Causes of red spots on the face
It is not always possible to determine in time that sores have appeared on the head. Women have long hair, which makes it difficult to see red spots and peeling around them. In men with short hair, such manifestations in the scalp are diagnosed much earlier. However, there is no need to despair.
- Allergy to irritants. This could be household chemicals, hairspray or low air temperature. Especially often, an allergic reaction that causes redness of the scalp worries people with sensitive skin.
- Seborrheic dermatitis. This disease has become widespread in the modern world.
- Psoriasis, which provokes excessively rapid cell renewal.
- Fungal infections. These include the commonly diagnosed pityriasis versicolor.
There are quite a few reasons for the development of allergic manifestations. Dust on the street, plant pollen, low-quality plastic combs and some products can provoke a reaction. In women, the factor behind redness on the scalp, in the scalp, is often dyeing.
Skin changes come in different forms:
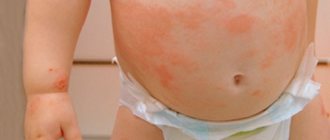
- itchy large and small pink spots on the chin, cheeks, nose, forehead;
- peeling;
- tightness, especially felt during facial expressions;
- compaction;
- ulcers with pink edging;
- itching and red spots on the face, covered with white scales.
Due to the individual characteristics of the skin, changes can occur from factors that do not affect the appearance of other people.
It can be:
- decorative cosmetics;
- the hardness of tap water (it often contains dissolved salts of calcium, magnesium, iron and other elements);
- cold (especially in windy weather);
- ultraviolet;
- the presence of allergens or other irritants in the atmosphere;
- pet hair;
- insect bites.
The face often itches and red spots appear under a certain condition:
- Avitaminosis. A lack of nutrients usually appears in the spring if a person does not take vitamin complexes in addition to his usual diet.
- Pregnancy. During this period, the woman’s body is weakened because it consumes useful elements for the development of the baby.
- Weakened immunity. The reasons are poor nutrition, taking antibiotics, previous diseases, etc.
- Depression. In this state, the body cannot cope with even minor factors that can trigger the occurrence of a rash.
Hidden pathologies of any system of the body can cause red spots on the face, itching and peeling:
- problems in kidney function;
- disturbances in liver function;
- blood clots in blood vessels;
- diabetes;
- damage to the stomach and intestines;
- intoxication of the body.
Chickenpox. It mainly affects children, but is no exception for adults. Watery blisters appear all over the body and are very itchy. The temperature usually rises, weakness and drowsiness are noticeable.
Scarlet fever. If red spots appear all over your body and face and itch, at the same time your temperature rises and you feel chills, it may be scarlet fever.
Rubella. First, your head starts to hurt, you feel weak, and your temperature rises. Then red spots and itching appear all over the body.
Measles. During infection, the red spots on the face itch and peel, and pigmentation appears. Additional symptoms include fever and itching.
Skin diseases
Acne. Acne manifests itself as purulent pimples, in place of which red spots appear on the face, peel and itch if no treatment has been carried out.
Pityriasis rosea. The disease is not transmitted by contact, it appears when immunity decreases, and often occurs as a result of stress. At the beginning of the disease, one pink spot appears (the so-called maternal plaque), over time the skin becomes covered with spots, which are accompanied by severe itching and tighten the skin.
Fungus. In most cases, the scalp is affected by fungal infection, but in some cases spots appear on the face that itch and peel.
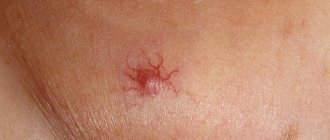
Hemangioma. A benign tumor on the face appears as a red dot and grows over time.
Rosacea. Enlarged capillaries that are visible through the skin. The grid gradually increases, forming red areas.
Pigmentation disorder. Spots appear on the face due to increased pigment production. A pigment spot is an area of skin colored brown or pink. The spots cover mainly the forehead, eyelids, temples, and cheeks. The skin does not peel off.
Lupus erythematosus. The face itches and the red spots on the cheeks are shaped like butterfly wings.
Eczema. Small blisters appear on the face, which can itch and cause a burning sensation. The lesion most often occurs due to an allergy to cosmetics. With eczema, in some cases, areas of dryness may appear on flaky skin, which leads to the damaged skin cracking.
Psoriasis. A chronic disease that manifests itself in the appearance of scaly pink plaques. In 20% of patients, the pathology is not accompanied by itching.
In addition to rashes, it is necessary to analyze the accompanying symptoms: weakness and dizziness, nausea and vomiting, joint pain, low blood pressure, high temperature, and in some cases mild pain in the heart may appear. Each of them indicates that red itchy spots on the face are not just a cosmetic problem.
