Reasons for the formation of nevi
The reasons for the formation of verrucous nevus are not fully known. According to recent scientific research, people with this problem have defects in genes that are responsible for the functioning of skin cells. Therefore, a verrucous nevus is formed during the intrauterine development of the fetus and becomes noticeable in the first years of the child’s life. This is the main difference from ordinary moles. Formations appear closer to the age of ten, when the first hormonal surge occurs in his body.
It should also be remembered that the appearance of such moles is impossible in adults. This formation can only slightly change shape and size with age. However, its transformation is insignificant. If changes occur too quickly, you should consult a doctor. This process is considered pathological and may indicate the development of malignant processes in the body.
Why does a warty nevus appear?
Scientists have come to the conclusion that the formation of moles begins at the embryonic stage of development.
Factors that provoke their formation in humans are:
- imbalance of female sex hormones in a woman during pregnancy
- the presence of infectious pathologies during pregnancy
- the influence of unfavorable environmental factors on a woman’s body during pregnancy
- hereditary factors
As a result of these reasons, the development process of melanoblasts, from which melanocytes are formed, is disrupted.
Melanocytes, concentrating in certain areas of the skin, turn into nevocytes.
Their difference from melanocytes is that they do not have processes that contribute to the spread of pigment.
What does a nevus look like?
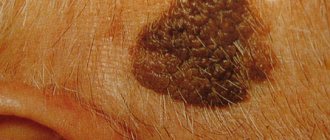
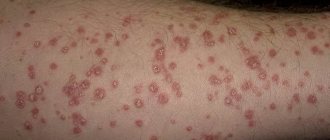
A warty nevus in appearance resembles an accumulation of a large number of warts in one place. Given this symptom, it is not difficult to distinguish this formation from other types of moles. A feature of a verrucous nevus is that it is a bulge on the skin. Its surface is often lumpy and may contain cracks, but is characterized by a complete absence of hair.
Over time, such moles grow, but only in height. As a person ages, the area occupied by the formation on the skin does not change. These growths are covered with a keratinized layer, their color becomes more saturated.
Any changes after injury are especially clearly visible. Such moles are very susceptible to various damages due to their shape. After injury, dark, hard crusts form on their surface. They significantly change the appearance of the nevus and can give impetus to the development of various negative processes .
Warty nevus: what is the danger
A birthmark usually does not pose a threat, but it should not be considered a completely harmless element or simply a cosmetic flaw:
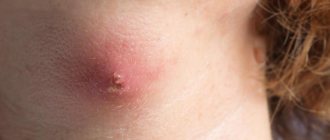
- In the area of its spread, various inflammatory processes can develop: pustular infections or bacterial eczema, they can also spread to nearby tissues.
- This is facilitated by scratches and constant friction of formations, for example, in skin folds, armpits, and groin. In these places, nevi are usually softer, so they are easily injured and inflamed.
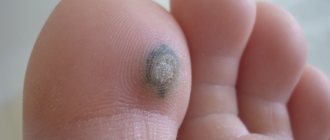
- In diaper rash, the lesions acquire an unpleasant odor and disturb the person. If moles form on the fingers of the extremities, they cause destruction of the nail plate.
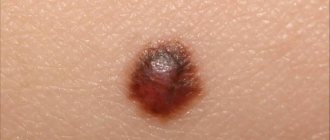
- Warty nevus has a tendency to degenerate into oncological forms.
Therefore, if nature has “rewarded” you with a birthmark, constant monitoring of it is necessary.
Localized form
Localized warty nevus appears as a limited area on the body. It is most often found on the scalp, but can be found on other parts of the body. Symptoms of this type of mole include:
- The diameter of the formation rarely exceeds 10 mm.
- Moles can be single or multiple. In the latter case, several bulges are found, placed close to each other.
- The top layer is rough and may contain small cracks. Its appearance is somewhat reminiscent of a cauliflower inflorescence.
- The color of the formation may not differ from the tone of the skin or be more saturated.
