Herpesvirus can manifest itself in different ways. According to medical practice, there are at least eight strains (types) of herpes that provoke various diseases. Four of the eight strains are capable of infecting the dermis, causing primary skin diseases. Herpes on the hands develops relatively rarely, since this localization is atypical for infection. This pathology is defined as a viral infection of the dermal layer of the skin of the hands (palms, hands, elbows, fingers, forearms). According to statistics, every twentieth person in the world is diagnosed with the disease. The virus can affect both adults and children. What should you know about such a condition?
Causes of the disease
For the occurrence of herpetic lesions of the hands, a combination of a triad of factors is required.
- First of all, it is required that infection occurs. Since the virus can be transmitted in a variety of ways (airborne, household, contact, nutritional and others), it can be said that almost everyone is infected (according to statistical information - 95% of people of any age).
- Secondly, it requires the immune system to weaken. As soon as the body’s defenses fail, signs of herpetic lesions appear not only on the hands, but also on other parts of the body. The degree and intensity of manifestations depend on the nature of the process and the type of viral agent.
- Thirdly, damage to the skin must occur. In this case, options are possible. The most common “conductors” of infection are the following diseases : Dermatitis. Defined as an infectious or allergic disease that causes cracking of the skin. Deep painful wounds form that take a long time to heal. This is the real gateway for the secondary occurrence of the disease.
- Neurodermatitis. It is considered a psychosomatic disease caused by increased production of cortisol, adrenaline and norepinephrine. It can be called a form of dermatitis that has a slightly different genesis.
- Eczema. Infectious or allergic lesion of the skin with the formation of focal changes in the dermis.
- Banal skin injuries: scratches, cuts, etc.
The trigger mechanism of the pathological process is often injuries or damage to the skin of another origin. However, there are other factors that indirectly increase the risk of infection. This:
- Tobacco smoking (reduces local and general immunity).
- Alcohol abuse.
- The use of drugs that inhibit the body's defense system.
- Frequent stress. In addition to causing neurodermatitis, they sharply reduce the functioning of the immune system.
- Endocrine causes, disorders of general metabolism. Observed during pregnancy, menopause, severe pathologies (diabetes mellitus and others).
- Acute respiratory diseases and infectious pathologies suffered in the recent past. They cause a general and local decrease in immunity.
In combination, these reasons give rise to herpes on the arms and legs (depending on the form of the disease, secondary damage to the lower extremities is possible).
Causes and risk factors
The herpes virus has been well studied; more than 100 species are already known. Eight of them are infectious to humans. But only three of them cause herpes on the palm and finger:
- Herpes simplex virus 1 (labial).
- HSV type 2 (genital)
- Herpes zoster (shingles).
In principle, the virus does not care which way it enters the human body. It is easier to do this through the mucous membranes than through the skin, but if there are abrasions, cracks, or wounds on the hands, then penetration is easier.
Provoke a relapse of the virus:
- Severe hypothermia.
- Weakened body after ARVI or other viral infection.
- Skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis and even eczema.
But the main reason, of course, is immunodeficiency. This is why rashes are often observed in HIV-infected and AIDS patients.
Who is more likely than others to get the herpes virus “directly”? Until recently, dentists who did not use protective equipment such as gloves were at risk. Remained at risk:
- Children. They have a tendency to suck fingers, and this allows the virus (with labial herpes) to easily enter the skin of the upper extremities on the fingers and between them. Therefore, it is in children that herpetic nail felon often occurs.
- Commercial sex workers.
- Athletes.
The women in question have direct manual contact with the causative site of a client with herpes. Herpes appears on any finger or palm.
Wrestlers come into close contact with each other during a fight, and minor skin injuries are common. In them, the herpes virus more often penetrates through damaged skin on the extremities, elbows, armpits and torso.
Don't forget about the role of the immune system. Those who have it weakened by stress, poor nutrition, dysbacteriosis, and hormonal imbalance are at greater risk. Exposure to the sun also reduces local skin immunity.