Provocateurs of illness
More than 80% of pathologies are caused by various malfunctions in the internal systems of the body, fungal pathogens (lipophilic yeast, dermatophyte molds) or inflammation.
The leading factors causing redness of the scalp can be considered dysfunction of the secretion of the sebaceous glands due to a failure of nervous and hormonal regulation, as well as non-infectious dermatosis.
Seborrhea
This is what seborrheic rashes look like
Chronic seborrheic dermatitis is caused by the proliferation of yeast. Many yellowish plates of dying skin cells appear on the head and in places covered with hair, and the head is very itchy. The oily type of ailment is characterized by excessive work of the sebaceous glands.
Dry seborrhea is accompanied by dandruff and acne. The catalyst for the disease is disorders of the immune system, psycho-emotional overload, and the influence of low temperatures. Affected areas may partially lose hair. Seborrhea can be accompanied by a bacterial infection.
Psoriasis
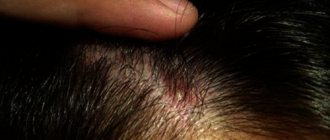
psoriasis on the head
Manifestations of psoriatic disease are often noticed in an advanced form, when the scalp is already completely covered with rashes and plaques. They itch and flake off. Epidermal cells divide much faster than normal, without having time to die. This disease affects all age groups.
A large proportion of cases are caused by genes, but there is also an opinion that chronic overload, disorganization in terms of rest and diet, and alcohol abuse lead to disorders. The constant influence of low atmospheric temperatures aggravates the already unpleasant condition. This pathology usually does not lead to hair loss. Psoriasis can cyclically stop and reappear. This disease is not contagious by contact.
Other Sources of Scalp Spots
Tinea versicolor is also of fungal origin. The epidermis is affected by brownish or whitish scaly lesions. The disease is inherited and is typical for people living in warm climates. You can become infected through contact with the things of a fungal carrier, or directly with him. Hyperhidrosis aggravates the disease.
Infection with mold microorganisms leads to dermatophytosis. Contact with a person infected with the fungus is contagious. Follow sanitary and hygienic rules at home if you discover similar symptoms in yourself or a loved one in the family.
An infection like ringworm attacks the hair follicles. The hairs break off directly, leaving smooth redness with dots from the roots. This is the most unpleasant fungal infection. To exclude complications, be sure to go to the hospital if you suspect this illness.
Symptoms of eczema include redness in the affected areas. Small pimples on the head are added to it, turning into itchy blisters, which, painfully bursting, form wounds. Progressive disease can cause a rise in temperature. During remission, the epidermis dries out.
The mechanism for the appearance of red spots on the head can be triggered by a hormonal imbalance, which is more likely after fifty years. Meteorological factors, such as air humidity, precipitation, frost, excess sunlight, also directly affect the skin and hair of the scalp. In addition, experiencing a stressful situation and psycho-emotional turmoil can affect the well-being of the hair and epidermis.
A fairly common cause of red scalp is an allergic response of the body. You need to take a closer look at your surroundings to see if there are potential allergens in it, such as the hair of your favorite pets, pollen, household chemicals and cosmetics, and certain foods.
A reaction may occur after dyeing your hair, from water with excess salts in the composition. Deficiency of certain vitamins leads to redness of the outer layers of the skin and baldness. The doctor will help you choose the right drug with vitamins and microelements.
Allergic reaction
Red spots on the scalp, caused by an allergic reaction, arise due to the increased sensitivity of the dermis to certain irritants:
- citrus and other products;
- chemicals contained in shampoos and other personal care products;
- animal hair, pollen;
- with active sweating on the head.
The allergic form of dermatosis on the head develops due to hereditary predisposition, endocrine pathologies, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract or severe stress.
An allergic reaction usually occurs almost immediately after contact with the irritant. In this case, the following phenomena are observed in men and women:
- intense itching;
- redness of the scalp;
- peeling of the skin.
Treatment
At the beginning of treatment of an allergic reaction, it is necessary to eliminate the exposure to the irritant. The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the cause of the appearance of red spots on the head.
- When the first signs of an allergic reaction appear, it is recommended to take antihistamines: Claritin, Zodak, Erius and others.
- For the symptomatic treatment of allergies, ointments that suppress the inflammatory process are used: tar, ichthyol and naphthalene.
- In severe cases, corticosteroid-based ointments are used to treat the skin.
- Entrerosorbents are used as an adjunct to drug therapy. These drugs help remove toxins from the body, thereby reducing the intensity of the allergic reaction.
