines, scientific laboratories.
Skin burns occur as a complication after radiotherapy sessions used in cancer patients when the maximum permissible doses of X-ray radiation are exceeded for certain types of examination.
Symptoms
Based on severity, radiation burns are divided into 4 groups:
- Grade 1 is the mildest, manifested only by hyperemia and peeling of the upper layer of the epithelium.
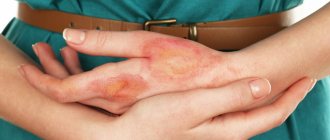
- 2nd degree - detachment of the epidermis from the dermis occurs with the formation of blisters of varying sizes, itching and pain occur.
- 3rd degree - burst blisters form erosions, deep, long-lasting ulcers, necrosis of all layers of skin develops down to the muscles.
- Grade 4 - severe, occurs immediately after exposure to radiation and is always combined with radiation sickness.
Symptoms of a burn appear gradually in several stages:
- The body's primary reaction develops either immediately after exposure (with a large dose) or after a few days. In mild cases, the skin in the affected area becomes hyperemic, peels, and becomes painful and itchy. Later a general reaction follows: weakness, headache, nausea. The duration of the first stage is several hours, then the painful phenomena disappear.
- The latent period, when there are no symptoms of a burn, both local and general. The duration of the stage is determined by the dose and type of radiation injury. So, with a sunburn, this period of imaginary well-being lasts for hours, and when exposed to radiation it can last up to several months .
- The period of hyperemia and edema. The skin turns red, thickens, swelling appears, and hair often falls out. Due to the persistent expansion of superficial capillaries on the skin, multiple telangiectasia - spider veins - appear. General symptoms return: fatigue, nausea.
- The period of necrotic changes. Blisters with serous contents appear in the layers of the dermis or erosions and ulcers form. Since the ability to regenerate is significantly reduced, the ulcers do not heal for months. During this period, the clinical picture of radiation sickness develops especially clearly: severe weakness, signs of intoxication, vomiting. The germ cells of the hematopoietic system in the bone marrow are affected, which provokes the development of anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, as well as complications in the form of bleeding and secondary infection.
- The regeneration period is slow, skin healing occurs with the formation of scars.
First aid
- Stop the effect of the traumatic factor.
- Cool the burn area with cold water or ice packs.
- Wet wipes soaked in antiseptic solutions are applied to damaged areas of the skin to prevent secondary infection.
- The victim is anesthetized with narcotic or non-narcotic analgesics, depending on the severity of the pain syndrome.
- In severe cases - emergency hospitalization in a specialized medical institution.
Conservative therapy
With 3-4 degrees of burn severity - inpatient treatment, the tasks of which include:
- Replenishment of plasma and protein loss - transfusion of plasma, blood products, albumin solution.
- Bringing hemodynamic parameters back to normal - infusion of Poliglyukin, Reopoliglyukin solutions.
- Maintaining the functioning of the cardiovascular system - cardiac glycosides, Dopamine.
- Detoxification - infusion of Hemodez, Neocompesan solutions.
- Treatment of radiation sickness - hematopoietic stimulants, anabolic hormones. In especially severe cases, a bone marrow transplant, plasmapheresis or hemosorption procedure are performed.
For 3-4 degree burns, local conservative therapy is not effective due to massive necrotization of the skin and the development of toxemia.
It is believed that only complete removal of all dead tissue followed by plastic surgery of the resulting defect will lead the patient to recovery and relieve him of the problems associated with long-term non-healing wounds and the risk of their degeneration into malignant tumors.
Surgical methods
The nature of the surgical intervention is determined by the time that has passed from the moment of receiving the radiation burn, the location of the injury and the severity of the patient’s condition.
The following types of operations have been developed:
- Necrotomy is a dissection of a dense layer of necrotic tissue, which compresses the underlying tissue, leading to poor circulation.
- Necrectomy - excision and removal of necrotic areas of burned skin to viable tissue.
- Dermatoplasty is the closing of a skin defect either with one’s own or a donor graft.
How to treat skin burns after radiation therapy
On the Internet you can find many reviews of people who complain of radiation burns that occur in a variety of places - on the face, nose, larynx, throat, even the esophagus.
The point is not even how unaesthetic some options look in the photo, because such diversity speaks primarily about how vulnerable the human body can be when it comes to radiotherapy.
Getting a burn is much easier than healing it. Let's find out what causes such disappointing statistics.
Although many cancer patients prefer radiation therapy, this does not say anything about its safety level. Moreover, it is known that radiation rays can affect not only cancer cells, but also healthy cells, and modern medicine can hardly resist this phenomenon.
Accordingly, the main reasons for the consequences are as follows:
- equipment that does not provide safety guarantees;
- imperfection of medical techniques, and, as a consequence, the inability of doctors to act exclusively on cancer cells.
An equally important problem in the treatment of burns is what was said earlier - they do not appear immediately. Months, even years may pass after therapy until at one point suspicious symptoms arise that cannot be attributed to anything.
There are no special preventive measures that could completely eliminate the possibility of radiation burns, but some methods can reduce the risks.
It is recommended to regularly lubricate the irradiated areas with a special ointment that accelerates the regeneration process. It is recommended to apply the ointment not immediately before the procedure, but some time before going to bed.
Treatment of burns after medical exposure is usually quite complex. Radiation burns occur in those people who are trying to get rid of cancer while feeling very poorly. Therefore, doctors try to stabilize their condition and help the body cope with skin problems on its own. The patient is prescribed:
- strict diet;
- drinking plenty of water;
- course of special ointments.
Burns after radiation therapy disappear very quickly when using effective balms or gels containing sea buckthorn oil or aloe vera. They reduce itching, burning, and help the disappearance of any redness.
The average person will not be able to distinguish mild damage to areas of the skin after irradiation from deep radiation anomalies of internal organs, so if you have even minor symptoms, you must definitely consult a specialist.
In both cases, the skin becomes red, pain appears, a stronger burning sensation, and over time, itching.
But burns after radiation therapy do not appear immediately and always in several places; this etymology is their main difference from thermal injuries. It has been observed that the skin reacts to irradiation differently.
If you are severely sunburned, you will most likely get a severe burn after exposure to even low levels of radiation.
The patient's condition will worsen significantly if he underwent chemotherapy before radioactive therapy. Such complications are natural, so do not panic when they appear.
Remember, burns after radiation therapy should be perceived as a side complication; it will certainly go away over time if you carefully care for the affected areas of the skin.
Unfortunately, in the modern world, radiotherapy is becoming increasingly widespread, as a result of which the patient may develop radiation burns.
This is a skin lesion, which, as with sun damage, directly depends on the strength and duration of exposure to ion irradiation. There are three types of radiation that cause the most damage to the skin: neutron, x-rays and gamma rays.
They have a high penetrating ability; it is very difficult to protect the body from their influence.
Burns following radiation therapy have varying rates of symptom onset. While the results of prolonged exposure to the sun are visible almost immediately, it takes time for radiation burns to appear.
