Content
In most cases, the disease occurs after injury or any damage to the integrity of the skin as a result of the development of various types of mycoses, candidiasis, and lichen.
Initially, fungi penetrate into wounds or cracks in the skin and, if favorable conditions exist, begin to multiply in it. Since the microorganisms themselves, the toxins and waste products they secrete, are foreign to the human body, it begins to actively fight them, which can lead to sensitization and, accordingly, allergic reactions in the form of eczema.
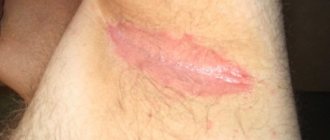
The disease manifests itself by the appearance of wounds around the affected area of skin, round rashes, the color of which ranges from pink to gray, and nodules that constantly cause discomfort to the patient due to severe itching.
Sometimes the nodules can open on their own, in such cases a weeping surface with purulent discharge opens underneath them, but over time, all elements of the rash become covered with small scales or yellow crusts.
Since in each individual case the type and nature of therapy is selected individually, self-medication is unacceptable, it can only aggravate the course of the disease or lead to erysipelas complications. Treatment of mycotic eczema should always be comprehensive, since it is necessary to fight not only the manifestations of allergies, but also the cause of its occurrence - the causative agents of mycoses and candidiasis. For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- Antifungal agents. In mild cases, the use of creams or ointments (Mifungar, Lamisil, Mycoseptin, Exoderil, etc.) is usually sufficient, but common mycotic processes can only be eliminated through systemic therapy with drugs such as Terbinafine, Fluconazole, Itraconazole.
- Antiallergic and antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin, Zyrtec, Erius, Claritin, Diazolin, etc.).
- Sedative herbal preparations (tinctures of motherwort and valerian, Persen).
- avoid contact with household chemicals;
- cover affected areas of the body with clothing;
- minimize the number of stressful situations and nervous strains.
In the presence of endocrine disorders that provoked the development of an allergic reaction, treatment of fungal eczema with corticosteroids in the form of ointments or injections is indicated, but they are not used for exacerbations of mycoses, since hormones provoke rapid growth and mutation of fungi.
No less important than drug therapy is careful attention to your condition. Therefore, patients need to make every effort to avoid further injury to the skin and follow the following recommendations:
It is also necessary to regularly treat the resulting scales and crusts with a solution of boric acid and healing preparations. A speedy recovery is facilitated by baths with the addition of weak solutions of antiseptics, baking soda or herbs (chamomile, string, etc.).
Since mycotic eczema is a variant of allergy, it is extremely important to exclude from everyday life all possible allergens, contact with which can aggravate the course of the disease. Therefore, patients are recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, which involves avoiding chocolate, spices, fatty foods, eggs, citrus fruits, nuts, etc.
- Allergy 325 Allergic stomatitis 1
- Anaphylactic shock 5
- Urticaria 24
- Quincke's edema 2
- Hay fever 13
- Atopic dermatitis 25
Full or partial reproduction of site materials is possible only if there is an active indexed link to the source. All materials presented on the site are for informational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; recommendations should be given by your attending physician during a face-to-face consultation.
Causes of fungal disease
Dermatitis of fungal etiology develops due to excessive fungal activity on the epithelium. Most often the top layer of skin is affected. Provoking factors include:
- hereditary nature of the disease;
- stress, nervous tension, fatigue;
- hormonal imbalance;
- decreased functioning of the immune system;
- disturbances in intestinal function;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- unbalanced diet;
- bad habits.
Infection with a fungus occurs quite simply - fleeting contact with the site of a fungal infection. This can be through touch, through personal hygiene products, clothing, etc. The most common cases of infection is when the fungus gets on the mucous membranes.
There are about 500 different types of fungal microorganisms that can cause mycotic eczema.
The main characteristics, causes and locations of the disease are described in the table:
- mold fungi;
- candidiasis;
- causative agent of trichosporia nodosum;
- ringworm and versicolor;
- pathogens of fungi of nails, feet, head;
- sensitization reaction of the body to stimuli.
- hormonal disbalance;
- medications (antibiotics, immunosuppressants);
- allergic reaction;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- genetic predisposition;
- vitamin deficiency, micronutrient deficiency;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- weakened immune system;
- permanent stress;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
- skin on hands;
- palms;
- places of skin breakdown;
- toes;
- feet;
- folds between fingers;
- skin of the legs.
- violation of the integrity of the skin (cracks, injuries, wounds);
- exposure to one of the types of mycosis;
- proliferation of fungal microorganisms;
- sensitization reaction to a fungal or bacterial infection;
- production of antibodies to foreign microorganisms;
- allergy;
- skin damage;
- symptoms of the disease.
One of the infectious skin diseases that is chronic is called fungal dermatitis. In this case, the inflammatory process, which is characterized by frequent relapses, affects the skin, as well as the scalp. Fungal dermatitis in children can be complicated by an allergic reaction of the body, which can significantly complicate the diagnosis of this disease. The symptoms and treatment features of this disease will be discussed in the article.
Features of the disease
The skin of a healthy person is constantly inhabited by many microorganisms, including fungi. If, under the influence of favorable factors, fungi begin to actively multiply, fungal dermatitis may appear. This disease can be acute or chronic with periods of remission and exacerbation.
Fungal dermatitis is divided into several subtypes, which differ in the depth of penetration of the fungal infection and the nature of the inflammatory foci. So, there are the following forms of the disease:
- keratomycosis is a fungal infection of the surface layers of the epidermis;
- candidiasis is a disease in which a fungal infection affects the mucous membranes;
- dermatomycosis - with this disease, the deeper layers of the epidermis become infected;
- deep mycosis is characterized by damage to subcutaneous tissue by microorganisms.
It is sometimes difficult to distinguish one variety from another from a photo, since mixed forms of the disease are often diagnosed. For example, a combination of mycosis and candidiasis or three or more forms of the disease at once.
Causes
Fungal dermatitis on the skin of a child or adult develops due to excessive activity and increased proliferation of a fungal infection. Usually the upper layer of the skin is affected. Factors that may contribute to the onset of the disease include the following:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Severe fatigue, stress, emotional overstrain;
- Decreased body defenses and immunodeficiency states;
- Dysbacteriosis, disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Long-term antibacterial therapy;
- Poor nutrition, strict diets;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
Primary infection of children with fungus can occur through direct contact with the source of fungal infection, through clothing, hygiene products, and toys. Most often, infection occurs through the mucous membranes.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of the fungus on the skin is characteristic rashes called mycids. In this case, the rash can be of two types:
- pustules are considered primary rashes and appear at the beginning of the disease;
- crusts subsequently form in place of the pustules.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How can you treat genital fungus?
