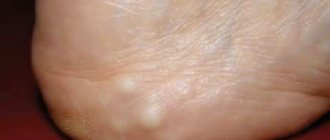
Water urticaria is very similar in its symptoms to other types of urticaria. Despite the fact that the main symptoms are skin phenomena, it should be considered as a sign of a systemic disease.
Aquagenic urticaria is a manifestation of one of the rarest types of allergies, namely an allergy to water.
In fact, it is not the water itself that causes the pathological reaction, because... in its chemically pure form it does not pose an allergic threat. The negative effect is caused by salts and other chemical compounds dissolved in water in low concentrations. The problem is that it is practically impossible for absolutely pure water to remain on human skin. Even if a person suffering from aquagenic urticaria uses distilled water for hygiene procedures, substances brought to the surface of the skin through sweat will immediately dissolve in it. Moreover, there are cases where the onset of symptoms was provoked by the patient’s own sweat.
A negative reaction to chlorine compounds dissolved in tap water used for disinfection is also typical.
What do the symptoms look like?
Upon contact with water in any form and at any temperature, the following signs appear:
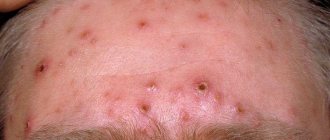
- Itching begins at the points of contact, quickly intensifies and continues for quite a long time. In some cases, aquagenic itching may remain the only symptom.
- Reddened and painful spots appear, very reminiscent of burns
- With extensive contact, such as bathing, rashes appear in the most sensitive areas. These include the elbow and knee bends, the face and neck, the arms around the wrists, and sometimes other areas of the body.
- Pathological dry skin develops, which can increase itching and lead to the appearance of microcracks.
- Irritation of the mucous membranes (mouth, eyes), accompanied by redness and pain.
- Coughing and shortness of breath may occur from inhaling fumes from chlorinated water.
- Cases of headache and deterioration of health simultaneously with other manifestations of aquagenic urticaria have been recorded.
- Minor gastrointestinal disorders, characteristic of many types of allergies, are possible.
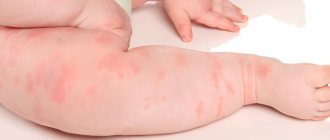
Pediatric allergic vasculitis
In children, allergic symptoms associated with manifestations of allergic vasculitis are characterized by an acute onset and pronounced symptoms. Vasculitis is difficult to tolerate if internal organs are damaged. Frequent relapses are a characteristic feature of childhood urticarial vasculitis. The most common causes of childhood illness are chronic infectious processes in the child’s body, which are treated with drugs that can cause allergies and lead to aggravation of the child’s health. Impaired immunity, allergic reactions to food, insect bites can cause allergies.
The destructive effect of infectious agents greatly affects the condition of the child’s blood vessels, therefore, at the first symptoms of allergic infections, it is necessary to treat children under the strict supervision of a doctor. Pediatricians treat children according to their age category, weight, taking into account the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
A very dangerous condition is when a child has allergies, when blisters filled with liquid content appear on the body.
When the itching is severe, children scratch them, causing the wound to become infected. This leads to infection of the damaged areas and further complications. They treat children with urticarial vasculitis using the most gentle therapy. Even if parents know how to treat their child, doctors strictly prohibit the use of drugs without consultation with doctors. Self-treatment can only cause harm.
Some of the most striking cases of pathology
This disease, like many others, can have varying degrees of severity.
In the most difficult cases, the problem for patients is not only washing and washing, but also physical activity that makes them sweat. The body reacts negatively even to drinking water and drinks, or eating fruit.
Encouraging factors include the following:
- Aquagenic urticaria is a relatively rare phenomenon; doctors have not yet observed a hereditary predisposition.
- There have been no recorded cases of angioedema, which can be life-threatening.
- There were no cases of anaphylactic shock.
Interesting cases of urticaria from water
Englishwoman Michaela Dutton develops itchy blisters and stripes after water gets on her skin; she cannot even drink water, tea, coffee or eat fruit, as all this causes swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat and a rash throughout the body.
Australian Ashley Morris cannot shower or wash herself, but the most incredible thing is that even the water that her own body secretes in the form of sweat causes hives. For this reason, she cannot endure any physical activity or play any kind of sport, because they can cause sweat.
Children's water allergy
This pathological condition is somewhat more common than true water urticaria. It usually appears in the warm season in children who have swum in a body of water with a low water temperature. It cannot be called a cold allergy with certainty, since in many children the pathology manifests itself solely as a result of a sharp temperature contrast between warm air and cold water. It is expressed in the rapid appearance of red spots on the skin. Does not pose a noticeable threat, but may cause some discomfort.