However, there is something in common between them - people with highly sensitive skin (we are talking about those who quickly burn under the sun) have a greater risk of being injured.
Radiation burns usually appear in several places on the skin.
Radiation exposure is difficult for patients with immunodeficiency and diabetes mellitus.
There are four degrees of severity:
- A mild degree occurs with exposure to no more than 1200 rad. Symptoms become apparent after a few weeks and their severity is insignificant. If the injury is mild, burns after radiation therapy do not require treatment.
- The average degree occurs when exposed to radiation in a dose of up to 2000 rad. It occurs secretly and is characterized by swelling and redness.
- Severe is manifested by the formation of ulcers and open wounds. Dead skin areas appear that are not restored, the latent period is short.
- The fatal degree is characterized by complete damage to the skin, muscles and even bones, in the most critical cases - charring.
Source: //mschmvd42.ru/zabolevaniya-kozhi/luchevye-ozhogi-prichiny-vidy-opasnogo-oblucheniya-stepeni-simptomy-pervaya-pomoshh-i-lechenie.html
Why does it happen?
Burns after radiation therapy differ from normal sun exposure to the skin. The reason for their development is the long-term use of radioactive rays from the outside. The contact method of treatment is used not only for skin cancer, but also for tumors of internal organs. In this case, the rays pass through the integument, subcutaneous tissue and all other structures that separate it from the malignant focus. As a result, there is an effect not only on atypical cells, but also on normal ones.
Burn complications occur when gamma radiation, X-rays and neutron rays are used. Passing through the patient's skin, they destroy the tissues with which they come into contact. This is manifested by the development of a protracted inflammatory process. Alpha radiation is safe for the skin; it can only damage mucous membranes. Beta rays can penetrate up to 2 cm into the skin and have a detrimental effect on healthy cells.
Degrees and periods
There are 4 degrees of severity of radiation burns:
- Grade 1 severity occurs when exposed to low doses of radiation and becomes apparent after 10-14 days. These are reddened areas of the skin, sometimes with the effect of peeling of its upper layers.
- Grade 2 appears 5-10 days after the body has experienced moderate exposure. These lesions result in large areas of redness with blistering, itching and pain.
- Stage 3 appears within 3-6 days after irradiation. Symptoms of this degree are slowly healing ulcers, swelling of the skin, erosions, blisters, and extensive necrotic areas.
- 4th degree, radiation burn - a dangerous injury. Immediately after exposure to rays on the skin, severe damage to the epidermis, muscle tissue, discharge mixed with pus occurs, the body is covered with ulcers and areas of necrosis.
The development of radiation injury occurs in three periods:
- period of primary reaction;
- latent period;
- necrotic changes.
The primary reaction, the first stage, occurs immediately after exposure to radiation. The first few hours pass. Slight swelling, redness, pain, and burning appear in the area of damaged tissue. The victim may immediately feel nausea, headache, and malaise.
The latent clinical period occurs after the signs of the primary reaction to the burn have smoothed out. A feature of this stage is the almost complete absence of any symptoms, as if the lesion had receded. Visible well-being can be observed from the first few hours to three weeks, depending on the source of radiation.
Necrotic changes are manifested by pain, severe redness, swelling and the appearance of seals on the skin. In some cases, the deep layers of the skin are damaged, hair falls out, large blisters and erosions appear. Necrotic areas are poorly restored and renewed, often become wet, oozing serous fluid, and periodically fester.
Throughout the entire period of the disease, the affected person experiences signs of damage: weakness, nausea. With severe burns, anemia, superficial and internal bleeding, and infection of the affected areas often occur.
We suggest you read: How to treat contact dermatitis on the hands of an adult
Radiation skin lesions come in four degrees of severity:
- 1st degree. Burns appear approximately two weeks after a small dose of radiation and are the least dangerous. Damage from this degree is insignificant and is expressed in the form of slight redness, the effect of hair removal and exfoliation of the upper layers of the skin.
- 2nd degree. Symptoms of such a burn appear in less than 2 weeks after exposure to moderate doses of radiation. This degree may be characterized by the appearance of blisters, extensive redness, secondary erythema, and in some cases accompanied by pain.
- 3rd degree. The onset of symptoms occurs from 3 to 6 days and is accompanied by the appearance of severely healing ulcers, erosions, swelling of the skin and blisters, followed by necrosis.
- 4th degree. This type of radiation burn is considered the most severe and dangerous. They appear almost immediately after a negative impact on the skin and is expressed by damage to the upper layer of the skin, muscles, the occurrence of ulcers and necrotic processes.
From the second to the fourth degree, in addition to the above symptoms, fever, regional lymphadenitis and leukocytosis may also appear.
After ultraviolet burns, complete healing occurs within 7–14 days, even in the absence of treatment. After 1 - 1.5 months, areas of hypopigmentation completely disappear.
Note! Recovery from burns associated with ionizing injury can take anywhere from one week to four months. At the same time, delayed consequences in the form of malignant skin tumors can develop over the next 10–15 years or more.
The essence of pathology
Radiation burns are injuries caused by side effects of radiation therapy. Ionizing radiation is used in the treatment of cancer. An increased dose of radiation provokes the development of injury.
Manifestations
A burn from radiation therapy differs from a thermal burn in the late onset of symptoms. They are divided according to the degree of injury.
Table. Characteristics of radiation burns depending on the degree of damage.
| Degrees | Symptoms |
| 1st degree Redness of the affected area | Appear in the second week of treatment. Redness, peeling, swelling, and sometimes changes in skin pigmentation are observed. The patient may complain of itching and burning in the injured area. |
| 2nd degree Bubbles can merge with each other | Blisters form on the skin, which sometimes merge with each other. The victim complains of nausea, weakness, dizziness, and pain at the burn site. |
| 3rd degree Ulceration | They begin by the middle of the first week of treatment. Accompanied by the appearance of edema, blisters with bloody contents, and the formation of difficult-to-heal ulcers. The subcutaneous layer is destroyed, which can lead to vein thrombosis. The victim develops a fever and skin sensitivity decreases. |
| 4th degree Tissue necrosis | Extremely severe degree of injury without a latent period. All the above symptoms are present. The skin at the burn site becomes dark, almost black. Nerves, ligaments, muscle and bone tissue die. Characterized by acute pain. |
Important! The extent of damage largely depends on the patient's skin type. If a person quickly burns under the sun's rays, then there is a high probability of getting a burn even after low-intensity irradiation.
First aid
Radiation injuries are dangerous due to delayed complications. Their severity depends on literacy and speed of provision of first aid. If redness occurs on the body 15-20 minutes after irradiation, you need to call a doctor at home. Such early local manifestations indicate absorption of a high dose of ionizing radiation by the body.
As first aid, apply a sterile or antiseptic bandage. You can also wash the exposed skin with plain or soapy water. Then you should go to the doctor.
