Types of birthmarks
A child may have a wide variety of birthmarks on his body - smooth or covered with fluff, reddish or brown, convex or flat. The main types of birthmarks in newborns are nevi and angiomas.
What shade can nevi be?
Nevi are among the most common types of skin marks. They usually come in a variety of brownish shades, ranging from dark brown to pale. The basis of nevi are melantocytes. These epidermal cells contain melanin, a pigment that affects skin tone. It is necessary to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation. Sometimes these cells are localized in one place, which leads to the appearance of a mole. Dark birthmarks indicate an abundance of melanin, while light ones indicate a lack of it.
A Mongolian spot in a newborn should also not be a cause for concern for parents. It is also a place of concentration of melanin and is a spot, or several spots of different sizes from 1 to 10 cm in diameter, blue, green or even black. The most common location is the baby’s lower back, mainly the tailbone or butt. Mongolian spots are safe, they do not cause any discomfort to the child and go away on their own before adolescence. This type of nevus is named so because of their frequent detection in Mongolian children (90%), Mongolian spots are also often found in Asians, representatives of the Mongoloid and Negroid races.
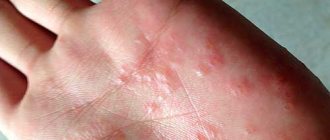
There are also white formations. These include anemic nevi that arise due to underdeveloped blood vessels.
They need to be distinguished from millet grasses - milia. The latter look like convex dots filled with whitish content. They are a type of skin rash. Anemic nevi are a congenital phenomenon, and they are easy to identify: you need to rub the spot. The surrounding skin will turn red, but the formation will remain white.
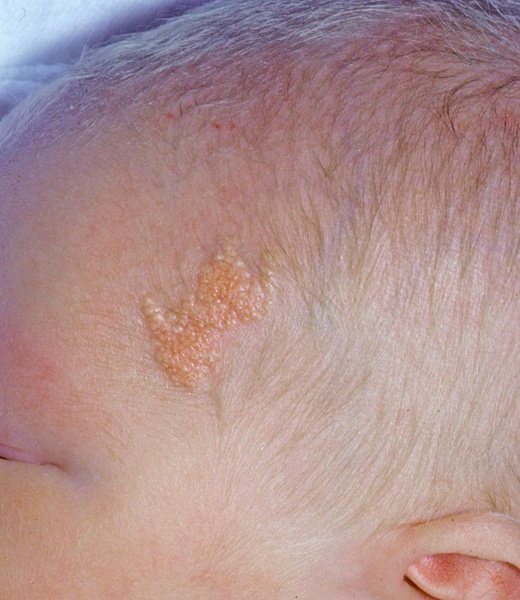
Light brown Jadassohn nevi indicate a congenital defect of the sebaceous glands. They are usually found on the baby's head, under the hairs. This occurs in 3 out of 1000 babies. It is recommended to remove it before adolescence, since in 10-15% of cases, they can subsequently develop into a cancerous tumor.
What if it’s a matter of blood vessels?
Another type of birthmarks is angiomas. They are of vascular nature. Congenital formations of small vessels on the skin are called hemangiomas. If such accumulations form in the lymphatic system, then they are classified as lymphangiomas. Even congenital, they appear externally only by the age of three.
In a newborn, only vascular hemangiomas can be detected. They are distinguished by a whole range of shades of red. Such formations are divided into several subtypes:
Strawberry (strawberry) hemangioma
These formations are convex, similar to red “berries”. They appear immediately after birth, usually on the face. The sizes can be different - from a millimeter to several in width. Strawberry hemangioma can increase in size, which is why it is dangerous, as it can affect the healthy tissues of the child.
Often this type of hemangioma stops growing, gradually brightens, shrinks and disappears completely by the age of 10.
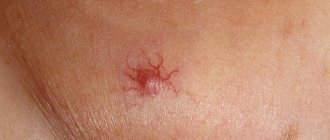
Stellate (spider) angioma
It looks like a star with a bright base and “rays” extending from it. Most often it occurs on the child's neck. Disappears on its own in the first years of life.
Cavernous hemangioma
Loose, purple hemangioma, deeply embedded in the skin. It feels warmer to the touch than the surrounding epidermis. If you press, the baby will cry due to unpleasant sensations. This type of neoplasm requires treatment.
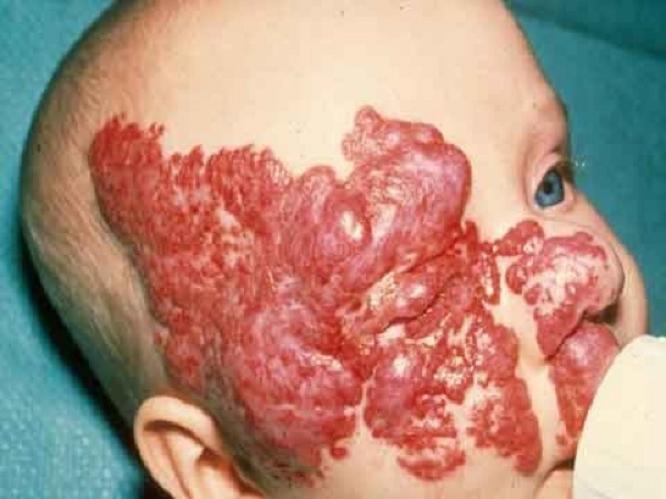
Flaming (fiery) nevus
Looks like a red or purple stain from spilled wine. It can appear anywhere on the baby’s body. Such formations do not go away on their own. If they are not removed, they will remain for life. If the “wine stain” is in a visible place or continues to grow, it is better to take the trouble to correct the defect.
