About staphylococci
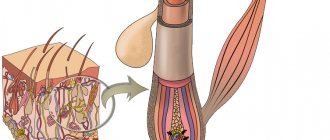
In appearance, staphylococci resemble balls (cocci) up to 1.5 microns. in diameter.
Clusters of bacteria resemble a bunch of grapes (Staphylе - bunch of grapes).
It causes purulent inflammation of various locations. The lesion may be local or widespread. Penetrating into the blood, bacteria can cause sepsis and toxic shock. Penetrating into the digestive tract they cause food toxicosis.
Staphylococci are extremely resistant in the external environment. At a temperature of 150° C, bacteria die only after 10 minutes. Microbes are extremely resistant to direct sunlight, drying, 100% ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, phenol solution and a number of antibiotics. Microbes persist for a long time in food, dust and household items.
The rapid development of resistance to antibacterial drugs makes Staphylococcus aureus the most dangerous microbial agent for adults and children.
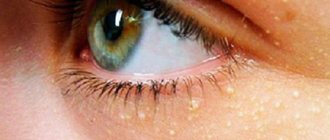
Rice. 2. The photo shows Staphylococcus aureus in the nose.
Symptoms of staphylococcus on the skin
The symptoms of staphylococcal infection largely depend on the location on the body, the stage of the disease and how the body itself fights bacteria. The microbe is capable of causing many skin pathologies, which have their own characteristic manifestations. What they look like is shown in the photo.
More on the topic: Trichomoniasis - what is it?
Furunculosis
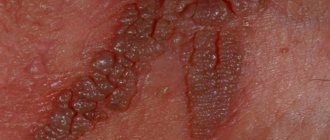
The formation of purulent boils is a common disease that can cause inflammation of the skin on any part of the body. The most dangerous is the appearance of ulcers on the neck and face. It is here that the infection is located close enough to the brain, where it can also cause an inflammatory process.
How it manifests itself:
- the appearance of small redness with white dots in the middle (accumulation of pus);
- swelling of the inflamed area;
- the appearance of painful sensations (twitching or pulsating attacks in the affected area);
- destruction of the protective film and leakage of purulent fluid outward, formation of ulcers.
Furunculosis - the appearance of ulcers on the body.
After opening the boil, a rod remains inside, which after a few days is independently removed along with a small amount of pus and blood. After this, pain and swelling decrease.
The most common areas where ulcers appear on the body are areas of skin prone to oiliness:
- face – nasolabial triangle (rarely on the lips), wings of the nose;
- forearm;
- neck;
- thighs and buttocks.
If there are a lot of purulent formations, the body temperature may rise, nausea, weakness, severe redness of the injured areas, and their swelling may occur. Similar manifestations occur when boils appear in the ear canal, in the nose area or in facial folds, which causes great discomfort to the patient.
Vesiculopustulosis or staphylococcal periporitis
A small staphylococcal rash most often occurs in infants. Vesiculopustulosis refers to pyoderma (purulent rash). Small pimples with purulent contents appear on the skin of a newborn - on the scalp, hips, buttocks, in folds and on the back. This happens due to violations of the baby’s hygiene rules. In a child, the rash is accompanied by itching, as a result of which the baby breaks the blisters, giving the infection the opportunity to spread further.
Characteristic signs of vesiculopustulosis:
- heat;
- small rash in the form of blisters with watery contents;
- general malaise like a cold.
More on the topic: How can you become infected with worms?
Staphylococcal periporitis occurs more often in infants
A feature of this disease is that only the upper layers of the skin are affected by staphylococcal infection; the rashes are shallow and are not accompanied by inflammation (swelling). The children's general health remains normal.
Staphylococcal sycosis
Sycosis caused by staphylococcus is a chronic disease prone to frequent relapses. It usually occurs in men on the facial skin in the area of the beard and mustache.
How it manifests itself:
- Formation of superficial follicles (damage to the hair follicle). Ulcers are located in groups, gradually filling healthy skin.