First aid for radiation burns:
- cloth wipes soaked in a solution of hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine are applied to the affected areas;
- within 10-12 hours after radiation injury, the affected areas are washed with a soap solution;
- for complaints of pain, non-narcotic analgesics are given - Naproxen, Ibuklin.
After emergency assistance is provided, a doctor is called or sent to the hospital. To prevent purulent complications, the victim is prescribed antibiotics and drugs to cleanse the blood of radionuclides.
Surgical manipulations for this pathological condition can be prescribed for deep burns that affect the muscle layers.
If the wound is severely infected, antibacterial treatment is first carried out, and only then surgery is started.
The wound area is thoroughly cleaned of dead tissue. This all happens under general anesthesia. This type of surgery is called necrectomy.
Subsequently, the operator transplants a graft taken from another area of the patient's skin.
If the patient experiences redness or burning at the site of irradiation, it is necessary to contact a specialist, since burns may not appear immediately.
It is important to be able to connect radiation therapy and changes in the skin, since burns do not occur immediately after the treatment procedure, but after some time. Also, lesions on the integument are concentrated not in one place, but in different ones, which must be differentiated from other skin diseases. If the patient experiences redness, burning, ulcerative changes, or erosions in the area affected by the beam, he should immediately go to the hospital.
Affected skin must be protected from environmental influences. All procedures must be carried out with sterile gloves to avoid introducing infection to the burn site. Using clean or sterile dressing material, all affected surfaces are isolated from external irritants. After applying the bandages, it is necessary to take the patient to a doctor for further treatment of burn wounds.
Providing first aid to a person with radiation burns must be done as soon as possible. Apply wipes soaked in a disinfectant solution to the affected area. The surface of the skin must be washed with soapy water for several hours. Afterwards, you need to lubricate the damage with baby ointment.
Severe radiation burns require emergency medical care in a clinic rather than at home. First medical aid consists of qualified treatment of wounds and the administration of painkillers; drugs are prescribed to improve the regeneration of affected tissues.
Treatment of radiation dermatitis
Tactics for radiation burns include first aid measures and further therapy. Treatment is aimed at improving trophic processes in the skin, removing necrotic masses, and stimulating healing.
First aid in case of defeat
Persons exposed to ionizing radiation must undergo decontamination within the first 6–10 hours. Partial sanitization involves washing exposed areas of the body with soap and water; complete sanitization is carried out by removing clothing and removing radioactive dust from it, and taking a shower. First aid for radiation injuries includes the administration of painkillers and antitetanus serum. Burn surfaces are covered with an aseptic bandage.
Conservative therapy
Qualified medical care is provided in a hospital. In the reactive period, acute radiation dermatitis requires the use of the following medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Local anesthetics (novocaine blockades).
- Antiseptics and antibiotics.
- Corticosteroids.
Ointment dressings are applied to acute erythema, the blisters are punctured under sterile conditions, and the ulcers are treated with regenerating agents. Chronic lesions need emollient creams, keratolytics, and vitamins. At the same time, radiation sickness treatment is carried out.
Surgical correction
To remove dead areas, delayed necrectomy is used - economical excision within healthy tissue. The resulting defects are closed using plastic methods. In cases of severe radiation sickness, bone marrow transplantation is considered.
Therapeutic tactics for radiation dermatitis are determined by the stage of their development and severity, and consist of conservative and surgical methods.
Under the influence of ionizing radiation, radiation burns form on the skin. Outwardly, they have some similarities with thermal ones, but are characterized by a three-phase course and are combined with signs of radiation sickness. After first aid, skin lesions require conservative and surgical correction.
Further treatment of radiation burns
In the hospital, a patient affected by radiation energy receives painkillers, antiseptic drugs, and protective bandages are applied to the damaged surface. If the lesions are grade 1 or 2, local anesthesia is administered.
If the patient is in critical condition, antishock therapy is administered. Cardiac activity and blood pressure are monitored. If necessary, the patient is operated on: necrotic formations at the burn sites are removed.
The main treatment consists of taking antibacterial drugs, undergoing a course of infrared radiation to relieve the acute form of the disease, accelerate the regenerative functions of tissues and prevent the proliferation of microbes in the affected area. Anti-burn medications (solutions, balms, ointments) are prescribed. You need to introduce more healthy foods into your diet, eliminate salt, and drink more water. Folk remedies are strictly prohibited!
Treatment
In most cases, the diagnosis is made after a visual examination and review of the patient's medical history. To exclude damage to internal organs, the patient may be prescribed an ultrasound, ECG, MRI.
For mild to moderate burns, drug therapy is recommended. Severe damage to the skin requires surgical intervention.
Therapeutic method
If radiotherapy has resulted in burns, the patient should adhere to a dietary diet. Eliminate fatty, spicy foods from your diet, limit your intake of sugar and salt. It is important to maintain a drinking regime, including at least 2 liters of water per day. Rosehip infusion, linden tea, and sea buckthorn decoction are useful as additional drinks.
Treatment of the skin should be carried out 2-3 times a day, using wound-healing aerosols, ointments and creams, for example:
- Panthenol;
- balm Rescuer;
- Olazol;
- Bepanten.
Therapy depends on the depth of tissue damage. If there are blisters, severe swelling and redness on the body, the sore area is washed with peroxide and dried . Then the skin is lubricated with wound-healing ointment. A sterile bandage is applied on top.
If an infection has penetrated into the lesion and suppuration has begun, antibiotics are prescribed. The duration of the course and dosage are determined by the doctor. To eliminate the infection, Levomekol, Vishnevsky's liniment, Tetracycline and Erythromycin ointments are usually used. To relieve swelling, antihistamines Diazolin and Suprastin help. You can soothe the burning sensation and pain with analgesics.
Operation
With extensive lesions and deep tissue necrosis, the patient is in critical condition. In such cases, antishock therapy is used with mandatory monitoring of blood pressure and cardiac activity.
For medical reasons, the patient undergoes surgery. Under general anesthesia, the affected tissue is excised and healthy skin taken from another part of the body is transplanted into this place.
Possible complications
Deep radioactive burns often cause complications. They are divided into 2 groups:
- Local – pathological changes in the affected areas. Non-healing ulcers, fistulas, and abscesses appear on the skin.
- General – dysfunction of vital systems. Changes occur in the functioning of the hematopoietic, cardiovascular, nervous, immune and other systems.
The mildest complications include radiation hangover, which is manifested by loss of appetite, decreased blood pressure, and emotional lability. Under the influence of radiation, neurological disorders, insomnia, and baldness occur.
The most dangerous complications occur with radiation sickness. Its symptoms depend on the total dose of radiation absorbed by the skin. Late consequences include:
- aplastic anemia - inhibition of the functions of the hematopoietic system: the synthesis of red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets by the bone marrow stops;
- Radiation cataract – clouding of the lens caused by radiation;
- pneumosclerosis - the formation of connective tissue adhesions in the lung tissue;
- radiation proctitis – inflammation of the rectum provoked by high doses of radiation;
- leukemia is a malignant blood pathology in which the bone marrow begins to produce immature leukocyte cells.