- Treatment of the pathological condition is recommended to be supplemented with a specialized diet, which has a positive effect on the functioning of the digestive system in adults and children.
Lichen
Lichen, like seborrheic dermatitis, occurs due to the activity of fungal microflora. Depending on the type of pathology, it develops after contact with animals or other carriers of the pathogen, as well as under the influence of factors that weaken the immune system.
A characteristic sign of lichen are spots of various sizes and shades that appear on the scalp. In the problem area, thinning and hair loss occurs. As the disease progresses, a person is bothered by itching and rash.
Treatment of lichen is carried out by treating problem areas with agents that suppress fungal microflora: Lamisil, salicylic and sulfur ointment, glucocorticosteroids.
In severe cases, systemic antifungal medications are used to treat lichen. In order to eliminate symptoms, antihistamines are introduced into the therapy.
Red spots on the head under the hair appear for various reasons. It is highly recommended not to ignore such tumors or self-medicate. Some medications used, for example, for ringworm, are contraindicated for psoriasis. Treatment of red spots must begin at the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process.
Sensitive scalp
Dehydration is the main reason that causes increased sensitivity of the skin on the part of the head covered with hair. Due to the reduction of the protective lipid-fat layer, moisture is not retained even in the deep layers. Natural evaporation occurs. The scalp becomes defenseless from external influences.
These same symptoms are possible due to other factors:
- hormonal imbalances;
- thermal damage when styling, being in the cold or under the scorching sun;
- mechanical injuries;
- chemical burns during the dyeing process;
- lack of vitamins;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
These factors are accompanied by redness and flaking, which differs from the occurrence of dandruff. Other symptoms appear. Flaky skin is found in the temple area, in the lower part of the back of the head, and along the edge of the scalp they are separated by a red stripe on the skin. In this case, the keratinized scales do not fall off.
Manifestations of hypersensitivity sometimes cause a change in the type of skin on the head. In cases where the epidermis is dry, the work of the sebaceous glands increases. This reaction of the body allows for at least minimal protection of the epidermis of the upper part of the head. At the same time, not only the skin, but also the hair becomes oily.
Treatment
People often use anti-dandruff shampoos as self-treatment. Their use for other purposes leads to sores and even more irritation of the skin. Bacteria are able to penetrate into the deeper layers of the dermis.
A timely visit to a trichologist will avoid complications. With the help of a doctor, the cause of the problem is found out quite quickly. The doctor will prescribe the necessary vitamin course and procedures for home restoration of hydro-lipid balance. To achieve this, treatment includes products that have moisturizing, restorative and soothing effects. It is recommended to use calophyllum oil, glycerin, lavender and peppermint extract, jojoba or macadamia oil.
Therapeutic measures
A trichologist will help determine the pathology after examination and, if the need arises, additional examinations. This could be a blood test, an allergy test, or a study of a sample of cells from the site of the lesion. Additionally, you may need to see a number of other doctors.
Only a qualified doctor can prescribe proper treatment. In some cases, periodic visits to specialized medical dispensaries are indicated. Don't make your situation worse by trying to heal yourself.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Signs characterizing seborrheic dematitis are the appearance of flaking and dandruff with a yellowish tint. It is also found on the eyebrows, mustache and beard. Red spots appear on the scalp.
The disease develops due to a malfunction of the exocrine glands. They produce an excess of secretion called sebum. The second cause of pathology is the uncontrolled proliferation of bacteria, which are normally found on the skin of most people. They concentrate around the ducts.
Hyperactivation of pathogenic microflora occurs due to changes in the composition of sebum. In this case, the protective functions of the epidermis are disrupted. The main causes of these failures are changes in genetic, hormonal, neurogenic or immune factors.
Seborrhea develops in one of three types:
- In the dry form of the disease, the ducts produce a reduced amount of secretion. In this case, the emerging symptoms are cracked, dry skin, brittle and dry hair, and the presence of a large amount of small dandruff. Seboreids appear on the affected areas of the skin - reddish spots.
- The oily type of the disease is marked by increased activity of the sebaceous glands. The skin becomes oily and shiny. There is a lot of dandruff, it is large in size. You have to wash your hair often. This happens because the hair quickly becomes oily and sticks together.
- The mixed form is characterized by the simultaneous manifestation of two types of seborrhea. For example, there is a dry variety on the face, and an oily one at the top of the head.
Therapy for seborrheic dermatitis that develops on the head is performed using anti-inflammatory and antifungal agents, exfoliants and medications that have a complex effect. Among other medications, Nizoral shampoo is often prescribed. It contains the active ingredient ketoconazole. It is a highly active antifungal agent.