- The appearance of redness and swelling, which only intensifies over time. Minor suppurations are accompanied by increased sensitivity of the epidermis and the occurrence of severe pain from touch.
- The appearance of crusts of a greenish or dirty yellow hue. The injured areas peel off all the time, after which a weeping surface appears. The purulent-inflammatory process progresses, which leads to a worsening of the skin condition.
Staphylococcal sycosis severely injures the skin of the face, which has a detrimental effect on the patient’s quality of life.
Staphylococcal sycosis is a chronic disease
Felon
Panaritium is an acute purulent inflammation that occurs on the skin of the hands (less often the legs), in particular on the fingers. The bacterium penetrates the epidermis through abrasions, cracks or abrasions on the phalanges.
Main manifestations:
- suppuration near the nail fold or from the distal part of the phalanx;
- redness and swelling of the injured area;
- formation of a blister with purulent contents;
- spread of inflammation to healthy fingers and nail plates.
In severe cases, panaritium can affect all layers of the skin, injuring fiber, tendon and bone tissue.
Panaritium appears more often on the skin of the hands
Phlegmon
Staphylococcus aureus can also cause purulent subcutaneous inflammations, which quickly spread throughout the tissues.
One of these diseases is phlegmon. Characteristic features include:
- severe swelling of the skin;
- redness of the affected area;
- increase in body temperature;
- weakness.
Cellulitis penetrates into the deepest layers of the skin, which can provoke tissue death.
Cellulitis is characterized by severe swelling of the skin
Erysipelas
The most serious disease caused by cutaneous staphylococcus. Most often, the infection occurs in adults and affects the skin of the lower extremities.
More on the topic: Ureaplasmosis – what is it, how to treat it?
How it manifests itself:
- redness and swelling, injured areas are hot to the touch;
- temperature rise to 39–40 degrees;
- nausea, vomiting, severe malaise.
- the appearance of small rashes (rare).
Important!
Erysipelas is a serious disease that is difficult for patients to tolerate and can cause serious complications.
Erysipelas usually appears on the legs
Properties of Staphylococcus aureus
Pathogenic staphylococcus synthesizes and secretes many substances that allow this type of microbe to survive in the human body and damage its organs and tissues.
Enterotoxins
Staphylococci, contaminating food products (meat, milk), release enterotoxins, which, when entering the human body, cause food poisoning. Enterotoxins are resistant to high temperatures and human digestive juices.
Exotoxins
Staphylococci produce a number of exotoxins. Exotoxins have the following properties:
- damage the membrane of red blood cells, causing their hemolysis;
- damage leukocytes;
- damage the skin of newborns (Ritter's disease), the skin of children and adults (bullous impetigo);
- cause toxic shock syndrome.
Enzymes
Staphylococci secrete a number of enzymes with multidirectional effects:
- facilitate the adhesion of microbes to human tissues and the penetration of the pathogen deep into the tissues, damaging them;
— destroy the sebaceous plugs of hair follicles, which contributes to the penetration of infection deep into the tissues;
- cause the coagulation of areas of blood plasma around microbes, which, like a cocoon, envelops staphylococcus, protecting it;
- protect the microbial population from the action of antibiotics.
Allergenic components
Toxins and microbial cell components have strong allergenic properties, which contributes to even greater skin damage.
Breeding factor
Staphylococci contain substances that promote the proliferation of microbes in phagocytes - cells that protect humans from microbes.
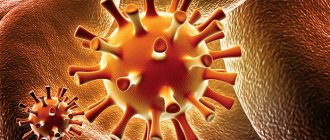
Rice. 3. The photo shows a cluster of Staphylococcus aureus.
Description of the disease
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that can cause a lot of harm to the body.