Complications can be caused not only by the radiation burn, but by the radiation therapy itself. After a burn of this type, a person may feel a deterioration in their general condition, and the most dangerous consequences are infection of the injured areas and possible bleeding. If severe damage has been sustained, the condition of the entire human body deteriorates significantly, and the greatest amount of damage goes to the organ that was closest to the site of irradiation.
You should not self-medicate. As soon as you notice similar symptoms, contact a specialist. If the therapist makes the correct diagnosis and prescribes effective treatment, the recovery period will be much shorter than with self-medication, and the risk of complications will be significantly reduced.
In the development of radiation burns, there are 4 degrees of severity, which determine the area and depth of tissue damage:
The degree of primary hyperemia, latent for 2 weeks or more after irradiation, is further manifested by redness, slight swelling, itching, peeling, pigmentation and baldness of the skin in the affected area. The mildest development of the lesion without severe consequences and complex treatment.
- The average severity of the lesion occurs latently for up to 14 days or less, then severe hyperemia, swelling of the irradiated area, blisters on reddened skin, burning, and pain appear. The patient's general condition worsens.
- Severe degree of burn development, signs of which appear no later than 6 days after exposure to radiation. Not only the skin can be damaged, but also the subcutaneous fat with signs of deep swelling, large blisters, erosions, non-healing ulcers and tissue necrosis. Intoxication is pronounced.
- A very severe degree of damage without a latent period; symptoms appear after exposure to radiation. At the same time, not only the skin is damaged by ulcers and deep tissue death, but also muscles, bones, tendons, nerve endings, and sensitivity is reduced.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to cauterize papillomas with hydrogen peroxide?
In severe burns, the temperature rises, the lymph nodes adjacent to the affected area become inflamed, and leukocytosis is detected in a blood test. In degree 2, blisters may open, dry out, and heal without scarring. Third degree radiation burns must be treated.
There are risk factors for the development of negative consequences after radiation burns:
- 3, 4 degrees of severity of damage.
- The affected area is at least 30%.
- Poor quality treatment.
- Diabetes.
- Children and old age.
- Hypersensitivity to antibacterial drugs necessary for treatment.
- Resistance of microorganisms that infected a burn wound to antibacterial drugs.
- Rejection of grafted skin.
The presence of at least one factor can provoke the development of major complications:
- burn wound infection;
- bleeding.
To prevent tetanus, it is necessary to administer antitetanus serum. In the future, the occurrence of trophic ulcers and the development of skin cancer at the site of the healed burn is possible.
- radiation reaction: dysfunction of the nervous, cardiovascular, endocrine systems;
- atrophic, hypertrophic, chronic radiation dermatitis;
- functional disorders of the lungs and bronchi;
- sclerotic processes in the myocardium, lungs, liver, kidneys and other organs;
- radiation pericarditis (heart damage);
- damage to the walls, intestinal mucous membranes, erosion;
- functional kidney failure;
- radiation cystitis;
- radiation lymphostasis;
- radiation tumors.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent damage in areas of increased radio radiation or in areas of high solar activity, it is recommended to use:
- sunscreens with photo filters;
- personal protective equipment for the face and open areas of the body;
- adoption of radioprotective agents;
- systematic medical examinations, including a hemogram.
Doctors make a prognosis for the treatment of received radiation burns depending on the area, depth of the burned area, the condition of the body, general health (concomitant diseases, complications, finger injuries), as well as the dose of radiation received and the period of damaging effect. If a radiation burn victim survives the first 3-3.5 months, he has a high chance of recovery and returning to normal life.
The article has been verified by the editors
Causes
Radiation burns are more common in people with weakened immune systems or sensitive skin. The radiation type of radiation, in this case, provokes special susceptibility and subsequent injuries. Among other things, active isotopes or elements used in the operation of nuclear power plants (rare) can cause such damage.
Trauma of this type is also typical for patients undergoing radiation therapy (prescribed for malignant neoplasms and other diseases). Depending on the degree of exposure and the individual characteristics of the body, various symptoms may appear.
Classification
Based on the depth of damage, there are 4 degrees of burns caused by radiation:
- The first occurs when the influence of hazardous particles is insignificant. It is characterized by slight redness of the epidermis, dryness and flaking. Symptoms usually become noticeable within a week after exposure.
- The second degree is characterized by the formation of blisters, burning, redness of the skin and swelling. External signs are observed 5 days after the lesion.
- The third degree develops if powerful radiation has occurred. After a few days, non-healing ulcers and small blisters appear on the body, and the dead epidermis peels off. The person is in severe pain.
- The fourth degree is noticeable immediately after injury. This is a dangerous condition that provokes purulent wounds, large areas of necrosis, bleeding, and muscle atrophy.
Radiation damage develops gradually. Doctors distinguish 3 stages in the formation of pathology.
OSTIOLucem traction orthopedic pillow is a unique product for women’s health
- After radiation exposure, a primary reaction occurs. The person feels a slight burning sensation, the affected areas turn slightly red and swell. If the radiation dose is high, you may experience nausea and dizziness. A few hours after the injury, the reaction stops.
- The hidden period begins. At this time, all symptoms of illness disappear. The deceptive state can last from a couple of hours to 2 weeks. The duration depends on the amount of radiation received.
- When the latent period ends, necrotic changes in tissues begin. Signs of radiation damage become more active, blisters and ulcers form, the skin swells, thickens and hurts.
Recovery from injury is slow. Swelling gradually decreases, pain subsides, and wounds heal. The process sometimes drags on for years.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms vary for each severity level.
- With a mild degree of severity, a slight burning sensation, itching occurs, the skin begins to peel off, mild swelling, pigment spots occur, and possible baldness of the injured area.
- Moderate severity is characterized by the appearance of blisters, nausea, headache, secondary erythema, weakness and lethargy.
- Severe radiation burns combine the appearance of swelling, painful erythema, erosions and ulcers, which are accompanied by fever and high leukocytosis.
The most serious degree, which is usually called extremely severe, combines many of the symptoms listed above and is also famous for the manifestation of necrosis of the upper layer of skin and muscles.
The main symptoms of an ultraviolet or radiation burn depend on its severity. So, it is characterized by the following signs:
- Redness;
- The appearance of blisters;
- Increased body temperature;
- Local soreness, itching.
After 5–14 days, the local reaction will begin to subside. First, the formation of scales on the epithelium and their gradual exfoliation will be observed. In place of the blisters, minor scars may form, which are then replaced by normal skin of a lighter tone.
Note! In the absence of infection, radiation burns go away completely without a trace, unlike thermal burns, the third and fourth degrees of which, as a rule, lead to the formation of rough scars.
Minor burns (first degree) are accompanied by itching and redness, sometimes peeling, swelling and slight pigmentation are observed. In the second degree, blisters, headache, nausea and vomiting, and acute pain in the damaged area appear.