By the age of 25, 90% of the world's population become carriers of the herpes virus, and a person becomes infected with type 1 virus before the age of 5 years, and type 2 during puberty.
What types of herpes provoke the onset of the disease?
There are four strains of herpes that can be sources of the pathological process. This:
- Strain of the first type (herpes simplex). In addition to violating the integrity of the skin on the hands, it causes the formation of papules on the lips and in the oral cavity (stomatitis).
- Strain of the second type. Known as genital herpes. It often enters the body through unprotected sexual contact. Violation of the integrity of the dermis of the hands develops as a secondary process.
- Strain of the third type. Probably the most famous pathogenic agent. It provokes the formation of chickenpox and herpes zoster.
- Strain of the fourth type (Epstein-Barr virus). This agent is highly contagious.
Symptoms
The incubation period (the time from the virus entering the body until the first symptoms appear) lasts from three to twelve days. During this period, the agent integrates into healthy cells and begins to use their apparatus for its own reproduction.
- The first sign includes a rise in body temperature to subfebrile levels. If the disease is mild, there may be no hyperthermia. In any case, there are manifestations of mild intoxication of the body with headache, dizziness, weakness and drowsiness. If the disease is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, these symptoms are always intense.
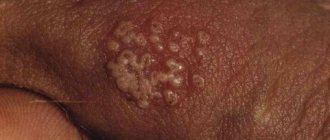
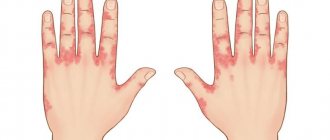
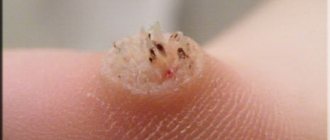
- After a few days, moist swellings form on the arm (usually on one at first), which do not yet have a shape. They look like reddish bumps, hot to the touch and somewhat painful. There is intense itching (skin itches) and a desire to scratch the affected areas. This should not be done under any circumstances: there is a high risk of mechanical transfer of the pathogen to healthy areas of the hands. The localization of the pathological process is different: redness may occur on the fingers and palms, on the forearms and elbows, on the periungual plates.
- On the back and frontal areas of the skin of the hands, papules form - vesicles filled with cellular fluid and pathogens. The exudate also contains dead leukocytes. This liquid is extremely dangerous because it contains not only dead viruses, but also active pathogens. Herpetic papules look like small bubbles of a yellowish or greenish tint, their sizes vary from 3 to 10 mm or more. It is possible for several papules to merge into large lesions. The formations are surrounded by a red halo, the tissues are hyperemic. There is burning and itching. The rash does not appear immediately. Single or multiple papules are possible.
- After a few days, the blisters open and wound erosive surfaces form. They become easily infected. Serous fluid comes out of the wounds. Almost a week after the start of the process, the papules resolve on their own with the formation of scars.
This clinical picture is formed gradually, passing through several stages of development. The further herpes progresses in its development, the easier it is to diagnose and the more difficult it is to treat.
Herpes symptoms
In order not to give the disease a single chance, it is important to know the symptoms of a herpes cold. Often, herpes on the hands first manifests itself in the form of painful sensations and burning sensations in places where painful rashes subsequently appear.
Bending and straightening the fingers can cause very unpleasant sensations in the patient, but such a symptom is not always a sign of impaired joint mobility. , redness and slight swelling appear over time . These symptoms usually appear no earlier than the third day of illness.
With the development of genital and labial forms of the disease, the patient has complaints of malaise, elevated body temperature, and headache . When herpes occurs on the hands, the symptoms listed above are not very pronounced or are absent altogether.
About three days after infection, painful papules , which are small blisters containing clear liquid, can be found on the fingers or palms. With herpes, papules remain on the skin for 3-4 days. Subsequently, they change into ulcers, in place of which, after some time, dry crusts appear. With large scale lesions, an extensive scab sometimes appears at the site of infection.
Herpes rashes, which occupy a large area of the skin, are observed in very rare cases. Visible lesions are concentrated within a small area no larger than the size of the palm of your hand. Herpes on the palms can be found on the back side, as well as the inner surface. Most often, herpes on the fingers occurs on the nail fold. The disease most rarely affects the forearms or the areas between the fingers.