“Stork marks” (capillary hemangioma)
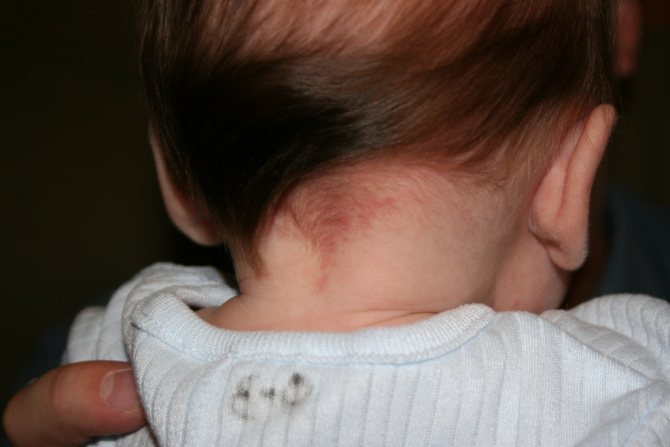
Such marks are also called “stork bites.” And if there is a mark on the baby’s forehead - “an angel’s kiss.” The formation is usually pink or red, but can also be orange, and resembles the mark of a bird's beak, which is how it gets its name. The formation is flat and does not rise above the skin. It is often found on the back of the baby’s head, in the neck area. When stressed, for example, when a baby cries, it acquires a brighter color. By the age of two, “stork marks” in most cases go away on their own.
In addition to the above, there are other types of birthmarks. But they are much less common.
If you notice that a child’s hemangioma is increasing in size, immediately contact a specialist (surgeon). He will be able to assess the danger of the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment or removal of the tumor.
Why may a white spot appear on a child’s skin, what does this symptom mean?
The white spot symptom is observed during asphyxia in newborns, as well as during severe shock conditions. This property was discovered back in the year by neurologist researcher Manteuffel. Following him, the symptom was described in detail in their works by Laignel and Levastin in the city.
The symptom is often a sign of obliterating endarteritis or neurointoxication. In states of shock, acute oxygen deficiency, a white spot can remain on the victim’s forehead or finger for more than 20 seconds. Manteuffel's symptom, or in another way - the white spot symptom, indicates a lack of blood circulation in the capillaries of the lower and upper extremities, caused by heart problems or lack of oxygen.
It is observed in shock conditions due to blood loss. On the finger in the middle of the nail bed, when you press on the end of the nail, a clear white spot will expand and contract. The same spot will appear on the feet near the toes when you press your finger on the skin.
A positive symptom is determined if the stain lasts for at least 3 seconds. Why does the stain stick around and not go away immediately after pressing? This occurs due to increased excitability of the autonomic nervous system during shock.
Sometimes complications occur during childbirth: the fetus is entangled in the umbilical cord, malpresentation, or other reasons. Such accidents during childbirth lead to the fact that the child lacks oxygen and is born with asphyxia. In this case, breathing and heartbeat may be completely absent, or breathing may be intermittent and inconsistent. The Apgar score is an overall assessment of a newborn's suffocation in the first minute of life. Based on the symptoms described in the table, doctors can differentiate between mild, moderate and severe asphyxia of the newborn.
White spot syndrome is present in severe to moderate suffocation. Within a few seconds of pressing on the heel, the stain does not go away. If breathing is extremely weak and there is no heartbeat, the neonatologist must take urgent measures to restore breathing and heart rhythm.
With timely assistance, the child quickly restores respiratory function. However, it is necessary to conduct some research and find out whether damage to brain tissue began from a lack of oxygen. Hypoxia from Greek - lack of oxygen in ancient Greek. People say - suffocation. It happens in children and adults, for example, with carbon monoxide poisoning.
The following signs may indicate suffocation:. Due to lack of air in the blood, the capillaries in the extremities immediately suffer. One of the characteristic signs of hypoxia is the studied manifestation lasting 3 seconds. Pressure should be applied to the base of the toes 1-3 and held for about 2-3 seconds.
According to the international ICD code, severe asphyxia of newborns is coded P. Heartbeat less than beats per minute. If the asphyxia is mild, and the newborn does not have a white spot symptom, then the doctor may not write this diagnosis into the child’s chart at all and may not take any special measures. In cases of shock due to severe fractures, knife wounds and blood loss associated with injury, it is imperative to check the white spot symptom.
If it is, it means that the body has already lost a lot of blood and is experiencing a lack of nutrients and oxygen. Any shock occurs in 2 phases. The shock reaction begins with the erectile phase, when psychomotor agitation increases.
Then comes the torpid phase, when the pressure gradually drops. The normal symptom of a white spot is literally a couple of seconds. If the mark persists for more than 5 seconds, then the second phase begins with a drop in cardiac output and the skin becomes paler. The shock caused by a heart attack, or cardiogenic shock, results in a sharp decrease in cardiac blood output.
In case of shock, qualified first aid is necessary for the patient. His skin becomes damp, cold due to the drop in temperature, and acquires an unusual marble shade. The pressure drops sharply and the person loses consciousness. The white spot symptom in shock caused by a heart attack is useless to check. Neurointoxication due to poisoning or infection will also be stressful for the heart.
The symptom of a white spot with shock of the 3rd degree will also be observed. In addition, other striking symptoms will be present:. First aid for severe intoxication is to induce vomiting. And immediately call an ambulance. In addition to the listed signs, in an emergency situation you have to deal with a pale gray tint of the skin, which is usually typical for diseases with bacterial intoxication.
The color of the skin must be compared with body temperature, as this helps to assess the severity of the fever and its prognostic value. An increase in body temperature, combined with pink, hyperemic, hot-to-touch skin, usually proceeds favorably and does not require emergency treatment. At the same time, the doctor should be extremely alert to fever accompanied by pale and cold skin.