More serious categories of burns are characterized by bloody blisters, ulcerations, necrosis, fever, and leukocytosis. Over time, scar tissue forms, after which it can fester and, in the absence of adequate treatment, turn into cancer. There is a risk of developing thrombosis of the venous system.
Clinical picture
Radiation burns go through several stages of development - primary reaction, latent period, necrotic changes. Their severity primarily depends on the dose received. A few minutes after irradiation, early skin manifestations occur:
- Erythema.
- Swelling.
- Pain.
Erythematous changes have the character of a pale pink itchy rash, which disappears without a trace after 1–3 days, and in severe lesions takes on a hemorrhagic character. At the same time, systemic disorders occur - weakness, headaches, nausea, vomiting (sometimes). Next comes a latent period without any clinical manifestations lasting up to 3 weeks.
Against the background of imaginary well-being, a phase of acute inflammation with secondary erythema begins. The skin is hyperemic, covered with telangiectasia, blisters with serous fluid. After opening the latter, painful bleeding erosions form. Deep damage is characterized by the formation of long-term non-healing ulcerative defects with areas of necrosis. General manifestations of radiation sickness progress.
The period of necrotic changes lasts up to several months. The clinical course of radiation burns is determined by the severity of the injury:
- Mild - the primary reaction is weak, the latent period is prolonged, secondary erythema is not accompanied by ulcers and necrosis.
- Medium – early changes are clearly expressed, the latent phase is shorter than 2 weeks, single bubbles form.
- Severe - early erythema occurs shortly after the lesion, the latent period is no more than 6 days, secondary changes are characterized by erosions and ulcers.
- Extremely severe - the primary reaction occurs quickly, the latent phase is short, necrotic changes are profound.
Recovery begins with the disappearance of erythema; erosions and ulcers heal very slowly. Local pigmentation may form at the site of the affected lesions. Other long-term effects include dryness, cracks, skin atrophy, hyperkeratosis, and hair loss. They correspond to the chronicity of radiation dermatitis and are often complemented by malignant processes.
Ionizing radiation burns are characterized by a three-phase inflammatory response, the severity of which is determined by the absorbed dose.
Causes of radiation burns
Burns appear after long-term radiation therapy, which is recommended to get rid of pathological tumors. The task of the doctor conducting the treatment is to minimize the risk by correctly calculating the time of the procedure and the power of the dangerous effect.
Radiation burns can sometimes occur when your skin comes into contact with toxic fallout during a nuclear power plant accident or when interacting with radioactive waste. In such situations, skin damage is often accompanied by life-threatening radiation sickness and damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes.
The most common and safest burns occur under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The cause is prolonged exposure to the sun and visiting a solarium. Such injuries rarely cause serious complications. Increases the risk of negative consequences from weakened immunity, skin hypersensitivity, and endocrine diseases.
A radiation burn is a skin response to high doses of radiation. There are two types of radiation that cause injury:
- Light. Damage is caused by solar rays, a radiation flux that is represented by a wide spectrum of electromagnetic waves. UV radiation in the wave range from 100 nm to 280 nm has a pronounced traumatic effect. In 84% of cases, sun rays cause shallow damage of 1st and 2nd degrees.
- Ionizing. The most dangerous is considered to be short-wave electromagnetic radiation - X-rays or gamma radiation. Natural sources of radioactive flux are thermonuclear reactions in the Sun, cosmic rays, etc.
The greatest health hazard is posed by ionizing radiation, as radioactive particles penetrate the skin into the internal organs. Burns are fraught with radiation sickness and skin atrophy. Causes of injury include:
- radiotherapy;
- tanning in a solarium;
- sunbathing;
- X-ray examinations;
- work with particle accelerators, etc.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Zinc ointment for burns: can it be applied?
Structural changes in the skin appear with high doses of radiation that the immune system is unable to withstand.
In 90% of cases, such injuries occur in people undergoing radiation therapy. Treatment is carried out with beta, gamma, neutron, and x-ray radiation. Not only pathological tissues, but also healthy tissues are affected by irradiation.
How to cure a radiation burn? Radiation burns: first aid
A radiation burn is a skin response to high doses of radiation. There are two types of radiation that cause injury:
- Light. Damage is caused by solar rays, a radiation flux that is represented by a wide spectrum of electromagnetic waves. UV radiation in the wave range from 100 nm to 280 nm has a pronounced traumatic effect. In 84% of cases, sun rays cause shallow damage of 1st and 2nd degrees.
- Ionizing. The most dangerous is considered to be short-wave electromagnetic radiation - X-rays or gamma radiation. Natural sources of radioactive flux are thermonuclear reactions in the Sun, cosmic rays, etc.
The greatest health hazard is posed by ionizing radiation, as radioactive particles penetrate the skin into the internal organs. Burns are fraught with radiation sickness and skin atrophy. Causes of injury include:
- radiotherapy;
- tanning in a solarium;
- sunbathing;
- X-ray examinations;
- work with particle accelerators, etc.
Structural changes in the skin appear with high doses of radiation that the immune system is unable to withstand.
In 90% of cases, such injuries occur in people undergoing radiation therapy. Treatment is carried out with beta, gamma, neutron, and x-ray radiation. Not only pathological tissues, but also healthy tissues are affected by irradiation.
Degrees of damage from radiation burns
Radiation burns cause various complications. Their severity depends on:
- exposure time;
- type of radiation;
- radiation energy flux density;
- affected areas;
- localization of the burn.
In dermatology, there are 4 degrees of severity of radiation burns:
- The first (erythematous dermatitis). The injury appears after exposure to a small dose of radiation - up to 1200 rads. Signs of acute inflammation appear after 14-20 days. Pain, pigmentation, swelling and burning appear. Mild burns disappear completely within 2.5-3 weeks.
- Second (bullous dermatitis). Local manifestations of radiation injury occur a week after exposure of the skin to radiation at a dose of up to 2000 rad. Pale blisters form on the reddened areas. Necrosis of the epidermis and underlying tissues occurs. Wounds do not heal for a long time; scars and pigment spots appear in place of the blisters.
- Third (purulent dermatitis). The burn appears 2-3 hours after irradiation with a dose of 2000 rad. Redness and severe swelling appear in the affected areas. After 7-8 days, skin rejection occurs with signs of purulent inflammation. The skin does not heal for more than 2 months, trophic ulcers and fistulas appear.
- Fourth (gangrenous dermatitis). Wounds appear an hour after exposure to damaging factors. The affected areas quickly swell and ulcerate. Due to ionization, blood vessels become brittle and bleeding occurs. The tissues affected by the burn begin to be torn away and rot. Local symptoms are combined with manifestations of radiation sickness.
For deep injuries, patients are treated in the hospital with detoxification agents. They remove radionuclides, which reduces the risk of cancer.