Classification
It is customary for the international community of specialists to divide nevi into groups based on similar characteristics.
The classification also includes other formations similar in appearance to moles. Among them are: spider-like hemangiomas, teratomas, sebaceous (seborrheic) and vascular or flaming, anemic nevi.
Melanocytic formations of epidermal development
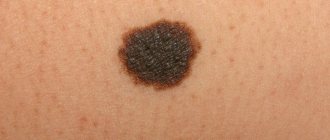
A common group of nevi. There are more than 5 moles of this origin on the human body. The shape is round with clearly defined edges. Flat or slightly convex surface. Color shades range from pinkish to dark brown.
There are 7 types of moles with similar appearance characteristics.
Borderline (intraepidermal)
Flat and dark brown in color. Located between the epidermis and dermis. Located on any area of the skin.
Intradermal (intradermal or fibroepithelial)
The mole has a dome-shaped and convex shape. The color is usually brown. But over time, it may turn black and the surface may become covered with growths. It can be warty, neocellular and pigmented.
Difficult
This is an average between the border and intradermal formation. The intersection is no more than 1 cm. The top is covered with papillomas.
Galonevus
Has spotty pigmentation around it, twice the size of the mole. It is observed in children at the stage of adolescence or in pregnant women. Education may disappear.
Formed by balloon cells
It differs from other types in structure. Its presence can be determined using laboratory diagnostics.
Recurrent type
It appears at the site of incorrectly removed moles of dermal origin. It is significantly larger in size than the previous formation.
Epithelioid (spindle cell)
Occurs in children. A dense nodule in the shape of a hemisphere. Nevus is skin-colored or pink. But it can also be brown with a reddish tint.
It is usually localized on the right or left cheek. A subspecies is considered to be the blue-black nevus of Reed. It appears on the hip area or legs in women.
Melanocytic dermal formations
Only dermal cells take part in the origin of nevi. The group is characterized by 4 types of formations.
Simple
A blue mole without hair. The main colors are black and gray with a hint of blue. Maximum size 1 cm.
Cellular
A mole differs from a simple one in size and the richness of its blue hue. The diameter can reach 3 cm. It is located on the buttocks and lower back. Rarely on the surfaces of the hands and feet.
Combined
Combines the features of simple, intradermal, complex and borderline types. The appearance is determined by the degree of borrowing from one of the formations.
Deeply penetrating
They are similar in appearance to a blue nevus. The type is characterized by a mixed structure of complex, blue and Spitz formations.
Harmless dermal melanoses
Benign nevi look like blue moles. The group includes 3 types of dermal melanosis.
Mongolian spot
A common formation of the Mongoloid race. Often manifests itself in representatives of the black population.
The occurrence of such a nevus occurs in only 1% of Caucasians. The size can reach up to 1 dm. The color is gray with a blue tint or brown. Closer to reaching the age of fifteen, it almost always disappears.
Nevus of Ota
Pigment spots in the eyes and cheekbones. The type can reach large sizes and change the color of the eye whites, lips and palate. Common among Asian peoples. It appears in most cases in girls.
Nevus Ito
A birthmark that differs from Oto in location. The localization area is the lateral surface of the neck.
Congenital
Verrucous nevus appears in 1% of children immediately after birth or after 1 week. It differs in size:
- small. Maximum size 1.5 cm;
- medium (from 1.5 to 20 cm);
- giant from 20 cm.
It is located in the form of a large mole on the back, stomach and pelvic area. Increases with the age of the child.
Clark's nevus
An atypical nevus is at risk of malignancy and has a chance of developing into melanoma. Manifestation occurs mainly during or before puberty.
Irregularly shaped spots no more than 5 cm. The edges may be reddened. It is usually localized in the upper part of the body (head, back, etc.).
Epidermal
The classification also includes benign tumors on the body. Their main difference is in their structural features.
They do not contain nevotsit and melanin. The similarity lies in the reasons for the manifestation of epidermal nevi. But other epidermal cells are involved in their development.