How to recognize and how to treat fungus on the labia in women and girls? When treating fungal dermatitis, it is necessary not to forget that in addition to the external manifestations of the disease, the patient has endogenous changes:
- there are disruptions in the activity of the endocrine system;
- the defenses of the human body are weakened;
- an allergic reaction may occur;
- there is increased skin moisture.
The process of the appearance of fungal dermatitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The patient feels severe burning and itching on the affected skin;
- These areas of the skin are very hyperemic;
- Peeling and increased dryness of the skin may also be present;
- In some patients, the disease is accompanied by excessive moisture of the skin, on which bubbles with transparent contents appear.
If treatment was not carried out or was not effective enough, secondary infection develops when microbial eczema, herpes or pyoderma develops against the background of fungal dermatitis. More severe forms of the disease are often diagnosed in the presence of the following concomitant diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- diabetes;
- vascular diseases;
- ailments of the musculoskeletal system;
- HIV;
- oncology.
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on a visual examination of the affected skin, as well as after examining scrapings from the epidermis affected by the fungus. A fluorescent lamp is considered an excellent diagnostic method.
Due to the immaturity of the immune and digestive systems, diaper dermatitis and dysbacteriosis are often present in infancy, which contribute to the spread of fungal infections. Most often, candidiasis is diagnosed on the skin and mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Also, in childhood, perianal fungal dermatitis is sometimes encountered. It develops due to the fact that a fungal infection from the skin and mucous membranes enters the intestines. This form of dermatitis often manifests itself as severe redness and weeping rashes in the anal area.
Treatment
From the moment of initial infection to the first appearance of signs of the disease, no more than seven days usually pass. In very rare cases, this period can extend for several weeks.
Treatment for this form of dermatitis is usually long-term and takes from 25 to 35 days. The basis of therapy is systemic drugs, as well as antifungal drugs for topical use. This disease must be treated by a dermatologist, who, in addition to various topical medications, prescribes histamine blockers.
Since inflammation of the skin and severe itching can cause sleep problems and nervous tension, the doctor prescribes herbal-based sedative medications, for example, Novo-Passit, Dormiplant, valerian, motherwort tincture, etc.
Treatment is required using immunomodulators and vitamins E, B and C, which strengthen the defenses of the human body. When treating particularly severe forms of the disease, hormonal drugs are prescribed.
Symptoms and signs of foot fungus
The causative agents of this disease are saprophytes, molds, candida and other pathogenic microorganisms.
The main types of pathogens:
- Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. These are two yeast-like fungi from the genus Trichopyton. They have a toxic effect, are able to remain dormant for a long time, and become active after exposure to negative factors. The first signs of the disease are itching between the fingers and an unpleasant odor, followed by a rash and peeling. The color of the integument may remain unchanged;
Trichophyton rubrum - Epiderrnophyton floccosum. An anthropophilic fungus that affects the stratum corneum of the epidermis. After infection, pink, scaly spots with characteristic blurry edges begin to appear on the skin. Transmits through tactile contact or through household objects.
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Mycologists distinguish four types of mycosis, which can be caused by various foot fungi:
- Intertriginous or interdigital is the most common. Most often, the primary lesion begins from the crease of the thumb and index finger, then spreading along the foot. Possible causes of occurrence are contact with an infected person (surface), injury and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Squamous-hyperkeratotic. An advanced form of this foot fungus can cause deep cracks and damage to the tissue of the leg up to the ankle. It is noteworthy that at the initial stage of the disease there are no external manifestations. The sole does not itch or hurt; small cracks occasionally appear;
- Dyshidrotic or vesicular form is mycosis, which provokes the appearance of rashes and local erosions on the epidermis. It is transmitted exclusively from the patient and is extremely rarely diagnosed on the skin of the legs. It is believed that this fungus prefers the hands and palms. In the absence of proper treatment, mycotic eczema occurs due to exposure to pathogenic microorganisms;
- The erased form is the lightest of all those described. It is characterized by slight itching between the fingers and slight peeling of the skin. The cause is the saprophyte Candida. Its incubation period is 2 weeks. Most often, patients simply do not notice signs of infection and spread the fungus. Even without treatment, the disease goes away on its own.
Foot fungus is accompanied by onychomycosis - damage to bone tissue. It’s quite easy to “see” the symptoms on your own, so if you have the slightest suspicion of the presence of a fungus, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of foot fungus
What symptoms indicate foot fungus infection:
- Peeling. The fungus feeds on keratin and other protein compounds. In the process of life, it almost completely destroys the protective skin layer, 80% consisting of these tissues;
Peeling
- Itching. Due to the destruction of the skin, the body tries to urgently “start” the regeneration process. This is the cause of discomfort. Also, the skin may itch under the influence of certain types of candida;
- Unpleasant smell. The appearance of fungus disrupts the functioning of the sebaceous glands. This causes increased sweating of the palms and feet (or, on the contrary, their excessive dryness);
- Change in skin color. When keratocontaining fibers are destroyed, the healthy shade of the epidermis changes. From beige-pink it can turn greenish, bluish or purple.
It is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms. First of all, this is an increased temperature of the hands or feet. Mycosis significantly affects the nails: they become brittle, fragile, change their thickness and color.
Heel color change
Any organism, pathogenic or not, dies only if it is exposed to negative factors. To ensure a quick recovery, it is important to act comprehensively, using baths, ointments and tablets. Let's consider inexpensive and effective drugs for the treatment of foot fungus.
Spray Domix Green Stop Fungus – varnish for the treatment of mycosis of nails and feet. It has a strong antifungal effect and helps disinfect shoes and clothes. Can be used to treat palms, nails and other affected areas.
Spray Domix Green
Lamisil is a cream with the strongest fungicidal effect. The composition includes Terbinafine, an active substance to which dermatophytes and molds are sensitive. The product will help against chronic foot and toe fungus, as well as strengthen the nails and protect them from onychomycosis. Provides a preventive effect.
Lamisil
Bifosin - a cream for foot fungus, will help quickly get rid of old mycoses caused by yeast-like fungi. In addition, it treats excessive sweating and eliminates unpleasant odor.
Bifosin
Instructions on how to treat foot fungus with Bifosin:
- The leather is carefully processed and wiped dry. It is important that the surface of the epidermis is completely dry and free of dust and sweat;
- A thick layer of ointment is applied to the skin. After which the affected area is covered with a clean cloth (preferably cotton or gauze);
Correct application of cream
- A day later, the compress is removed, the skin is washed with warm water and soap, after which the epidermis is re-treated with cream.
The average duration of such treatment is 7 days, provided that the procedures are performed regularly.
Vishnevsky's balsamic liniment is the cheapest ointment for foot fungus. The composition includes birch tar, castor oil and creroform. The product is used to treat mycosis on the heels, palms, nails and other parts of the body. Thanks to natural ingredients, it is used to treat skin diseases during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It has a pronounced irritating effect and may cause some discomfort when used: itching and burning.