Periods of the disease and characteristic symptoms
When exposed to relatively low doses of radiation, burns do not appear immediately. Dermatologists distinguish 4 periods of the disease, which are manifested by different symptoms:
- First. Early symptoms appear several hours/days after exposure. A radiation burn is manifested by redness of the skin. Sometimes serous blisters appear. Patients complain of headache, nausea, tachycardia, and fatigue. With deep radiation burns, symptoms persist for at least 2 days.
- Second. Clinical manifestations of radiation injury subside. Depending on how deep the burn is, this period lasts from several hours to 15 days.
- Third. There is acute inflammation of the skin. They become marbled, after which they turn red again. The pain intensifies and severe swelling occurs. With third degree burns, blisters form and quickly burst. The most likely complications include the possible occurrence of bleeding due to erosions and ulcers. The period of acute inflammation lasts from 1 week to 1.5-2 months.
- Fourth. Recovery is slow. First, secondary redness and swelling disappear. Painful sensations decrease, erosions and ulcers gradually heal. At the site of a healed burn, pigment spots and scars remain.
In patients with severe injuries, the wounds do not heal for several years. In 97% of them, atrophic changes occur in the epidermis. The skin becomes thinner, cracks and secondary trophic ulcers form on it.
First aid
Radiation injuries are dangerous due to delayed complications. Their severity depends on literacy and speed of provision of first aid. If redness occurs on the body 15-20 minutes after irradiation, you need to call a doctor at home. Such early local manifestations indicate absorption of a high dose of ionizing radiation by the body.
As first aid, apply a sterile or antiseptic bandage. You can also wash the exposed skin with plain or soapy water. Then you should go to the doctor.
First aid for radiation burns:
- cloth wipes soaked in a solution of hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine are applied to the affected areas;
- within 10-12 hours after radiation injury, the affected areas are washed with a soap solution;
- for complaints of pain, non-narcotic analgesics are given - Naproxen, Ibuklin.
After emergency assistance is provided, a doctor is called or sent to the hospital. To prevent purulent complications, the victim is prescribed antibiotics and drugs to cleanse the blood of radionuclides.
Further therapy
Radiation burns are treated in a hospital or at home. Features of therapy are determined by the depth and area of the lesions. To speed up the regeneration of affected areas, a high-calorie diet is prescribed. Particular attention is paid to the drinking regime. Drinking plenty of water speeds up the elimination of toxic substances from the body.
For superficial damage, local therapy is limited.
Bandages soaked in antiseptics are applied to the affected areas. When weeping, applications of a 10% dimexide solution are used. To speed up scarring, bandages with troxevasin and levosin are used.
Treatment of burns after radiation therapy is carried out with drugs from the following groups:
- antihistamines (Diphenhydramine, Suprastin) – relieve inflammatory reactions and swelling;
- painkillers (Analgin, Ketanov) - reduce pain;
- antibacterial (Levomycetin ointment, Baneocin) – destroy bacteria, preventing purulent inflammation of wounds;
- corticosteroids (Elocom, Lorinden) – relieve acute inflammation, itching and irritation;
- wound healing (D-Panthenol, Sudocrem) - soften the affected areas, stimulate the healing of the epidermis.
For deep injuries, in addition to local therapy, surgical care is required:
- necrotomy - dissection of charred skin down to viable layers;
- necrectomy - removal of dead skin, gangrenous areas;
- skin grafting – closing wound defects with artificial or own skin.
For radiation sickness, restorative and immunostimulating drugs are prescribed. The treatment regimen depends on the patient's condition and the extent of the damage.
Dangerous complications
Deep radioactive burns often cause complications. They are divided into 2 groups:
- Local – pathological changes in the affected areas. Non-healing ulcers, fistulas, and abscesses appear on the skin.
- General – dysfunction of vital systems. Changes occur in the functioning of the hematopoietic, cardiovascular, nervous, immune and other systems.
The mildest complications include radiation hangover, which is manifested by loss of appetite, decreased blood pressure, and emotional lability. Under the influence of radiation, neurological disorders, insomnia, and baldness occur.
The most dangerous complications occur with radiation sickness. Its symptoms depend on the total dose of radiation absorbed by the skin. Late consequences include:
- aplastic anemia - inhibition of the functions of the hematopoietic system: the synthesis of red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets by the bone marrow stops;
- Radiation cataract – clouding of the lens caused by radiation;
- pneumosclerosis - the formation of connective tissue adhesions in the lung tissue;
- radiation proctitis – inflammation of the rectum provoked by high doses of radiation;
- leukemia is a malignant blood pathology in which the bone marrow begins to produce immature leukocyte cells.
Some delayed complications are fatal. Radiation doses of more than 1 Gy (100 rad) are often accompanied by pathologies of the bone marrow and gastrointestinal tract.
Grand Central Station in New York
Due to the large amount of granite, the station emits more radiation than is legally permitted at nuclear power plants.
Due to the large amount of granite used in its construction, Grand Central Terminal in New York emits more radiation than is legally allowed for even a nuclear power plant.
Treatment
First and second degree burns do not require medical treatment. Rehabilitation of damaged skin areas occurs independently.
It is also recommended, to speed things up, to adhere to a salt-free, high-calorie diet, to use folk remedies that help accelerate skin regeneration, preferably with aloe and sea buckthorn extracts, as well as additional gels and balms that eliminate not only damage, but also burning, itching, etc. .
The skin of the injured area is rewound with a bandage previously soaked in an antiseptic solution; this method is used to eliminate the inflammatory process.
If an infection gets into the wound, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics and sulfonamides. If the victim has severe pain, then analgesics are prescribed.
The entire period of drug treatment must be accompanied by taking vitamins.
Source: https://GolovaNeBoli.ru/krov/luchevye-ozhogi-pervaya-pomoshh-i-lechenie-travm.html
Diagnosis
The doctor first of all pays attention to the occurrence of erythema, since at some stages it appears immediately and quickly passes. Next, the doctor asks about the symptoms. If radiation burns were caused by therapy, then medical records are collected to determine the radiation power, the frequency of its implementation and the state of health in general.
Such burns are often accompanied by problems with the endocrine and cardiovascular systems. To determine whether violations have arisen in these areas, detailed medical studies and consultations with specialists in this type of activity are carried out.
How to prevent radiation burns
With radiation therapy, it is almost impossible to avoid burn wounds. But following medical recommendations reduces the risk of complications. To prevent radiation injuries, you should:
- avoid hypothermia;
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- avoid damage to the skin;
- stop taking antibiotics that increase radiosensitivity.
Skin tolerance to ionizing radiation decreases when irradiated areas of the body are treated with ointments containing provitamin B5. Therefore, after each radiotherapy session, dermatologists advise using anti-burn ointments and following a high-calorie diet.
Manifestations and possible consequences
If after a radiotherapy session the patient receives a slight burn (not higher than 2nd degree), the following traditional medicine can be used to treat it:
- Sea buckthorn oil has anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. They should soak a sterile napkin and apply it to the burned surface. This manipulation must be repeated every 3 hours. The affected tissues will recover faster, and pain will significantly decrease or go away altogether.