It is necessary to differentiate between allergic, hemorrhagic and infectious exanthemas. Prognostically, the most unfavorable is a pinpoint hemorrhagic rash during meningococcemia, localized in the area of the inner thighs and in the lower third of the anterior abdominal wall. This rash should be looked for purposefully in case of hyperthermia of unknown origin, especially when it is combined with lethargy and lethargy against the background of tachycardia and arterial hypotension. Examination of the neck reveals a number of threatening signs, the most important of which include swelling and pulsation of the neck vessels, participation of the deep muscles of the neck in breathing, deformation of the neck and the presence of tumor-like formations in this area.
Swelling of the veins of the neck indicates difficulty in cardiac return, the cause of which is differentiated by the nature of the venous pulse.
Positive venous pulse is one of the symptoms of cardiac... Percussion of the chest Percussion of the chest should solve two problems: to determine the position of the mediastinum and to determine the nature of the percussion sound over the pulmonary fields. Hence, first of all, it is necessary that it be comparative and include the definition of the boundaries of cardiac dullness.
During comparative percussion, attention is paid to the boxy nature of the pulmonary tone and its dullness. In combination with mediastinal displacement, these... With toxic pneumonia, intestinal paresis is combined with symptoms of severe hypoxia, and limited mobility of the diaphragm also contributes to an increase in oxygen deficiency.
Unlike pneumonia, with primary peritonitis there are no signs of hypoxia, but the child has a painful abdomen, swelling is localized in the pubic region. There is also hyperemia of the skin. If the child is restless, kicking his legs, then you should check whether he has... An emergency physician does not directly hospitalize a patient.
If necessary, depending on the severity of the child’s condition, he calls ambulance transport, leaving a referral for inpatient treatment, or an ambulance, thereby ensuring transportation accompanied by a doctor.
If a patient has decompensation of vital functions, the emergency pediatrician should begin primary therapy and at the same time call a specialized team...
When pressing with a finger on one or another area of the skin of the subject, a white spot appears, the color intensity and duration of manifestation of which depend on the strength, duration of pressure, the state of blood flow in the capillary network and the innervation of the vessels.
Most often, the symptom is detected on the back of the foot near the base of the I-III toes. Rusetsky suggests applying pressure for 3 seconds, after which, normally, a white spot appears at the site of pressure, lasting 2-3 seconds.
In various vascular diseases caused by impaired sympathetic innervation, when the excitability of the autonomy of the nervous system increases, the white spot disappears more slowly. This symptom is considered positive when there is a slowdown in the disappearance of the white spot.
It is often observed in obliterating endarteritis and other vascular diseases of the extremities. The symptom was described by the German neurologist Manteuffel in the city.
Refers to alternating syndromes. It consists of complete or partial paralysis of the oculomotor nerve and extrapyramidal hyperkinesis in the limbs on the side of the lesion: On the opposite side there is mild spastic hemiparesis and damage to the red nucleus.
It is possible that sensory disorders may occur due to the involvement of sensitive conductors in the pathological process. Deviation of gaze towards the hearth. The syndrome is caused by the localization of the pathological focus in the medial-dorsal part of the midbrain with the preservation of the pyramidal fasciculus.
Described by the Austrian neurologist M. Benedikt in the city. It is caused by percussion of the brachial process of the clavicle; At the same time, flexion of the forearm is noted. The physiological reflex increases when the pyramidal tracts are damaged. Although the spots themselves are harmless, you need to know that in some cases they indicate the presence of congenital diseases, and quite serious ones at that.
MedAboutMe tells you all about unusual marks: why they appear, what they indicate, and what to do if they don't disappear with age. It is impossible to prevent the appearance of stains, nor can it be predicted. It is not clear why some children develop them, while others, even from the same family, have nothing. In general, the professor’s theory was justified: congenital melanocytosis appears much more often in people with dark skin.
My mother-in-law said that all the boys in their line have this, it seems that it appeared after my great-great-grandfather, who was originally from the Far East. Mongolian spots usually appear on the back and buttocks and occur with equal frequency in boys and girls. These are accumulations of pigment in the deep layers of the baby’s skin, and due to the difference in the amount of pigment and the color of the skin, they can be blue, greenish, gray, almost black.
The pigmented areas of the spots are flat and smooth and may look like bruises. But, unlike bruises, they do not change color after a few days, do not cause pain, and are not the result of injury. These are birthmarks, although with their own characteristics. Mongolian spots themselves do not pose a health risk.
They do not require special attention or care.
The white spot symptom is observed during asphyxia in newborns, as well as during severe shock conditions. This property was discovered back in the year by neurologist researcher Manteuffel.
Causes of skin formations
The reasons for a birthmark in a newborn, of course, are not that his mother loved to pet dogs and cats, as the ancients believed. However, scientists cannot say exactly why such marks may appear. Only risk factors for their occurrence have been identified.
Why do birthmarks appear in newborns? This is affected by:
- Hereditary factor;
- Hormonal surges in the expectant mother;
- Exposure to toxic substances on the body of a pregnant woman;
- Bad ecology;
- Climate change;
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
But it happens that a birthmark appears in a newborn even without exposure to risk factors.