Liniment balsamic Vishnevsky
Easy Step cream is the best remedy for foot fungus. Its active components are Farnesol, Climbazole and peppermint oil. The product is characterized by a powerful fungicidal and antimicrobial effect. In addition, it has a deodorizing effect, restores the nail plate, and helps relieve itching and burning.
Easy Step Cream
Fratti NV Shungit contains tea tree essential oil. Helps with local fever, scabies, pain. This product is rather a preventive component of treatment than the main one. They are recommended to treat the skin of their feet and hands when visiting swimming pools, saunas and gyms.
Fratti NV Shungit
Levomekol is a popular bactericidal ointment that is used at home to treat foot fungus, nail fungus and some types of lichen (red and ringworm). The product allows you to quickly heal microcracks, resume regenerative processes and normalize the functioning of the sweat glands.
Levomekol
Miramistin is an antiseptic drug for the treatment of superficial mycoses of the feet, palms and nails. This is a solution that needs to be applied to the affected areas twice a day. Can be used during lactation, but is prohibited for use in children under 3 years of age. The composition contains powerful components, so the product is characterized by an aggressive effect. After application, a burning sensation or increased temperature may be felt on the epidermis. An analogue of the solution is Okomistin drops.
Miramistin
Stop active oil for foot and nail fungus is an effective medicine for the treatment of interdigital and through forms of the disease. Consists of completely natural ingredients: mumiyo and beaver musk. Sold in pharmacies and company stores. It has a softening and restorative effect, quickly relieves itching and swelling. But it is important to understand that this is rather a prevention of fungus than its main treatment.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Preparations for itchy skin. Tablets for itchy skin - inexpensive and effective drugs
Oil Stop active
Fukortsin is a combined medical product with antiseptic and antifungal properties. The solution is sold exclusively in pharmacies and has no analogues. Able to relieve itching and swelling after the first use. You need to take baths with it, a course once a day for a week. Previously, they used potassium permanganate instead, because it has a similar effect.
Fukortsin
Exoderil is a certified drug for the treatment of various forms of mycosis. Available in the form of drops and ointments. Contains naftifine hydrochloride. Included in the ranking of the most popular means for treating fungi in the CIS (data for 2020). Used to treat diseases in the initial stages, as well as advanced forms.
Exoderil
Clotrimazole is an ointment that has a complex effect. It is used for the treatment of various mycoses (including lichen, thrush and onychomycosis). In addition to the cream, the dermatologist may prescribe Clotrimazole tablets to be taken orally.
Clotrimazole
Formidone is a solution of formaldehyde. The aggressive composition of the product destroys spores and prevents the development of fungi. Has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. The drug should not be used for cracks or other damage to the skin of the foot.
Formidon
Iodinol is an iodine solution for skin disinfection. Used as additional measures in the treatment of fungal diseases. Necessary for cleansing the skin before applying the cream. It is successfully replaced by the more affordable Chlorhexidine.
Iodinol
Teymurov's paste is a popular remedy for the treatment of hydroperhidrosis. It contains boric acid, zinc, formaldehyde, glycerin and some other aggressive substances. To treat mycoses, the product should be applied to the epidermis twice a day in a thin layer.
Pasta Teymurova
Mycocid is a good gel for mycosis. Contains bifonazole. This is a rather aggressive drug for fighting fungi. Approved for use during pregnancy and lactation, but only if there are appropriate instructions from a doctor. It has a locally disinfecting effect and quickly relieves symptoms of infection by pathogenic microorganisms.
Mycocide
In addition to external medications, for effective treatment you need to take tablets for foot and nail fungus. They normalize the functioning of the immune system and allow you to destroy the mycelium from the inside.
Stop Biopag granules are an active drug for the treatment of fungus. The composition includes Guanidine, which destroys spores and fungal microorganisms. The tablets can be used during pregnancy, but only after consulting a doctor. The course is a week.
Stop Biopag granules
Furacilin - often used in folk medicine to treat sweating feet, but it can also be used to remove fungus. Take 2 tablets per 1 liter of water, the procedure lasts 30 minutes. Repeat every day until symptoms disappear completely.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease
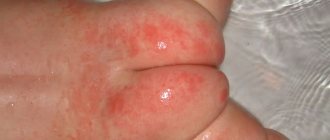
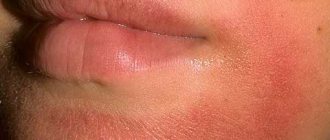
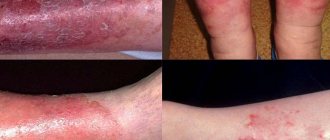
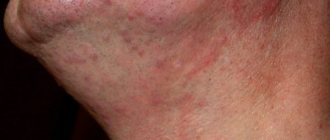
Mycotic eczema has very pronounced manifestations, which cause a lot of inconvenience of an aesthetic and physiological nature. They are characterized by the symptoms of a fungal and allergic disease at the same time. Main symptoms of the pathology:
- redness, itching, burning of the skin;
- grayish-pink round or faceted spots on the skin with clear contours;
- rash characterized by small, swollen nodules with fluid inside;
- spontaneous opening of nodules;
- weeping, moisture in areas where the skin is affected;
- long-term non-healing erosions;
- purulent discharge;
- swelling of the skin at the affected sites;
- scaliness, formation of yellow or pink crusts;
- spreading to nearby areas;
- death of keratinized tissue;
- recurrence.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Mycotic dermatitis is sometimes difficult to distinguish from a regular fungus on your own, since the symptoms of the diseases are very similar. But for a doctor, diagnosis is not a problem. To accurately determine the pathology and type of pathogen, the following research methods are used:
- taking anamnesis;
- visual inspection;
- physical examination;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine (general, biochemical);
- inoculating the contents of the nodules for microorganisms.
How to prevent the development of the disease?
Fungal eczema is not easy to get rid of. Even if all traces of the disease have disappeared, it can remind itself at any moment, as soon as favorable conditions appear. To avoid this, you need to adhere to certain preventive measures:
- avoid stress and emotional stress;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- promptly disinfect wounds, cuts and scratches on the body;
- do not use other people’s hygiene products;
- do not walk barefoot in public places;
- do not take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription;
- consume enough vitamins and minerals.
You should also wear clothes made from natural fabrics, eat a balanced diet, and exercise. At the same time, you should not overuse sunbathing, you should avoid contact with household chemicals, and try to avoid injuries, colds and infectious diseases. If you detect the slightest signs of skin pathology, you should immediately consult a doctor, since self-medication is likely to be ineffective and will only worsen the situation.
Copying site materials is possible without prior approval if you install an active indexed link to our site.