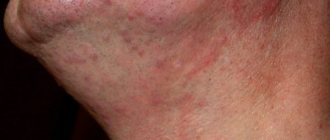
Staphylococcus rashes most often appear on the face
Together with the blood, the infection spreads throughout the body, affecting the internal organs. This bacterium lives on mucous membranes, such as the mouth.
If staphylococcus begins to actively multiply, it will cause serious diseases.
Dysbacteriosis, blood poisoning, sore throat, pneumonia, and various skin rashes may appear.
Often staphylococcus occurs in doctors and those who have recently been in the hospital. Who is at risk? Primarily people with weakened immune systems. For example, those who have recently been treated for a virus or even a common cold. Staphylococcus can appear in women during pregnancy.
In such a situation, it is important to defeat the infection in time to preserve the child’s health. A gynecologist should take part in the treatment.
In infants, while their immunity is still too weak, this disease also often occurs, so any rash on their skin should not be ignored.
People who abuse junk food are also at risk
People who abuse junk food are also at risk. Improper nutrition can cause staphylococcus.
You need to monitor your diet and eat only high-quality foods that contain many vitamins and minerals.
Various injections can also cause the disease. For this reason, diabetics are at risk. They should monitor the condition of their skin and their well-being in order to diagnose Staphylococcus aureus in time if it appears.
Any purulent processes, inflammation and acne can provoke the spread of infection in the body. Staphylococcus is a consequence of a person’s weakened immune system. It is important to diagnose the disease in time in order to select effective treatment.
Epidemiology
The infection is spread by patients and carriers of pathogenic strains of staphylococcus. Open purulent wounds, purulent inflammation of the eyes, mouth and pharynx, pneumonia and intestinal disorders are the source of staphylococcal infection. Food, contact and airborne droplets are the main ways of spreading infection. Surgical interventions, intramuscular and intravenous injections, various implants are also sources of infection. The infection can be transmitted to the fetus in utero, during childbirth and after the birth of the child.
Healthy carriers working in medical institutions, maternity hospitals and catering units are the most dangerous spreaders of infection.
How to treat staphylococcus? 12 best drugs for the treatment of staphylococcus
The human body can serve as a home for thousands of microbes and bacteria, and such proximity does not necessarily end in disease. The immune system reliably protects us, restraining the activity of uninvited guests and forcing them to follow the rules of good manners. Staphylococcus is no exception; it is normally found in about a third of the world's population, but does not manifest itself in anything for the time being.
A weakened immune system, simple hypothermia, or the presence of another infection in the body against which antibiotics were used are the reasons why staphylococcus can go on the offensive. Therefore, it is important to understand two things: you cannot be treated with antibiotics in case of the slightest ailment or cold, and it is simply pointless to use them against staphylococcus as a preemptive measure. You still won’t get rid of the carriage, but you will introduce your staphylococcus to antibacterial drugs and negate their effectiveness in the future, when they may really be needed.
The only reasonable measure to prevent staphylococcal infections is local sanitation of the skin, mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract during the cold season, as well as taking medications that strengthen the immune system. The prescription of antibiotics is justified only in the case of severe, life-threatening diseases: pneumonia, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, multiple purulent abscesses on the skin and soft tissues, boils on the face and head (in close proximity to the brain). But before choosing an antibiotic against staphylococcus, a qualified doctor always performs a bacterial culture.
At a sanitary and epidemiological station, a skin and venereal disease clinic or a medical office of a specialized specialist (ENT specialist, dermatovenereologist, gynecologist, urologist, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist), a bacterial culture is collected from the site of localization of the staphylococcal infection. This can be a swab from the throat, purulent skin abscess, vagina or urethra, as well as a sample of blood, sputum, urine, saliva, gastric juice, semen and other bodily fluids.
The resulting material is placed in a nutrient medium, after some time the colony of staphylococci multiplies, and the laboratory assistant can determine what type of pathogen it is and what antibiotics it is sensitive to.
The culture result looks like a list in which one of the letter designations appears next to the names of all current antimicrobial drugs:
S (susceptible) - sensitive;
I (intermediate) - moderately sensitive;
R (resistant) - stable.