- A mixture made from beeswax and olive oil has a similar effect. These substances should be mixed in a ratio of 1:3 and applied to inflamed tissues 3 times a day.
- You can prevent the appearance of blisters by applying honey or potato pulp to the affected area. Honey, among other things, is an excellent disinfectant.
- You can ensure speedy healing of the burned area, as well as protect it from infection, using a mixture prepared from dry propolis (20 g) and vegetable oil (80 g). These ingredients are combined and placed in a water bath, where they must be infused until the propolis is completely dissolved. The resulting mixture is filtered through a fine strainer. After complete cooling, the ointment is applied to a sterile napkin and applied to the wound. You should be careful with such a medicine: bee products often provoke allergic reactions in people.
In addition to dressings with antiseptic solutions, antibiotics and sulfonamide are prescribed (provided there is normal blood circulation) if the affected area is infected. Swelling is relieved by taking antihistamines (local and general). Additionally, the patient undergoes a course of vitamin therapy. If therapeutic and medicinal treatment does not bring the expected result, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Traditional medicine methods for treating burns after radiotherapy
Preventive measures include the following:
- Radiotherapy should be prescribed on an individual basis. For each patient, the dosage and frequency of isotope radio emission will be determined by the general state of his health.
- In order to protect the eyes from burns before and after radiation therapy, they are instilled with artificial tears: 1-2 drops in each eye. This will minimize the risk of developing photophobia and dry eyes in the future.
- After each course of radiotherapy, the immediate areas of exposure must be treated with wound-healing agents. A similar procedure should be performed before going to bed.
Rate
Radiation treatment for skin burns
Local treatment consists of lubricating the affected areas of the skin with oils - for example, sea buckthorn, peach, apricot, olive, citral, etc. Fish oil can be used to lubricate areas of radiation burns; ointments with vinylin, anesthesin, methyluracil ointment, etc. are used.
General treatment: if infection is suspected or if infection occurs - antibiotics, sulfa drugs; for edema - hormonal and antihistamines; for pain - analgesics; be sure to include vitamins (especially C and group B).
If conservative treatment is ineffective (radiation burns of II-III degree), it is necessary to resort to surgical methods.
Treatment of radiation burns, local, general - section Radiation burns
Prolonged intense exposure to sunlight provokes inflammatory damage to the surface layers of the skin. Within a few hours, pronounced symptoms appear. Ultraviolet radiation causes skin burns in the summer when exposed to the sun for a long time. Excessive exposure to rays from tanning beds can damage your skin at any time of the year. Such burns can be treated quickly and successfully.
The penetrating ability of alpha particles that cause burns is low. They affect the upper layers of the skin and mucous membranes. Beta rays are a little more intense. These rays penetrate very deeply:
X-ray;
- neutron;
- gamma.
The penetrating power of X-rays, neutrons and gamma rays is very high. They damage all organs and tissues. They are difficult to defend against. The causes of this type of injury from ionizing radiation and photon radiation are:
- the use of nuclear weapons during military operations;
- man-made accidents and catastrophes at enterprises using nuclear energy, processing and transporting radioactive materials, nuclear research facilities;
- use of medical devices for examination and radiation therapy;
- receiving local exposure from radioactive fallout due to stellar explosions and solar flares.
Small doses of radiation on working equipment are used in medical institutions without harming the patient’s health. Currently, local treatment of cancer with radiation is very effective. Its doses can be significant.
Radiation affects not only tumor cells, but also healthy tissue located nearby. It damages them. Burns from radiation therapy take time to appear and may take months to be visualized. They often develop severely, with complications, in particular:
Radiation of the mammary glands or chest organs causes lung damage. A scar forms at the site of the lesion;
- the use of radiotherapy for the treatment of tumors of the pelvic organs provokes a disease of the sigmoid colon - radiation sigmoiditis, which develops as ischemic or ulcerative colitis.
Exposure to ionizing and photon radiation depends on the dose, intensity and depth of penetration. Such burns are characterized by slow development and tissue restoration. If up to 10% of the entire surface of the body is affected, it is a burn; if more, it is a burn disease.
Radiation burns (radiation): causes, symptoms, treatment
With prolonged exposure to radiation on the skin, radiation burns occur. This defeat can lead to serious consequences. The danger of the disease is that the symptoms do not appear immediately. Visual symptoms develop over several days, or even weeks. This makes timely diagnosis and treatment difficult.
Classifications of radiation burns
The lesion develops in four periods:
- Primary reaction. Appears within several hours after radiation exposure. Expressed in the form of slight swelling, burning and redness. Possible physiological changes in condition: weakness, headache, nausea;
- After the primary symptoms have subsided, the latent period begins. It is characterized by the absence of any signs of radiation. Depending on the causes of the lesion, this condition lasts from several hours to two to three weeks;
- Necrotic changes characteristic of this period are characterized by severe pain and swelling. Burn blisters and erosions appear. Severe injuries are accompanied by anemia, bleeding, and wound infection. Repeated suppuration is possible;
- The recovery period slows down significantly. It can last for many months and years. Ulcers and erosions do not heal well. An unstable, thin scar layer forms at the sites of healed injuries. Relapses of radiation sickness can occur after several years. Ulcers that do not heal for a long time can transform into malignant formations. This type of cancer cannot be cured.
The severity of burns is also divided into four groups:
- The mild form of the lesion is tolerated satisfactorily by patients. Curable even with weakened immunity;
- Moderate burns. The damage is characterized by swelling and changes in skin color. The initial period is asymptomatic. Complications appear after two weeks. Treatment and rehabilitation take about a month;
- Severe form of damage. Burns in this group are characterized by open wounds and ulcers. Tissues damaged by necrosis are not restored;
- Deadly form. The entire skin, muscles, bones and internal organs are affected. Possible deep charring of the flesh.
Causes
During the life cycle, a person is systematically exposed to radiation. Sources of natural, natural radiation can be considered:
- space;
- 60 radioactive substances that are contained in water, air, and soil.
Common artificial sources include:
- radionuclides that are used by agricultural and light industry;
- medical equipment;
- radiochemical production;
- man-made disasters, use of nuclear weapons, radiation waste and emissions.
Irradiation causes biological changes. Illness is the body's overall response to the volume and strength of energy absorbed. The reasons can be external and internal.
The first arises as a result of environmental contamination with isotopes emitting gamma rays. Every atom of air becomes a source of radiation. The consequence of this process can be both superficial lesions of the epidermis and death of a person.
This radiation negatively affects both the skin and organs. In severe cases, it causes detachment of the epidermis, the formation of ulcers, complete hair loss, and muscle atrophy. This depends on the dose of radiation and the time of exposure.
Radiation injuries can occur as a side effect of cancer therapy. External manifestations are similar to those of sunburn: erythema, itching, small blisters, peeling. The extent of damage depends on the susceptibility of the surface.