The information on the site is provided for general information purposes only. We recommend that you consult your doctor for further advice and treatment.
Prevention
Prevention of fungal dermatitis involves the following measures:
- maintaining personal hygiene,
- refusal of self-treatment with systemic drugs, especially glucocorticosteroids and antibiotics,
- proper nutrition,
- increasing the body's protective functions,
- avoidance of stressful situations.
The child’s body does not develop immunity to skin diseases, so it is also necessary to adhere to some preventive measures:
- keep your baby's skin clean,
- For washing, use only baby soap,
- after bathing, do not rub the baby’s delicate skin, but only gently pat dry with a towel,
- carry out air baths regularly.
Another important measure to prevent mycosis is maintaining hygiene in saunas, swimming pools, gyms and showers. In public places, do not walk barefoot, do not use other people's personal items, and do not sit on uncovered benches.
Fighting fungal dermatitis is a long and difficult journey. Only strict adherence to the doctor’s prescriptions and a serious attitude towards treatment will help you forget about this disease forever.
Etiology
Fungal dermatitis can be caused by almost all pathogenic and opportunistic fungi for humans. Some of them are part of the normal microflora and constantly live on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. Infection with others occurs when fungal spores enter from the outside or through direct contact with the affected areas of the body of a person with dermatomycosis.
Currently, there are about 500 fungi that have the potential to infect humans and animals. But the main causative agents of fungal dermatitis in humans include:
- Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (Candida Albicans). In small quantities they are part of the natural microflora of the skin, oral cavity, intestinal and vaginal mucosa. They are considered opportunistic, showing a tendency to infect the skin and mucous membranes only if conditions are favorable for them. They cause candidal dermatitis, perianal fungal dermatitis, candidiasis of the vagina, oral cavity and other organs.
- Mushrooms of the genus Trichophyton, of which there are 22 species. They are pathogenic and lead to the development of trichophytosis of the scalp and smooth skin, favus, and parasitic sycosis. Rubrophytia is distinguished separately. This is dermatitis caused by infection with a certain species of Trichophyton - Trichophyton Rubrum.
- Fungi of the genus Microsporum (Mikrosporum), 16 species pathogenic to humans. They cause microsporia of smooth skin on the face and body, and scalp.
Candidal dermatitis is the most common type of mycotic infection in children and adults. This is often what is meant when talking about fungal skin infections. In this case, dermatitis is often combined with candidiasis of the mucous membranes.
1. Candidiasis of the skin of the inguinal folds 2. Candidiasis diaper dermatitis
1. Trichophytosis 2. Microsporia
Causes of fungal dermatitis in children: symptoms and treatment
Mycosis is a general term meaning that the skin or other organ is affected by fungi. The fungus is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that are aggressive towards the human body. Mycosis does not have favorite places, so its symptoms appear in different areas of the body.
To date, scientists have studied about 2 million fungi. Each of them has its own structure, shape and size. They live in the surrounding world and can affect the human body, in particular, the genitals, gastrointestinal tract, and oral cavity. But the priority place for these organisms is the skin.
The main pathogens of fungal pathology in adults and children:
- dermatophytes;
- yeast;
- mold.
Physical contact with an infected person most often becomes a source of infection with the fungus. The conductor is damaged skin, sweat glands. Fungal dermatitis in children is most often observed in dermatological practice. Their immunity and digestive tract organs are only at the development stage, so babies are very vulnerable to infectious agents.
Fungal dermatitis is classified depending on the source of infection and the type of pathogen. If we talk about the localization of the inflammatory focus, then mycosis is divided into:
- superficial – mycosis of the foot, fingers, head;
- deep - mycosis of the mucous membranes, esophagus, lungs, intestines, genitals, epidermis (in advanced situations - mycosis of the skeletal system and brain).
We suggest you read: How to remove unpleasant odor from sneakers
Fungal superficial dermatitis is divided depending on the type of pathogen into:
- Dermatomycoses. They are caused by mold fungi. A person scratches the skin vigorously and feels a burning sensation. There is also a change in color and small scales appear. The feet and toenails are most affected. Because of this, the lower extremities begin to smell unpleasant, and the nail plate turns yellow and may collapse.
- Candidiasis. Caused by yeast. Favorite places are the genitals, mucous membranes, nails, and skin. Externally, the fungus looks like diaper rash; a whitish coating covers it on top, which can be easily wiped off with a cotton swab. Often this type of dermatitis affects young children, overweight people and excessive sweating.
- Keratomycosis. They develop due to an imbalance of microflora. With this type, depigmentation of the skin is observed.
Deep fungal infections include:
- cryptococcosis (affects mucous membranes, central nervous system, skin, lungs);
- histoplasmosis (develops mainly in the pulmonary system);
- verrucous dermatitis (favorite places are subcutaneous tissue).
Lack of treatment can lead to the spread of infection to all systems of the body.
The symptoms of mycosis are as follows:
- skin changes color and structure;
- a rash appears (pustules, diaper rash, round red spots, weeping), small scales on the head, smooth skin;
- a lumpy ring forms around the spot protruding above the surface;
- the affected areas of the skin are very itchy, which leads to the formation of crusts;
- if a bacterial infection is attached, a purulent process is observed.
Simultaneously with these signs, there is a deterioration in general health, weakness, fatigue, loss of strength, and fever.
The symptoms of fungal dermatitis are very similar to other skin ailments, which makes it difficult to diagnose.
Fungal skin infections in children are most often presented in the form of diaper dermatitis, seborrheic and candidiasis. The latter is characterized by a white coating in the mouth. Seborrheic dermatitis is:
- yellowish-white scales on the face and scalp;
- burning sensation, itching, pain in the affected skin area.
Diaper dermatitis is characterized by blisters, their subsequent drying, and crusting. The skin burns, hurts and itches.
Depending on the nature of the foci of inflammation, the following forms of fungal dermatitis are distinguished:
- keratomycosis. With this disorder, the stratum corneum of the epidermis is affected. The pathological process does not extend to skin appendages (hair, nails). Adolescents and middle-aged people are more susceptible to developing the disease.
- candidiasis. The disease is caused by the Candida fungus, which actively multiplies against the background of a decrease in the body's defenses. Most often, candidal dermatitis develops on the skin and mucous membranes. The disease occurs mainly in adolescents and older people.
- dermatomycosis. The pathological process can develop in any part of the body and affects the deeper layers of the epidermis.
- sporotrichosis. Rashes appear on the extremities and in the groin area. The disease occurs when interacting with plant elements - oak bark, flowers, hay. In some cases, pathology develops after contact with a cat or horse.
Symptoms
The causative agents of this disease are saprophytes, molds, candida and other pathogenic microorganisms.