Possible causes of red spots on a child's skin
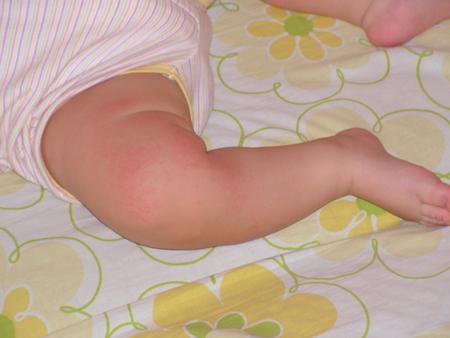
allergic reaction;- infectious diseases;
- hereditary diseases;
- changing care settings;
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system or other organs (kidneys, pancreas, liver, intestines);
- reaction to an insect bite;
- prickly heat.
Birthmark on a baby: what to do?
Is your baby's birthmark small, smooth, does not grow and does not cause concern to the baby? Everything is fine, nothing to worry about. But you need to take the new growth seriously. Observe the nevus and notice whether the mark grows or hurts. If changes occur, you should visit a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist.
If a newborn has a birthmark on his body, several rules should be followed:
- Keep this area away from direct sunlight.
- Make sure that the baby does not scratch the area with the mark.
- Try to ensure that the nevus is never exposed to caustic substances, such as household chemicals.
In rare cases, marks on the skin can be fatal. Where can it appear? Under the influence of negative factors, a simple mole degenerates into a malignant formation - melanoma. Therefore, if the spot increases in size, you should urgently contact a specialist. If the formation is removed in time, there will be no health consequences.
Should moles be removed from babies?
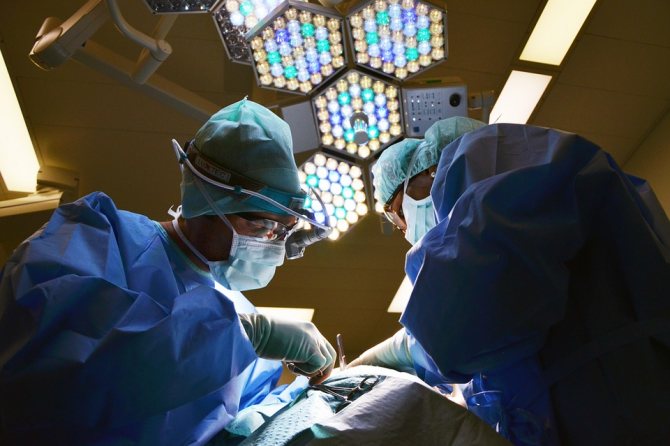
In babies, the immune system is not yet very developed, and any intervention can lead to serious consequences. In what cases do doctors recommend surgery at an early age:
- The birthmark is very large;
- The formation rapidly increases in size;
- There are more than five marks, and they are concentrated in one place;
- The mole is located in a traumatic place (under the armpits, on the belt, on the skin of the eyelid, in the anus);
- Nevus interferes with the normal functioning of organs (on the hand, in the nose, in the eyes).
Particular importance should be given to those cases if a mole transforms - changes color or shape, grows, hairs fall out of it, it begins to bleed or itch.
How to remove rashes
Red pimples on a newborn's face look different. They can cover the entire facial skin or be localized in one place.
In order for the rashes to disappear, you need to keep your skin clean and dry. It is undesirable to treat them with alcohol tinctures, which are harmful to the child.
It is better to arrange a visit to the pediatrician and consult. Most likely, your doctor will advise:
- Get diagnosed and examined. Only after a set of measures should we engage in prevention and treatment.
- Adhere to the mother's strict diet while breastfeeding (if the cause of the rash lies in allergies).
- Bath exclusively in decoctions of medicinal herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect. This could be chamomile, calendula or string, which eliminate redness.
- Pay attention to the mixture and change the diet if the baby is on artificial or mixed feeding.
- Apply Bepanten cream to the baby's face.
- Wipe pimples with Furacilin.
Age spots on the face: causes and treatment
Rashes of an allergic nature are removed with antihistamines only after the instructions of specialists in the field of allergology and immunology.
Note! Only a doctor can give specific advice about treatment. You cannot “prescribe” diagnosis and therapy on your own.
How to get rid of formations?

The doctor may recommend one of the methods for removing nevi, depending on the size and condition of the formation, as well as the health of the baby:
Use of pharmaceuticals
Special medications are injected into the mole tissue to promote the death of overgrown cells. No anesthesia is required, but is not suitable in case of allergy to the active substances of the drug.
Using a laser
Excision of pathological tissues with a laser beam. It is quick and painless, but the procedure is not always possible for hard-to-reach areas.
Cryotherapy
Exposure of the mole to low temperatures. Suitable for eliminating small nevi.
Surgery
Removal of the formation using surgical instruments. It is used in cases where other methods cannot be used.
Carrying out the intervention under the supervision of a doctor, with preliminary examination of the tissues of the birthmark, reduces the likelihood of complications to zero. After removal of large formations, scars may remain. If they are located in a visible place, when the baby grows up, you can remove the scar using cosmetic procedures.
If you believe in fate, try telling your baby's destiny using moles. But pay attention only to happy signs:
- A mark on the baby’s cheek means love;
- A spot under the hair means high intelligence;
- Moles on the hands - to talents and good luck;
- Nevi on the back - to a life without worries;
- Mark on the leg - to hard work, calmness, confidence;
- A “sign” on the butt means success with the opposite sex.
As you can see, a mole is not a reason to panic at all. With the right approach, it will not be the cause of illness, but a happy sign that emphasizes the individuality of your son or daughter.
Remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis; do not self-medicate without consultation and diagnosis by a qualified doctor.
Skin spots
What to do if you notice an unknown spot on your baby’s skin? Be sure to contact your pediatrician: he will determine which category it belongs to and whether the child will need treatment. The spots that you may find on your baby's skin usually belong to one of the following groups.
Cafe-au-lait pigment spots Usually they are not very noticeable, although sometimes they are the size of a five-ruble coin. Most likely, they will stay with the baby for life. If you notice more than five of these spots, consult a doctor.
Dark birthmarks—various shapes, sometimes covered with hairs—can appear on any part of the body. They also last a lifetime and are usually no hassle. You should consult your doctor if they begin to change shape or grow.
Nevi
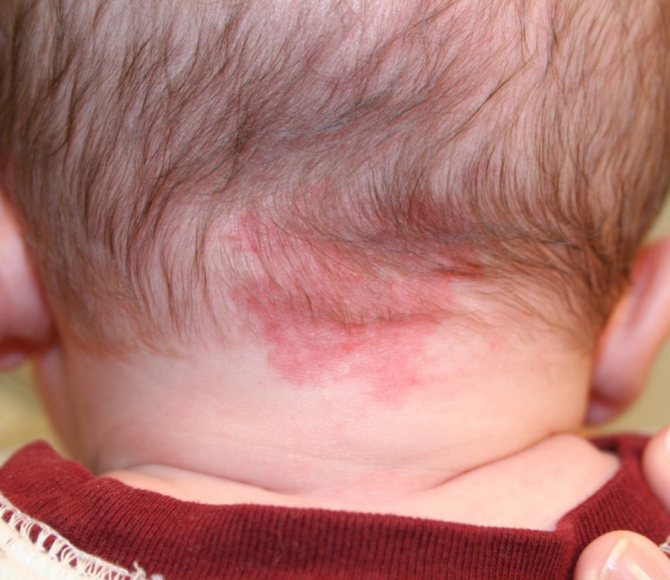
Nevi are moles or pigmentation that are brown or red in color. Most often, such formations appear in children aged two years or during puberty. It is less common to notice red spots on the face of a newborn baby.
Nevi can be of several types.
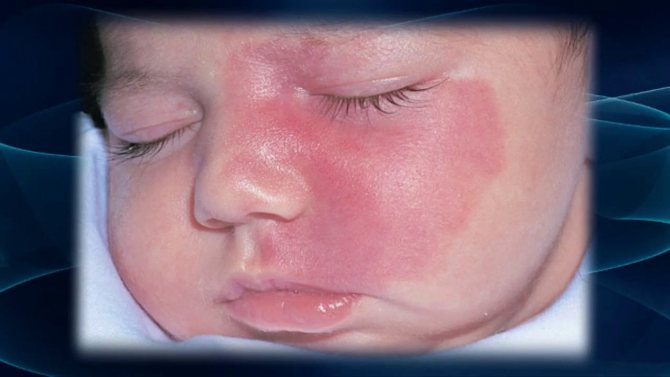
1. Simple nevus. They may present as red spots on the cheeks of infants and on other parts of the body. The sizes of formations may vary. Another name for the spots is Unna's nevus, or “angel's kiss.” The latter is used in everyday life. Unna's nevus can be located on the back of the head, forehead, area between the eyebrows, as well as on the tip of the nose and lip. The spots are located on the lumbar region and can be shaped like a triangle or diamond.
Simple nevi are harmless rashes. They are located on the skin without standing out above its surface. Over time, the color intensity decreases. As the year approaches, it disappears completely. On the face and lower back, nevi can persist for up to one and a half to two years. As a rule, if the child is in a calm state, the formations are barely noticeable. The color intensity increases during crying.
Birthmarks in the neck area persist longer. They may disappear in adulthood or accompany the child throughout his life. The spots do not require treatment. Parents need to know that nevi are an excellent background for the appearance and development of seborrheic dermatitis.
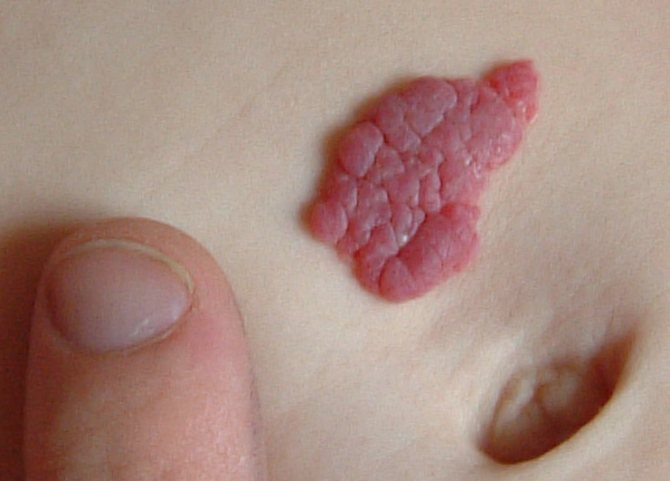
2. Fire nevi. They differ from simple formations. The spots do not lose color intensity. In addition, fiery nevi have an elevation above the surface of the skin. Convex spots change in size, increasing with the child. Formations can be located on absolutely all parts of the body. However, most often fiery nevi are located on the baby’s face. The formations do not become inflamed or bleed. There is no itching at the location of the nevi. With age, the convex spot acquires a bluish tint and is accompanied by the appearance of vascular nodules.
If a doctor has diagnosed a fiery nevus in a baby, parents should regularly visit a dermatologist and pediatrician. Observation is required. The presence of such education can cause a deterioration in the child’s quality of life, since it contributes to the appearance of complexes and interferes with normal communication with peers. If desired, the stain can be removed using a laser. Timely medical procedures will save the child from possible problems in the future.
Doctors draw a correlation between fiery nevi and brain disorders. That is why, in addition to the pediatrician and dermatologist, parents and their child need to regularly visit a neurologist.
Hemangioma: diagnosis and treatment
Hemangiomas can occur on the body of babies in any place and even go deep into the skin. They come in a variety of sizes and shapes: round and elongated, like stars or spiders. Hemangiomas are treated much more often than other spots on the skin.
Hemangiomas can be flat or convex. Convex - soft red formations - form in the last weeks of pregnancy or immediately after the birth of the baby: a red dot appears on the skin, which quickly increases in size. The child does not experience any unpleasant sensations from the growing spots; some tumors disappear on their own by 2–3 years. But if the hemangioma is located in an awkward place, such as under a diaper, irritation may occur due to friction. As for flat formations, there are almost no problems with them; they do not grow, and therefore there is no need to treat them.
Most often, hemangiomas are harmless: the spot does not hurt, does not itch, and even if it appears on the eyelids, lips or tongue (and this also happens), it does not affect the functioning of the organ. But it happens that hemangiomas become inflamed and become infected. And the fact that the unpleasant spot is gradually increasing in size is a strong argument for parents to quickly begin treating the baby. After all, even doctors cannot predict how quickly and how much a hemangioma will grow.
There are two ways to get rid of a hemangioma: either remove it surgically (with a laser), or act on its cells so that they die on their own. The first method is used in difficult cases, for example, when the spot grows quickly or goes deep into the skin. In other situations, doctors will most likely try to freeze the hemangioma - this method is called cryotherapy and is now considered the most effective.
The treatment procedure lasts no more than a minute: using a special apparatus, a small disk cooled with liquid nitrogen is applied to the stain. Under the influence of cold (and the temperature of liquid nitrogen is minus 196 °C!) hemangioma tissue is destroyed in just 7–10 seconds if the spot is on the mucous membranes, and in 20–25 seconds if it is located on the skin.
After a few hours, a flat bubble appears at the site of the hemangioma, which is replaced by a dry crust on the 5th–7th day. It disappears on the 25-30th day, leaving a pink scar, which after 3-4 months becomes almost indistinguishable from healthy skin. Using this method, it is possible to get rid of a small hemangioma in just one session, and a large one - in several procedures.

Skin problems and their solutions
Redness on the cheeks or a rash on the bottom occurs at least occasionally in any baby. We will tell you what skin problems bother babies most often and how to help your baby.
Diaper rash. This is redness of the skin on the butt, around the anus, in the groin and between the buttocks. It occurs due to moisture and friction if the mother changes the diaper too rarely (the temperature in an overfilled diaper can reach +40 °C!).
You need to change the diaper every 3-4 hours, and after washing the baby, leave him naked for 10 minutes so that the skin can breathe. You can apply baby cream or powder to the reddened areas (you cannot combine both products!). If the damaged area begins to get wet, rinse it with a decoction of chamomile or bay leaf and lubricate it with a drying cream with zinc oxide.
Diaper (contact) dermatitis. The problem is more common among girls than boys; artificial babies, allergy sufferers. The appearance of pimples with a whitish liquid on the baby’s butt, genitals and thighs (and before that, redness, swelling and peeling are possible) may mean that the diaper or detergent used to wash the onesies is not suitable for him. Wash your butt several times a day with running water, wipe it dry and lubricate it with a drying cream. Do not use wet cleaning wipes or, in extreme cases, diapers.
Prickly heat. If the apartment is hot and the baby sweats a lot, then a small red rash appears on his shoulders, back, and in the folds of the skin (on the butt and groin). Heat rash indicates that the baby is overheating, and since the work of the sweat glands is not yet established until the age of 2, sweat accumulates and clogs the ducts of the glands. Open the baby often, rinse it with warm water, and dress it in cotton clothes. A cream with zinc oxide will help soothe the skin.
Fungal infection. Harmful microorganisms and fungi can get into the damaged areas - then round reddish spots with fringed edges, pustules or ulcers will appear on the baby’s skin. The doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment for the baby: ointment, antifungal drug, vitamins, and means to strengthen the immune system.
Spots in newborns
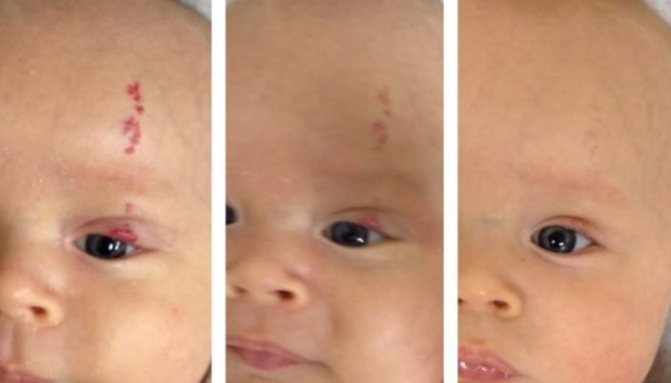
Vascular spots on the skin of infants cause concern among parents, because doctors are not always able to clearly explain the features of such marks. And vascular spots in newborns on the face or open areas of the body, as well as formations of especially large sizes and rich colors, become a cause of serious anxiety.
In fact, a vascular spot on the skin of a newborn does not always require anxiety and panic. Sometimes such a phenomenon is considered completely natural and transitory. So, doctors distinguish several types of such marks:
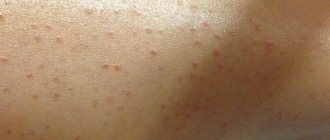
- Reddish bundles of choroid plexuses that are visible through thin skin. Such meshes are especially often visible on the head, namely on the eyelid, in the middle part of the forehead, and also on the back of the neck. Such spots are considered completely safe; they disappear without a trace or become noticeably pale when the baby grows a little, and his skin naturally becomes thicker.
Only a qualified doctor can accurately determine the cause of the appearance of red spots on the skin of a baby. Additional research techniques may be necessary.
How dangerous is redness on a baby's back?
If we talk about a common heat rash, we can say that it is not dangerous for a baby. But a constant feeling of discomfort does not allow the child to rest peacefully. The itching that haunts the baby day and night is annoying and unnerving. The child is constantly worried, crying, showing how uncomfortable he is. You need to fight prickly heat systematically and without unnecessary panic.
Urticaria, like miliaria, is a pronounced reaction to an irritant. It must be promptly identified and excluded from the child’s life. Hives do not pose any danger if you take care of your baby’s health in a timely manner.
As soon as parents see red spots on the baby’s back, they must immediately begin to search for and remove the cause. If you do not pay attention to them, over time the spots can develop into more serious skin disorders that will have to be treated with medication.
Telangiectasia
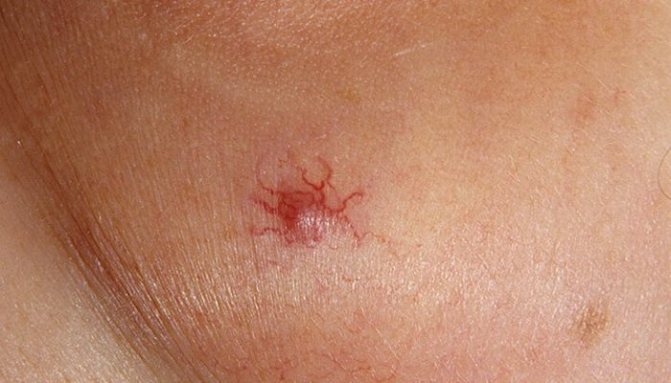
The occurrence of such formations is explained by the prolonged presence of the fetus in the mother's womb in a forced position (embryonic position). Shortly before birth, the baby is pressed tightly against the mother's muscular wall and the bones of her pelvis, and local ischemia (inadequate blood supply to tissues) may develop in areas of maximum pressure. As a result of this, the baby is born with red spots on the skin - areas of expansion of superficial vessels:
As a rule, as the baby grows, telangiectasias begin to gradually fade, becoming more noticeable during periods of great anxiety and tension. Most often, they disappear without a trace by the age of five years of a child’s life. However, there is a risk that such marks will remain with the baby for life.
Doctors usually do not provide targeted treatment for telangiectasia. The areas of dilated vessels are completely safe for the child, cannot increase in size and gradually fade.
It is important to consider that red spots on the back of the baby’s head, as well as on other parts of the body, even with all their similarity to “stork bites,” can be caused by other factors, for example:
- Birth trauma.
- Various skin diseases.
- Allergic reactions.
- Heat rash, etc.
Only an experienced specialist can accurately determine the cause of the appearance of red spots.
Causes of red spots and rashes
There are four main groups of sources of development of these signs in children:
- Diseases of an infectious and parasitic nature.
- Allergic reactions.
- Diseases of the blood and blood vessels.
- Poor hygiene.
Infectious diseases
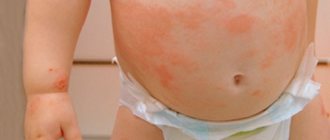
If an infection appears, then in addition to red spots, the child will have a fever , cough, chills, runny nose, nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, sore throat and stomach. Red spots of the rash may not appear immediately, but on the second or third day.
The rash accompanies infectious childhood diseases such as measles, rubella, chicken pox, roseola, scarlet fever and others.
Measles.
The incubation period of this disease is 9-17 days. The infected person is dangerous to others until the 5th day after the rash appears.
First, the child develops a high temperature of up to 40 degrees, which lasts for 4 days, cough with runny nose, photophobia, and conjunctivitis. On the fifth day, a rash appears in the form of pinkish spots, merging into irregular shapes. The rash covers the body from top to bottom - first it forms on the face, then on the torso, then on the limbs. In the photo with the description you can see characteristic spots. All this time the temperature remains high. The rash disappears, replaced by brown pigmentation and peeling spots.
Chicken pox.
The disease is common and contagious. Occurs from contact with a sick person or object.
The incubation period of the disease is up to three weeks, then there is a sharp increase in body temperature to 40 degrees, when the child becomes lethargic. Gradually, red spots form on the body, which turn into itchy blisters. The largest accumulation of them can be seen between the fingers, in the armpits, on the feet and in the oral mucosa. The red spots itch, especially at night.
In young children, the disease is not so aggressive. Sometimes the body temperature barely exceeds 37 degrees. There are times when it does not rise at all.
Rubella.
This disease is highly contagious. It can be infected by airborne droplets. A child can transmit the virus up to a week before the rash appears. Small pink spots spread throughout the body. The largest accumulations can be observed in the face, chest, and back of the child; there is a high probability of appearing on the oral mucosa. Red spots do not last long, after three days you can already forget about them. The disease rarely causes fever in children.
Scarlet fever.
This disease is caused by streptococcus. Symptoms include fever and sore throat. After three days, a small itchy rash appears on the child’s body. She especially loves to “settle” in skin folds, armpits, and groin. Only the nasolabial triangle remains devoid of spots. The fifth day of illness is characterized by pallor of the integument and the beginning of severe peeling.
Erythema.
This disease, with redness of the skin and irregular red spots or rashes, occurs due to a strong rush of blood to the capillaries. Its variety, non-physiological erythema of Chamera, is caused by a pravovirus.
From the first day, the infected person’s face becomes covered with a small rash, which gradually develops into a red spot. Then the rash spreads to the arms, legs, and torso. After some time, the red spots acquire a pale tint, after which they completely disappear. The illness lasts about 15 days.
Erythema Chamera is spread by airborne droplets.
Roseola
The disease begins with a high fever that lasts about 4 days. When the temperature drops, red rash spots begin to spread throughout the child's body. However, it is not itchy or painful. After appearance it disappears on the 4th or 5th day. The disease is caused by herpes virus type 6.
Allergic reactions
The first thing that comes to mind when we find red spots on a child’s skin is an allergy. The body’s reaction to an irritant can occur for the following reasons:
- Eating “wrong” foods, such as: eggs, shrimp, fruits or berries, juices, sweets. Milk allergy occurs in 2-5% of babies.
- Exposure to household chemicals, for example, powder, children's cosmetics.
- Contact with new items of clothing, toys, diapers, etc.
Diseases of the blood and blood vessels
The rash in these diseases occurs due to hemorrhages in the skin. Large bruises are painted in all the colors of the rainbow, but there is also a small reddish rash that spreads over the entire surface of the skin. The reasons are:
- A decrease in the number of platelets that participate in the process of blood clotting, as well as disruption of their work. This is often a congenital anomaly.
- Violation of vascular permeability.
Poor hygiene
In infancy, common diseases include prickly heat, diaper dermatitis, and diaper rash. They occur due to skin characteristics and frequent hygiene violations.
There is no need to over-bundle your baby. Try to keep your baby away from wet diapers. You should frequently bathe and wash your baby and leave his skin uncovered, thereby providing air baths.
So, what should you do if you notice a rash with red spots on your child's body? You should call a doctor at home. This is necessary so that in transport and in the hospital you do not infect others if the infectious basis is confirmed. Moreover, rubella is especially dangerous for pregnant women. Call an ambulance immediately if you suspect a meningococcal infection or if you notice subcutaneous hemorrhage. Before the doctor arrives, do not treat the red spots of the rash with brilliant green or other dyes; this will not improve your health, since the cause is internal, and it will be more difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis.
Red spots on the body in children
Hemangiomas
Hemangiomas of various types occur in almost every tenth child. Such tumors are a type of birthmark and are abnormally multiplied endothelial cells from various types of vessels. To date, the exact cause of their occurrence is not yet known to doctors, but experts suggest that hemangiomas arise due to disturbances in intrauterine development at the stage of formation of the fetal circulatory system.
Fortunately, such a birthmark most often resolves on its own before the age of seven (maximum ten years), but in some situations there is a need for targeted therapy.
Hemangiomas can be localized in different parts of the body, but in the vast majority of cases they are found on the head, namely on the face, eyelids, neck or forehead. Their color and shape may differ and are determined by the initial structural features of the vascular wall. A birthmark may not be larger than the size of a pinhead, or it may reach up to one hundred square centimeters. There are light pink neoplasms, dark red, deep scarlet, burgundy, etc. Removal of hemangioma is carried out:
- With rapid growth or large size.
- High risk of malignancy.
- When localized near the eyes or ears.
If you find a birthmark on your child’s skin, you should definitely consult a doctor. The specialist will determine the type of formation and, based on the data obtained, will be able to make a decision on further therapy.
How to prevent spots from forming on your baby's back?
- Maintaining baby hygiene from the first days of life will help avoid the appearance of redness. Bathing a child should be every night. Each time you need to thoroughly rinse your skin after using cosmetic foams, gels and shampoos. It may be wiser to wash your newborn with regular baby soap with string or chamomile. No matter how much manufacturers try to convince customers that their product is safe, their main goal is to sell. And the task of parents is to protect the child from unnecessary negative influence.
- After bathing, the child's skin needs to be thoroughly treated with talcum powder. No need to skimp on powder. It is she who absorbs the liquid released from the baby’s skin, preventing the appearance of diaper rash and rashes. The back, folds on the neck, arms and legs - everything needs to be sprinkled with powder.
- A nursing mother should watch what she eats. A diary of a nursing mother is considered a good assistant and controller in this matter, where a woman should write down everything she eats during the day. The memory does not always retain certain little things that can cause redness on the baby’s skin. You need to follow the diet for at least the first six months, until the child learns to roll over and sit down. It is advisable to carefully select products and read their composition. It is better to exclude sweet and spicy foods from your diet for now.
- The washing powder in which children's clothes are soaked must be special, hypoallergenic, and free of dyes and strong fragrances.
Angiodysplasia
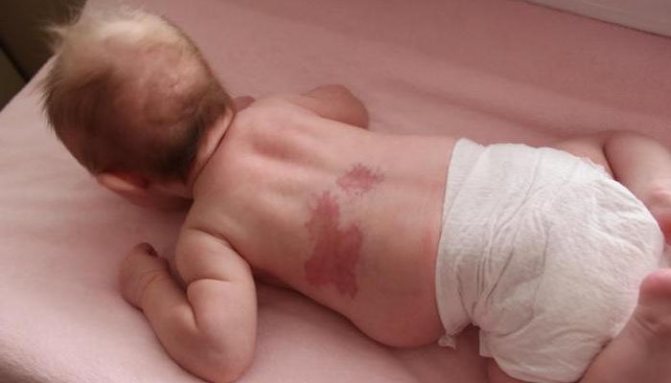
This is a fairly rare and serious disease, which is characterized by an abnormal increase in subcutaneous vessels, accompanied by circulatory disorders. Manifestations of congenital angiodysplasia are most often noticeable:
- On the face.
- On the lower extremities.
- On hands.
With this pathology, the affected areas become covered with many red spots and bruises. At the same time, the skin above them may heat up. A newborn baby is characterized by increased capriciousness and constantly cries.
Correction of angiodysplasia in newborns is quite a difficult task. This disease has not yet been fully studied.