Among the antibiotics from group “S” or, in extreme cases, “I”, the attending physician chooses a drug with which the patient has not treated any disease over the previous several years. This way there is a greater chance of success and avoiding the rapid adaptation of staphylococcus to the antibiotic. This is especially important when it comes to treating protracted and often recurrent staphylococcal infections.
Risk factors for developing staphylococcal infection
- The use of catheters in hospital conditions, the use of ventilation, during surgical manipulations through surgical instruments.
- Immune suppression before transplantation or implantation.
- Carrying out hemodialysis.
- Intravenous nutrition of premature infants.
- Diseases accompanied by decreased immunity (AIDS, diabetes, cancer, some lung diseases, skin and heart diseases).
- Intravenous drug administration.
- Piercing, tattooing.
Rashes on the face
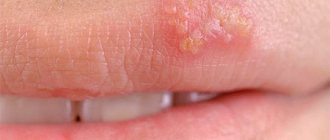
What do staphylococcus skin rashes look like? Outwardly, they often do not differ from acne, so only a specialist can identify the cause of their appearance. Staphylococcus rashes are purulent red bumps.
If the pus is deep under the skin, it will not be visible externally. Touching such pimples is very painful. You should not try to squeeze them out at home, because the infection can spread throughout the body. If inflammation and infection begin, it will be much more difficult to treat the disease.
Is there then a way to determine whether the rash is actually due to staph? In what situation should you consult a doctor?
Infants are at risk
First of all, you need to pay attention to purulent tubercles that appear suddenly and in large numbers.
If a person carefully takes care of himself and his skin was previously clear, then the occurrence of pimples and blackheads that do not go away within 1 week should alert him and become a reason for a visit to the doctor.
Where do staphylococcus rashes most often appear? You can find them on the face. They occur especially often on the cheeks and chin. It is also worth paying attention to purulent tubercles that suddenly appear on the head or back.
If treatment is not started on time, the rashes will begin to grow, which will not only spoil the person’s appearance, but will also significantly harm their health. Once the infection spreads, it will disrupt the functioning of internal organs.
It is also worth noting that in some cases, the appearance of a large number of pimples and blackheads may be accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea and high fever. These symptoms are a sign that the disease is advanced and treatment should be started immediately to avoid possible complications.
Treatment
How to treat a staph infection?
First of all, it must be confirmed by special research.
The detection of staphylococcus does not yet indicate infection; they look, first of all, at the number of these bacteria. And only if this value is exceeded, then special measures are prescribed.
For staphylococcus, especially for Staphylococcus aureus, only a complex of therapeutic measures is effective:
- fight against bacteria that cause the disease;
- strengthening the immune system.
Treatment is usually carried out with the following groups of medications:
- antibacterial drugs of systemic action
- are prescribed for an extensive inflammatory process, when there are many ulcers and they are not localized in one area, for example, the chin, but affect several parts of the body. The selection of antibiotics is purely individual. Drugs are selected after determining the sensitivity of the bacteria to them;
- if the rash is localized to one area of the body (on the face, neck, chest, etc.), then topical antibiotics are used. These are ointments and creams Baneocin, Bactroban, Altargo, etc.;
- staphylococcal bacteriophage
is a drug based on viral particles that selectively act on different bacteria, staphylococcal, respectively, on different types of these particular microorganisms. Viruses penetrate the bacteria, causing its destruction. Outside the bacteria, they themselves die, without bringing any harm to humans; - staphylococcal toxoid
is a drug that increases the body's resistance to toxic substances produced by bacteria. It is used when the situation is complicated by extensive infection and contamination; - immunostimulating drugs
- they complement drug therapy, strengthening the human immune system, since the proliferation of staphylococci occurs against the background of its decline.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection is a serious undertaking that requires an individual approach, so it should be entrusted to a specialist.