The main types of pathogens:
- Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. These are two yeast-like fungi from the genus Trichopyton. They have a toxic effect, are able to remain dormant for a long time, and become active after exposure to negative factors. The first signs of the disease are itching between the fingers and an unpleasant odor, followed by a rash and peeling. The color of the integument may remain unchanged; Trichophyton rubrum
- Epiderrnophyton floccosum. An anthropophilic fungus that affects the stratum corneum of the epidermis. After infection, pink, scaly spots with characteristic blurry edges begin to appear on the skin. Transmits through tactile contact or through household objects.
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Mycologists distinguish four types of mycosis, which can be caused by various foot fungi:
- Intertriginous or interdigital is the most common. Most often, the primary lesion begins from the crease of the thumb and index finger, then spreading along the foot. Possible causes of occurrence are contact with an infected person (surface), injury and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Squamous-hyperkeratotic. An advanced form of this foot fungus can cause deep cracks and damage to the tissue of the leg up to the ankle. It is noteworthy that at the initial stage of the disease there are no external manifestations. The sole does not itch or hurt; small cracks occasionally appear;
- Dyshidrotic or vesicular form is mycosis, which provokes the appearance of rashes and local erosions on the epidermis. It is transmitted exclusively from the patient and is extremely rarely diagnosed on the skin of the legs. It is believed that this fungus prefers the hands and palms. In the absence of proper treatment, mycotic eczema occurs due to exposure to pathogenic microorganisms;
- The erased form is the lightest of all those described. It is characterized by slight itching between the fingers and slight peeling of the skin. The cause is the saprophyte Candida. Its incubation period is 2 weeks. Most often, patients simply do not notice signs of infection and spread the fungus. Even without treatment, the disease goes away on its own.
Foot fungus is accompanied by onychomycosis - damage to bone tissue. It’s quite easy to “see” the symptoms on your own, so if you have the slightest suspicion of the presence of a fungus, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of foot fungus
What symptoms indicate foot fungus infection:
- Peeling. The fungus feeds on keratin and other protein compounds. In the process of life, it almost completely destroys the protective skin layer, 80% consisting of these tissues; Peeling
- Itching. Due to the destruction of the skin, the body tries to urgently “start” the regeneration process. This is the cause of discomfort. Also, the skin may itch under the influence of certain types of candida;
- Unpleasant smell. The appearance of fungus disrupts the functioning of the sebaceous glands. This causes increased sweating of the palms and feet (or, on the contrary, their excessive dryness);
- Change in skin color. When keratocontaining fibers are destroyed, the healthy shade of the epidermis changes. From beige-pink it can turn greenish, bluish or purple.
It is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms. First of all, this is an increased temperature of the hands or feet. Mycosis significantly affects the nails: they become brittle, fragile, change their thickness and color.
Heel color change
Any organism, pathogenic or not, dies only if it is exposed to negative factors. To ensure a quick recovery, it is important to act comprehensively, using baths, ointments and tablets. Let's consider inexpensive and effective drugs for the treatment of foot fungus.
Spray Domix Green Stop Fungus – varnish for the treatment of mycosis of nails and feet. It has a strong antifungal effect and helps disinfect shoes and clothes. Can be used to treat palms, nails and other affected areas.
Spray Domix Green
Lamisil is a cream with the strongest fungicidal effect. The composition includes Terbinafine, an active substance to which dermatophytes and molds are sensitive. The product will help against chronic foot and toe fungus, as well as strengthen the nails and protect them from onychomycosis. Provides a preventive effect.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Best ointments and creams for the treatment of dermatitis: a list of effective drugs
Lamisil
Bifosin - a cream for foot fungus, will help quickly get rid of old mycoses caused by yeast-like fungi. In addition, it treats excessive sweating and eliminates unpleasant odor.
Bifosin
Instructions on how to treat foot fungus with Bifosin:
- The leather is carefully processed and wiped dry. It is important that the surface of the epidermis is completely dry and free of dust and sweat;
- A thick layer of ointment is applied to the skin. After which the affected area is covered with a clean cloth (preferably cotton or gauze); Correct application of the cream
- A day later, the compress is removed, the skin is washed with warm water and soap, after which the epidermis is re-treated with cream.
The average duration of such treatment is 7 days, provided that the procedures are performed regularly.
The main symptom of fungal dermatitis is a pustule filled with fluid.
How to distinguish nail fungus from other diseases
Symptoms of various diseases are often similar or repeat each other. To distinguish one disease from another, doctors carry out differential diagnosis.
Even with similar symptoms, it is possible to find differences to speed up diagnosis. Nail fungus can be distinguished from other skin pathologies by its characteristic features. Each disease has its own characteristics, which a dermatologist can determine.
For allergies
The cause of an allergy is contact with the agent that causes the reaction. These are dust particles, some food, plant pollen, household chemicals, less often sun rays and cold. Upon contact with an allergen, a red rash appears on the skin. It looks like a nettle burn. This kind of rash occurs only due to allergies.
Manifestations of the fungus are characteristic of areas of the body with hair, nails, and fingers. Redness of the skin is also characteristic of mycosis, but does not appear in the form of a rash. The stratum corneum of the epidermis in these places peels off and the scales fall off. The lesions grow over time. In the center of the spot, the scales finally fall off, but the redness around it remains.
It looks like rings on the skin. There are different types of lichen, each of which is treated in its own way. It is important to start therapy at the first stage of the disease to prevent spread and extensive damage to the skin.
For scabies
Scabies is an anthroponotic disease caused by itch. This is the name of a type of tick that crawls under a person’s skin and parasitizes, tearing out passages and leaving eggs in them. A characteristic sign of scabies is unbearable night itching, insect burrows and a rash. It appears due to toxins secreted by insects. They irritate the skin, causing allergic rashes.
The appearance of symptoms occurs a week after infection with increased sensitivity of the body to toxins. The manifestation of the disease can take up to a month if immunity is high. This is not considered an incubation period, since when the pathogen gets under the skin, it immediately begins to gnaw through the passages, laying eggs in them.
Symptoms that make it easy to recognize scabies:
- Unbearable itching, especially at night;
- Blisters, rashes;
- Peeling of the skin of typical localization;
- Scratching that festeres over time.
The most characteristic sign of infection with itching is the presence of scabies. They reach a length of 7 mm, in appearance they resemble worms, as they wriggle and have a light color. At the end of this passage there is a vial with tick eggs. At one time, the female is able to lay from 10 to 25 eggs.
The tick burrows fester, forming scabs and weeping abrasions. Eczema and pyoderma often occur as complications. The boundaries of the lesions are clear, inside there is a large number of small purulent inflammations. Scabies rashes are characterized by single and paired arrangement of pimples, and polymorphism occurs less frequently.