Internal radiation is caused by radioactive substances that enter through the air, skin, water and food. Causes pathology of the bronchi and gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms
Signs, similar to the severity of the lesion, vary in degree:
- The mild form is characterized by burning, itching, peeling, slight swelling and pigmentary changes in the skin;
- Symptoms of the second degree are nausea, weakness, headaches, the appearance of erythema and burn blisters. The skin after regeneration is very thin;
- The condition is complicated by fever, severe painful erythema, and the appearance of abscesses under the blisters. Because the lesion causes the subcutaneous layer to die, scarring occurs slowly. Ulcerative relapses are possible. There is a risk of developing vein thrombosis;
- The condition is extremely serious due to deep charring of tissue over a large area.
Diagnostics
During a visual examination, the doctor pays special attention to erythema. Its condition, severity and time of appearance are important. Taking an anamnesis allows you to clarify when the injury occurred, symptoms, causes and circumstances of the injury.
If a burn is a side effect of therapy, then information about the intensity of radiation is taken from the patient's medical record. The consequences may be disturbances in the functioning of the heart and internal secretion organs. To determine pathologies, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed - MRI, ECG, ultrasound. If necessary, other specialists are involved.
Therapeutic method
All measures are aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition. The victim is recommended to use local anesthesia for small localizations. Drugs with morphine and promidol are administered to a patient with severe burns.
The entire affected surface is treated with antiseptic substances. A protective bandage is applied. Infusion therapy is carried out to relieve the effects of shock and to restore fluid and protein levels. Cardiac activity and blood pressure readings are continuously monitored.
After stabilization of the patient's condition, infrared radiation therapy is prescribed. Antibiotics are used at the same time. Goal of treatment: relieve inflammation, prevent infection, remove intoxication.
Be sure to follow a salt-free diet high in calories and drink plenty of fluids.
Medication method
If there are no blisters on the affected surface, the doctor prescribes ointments for treatment (Panthenol, Bepanten, etc.). Antihistamines relieve swelling and itching. Bubbles must be treated with antiseptics. Antibacterial creams are applied under a sterile dressing.
The patient is immediately prescribed antibiotics upon arrival at the medical facility to block possible infections. A tetanus vaccination is required. To prevent intoxication, the patient receives intravenous glucose, vitamins, and calcium gluconate.
To relieve pain from lesions of the mouth and throat, rinsing at least three times a day and painkillers are prescribed. If inflammation of the respiratory tract cannot be avoided, medications containing corticosteroids are prescribed. For pulmonary injuries, inhalations, magnetic therapy and electrophoresis are used.
Operation
Surgical treatment is performed for lesions that affect the deep layers of tissue. Necrotomy is necessary to cleanse the damaged area of dead cells. In the future, skin grafting is possible.
Traditional methods
Homemade recipes for treating burns are allowed for use only if the severity level is not higher than second. That is, there are no open wounds, and the integrity of the damaged area is not compromised. Herbal medicine can cope with injuries and completely restore tissue. This seriously relieves pain and significantly improves the condition:
- Sea buckthorn oil has powerful healing properties. There are many recipes for using it. Most often, a sterile napkin is soaked in it and placed on the burn. If the procedure is repeated every three hours, the pain quickly disappears and regeneration is significantly accelerated;
- If it is not possible to apply a bandage, the frequency of the procedure at the initial stage depends on the ease of absorption. Later, twice a week is enough;
- When treating esophageal cancer, sea buckthorn oil is taken orally. The course involves prophylactic administration during radiation therapy 3 times a day and then the regimen is continued for another three weeks;
- A product made from olive oil and wax has the same valuable qualities. The components mix well and apply to the affected areas. It is recommended to change the compress every two to four hours;
- Honey can serve as a preventative against blistering. In addition, it is an excellent antiseptic;
- Homemade ointment made from propolis and vegetable oil can stimulate regeneration and prevent infection. The ingredients are heated in a water bath and infused until a homogeneous consistency is obtained. After cooling, the product is applied to a napkin and applied to the burn;
- Freshly squeezed plantain juice has strong antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, healing and analgesic properties. They treat the affected surfaces several times a day. The product is well suited for lotions and compresses. Nettle has similar properties.
Disease prevention
In areas of high solar activity or increased radio radiation, it is recommended:
- apply protective creams;
- use personal protective equipment;
- use of radioprotective drugs;
- regular medical examinations;
- passage of the hemogram.
The dose calculation for radiation therapy is carried out separately in each specific case. The use of creams that stimulate regeneration is necessary throughout the entire course.
Complications
Radiation injuries cause:
- failure of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems;
- various types of dermatitis;
- disruption of the respiratory system;
- liver and kidney dysfunction;
- damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa and others.
The most dangerous consequence is the acquisition of injuries that result in malignant changes. Radiation-induced cancer cannot be cured.
Source: https://firetravma.ru/ozhogi/luchevye-ozhogi
What not to do for burns
For any thermal damage to the skin, the victim (and the person who will provide first aid for a burn) should be careful with the affected area, especially if it is extensive and necrotization processes begin. Doctors prohibit:
- puncture blisters;
- apply a plaster, cotton wool, or foreign tissue (except for a bandage) instead of a bandage;
- treat the affected area with oils (only sea buckthorn and St. John's wort are allowed), alcohol-containing liquids, and acid;
- use ice topically;
- comb and constantly feel the damaged area;
- tear off clothing stuck to the burn area.
- Vinilin - instructions for Shostakovsky balm
- Traumatic shock - causes and stages. Algorithm for emergency care for injuries and traumatic shock
- Hydrogen peroxide getting into your eyes: what to do if you get a burn
First aid
Immediately after receiving a burn, a person experiences symptoms of the first degree of damage: mild hyperemia, burning, slight swelling. They pass within a day and can remain ignored, because after that the stage of “imaginary well-being” begins. Doctors argue that first aid for burns caused by radiation therapy should be provided immediately at this moment in order to increase the chances of rapid tissue restoration and to prevent infection. Algorithm of actions:
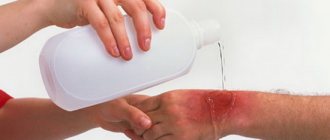
- Rinse the affected area with cool water.
- Soak a gauze bandage in Chlorhexidine solution or use a special antiseptic wipe. If blisters break, replace Chlorhexidine with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- Apply a bandage to the damaged area, securing it loosely to maintain normal blood circulation.
- Give the victim an analgesic if he complains of pain, an antihistamine for severe itching. Be sure to provide drink.
- In persons with mild damage, after first aid for radiation burns has been provided, Panthenol (and other pharmaceutical products based on it), sea buckthorn oil, and baby ointment can be used for further tissue restoration.
- If severe skin damage is observed, the symptoms of which appear after 1-3 days, the patient needs urgent medical attention. After completing the above steps, you need to dial an ambulance number or take the victim to the hospital yourself.