The first signs of pathology occur when a fungal infection parasitizing the scalp becomes active. This leads to:
- weakening of immune defense;
- endocrine pathologists and hormonal imbalance;
- severe stress.
The disease causes redness of certain areas of the skin, the surface of which begins to peel off over time, pink spots and dots appear on the back of the head and other parts of the body. The course of the pathology is accompanied by intense itching and, in rare cases, pain. Seborrheic dermatitis worsens due to poor nutrition.
In a child or teenager, the disease can cause rashes in the form of acne. Such neoplasms occur against the background of active sebum secretion, which closes the hair follicle. As a result, the latter becomes inflamed. This leads to acne.
Treatment
For seborrheic dermatitis, complex treatment is carried out, including the use of the following drugs:
- Antihistamines and hyposensitizers. These medications are used for symptomatic treatment. The first group of drugs (Clemastine, Chloropamine) relieves itching and restores skin color. Hyposensitizing agents (sodium thiosulfate, calcium gluconate) are injected directly into muscle tissue or veins.
- Antifungal. Medicines in this group (Clotrimazole, Fluconazole) stop the growth and reproduction of fungal microflora in the scalp. Antifungal drugs are used in the form of ointments (for mild forms of the pathology) and tablets (for severe forms).
- Glucocorticosteroids. Prescribed when an inflammatory process is detected. Glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Beclomethasone) for seborrheic dermatitis are used in the form of ointments.
- Keratolytic. Used to remove dead skin parts. The group of keratolytic drugs includes medications including zinc, salicylic acid, and urea.
In case of secondary infection, drug therapy is supplemented with tetracycline antibacterial drugs.
If seborrheic dermatitis relapses, it is recommended to abandon the use of usual cosmetics in favor of specialized shampoos or shower gels that suppress the activity of fungal microflora.
Psoriasis
This non-infectious disease has another name - scaly lichen. The pathology is chronic. There are many reasons for the manifestation of the disease. This is a multifactorial disease. Psoriasis, which manifests itself on the scalp, is the most common type of pathology. It can be triggered by:
- disturbances in metabolic processes;
- immunological disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- infections;
- hormonal imbalances in adolescents, during pregnancy or menopause;
- scalp injuries;
- stress or frequent nervous tension;
- poisoning by toxic compounds;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
The inflammation process is accompanied by severe itching. The affected areas are:
- areas near the ears;
- back of the head and forehead;
- on the back of the head – the neck area;
- place of parting;
- earlobes.
In the mild stage of psoriasis, single and small lesions appear on the scalp, in the scalp. They are covered with thin small scales. The severe form differs in the severity of the disease. The entire surface of the scalp is affected, rarely the forehead area. The scales formed are quite thick, their sizes are much larger. The skin becomes thickened and rough, sores crack, abrasions and wounds appear, and the disease continues to progress.
In younger children, the developing pathology resembles diaper rash, but it does not go away for a long time and is difficult to treat. If the skin on your child’s head turns red and peels, you should not put off visiting a doctor. You can’t wait until unpleasant-looking sores appear.
Treatment
There are various methods to get rid of psoriasis. They include general maintenance of the body, local treatment, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures. The following medications are used:
- sedatives;
- antihistamines;
- aromatic retinoids (Acitretin, Etretinate);
- immunomodulators (Methyluracil, Dekaris);
- nonspecific immunotherapy drugs (aloe, Pyrogenal).
A hemodez solution is also used, intended for intravenous administration using a dropper. In severe cases of the pathology, corticosteroids and cytostatics are used. When an infection occurs, antibiotics are used.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. It is extremely difficult to establish why pathology develops in a particular patient. It is believed that factors that weaken a person’s immune system can provoke a relapse of the disease:
- infectious, viral and other diseases;
- severe stress;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight (useful in small doses);
- taking medications and more.
After an exacerbation, the pathology goes through several stages of development, each of which is characterized by certain signs:
- itching and redness of the dermis, over time the skin itches more and more;
- peeling of the skin;
- the appearance of large spots covered with white flakes (dead tissue);
- cracks and abrasions on the head.
The elasticity of the skin in the problem area decreases, as a result of which the dermis is easily injured.
Treatment
Psoriasis requires an integrated approach to treatment. Therapy of the disease involves the use of:
- corticosteroids and cytostatics (in severe cases);
- antihistamines;
- sedative and hyposensitizing drugs;
- vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
The use of these drugs is intended to relieve symptoms characteristic of psoriasis and increase the duration of the remission stage. However, it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathology. In case of secondary infection, treatment of psoriasis is supplemented with local antibacterial drugs.