Tick burrows are located in typical places with a developed stratum corneum:
- The reverse side of the elbow and knee is on the bend;
- On the side of the fingers and on the skin between them;
- The back of the palm;
- Wrist at the bend;
- Anterolateral surface of the body;
- Legs in front;
- In the armpits;
- In the area of the mammary glands;
- Genital organs.
In children, the disease sometimes manifests itself in atypical places of localization - on the soles and palms, in the hair, on the face.
The main signs of scabies:
- Sezari's symptom - identification by touch of a tick tract;
- Ardi-Gorchakov’s symptom – localization of peeling, crusts and pimples in the elbow area;
- Michaelis symptom - crusts of dried blood are detected between the buttocks.
The fungus is very different from scabies. Its pathogens do not form passages, and itching accompanies the patient constantly and is not associated with the time of day. The main difference between mycosis and scabies is the absence of a rash that appears as a result of the action of mite toxins on the skin.
For eczema
Eczema is a non-infectious disease of inflammatory etiology. Another name for this disease in adults is neurodermatitis.
The affected areas are located on the inner part of the flexor surfaces. The fungus is located in the nail area, on the feet and other areas of the skin.
Neurodermatitis provokes skin hyperemia with the appearance of a small rash. The bubbles open, forming weeping surfaces and erosions. A serous fluid is released from them. The rash in this disease has pronounced polymorphism.
Foci of fungal infection are characterized by dryness, liquid is never released from them, and pronounced peeling occurs on the skin. What mycoses and eczema have in common is itching, the appearance of which is not related to the time of day.
Eczema of microbial etiology occurs at the site of localization of ulcers, trophic ulcers and other damage to the integrity of the skin. The lesions are formed by a weeping wound, a crust of pus, and numerous blisters. They have clear boundaries and are larger in size compared to areas affected by mycosis.
Foci of fungus never merge together, unlike eczematous ones. Patients with seborrheic dermatitis note the appearance of lesions with red, scaly spots and yellow rashes. Rashes are not typical for a fungus. Since not every patient can distinguish eczema from a fungus, it is better to consult a dermatologist to make a diagnosis.
For psoriasis
It is not difficult to distinguish a fungus from psoriasis by the area affected. Mycosis occurs locally, although sometimes it can develop into a generalized form. The transition from local small lesions to damage to the entire body takes a long time. With psoriasis, skin changes occur simultaneously in several places and occupy a significant area.
The lesions are located in places with the greatest friction:
- On the buttocks;
- On the bend of the elbow;
- Under the kneecaps.
Less commonly, the disease affects the scalp, hands, feet, genitals and nail plates, up to onychodisis. Psoriasis is a chronic pathology, while fungus always manifests itself in an acute form. And only in the absence of adequate therapy does it move to the next stage.
Patients with psoriasis suffer from a rash that looks like a scattering of bright pink nodules. The surface of the rash is covered with silvery scales.
Typical symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Characteristic plaques are red or pink elevations above the skin with silver scales, localized in certain places;
- Bleeding lesions caused by torn skin;
- Deformation of the nail plate - the appearance of small pits, separation of the edges, change in color to dull yellow;
- Itching in areas of greatest friction;
- Symmetrical plaques relative to the body axis;
- The rash resembles drops in appearance;
- The joints are painful, swollen and overly sensitive.
Fungal infections never occur symmetrically, and itching does not depend on the location of the lesion. Mycosis does not affect the joint capsules, so patients do not notice changes or pain in their locations.
For herpes
Herpes is caused by a virus, which has 5 types. With this disease, a characteristic rash of blisters with liquid appears. Over time, they open up, forming crusts. Typical symptoms also include itching, burning, and redness of the skin. Herpes is often accompanied by fever and chills.
The shingles type of the disease differs from others in the localization of the rash along the nerve. The contents of the vesicles change from serous to purulent, streaked with blood, as the disease progresses. The lymph nodes become enlarged and the patient experiences fever. A distinctive feature is pain along the nerve fiber, which persists after the disappearance of other symptoms.
Herpes is characterized by the following localization of lesions:
- Corners of lips;
- Cheeks;
- Nasolabial triangle;
- Eye mucosa (keratitis, conjunctivitis);
- Skin of the face and eyelids;
- Gums;
- Mucous membranes of the genitals;
- Red border of the mouth.
It is not uncommon for rashes to occur in all of these areas at the same time.
The fungal infection spreads to other areas, most often affecting the nails and skin of the extremities, as well as the oral mucosa.
For corns
Dry calluses (corns) are areas of compaction of the stratum corneum on the plantar part of the foot. The reason for their appearance is excessive mechanical friction or compression of the skin. Itching is not typical for these formations. They are painful when pressed. Corns are localized at the beginning of the toes, as well as on the pad of the first phalanx.
The formations are fuzzy, cloudy yellowish in color. The skin in these places is not prone to peeling, as with fungus. It is compacted, often smooth to the touch.
From prickly heat
Symptoms of prickly heat vary depending on the type. It is not difficult to determine it by the nature of the rash:
- Papular – typical for adults. The rash is small (up to 2 mm), flesh-colored. Typical localization is the anterolateral part of the body, limbs. The skin peels, the patient is bothered by itching;
- Red – typical for all ages. A rash of small diameter (up to 2 mm) with a cloudy liquid surrounded by a red border. The patient complains of itching. The rashes do not tend to merge. Typical localization - places of greatest friction - under the mammary glands, between the buttocks, under the diaper, on the inner surface of the thighs;
- Crystalline – characteristic of children. The rash is larger than with other types of disease, white or cloudy in color. The bubbles are able to merge, forming a large spot. This species is characterized by the appearance of crusts and protruding flakes of skin. Typical localization is face, neck, shoulders, back, abdomen.
The rashes that occur with prickly heat are very different from the lesions with mycosis. The red type has a similar edging of the blisters, but the pimples are too small to not notice the difference between it and lichen.
The differences between these diseases in therapy are clearly visible. Miliaria goes away when the rash is cauterized with potassium permanganate. In case of mycosis, such treatment will only worsen the situation, as it will dry out the affected skin even more.
From injuries
Onychodystrophy, characteristic of mycosis, often occurs due to trauma to the nail plate. Contusion of soft tissues under the bed leads to changes in the upper layer. The nail changes its structure, color and growth pattern. Injuries are distinguished from skin diseases by the presence of a bruise, which is visible under the plate. It needs to be drained of blood to speed up healing.
Traumatic injuries to the nail plate do not require special therapeutic treatment. It is necessary to keep the damaged area at rest and treat it with wound-healing drugs, if possible.
Differential diagnosis of fungus from other diseases should be carried out by a doctor. This will help to accurately establish the diagnosis, which will significantly speed up treatment.