Formations are formed in the first year of a child’s life and are linear in nature. They appear most often on the bends of the limbs and on the head. They are usually dry to the touch and flaky.
System form
Verrucous nevus does not have a clearly limited area of location. It is located along the body and in appearance resembles a garland. Its characteristic symptoms include:
- This formation can be located on almost any part of the body. Most often it can be found along large vessels.
- Such moles are usually elongated. In one place, several formations are found that occupy a large area.
- The upper keratinized layer has a heterogeneous color (usually dark brown).
- The surface of the mole has a granular structure.
- If you touch the bump on the skin, you find that it is hard.
Diagnostics
Only a specialist can distinguish a warty nevus from other types of skin formations. Visually, it can be very similar to lichen ruber or coal-shaped moles. Therefore, only a dermatologist can make an accurate diagnosis based on various diagnostic procedures:
- Visual inspection. The size, structure, color and other external characteristics of the formation are assessed. It also determines whether they change over time and how much.
- Examination of a smear taken from the surface of a nevus. This procedure is relevant if blood or other liquid is oozing from the formation . A smear analysis allows you to determine the type of cells that are on the mole.
- Luminescence microscopy. It involves examining the formation under a microscope with preliminary application of a special composition to its surface.
- Biopsy. Histological examination allows us to determine whether a given formation is benign or malignant. To do this, it is completely removed from the patient's skin.
Removal of verrucous nevus
Eliminating wart growth is not easy:
- local drugs only reduce the inflammatory process in the tumor area and alleviate the feeling of discomfort;
- give an exfoliating effect;
- surgical methods of destruction do not always guarantee the absence of relapses, and with deep removal they leave scars;
- large growths require multi-stage sessions and procedures.
Removal of a warty nevus occurs using conventional techniques:
- Electrocoagulation is a possible method, but already outdated; the current burns nearby tissues, and the healing of burn wounds is delayed. Afterwards, noticeable scars remain, and the risk of tumor regrowth is high.
- Dermabrasion is a mechanical peeling method that removes the surface layer of growth. It brings temporary relief, but relapses often occur after its use. If the procedure is carried out too deeply, noticeable scars remain.
- Laser removal. Warty nevus responds well to laser, and even with large sizes, healing is successful. Sometimes the process slows down on the legs and back.
- Removal by cold. The structure of a warty nevus allows it to be eliminated by cryodestruction using liquid nitrogen.
- Surgical removal is the most accessible and profound method. Its advantage is that you can freely conduct histology of the tumor to find out whether it poses a danger to the body. The only drawback is the scars.
- Using the radio wave method, the nevus is bloodlessly eliminated along with a flap of skin or just the formation itself; the depth of penetration is determined by the doctor.
You should not remove the nevus yourself; the attempt will most likely be unsuccessful. Means that are intended to destroy other skin formations will not be able to penetrate to a sufficient depth, therefore, a relapse is possible or an unaesthetic scar will remain. If its removal is unsuccessful, the risk of degeneration into melanoma increases significantly. Therefore, at the slightest damage to the growth, you should consult a dermatologist.
Removing a warty growth is not as easy as it seems. There is no universal method that would help everyone. The doctor selects therapy on an individual basis. This may be either removal of the growth or drug treatment. Often both are combined. Therapy helps improve skin condition and minimize discomfort.
Advanced stages of the disease sometimes require multi-level, complex treatment regimens. It all depends on the location of the growth and its neglect. If the nevus is at the first stage of development, it is recommended to remove it surgically in the clinic. It is necessary to observe the golden mean: if the nevus is excised shallowly, a relapse may occur; if the nevus is excised too deeply, noticeable scars may occur. The following removal methods are used.
| Methodology | Nuances | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dermabrasion | During the procedure, shallow layers of the dermis are affected, so the disadvantage is the possibility of relapses. If the doctor penetrates the device too deeply, this is fraught with massive scars at the site of exposure. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cryodestruction | After the procedure, swelling at the excision site and spots from light to dark shades are possible. Most often, spots heal slowly. The procedure is optimal only in the first stages of the disease. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laser correction | This is the most optimal treatment option for skin diseases. New generation devices allow you to select the desired depth of penetration of the laser beam under the skin. For small tumors, even one session will be enough. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radio wave method | Frequently used method. However, compared to a laser, it is not entirely convenient due to the inability to choose the ideal penetration depth. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Treatment options
Doctors often recommend removing verrucous nevus. This is due to the fact that this formation is susceptible to injury due to its specific shape. There is also always a risk of its malignant degeneration. But the removal of such a mole should occur exclusively in a medical facility. Several methods are used for this:
- Laser removal. It is carried out only in cases where the warty nevus is eliminated for aesthetic reasons. After the procedure, there are no scars left on the skin.
- Surgical intervention. A classic method for removing nevi, which allows subsequent histological examination of the resulting samples .
- Radio wave surgery. Refers to the most gentle methods. When removing formations that occupy a large area, sutures are applied.
The choice of a specific method of performing a mini-operation is chosen by the doctor based on the patient’s condition and the nature of the formation.
Features of care for verrucous nevus
Warty nevus is divided into subtypes, differentiation occurs:
- according to the drawing;
- distribution features:
- presence of inflammation.
Usually the plaques are located in one part of the body and are small in size. It is a dark brown or yellowish warty growth. Among them you can see soft ones with a dark velvety surface. The growth consists of several tubercles located very closely, with a flat top.
This is the name for the type that is located on one side of the body. It resembles linear garlands on the limbs or is located in bunches on the body. Spreads in areas along Blaschko lines, alternating with clean skin. It happens that a skin formation covers the human body, going down from head to toe.
The form extends to equal areas of the body, being located on both sides of the body, usually symmetrically. It refers to extended growths and causes significant aesthetic discomfort to a person. The elements also extend along Blaschko's lines; the growths can be of different lengths, but the species is characterized by an arrangement strictly up to the middle of the body. Sometimes several growths merge into one large element.
This type is characterized by the presence of inflammation. This type is always located on one side: usually observed in the lower half of the torso and limbs, often in the gluteal region. It is distinguished from the classic warty nevus by:
- more scales;
- it is accompanied by itching;
- redness.
It is often confused with lichen planus and linear lichen or manifestations of psoriasis, although these are completely different diseases. Sometimes a histological examination is required to clarify the diagnosis.
If elements of a wart nevus are found on a patient’s body, doctors suggest removing it to remove the cosmetic defect.
If the patient for some reason does not want or cannot do this, then he must follow a number of rules that will help avoid the development of complications.
The basic rules are as follows:
- Eliminate factors that may cause overheating of moles. Prohibited: visiting saunas, baths, spa treatments.
- In the warm season, avoid being under the rays of the sun during the hours of its greatest activity: after 10 a.m. and before 4 p.m. Avoid visiting the solarium. It has been proven that protective agents cannot prevent the development of melanoma;
- Before taking hormonal medications, you should first consult with a specialist.
- Monitor the condition of the nevus elements and consult a doctor at the first symptoms of malignancy of moles.
You should pay attention to the following changes:
- accelerated nevus growth
- the appearance of unpleasant sensations that were not there before: pain, itching, burning, etc.
- change in the color of the neoplasm, it may become multi-colored
- appearance of peeling
- formation of cracks on the nevus
- hair loss
- asymmetrical growth, torn edges
- acquisition of granularity by a mole
- formation of outgrowths
- the appearance of discharge of various types
If at least one of the above symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If treatment turns out to be timely, then birthmarks will not pose a danger to a person in terms of malignancy.
And modern treatment methods will eliminate the presence of discomfort, both physical and cosmetic.
It is important to understand that self-medication can cause irreparable harm to health.
Removal of tumors should only take place in a medical facility and be carried out by a specialist.
Doctors' recommendations
If there is a verrucous nevus on the body, and a person does not plan to remove it, it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations to prevent the development of malignant processes:
- It is advisable to avoid visiting bathhouses and saunas. It is also not recommended to carry out any warming procedures at the site of the skin defect.
- It is forbidden to sunbathe a lot, especially in a solarium.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight between 11 and 16 hours.
- When staying outdoors during periods of high solar activity, it is advisable to cover the areas where the nevus is located with a light cloth.
- Before visiting the street, it is advisable to apply a special sunscreen to the area of skin where this defect is located.
If the nevus has changed its color, shape or structure, you should not hesitate to consult a doctor. This is a very alarming symptom that indicates the development of certain complications. Folk remedies for the treatment of warty nevus are not used due to the high risk of damage to the formation and its degeneration into malignancy.
When to delete
Sometimes the doctor strongly recommends removing a warty nevus, in which cases this happens:
- The reason is a cosmetic problem that creates psychological discomfort for a person.
- During the examination, the doctor determines the possible risks of the skin lesion degenerating into melanoma.
- Sometimes a specialist suspects that a nevus has developed into melanoma or sarcoma, but based on external signs it is not possible to exclude the disease.
The criteria for assessing danger are:
- deviations that appeared:
- color change;
- loss of clarity of boundaries;
- proliferation;
- asymmetry.
When signs appear on the surface of the nevus, you should consult a doctor.
Removal of a verrucous nevus is carried out using one of the following methods.
Surgical excision of moles is a classic method of ridding a patient of skin tumors.
After anesthesia and antiseptic treatment of the skin and surface of the nevus, it is cut out with a scalpel.
Then the wound is treated with a disinfectant and a sterile gauze bandage is applied.
This technique has negative aspects: infection of the wound surface and the formation of a postoperative scar are possible.
Removal of a nevus using radio wave radiation - this technique has many advantages:
- the ability to control the depth of exposure to radio waves, which avoids damage to healthy tissue around the tumor
- absence of bleeding due to their coagulation
- the procedure is painless
- the procedure is carried out very quickly
- radio waves can be used on any area of the skin
- There are no negative consequences after surgery
Laser therapy is one of the most common.
The laser beam can be used for keratotic moles on the scalp, as well as in the facial area.
Benefits of using laser:
- it is impossible for infection to penetrate at the site of exposure
- Coagulation of the wound eliminates the development of bleeding
- after removing the growth, a crust remains
- the risk of scarring is minimal
Removing nevus with liquid nitrogen: the use of low temperatures allows you to remove small tumors.
The procedure is painless.
Pain appears some time after exposure to nitrogen.
A disadvantage of the technique is also the need for repeated sessions, since the technique does not allow accurately calculating the time of exposure of the pathological tissue to nitrogen.
Electrocoagulation method - high frequency currents are used for treatment.
Before removal, the doctor administers local anesthesia.
As a result of exposure to electric current, a crust forms at the site of removal, which protects the wound from infection.
If for some reason there is an injury to the nevus or signs of degeneration of the tumor appear, then urgent consultation with a specialist will be required.
People don't always know where to go with such problems.
The choice of specialist depends on the purpose of the visit.
- To carry out the examination, it will be enough to go to an appointment with a dermatologist. This specialist conducts an appointment at the district clinic. The doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe an examination, and then, based on the results obtained, tell what to do next. You may need to visit an oncologist.
- If the nevus is damaged, drug therapy or alternative treatments may be prescribed. If there are signs of malignancy, you will have to undergo some tests.
- In case of mechanical damage or degeneration of the mole, removal is carried out. This can be done by a surgeon or oncologist.
Often people with a problem go to a cosmetologist.
It is better not to do this, since this specialist will not be able to conduct a high-quality examination of the patient and prescribe treatment without a medical education; he does not have the right.
In addition, you can miss precious time and the process will become malignant, which can have negative consequences and even cost the patient’s life.
If you are concerned about a warty nevus, contact the author of this article, a dermatovenerologist in Moscow with many years of experience.