The disease lasts for at least 7-10 days . However, treatment must begin immediately after the first symptoms of herpes are detected. Under no circumstances should you independently select treatment tactics and drugs suitable for fighting the infection. This should only be done by a specialist, based on the results of laboratory tests to determine the type of pathogen.
Diagnostic measures
They are carried out by a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist (you shouldn’t be afraid of the latter’s specialty). At the initial appointment, the specialist conducts an oral interview, identifies characteristic complaints and tries to build a clinical picture. For the same purposes, anamnesis is collected. It is extremely important to establish the factors that preceded infection.
In the early stages, it is almost impossible to diagnose herpetic lesions of the hands and distinguish them from eczema and dermatitis. Therefore, the disease is not diagnosed “by eye”. As soon as the patient comes to the hospital, he is prescribed the following examinations:
- General blood analysis. When affected by the Epstein-Barr virus, an increase in the number of atypical mononuclear cells is possible, an increase in the concentration of leukocytes is observed in the blood formula, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases.
- Serological studies.
- PCR and ELISA diagnostics. Necessary for identifying traces of viral agent DNA in the patient’s bloodstream.
- Finally, immunological studies are necessary to detect specific antibodies to a particular strain of the virus.
It is mandatory to carry out dermatoscopy - examination of the skin using a special device. These measures are sufficient to make a correct diagnosis and its verification. Then treatment can begin.
Therapy for herpetic lesions of the hands
Several groups of drugs are used for therapy. The pathology can be treated at home. Treatment of herpes on the hands should be comprehensive. The following tools are used for this:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal). In the form of ointments and tablets for oral administration. They relieve local inflammation, normalize the condition of the skin, relieve pain and discomfort.
- Analgesics. Relieves pain.
- Antihistamines: Pipolfen, Tavegil, Suprastin and other medicines. It is recommended to smear your hands with Fenistil. Antiallergic drugs act on itching mediators, reducing the intensity of burning and the desire to scratch the affected areas of the skin.
- Antiherpetic drugs are prescribed without fail. The most popular and effective is Acyclovir and its analogues . This medication has a complex effect on the virus, inhibiting its genetic material and killing the pathogenic organism. The drug is considered safe even for self-administration. Reduces the duration of the disease by almost half. Cheap remedies include oxolinic ointment, zinc ointment, Tsindol, and Calamine.
- Antiseptics. Used to disinfect surfaces and destroy viruses. The use of Miramistin, brilliant green, Fukortsin (including its modern modifications) is indicated.
- The use of immunomodulators is necessary. Viferon ointment, which naturally increases the local production of interferon, and others are suitable.
These remedies can quickly cure the disease.
Once the acute phase is over, wound healing medications can be used to prevent scarring. These are Contractubex and other ointments.
Complications
With serious disturbances in the immune status, the disease becomes protracted. In addition, it may spread to the skin of the hands and body. A bacterial infection cannot be ruled out. Often complications arise after the patient opens the blisters.
In pregnant women, herpes on the finger is dangerous only in that, against the background of weakened immunity, a woman can transfer it to the genitals during hygiene procedures. And this threatens the fetus with infection through the mother’s birth canal.
Preventive actions
There are no specific measures to prevent viral damage to the dermis of the hands. It is enough to follow the general recommendations:
- You need to keep your immune system in working order. For these purposes, proper nutrition, rational physical activity, hardening, etc. are recommended;
- It is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene: wash your hands more often;
- Unprotected sexual intercourse is excluded. Otherwise, there is a high risk of infection;
- you need to give up smoking and alcohol abuse;
- use only your own hygiene products, do not use others;
- avoid physical contact with infected people (shaking hands, etc.).
Herpes on the hands is an unpleasant condition that does not pose a threat to life, but significantly reduces its quality. It is recommended to consult a doctor promptly and undergo a specialized examination. This way you can “nip” the disease in the bud.