Predisposing factors to fungal dermatitis
Normally, the skin is an insurmountable obstacle to any microorganisms, including all types of fungi. This is facilitated by many factors: the absence of dryness and excessive humidity, the integrity of the epidermis, normal acidity on its surface, the functional integrity of the immune system.
There are many predisposing factors that increase the likelihood of developing fungal dermatitis. These include:
- Recurrent and poorly healing microdamages of the epidermis. This is facilitated by occupational hazards (mechanical injuries, exposure to contrasting temperatures, contact with irritating substances), excessive dryness of the skin on the hands due to irrational care, frequent washing and the use of local disinfectants. In some patients, violations of the integrity of the epidermis are caused by dermatitis of another etiology (atopic, allergic, contact, seborrheic).
- Increased skin moisture. This condition is possible with excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) due to excess weight, endocrine and neurological disorders, and the individual characteristics of the patient. In addition, high humidity is facilitated by prolonged wearing of personal skin protective equipment with low air permeability, prolonged stay in rubber shoes, and insufficiently thorough drying of the skin before dressing after visiting the pool, sauna, bathhouse.
- Exposure to chemical factors. For example, fungal dermatitis in infants often develops with prolonged contact of the infant's skin in the perianal area with diapers soiled with urine and feces. It has been proven that it is the maceration of the epidermis under the influence of urea breakdown products and residues of digestive enzymes that contributes to fungal infections of the perineum.
- Endocrine diseases. The most significant pathology is diabetes mellitus, which is accompanied by changes in skin acidity and increased proliferation of microorganisms.
- Decreased immune system reactivity. Immunodeficiency can be caused by HIV, a severe infection, the use of cytostatics, radiation therapy, certain blood diseases, and bone marrow pathology. Functional disorders are also possible due to stress, neurotic and affective disorders, and pathology of the digestive system.
- Irrational antibiotic therapy, which disrupts the balance of natural microflora and negatively affects the functioning of the immune system.
- Long-term use of glucocorticosteroid drugs of topical and systemic action, which leads to dyshormonal disorders and a decrease in the activity of local protective mechanisms. Therefore, candidal dermatitis in adults often occurs against the background of steroid therapy for systemic connective tissue diseases and multiple sclerosis.
If at least one of these factors is present, fungi are able to overcome the natural skin barrier and can begin to actively multiply.
Mycosis begins with fungal flora entering the skin through cracks or abrasions (without violating the integrity of the epidermis, a foreign agent will not be able to penetrate there). Such flora is divided into pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic. The first type of infection occurs due to exposure to foreign organisms.
Like any other disease, it is better to start treating dermatological inflammations of a fungal nature immediately, otherwise they will take a chronic, difficult-to-treat form.
The main provocateurs of fungal disease:
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics, glucocorticosteroid drugs;
- decline in immunity;
- cancer;
- HIV infection, diabetes mellitus and other autoimmune diseases, vascular diseases;
- constant or chronic stress;
- intense physical work and excessive passion for sports training;
- too frequent or constant use of antibacterial agents;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system, hormonal changes in the body;
- use of things of a patient with dermatitis;
- frequent visits to public places - baths, swimming pools, saunas, shared showers.
Dermatitis in infants is a consequence of underdevelopment of the immune and digestive systems, inadequate care of the baby’s skin, and poor hygiene. All these factors make the body vulnerable to fungal infection, and it is unable to resist the disease.
The drug Akriderm GK against nail fungus: description and instructions
Price
Have you been trying to cure FUNGUS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure fungus by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
Akriderm GK cost:
- Cream (15 g) – 356 rub.;
- Ointment (30 g) – 357 rub.
Where can I buy
Available without a prescription.
Can be purchased from online pharmacies:
- apteka.ru;
- gorzdrav.org.
Release form
- The ointment is white or cream in color, with a slight specific odor;
- The cream is white, almost odorless.
Both forms have identical composition and concentration of the main active ingredients (betamethasone, gentamicin, clotrimazole) and differ in excipients.
What to choose
Due to the similar composition, Akriderm GK ointment and cream are interchangeable dosage forms.
For onychomycosis, it is better to choose an ointment - it is more suitable for treating cuticles and nails.
Composition of the drug
Main active ingredients per 1 g of the drug:
- Betamethasone (0.64 mg) is the main hormonal component. Reduces swelling and itching. Relieves inflammation and blocks allergic reactions.
- Clotrimazole (10 mg) is an antifungal agent. It is present only in Akriderm GK, so other drugs in this series are not suitable for the treatment of nail fungus.
- Gentamicin (1 mg) is an antibiotic characterized by a wide sector of action. Causes a pronounced antibacterial effect.
Excipients:
- Nipazole – antibacterial and antifungal effect;
- Vaseline and petroleum jelly are the basis for the ointment;
- Isopropyl myristate - improves the effect of components on the treated surface.
Analogs
- Triderm (cream, ointment) – 653-678 rub. for 15 years
- Kanizon plus (cream) – 419 rubles. for 15 years
- Triacutan (cream, ointment) – 250-300 rubles. for 15 years
The drugs have an active formula identical to Akriderm GK consisting of three main components: betamethasone, clotrimazole and gentamicin in a similar concentration.
Despite the similar composition, changing one drug for an analogue is possible only with the permission of the attending physician.
Properties of the drug
- Antiallergic: quickly eliminates itching
- Anti-inflammatory: relieves redness, inflammation.
- Antiseptic: actively fights infection.
- Antifungal: Treats fungal infections.
Thanks to the presence of clotrimazole, Akriderm GK is active against dermatophytes and yeast-like and mold fungi.
How it works
The hormone betamethasone relieves allergic itching. Clotrimazole penetrates the nail plate and destroys the cell membranes of fungi that cause mycosis.
Indications for use
- dermatitis;
- lichen;
- eczema;
- dermatomycosis (skin fungus);
- onychomycosis (nail fungus).
Instructions for use
Suitable for use within 24 months. from the date of production. The optimal storage temperature is 15-25 C.
Pensioners! Don't cut fungal nails! They are derived simply: take 9 grams...
Military doctor: So that the soldiers do not have fungus, they 2 times a day...
Apply externally to affected areas.
Avoid contact of Akriderm GK with mucous membranes (eyes, respiratory tract).
Before use, please read the contraindications.
For children from 2 to 8 years old, as well as pregnant women and during lactation, the drug is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician in minimal doses and for a short period of therapy.
Official instructions (296 KB).
Mode of application
- Before applying the drug, thoroughly clean your nails (5-10 minutes in a warm bath with soap or other ingredients - more details...) and dry with a sterile towel.
- Apply a thin layer of Akriderm GK to the nail plates and the skin around the affected nails.
- Regularly treat shoes and items of clothing that come into contact with affected nails.
Dosage
To treat nail fungus, 2 times a day is enough.