Antihistamines and warm baths with a small addition of baking soda or starch are recommended as first aid. Please note: these baths are recommended only for children with water allergies!
Causes of aquagenic urticaria
Water intolerance can appear suddenly in both childhood and adulthood. Any water can cause a reaction: tap water, melt water, rain water, river water, and even ordinary tears or human sweat. In most cases, water urticaria is a reaction of the body to a specific type of liquid, for example, an allergy to sea water or mineral water. But sometimes it occurs on any liquid, which is a serious obstacle to normal human life.
Doctors have identified several reasons why aquagenic urticaria occurs:
- weakened immunity after taking antibiotics;
- inflammation of the liver or kidneys;
- deficiency of immunoglobulin class E.
Why does the disease occur? Through long-term research, it was found that allergies do not arise from the water itself, but from the impurities it contains. Over time, the symptoms become so intense that they become impossible to ignore.
Treatment of water urticaria.
The main problem in diagnosis and treatment is the rarity of the disease, which has become the reason for poor study of this problem. Doctors do not even have a generally accepted theory about the influence of histamines in this pathology, and, consequently, about the effectiveness of the use of antihistamines.
So far, the following measures are considered truly effective:
- Limit physical contact with water.
- Use clean, non-chlorinated water whenever possible, and constantly use high-quality filters for purification.
- Reducing the duration of contact with water during hygiene procedures to a minimum - the relationship between bathing time and the strength of symptoms has been established. You can choose a lotion, cleansing milk that does not cause a reaction, or use sanitary napkins.
- Using carefully selected hypoallergenic products for hygiene procedures, with a minimum of aromatic, coloring and stabilizing additives.
- Use oil-based protective creams before possible contact with water.
In some cases, a positive effect of using antihistamines was noted.
As preventive measures, it is recommended to normalize diet and lifestyle, and strengthen the immune system. This does not help to completely get rid of the disease, but it makes pathological manifestations more rare and less severe.
It is also recommended to use water with a decoction of chamomile, tricolor violet, and bay leaf for washing or washing, as means that reduce skin irritation. However, it is difficult to confidently call this an effective remedy, since there is not enough statistical data on this issue.
Notes
- Monarch Disease Ontology release 2018-06-29sonu - 2018-06-29 - 2018. Retrieved July 28, 2020.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Skrypnik, Ksenia
Allergy to water: only 50 people in the world suffer from a rare disease
(unspecified)
.
Vesti.Medicine
(February 27, 2018). Retrieved July 8, 2020. Archived April 27, 2020. - ↑ 1 2 3 4
Aquagenic urticaria (English).
Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) - an NCATS Program
. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved February 9, 2019. - ↑ 123456
Gorvett, 2006. - ↑ 12
Hadlow, 2020. - Dice JP, Gonzalez-Reyes E.
Physical (inducible) forms of urticaria.
UpToDate
. Retrieved March 6, 2020. - Sibbald RG et al.
Aquagenic urticaria: Evidence of cholinergic and histaminergic basis (English) // British Journal of Dermatology (English) Russian. - 1981. - Vol. 105, no. 3. - P. 297-302. - doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1981.tb01289.x. - PMID 7272209. - Harwood CA, Kobza-Black A.
Aquagenic urticaria masquerading as occupational penicillin allergy (English) // British Journal of Dermatology (English) Russian. - 1992. - Vol. 127, no. 5. - P. 547-548. - doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb14862.x. - PMID 1467303. - Martínez-Escribano JA et al.
Treatment of aquagenic urticaria with PUVA and astemizole (English) // Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (English) Russian - 1997. - Vol. 36, no. 1. - P. 118-119. - doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70344-x. - PMID 8996279. - Solonenko, 2020.
- ↑ 1 2 Bartlett N.
Girl is so allergic to water she can't even cry (English).
Mirror
(7 November 2015). Retrieved February 19, 2020. - Kondratyeva T.
“I am allergic to water, so the doctors forbade me to cry”
(unspecified)
.
Life
(September 23, 2018). Retrieved February 19, 2020. - Tsoulis-Reay A.
What It's Like to Be Allergic to Water (English).
The Cut
(27 October 2015). Retrieved February 19, 2020. - Park N. et al.