The duration of the course is determined by the attending physician (on average 2-3 weeks).
If there is no improvement, this drug should be gradually discontinued and the treatment regimen reconsidered.
Overdose
In case of overdose, hypercortisolism develops (Cushing's syndrome or excess adrenal hormones), as a consequence of prolonged exposure to the hormonal drug on the body. In such a situation, a gradual cessation of the use of Akriderm GK and symptomatic therapy will be required.
Features of use with other drugs
According to the instructions, no interactions with other drugs have been identified.
Application schemes
In case of advanced fungus, Akriderm GK must be combined with oral antifungal drugs.
Contraindications
- Sensitivity to the active components of the drug (allergic reaction).
- Serious skin diseases (tuberculosis, syphilis, herpes, chicken pox), open wounds and skin atrophy. The use of Akriderm GC in areas with significant damage to the skin helps to increase the absorption of the product and increase side effects.
- Age up to 2 years. The baby's skin absorbs more of the product, which leads to an overdose and systemic side effects (including increased intracranial pressure, impaired growth).
Under the supervision of a doctor
For women during pregnancy (especially 1-3 months), lactation, as well as children 2-8 years old, the drug is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. Indications for the use of this drug are cases where the positive effect of antifungal therapy is significantly higher than the potential risk to the patient's health.
Side effects
When using Akriderm GK externally, the following are possible:
- burning;
- itching;
- irritation and dry skin;
- acne;
- hyperpigmentation;
- hypertrichosis;
- dermatitis;
In case of an overdose, a number of systematic negative symptoms occur, including against the background of hormonal imbalance.
- menstrual irregularities;
- Cushing's syndrome or hypercortisolism;
- hyperglycemia;
- weight gain;
- increased blood pressure;
- Osteoporosis;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- insomnia and increased excitability.
Reviews
Pros and cons of the product
Advantages:
- availability;
- reasonable price;
- complex therapeutic effects;
- effectiveness of the drug.
Minuses:
- presence of contraindications;
- serious consequences of overdose, side effects.
Review and review of the Akriderm line of drugs from a doctor:
Pathogenesis
Violation of the barrier function of the skin leads to increased permeability to fungi. Initially, pathogens penetrate the surface keratin layer, softening and loosening it. If this occurs in areas with increased keratinization, the patient may notice a change in the thickness and texture of the skin. In all other zones, this stage occurs quickly and unnoticeably.
By actively multiplying and plunging deep into the dermis, fungi contribute to the appearance of local skin changes and the activation of immune mechanisms. Cellular immunity is primarily used to counteract mycotic infection. True, in many cases it remains incomplete and does not lead to the complete destruction of the pathogen.
Additional inclusion of humoral protection is not able to have a clinically significant effect on the course of fungal dermatitis and does not protect against re-infection. The antibodies produced are type-nonspecific. Because of this, false-positive reactions to fungi that are not detected in a given patient are quite common. Cross serological reactions to some epidermal factors and even to group IV blood isoantigens are also possible.
Imperfect immune reactions and a high probability of allergization are factors contributing to the recurrent course of the disease.
Causality of the disease in children
Already in the first year of life, newborns are likely to develop fungal dermatitis. And all because the still fragile child’s body is too weak in the face of foreign elements:
- immature digestive and immune systems are susceptible to the development of dysbiosis,
- thrush can be caused by intestinal infections, acute respiratory viral infections, allergic dermatitis,
- Negligent attitude towards baby hygiene leads to the development of diaper dermatitis: excess moisture, untimely diaper change, improper bathing,
- an insufficiently acidic environment in the baby’s mucosa provokes the active work of Candida fungi, which causes damage to the genitals,
- poor nutrition leads to the appearance of symptoms of fungal dermatitis in the baby’s anus, and regurgitation – on the tummy, face, and neck.
Excessive bathing with soapy detergents can also be a factor that provokes infection and proliferation of the fungus. The protective fatty film is washed away, the skin is injured, through which the infection penetrates into the dermis.
Candida fungi are activated in an insufficiently acidic environment
Why is it necessary to undergo treatment?
Dermatitis of fungal origin is a contagious and often recurrent disease that disrupts the integrity and structure of the skin and reduces local immunity. Often complicated by:
- allergic dermatitis;
- eczema on the arms, legs and other parts of the body;
- contact dermatitis;
- ulceration of the affected skin.
In case of secondary infection, other skin pathologies may be observed - microbial eczema, herpes, purulent pyoderma.
Treatment of fungal dermatitis begins only after laboratory confirmation of the etiology of the disease. In this case, antimycotic agents of local and systemic action are prescribed, which makes it possible to influence the pathogen in all layers of the skin.
The choice of the main drug is made taking into account the type of fungus and its sensitivity. The doctor may recommend taking a drug with a broad spectrum of action or that has an effect only on certain pathogens. Considering the fairly high potential toxicity of antifungals, you should not violate the recommended dosage regimen, arbitrarily replace the medication, or take any additional remedies for fungal dermatitis.
Antihistamines are prescribed to suppress allergic reactions. Also, if possible, drugs that help maintain a fungal infection are discontinued: corticosteroids, antibiotics. Detected carbohydrate metabolism disorders must be corrected. Parents are taught the principles of infant skin care.
Symptoms of dermatitis
The symptoms of this skin disease are similar to similar skin lesions. Therefore, it is quite difficult to independently determine the type of disease. Most signs are determined only as a result of diagnosis and testing in a clinic.
Signs of fungal pathology:
- at the first stage, the skin becomes covered with pustules - a purulent rash that looks like water blisters;
- at the second stage, the pustules turn into dense crusts;
- the child is capricious because the inflamed areas itch and he is tormented by a painful burning sensation;
- inflamed skin is dry, peeling, and at the site of pustules it is wet and purulent;
- the skin of almost the entire body is constantly moist;
- The disease is accompanied by disruption of the endocrine system and immunity.
Dermatitis appears on any part of the body - back, arms, head. The location depends on what caused the purulent-inflammatory process.
Epidemiology
How safe is a patient with a fungal infection for others? Is candida dermatitis contagious? This is exactly what relatives usually ask the doctor about.
The skin of a healthy person is an excellent barrier to all kinds of fungi. Mycosis will not develop even in the presence of damage (abrasions, scratches), if the person does not have other predisposing factors. The most important of these are immunodeficiency states, recent long-term use of antibiotics, and the presence of latent or treatment-requiring diabetes mellitus.
The exception is ringworm, a fairly contagious fungal disease that can develop without previous underlying conditions. In all other cases, in the absence of risk factors, there is no need to worry about infection even in close direct contact with
patient. Natural defense mechanisms will prevent dermatitis from developing. To prevent infection, it is sufficient to carry out only basic nonspecific prophylaxis; the use of any drugs is not required.