Aquagenic urticaria: A report of two cases (English) // Annals of Dermatology : journal. - 2011. - Vol. 23, no. Suppl 3. - P. S371—S374. - doi:10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S371. - PMID 22346281. - Rothbaum R., McGee JS
Aquagenic urticaria: diagnostic and management challenges (English) // Journal of Asthma and Allergy (English) Russian. : journal. — 2016. — Vol. 9. - P. 209-213. — ISSN 1178-6965. - doi:10.2147/JAA.S91505. - PMID 27942227. - ↑ 12
Chittenden, 2020. - Aquagenic Urticaria: Signs, Causes & Treatments. MDhealth.com
. Retrieved November 29, 2020.
Diagnosis
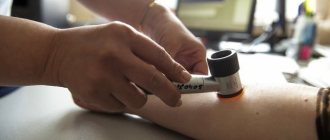
For an accurate diagnosis, firstly, it is necessary to establish an undoubted connection between contact with water and the manifestation of symptoms. Next, testing is carried out for some other irritants in order to exclude allergies to them.
In order to clarify the diagnosis during remission (attenuation of the disease), a test is carried out: a compress with water warmed to approximately 35 ° C is applied. If after a few minutes characteristic redness and itching appears at the site of the compress, this almost certainly indicates the presence of aquagenic urticaria.
A complete cure for this disease has not been recorded. The goal of treatment is to reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
Author – Tatyana Dobrovolskaya
Types and forms
Doctors distinguish two forms of water urticaria:
- spicy. Signs develop immediately after water procedures, with profuse sweating or crying. After taking antihistamines, normalizing the general condition, and following preventive measures, the risk of relapse decreases;
- chronic. In a third of patients, a negative reaction to water appears periodically after contact with an irritant against the background of increased provoking factors. The strength of negative symptoms differs depending on the degree of sensitization of the body, the duration of water procedures, and the amount of sweat produced. Fortunately, doctors have found that anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema practically do not develop with water urticaria.
Aquagenic urticaria ICD code – 10 – section L50.
What it is
Cold urticaria is a skin allergy to exposure to cold that is accompanied by itchy red sores such as rashes, rashes, blisters or sores. Sometimes the wounds have a pink tint. Classifier code for cold urticaria L50.2 according to the ICD-10 reference book. The disease can be accompanied by symptoms of varying severity.
What is cold urticaria
Some patients experience minor reactions to cold exposure that are almost unnoticeable, while others, on the contrary, notice serious symptoms.
Cold allergy
The most common cause of cold allergies is swimming in cold water. In addition to skin reactions, patients may experience symptoms such as low blood pressure, general malaise, or even fainting. In some cases, patients experience coughing attacks and headaches.
The symptoms of cold urticaria are very similar to those of dermatitis
Note! According to statistics, young patients most often experience cold urticaria. And symptoms, as a rule, can manifest themselves over several years, causing a person a lot of discomfort.
Treatment and prevention of rashes
If a small red rash appears on your body while on vacation at sea, you should not immediately panic. First you need to try to find out the reasons for this phenomenon.
Such problems often arise among those tourists who do not know how to choose the right time to visit the beach. From 11 a.m. to 3 p.m., the intensity of ultraviolet radiation increases sharply, which causes allergies and other phototraumatic effects.
People with pale, sensitive skin need to be especially careful at this time, as their bodies do not produce enough melanin pigment, which helps neutralize the sun's rays.
They need to use tanning products. The protective cream cools the skin and protects it from sun rays, significantly weakening their influence.
The sea contains a lot of mineral salts, so it produces a drying effect. People with oily skin types experience a significant improvement in the condition of their skin after bathing.
But if your skin is already dry, it becomes more sensitive to everything and can easily become inflamed when exposed to very salty water.
As a rule, an allergic reaction develops, which causes the appearance of dermatitis, accompanied by severe itching.
To avoid this, it is advisable for people with sensitive skin to lubricate their body with a rich cream before each dive into water. After swimming, you should immediately dry yourself with a dry towel or take a shower with fresh water.
READ ALSO: Spoon-uno from Aliexpress: how to get rid of blackheads? How to squeeze out pimples correctly? How to remove millet grass (white subcutaneous tissue)? BEFORE and AFTER PHOTOS
The measures taken will help avoid drying out the skin, since it is especially vulnerable on the beach - after all, it is affected by three elements at once: the sun, water and wind. The wind dries the skin, leaving a film of mineral salts on it after the water evaporates. This increases the burning effect of sunlight and causes immunopathological reactions.
What to do about sun allergies? Video: