Psoriasis is a fairly common disease in the world. There are a large number of forms of this pathology.
One of these types of disease is generalized psoriasis. This disease is severe and can pose a threat to human life, although there are pathologies that affect certain areas of the body. The risk group includes representatives of both sexes. Most often, the development of the disease is recorded in people in the age group from 15 to 35 years.
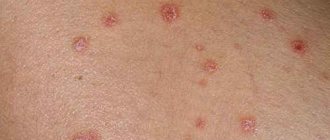
The disease is characterized by the formation of a blistering rash, which over time turns into small, bright pink pustules. As the disease progresses, pustules and blisters merge into large affected areas, covered on the outside with leukocyte crusts that are brown in color.
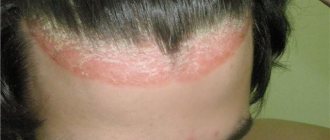
When the affected areas located under the crusts are injured, non-healing erosions and ulcers form. Most often, the rash forms in the groin and joint area; there are cases of damage to the mucous membrane, nail plates and areas of the scalp. Damage to areas of the scalp is called Tsumbusch psoriasis.
What is this article about?
Causes of pustular psoriasis
Three factors can provoke the development of the described pathology:
- genetic predisposition;
- a sharp weakening of the immune system;
- long-term treatment with systemic drugs (hormones and cytostatics).
Often, the appearance of symptoms of pustular psoriasis occurred against the background of long-term use of external agents that have a pronounced irritating effect (ointments containing tar, salicylic acid or fucorcin). There have been cases where pustular type psoriasis appeared as a complication of a chronic infection or psycho-emotional disorder, hormonal surge or jaundice. In some patients, the characteristic clinical picture was the result of prolonged ultraviolet irradiation or exposure to aggressive chemicals. It has been noted that the combination of these factors increases the risk of developing the disease significantly.
Origin and symptoms of psoriasis
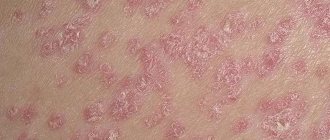
How to recognize the disease? Psoriasis announces its appearance quite clearly - for example, on the skin of patients with the corresponding diagnosis, first single, and then multiple rash elements appear, which look like convex inflamed spots with a heterogeneous relief of a red-pink color. A characteristic identifying sign of psoriasis is the so-called scales - silvery-gray flaky particles covering the main elements of the rash.
It is noteworthy that the course of psoriasis of any form is associated with a lot of unpleasant physical sensations and psycho-emotional discomfort. Thus, the spread of the rash throughout the body is accompanied by unbearable itching and peeling; the foci of psoriasis themselves are hyperemic, swollen, and painful. During periods of exacerbation of pathology, patients may experience an increase in body temperature, patients experience headaches, general weakness, apathy, neuropsychic disorders, and decreased ability to work.
Unfortunately, psoriasis is not only a medical problem.
Patients, embarrassed by the “renewed” unaesthetic appearance of their once healthy skin, withdraw into themselves, become asocial, develop complexes and break off most social communications. Needless to say, psoriasis has long turned into a real socio-psychological disaster, and patients with the corresponding diagnosis began to regularly visit psychotherapists.
The danger of psoriasis lies, among other things, in the fact that the nature of this disease has not been fully studied. Of course, modern medical scientists put forward a lot of versions that interpret the etiology of the disease from different points of view, but none of these assumptions are officially recognized by modern dermatology.
The autoimmune theory of the origin of psoriasis has the largest number of “fans”. It is based on the idea that psoriatic plaques are the result of enhanced immune attacks directed at healthy epidermal cells under the influence of a number of conditioning factors. Such attacks by the body's defenses lead to the fact that abnormal elements begin to grow rapidly, multiply intensively and spread throughout the body.
Among other versions explaining the nature of psoriasis, it is worth mentioning:
- Metabolic (exchange);
- Hormonal (endocrine);
- Medicinal;
- Allergic;
- Toxic;
- Neurogenic (stressful);
- Viral, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wp5PIlSCZDQ
Psoriasis is a disease that is inherited from parents to children. It is believed that not only the pathology itself, but even the predisposition to the appearance of a characteristic skin rash can be genetically determined. The disease unexpectedly announces its appearance at any age against the background of immune, metabolic, hormonal failure, skin injuries, or after a serious illness (infectious or viral nature).
The fact that the exact cause of the development of psoriasis is unknown explains the lack of a single universal method for effectively combating this serious disease.
Unfortunately, psoriasis is still included in the list of incurable pathologies. Treatment of the disease is symptomatic and solves the following problems:
- Relieving the inflammatory process on the skin;
- Minimizing discomfort in areas affected by psoriasis;
- Removing plaques from affected areas;
- Prevention of exacerbations (complications) of pathology.
Features of clinical manifestations of pustular psoriasis
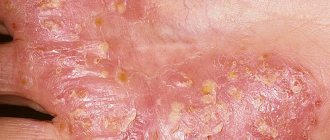
Pathology debuts with the appearance of red spots. Then bubbles with purulent contents form inside them. Individual elements of the rash gradually merge and form large “purulent lakes.” When the pustules are released from the pus, a large erosion forms. Over time, it becomes covered with a yellow-brown crust.
The described processes are accompanied by intense itching, they cause fever with chills, weakness and fatigue. The patient may complain of restless sleep.
Classification
Depending on the spread of skin lesions, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
- localized;
- generalized.
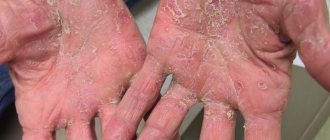
With localized pustular psoriasis, lesions appear on a limited surface (on the palms or soles, on the chest or back, on the skin of the bends of the limbs). Generalized psoriasis leads to the fact that all parts of the body are involved in the process of damage. This form is always difficult with a sharp deterioration in general health and the appearance of symptoms of intoxication. If left untreated, extensive swelling forms and nephropathy develops. It gives rise to dystrophic processes. This phenomenon requires immediate hospitalization of the patient.
Each form has its own varieties. The following tables clearly demonstrate them best.
Localized form
| Name | Clinical manifestations | Affected areas |
| Barbera psoriasis | The pathology develops in waves and is difficult to treat. Red, scaly spots with clear boundaries first appear on the affected areas. After two days, blisters with clear liquid form inside. When they open, erosion is exposed. Over time, it dries out and becomes covered with a dense brown crust. Barber's psoriasis can cause skin atrophy | Pads of toes, arches of feet, heels |
| Localized acrodermatitis Allopeau | First, tension occurs, then the skin becomes red, with a blue tint, and pustules appear around the nail plates | Tips of the phalanges |
| Psoriasis with pustulation | Purulent rashes form within the boundaries of the inflamed red spots of vulgar psoriasis or directly along their contour |
Barbera psoriasis
Generalized form
| Name | Clinical manifestations | Locations of damage | Features of the course of the disease |
| Tsumbusha psoriasis | It starts suddenly and always proceeds violently. Red spots appear on the skin, within which severe inflammation occurs. Its borders are clearly defined, the edges are swollen, so they rise significantly above areas of healthy integument. Inside the affected area, group formations similar to bubbles form, they unite and, when mature, erupt. After which erosions appear on the skin, which do not heal for a long time. At the same time, crusts, erosions and fresh rashes can be seen on the affected areas. | Spots can appear anywhere on the body, on the face, on the scalp. Nail plates and oral mucosa may be affected | The disease is recurrent in nature, the acute period can last up to two months, then the symptoms subside, but do not disappear completely |
| Persistent acrodermatitis Allopo | Small inflamed spots with clear boundaries appear on the affected areas, and rashes are noted inside them. As a result of their opening, erosions appear, which eventually become covered with red crusts. Afterwards atrophy and scleroderma-like transformations develop | Hands, soles | The disease constantly recurs |
| Impetigo herpetiformis | This form is diagnosed in pregnant women in the second trimester. It always debuts acutely with the appearance of a group of painful pustules. Over time, they merge and form shaped plaques, constantly increasing in size. Inside the elements there is green pus, it matures and then erupts, instead a small ulcer forms, which is covered with a brown crust. | Groin, armpits, neck, back of head, inner thighs. The disease can cause damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth, larynx and esophagus | The pathology is recurrent in nature |
All types of generalized forms are characterized by the presence of pronounced edema. They can lead to irreversible impairment of vascular permeability. Many patients develop thrombophlebritis. There are risks of symptoms of oliguria and renal failure.
Impetigo herpetiformis
Types of pustular psoriasis
Based on the extent of damage to skin areas, the disease is divided into localized and generalized forms. Generalized psoriasis manifests itself as a pustular rash that can appear all over the body. The pustules merge and form large-scale oozing. This type includes:
- Tsumbusch psoriasis.
- Acrodermatitis Allopeau begins from the tips of the fingers and toes, gradually moving to the palms and soles.
- Impetigo herpetiformis. May appear during pregnancy on the inner thighs, under the breasts.
Generalized pustular psoriasis appears abruptly, the rash is hot to the touch. This form may be accompanied by elevated body temperature and aching joints.
Localized psoriasis often lasts a long time, and its elements are difficult to treat. Constant walking, sweating feet, washing hands - all this does not have the best effect on drying out the elements of the rash. This type of pathology includes:
- Localized Allopo's dermatitis (the affected area is the pubic area).
- Barber's pustular psoriasis. Favorite places for localization are the feet and palms, which prevents a person from working.
During an exacerbation of the disease, the patient is required to issue a sick leave certificate.
Treatment methods
To reduce the symptoms of exacerbation, a set of therapeutic measures is used. Patients are given an appointment:
- antihistamines (“Suprastin”, “Tavegil”);
- sedatives (neuroleptics and bromine solutions);
- vitamin complexes;
- immunosuppressants (“Cyclosporine”);
- cytostatics (“Metatrexate”).
To treat the affected area, creams and ointments are used, which contain tar or salicylic acid, corticosteroid hormones (Elokom, Diprosalik), analogues of vitamin D-3 (Calcipotriop). When papular rashes appear on the head, patients are advised to use medicated shampoos (Friderm).
If generalized forms are diagnosed, the patient must be hospitalized. In the hospital, the body is detoxified and corticosteroids are prescribed in high doses, but in short courses. They help relieve swelling and inflammation.
In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy methods are actively used. Hemosorption, plasmapheresis, and ultraviolet irradiation of blood are used. This is a general treatment regimen and can be adjusted.
Traditional medicine recipes
Traditional medicine recipes can also be actively included in the main drug regimen. There are many agents that can be used as adjuvant therapy.
- To relieve severe itching, compresses and lotions from decoctions and infusions prepared from chamomile, oak bark, calendula and celandine are often prescribed.
- To strengthen the immune system, vitamin teas brewed with rose hips, currants, sea buckthorn or raspberries are prescribed.
- To gently soften the crusts, traditional medicine suggests using avocado, olive oils or propolis-based ointment. It couldn't be easier to prepare. Place half a kilo of butter and 50 grams of propolis in an iron bowl. The ingredients are melted over low heat, mixed thoroughly, the product is evaporated by half, cooled, and then used for its intended purpose.
- To cleanse the body of toxins, experts advise preparing infusions of herbal teas that have anti-inflammatory and choleretic effects. To prepare one such collection, you need to take three spoons of the series, one spoon each of valerian root, St. John's wort and celandine leaves; to prepare the second collection, you need to take licorice root, oregano leaves and celandine leaves in equal proportions.
Similar collections can also be used to prepare medicinal baths.
Prevention measures
There is no specific prevention of pustular psoriasis. Experts cannot yet understand what provokes its appearance, so doctors today are formulating general recommendations that should be followed by all those who have a history of predisposition to skin pathologies of this type. Important:
- Protect your body from direct sunlight and insect bites.
- Give up bad habits: smoking and alcohol disrupt the normal functioning of the body and reduce the functioning of the immune system.
- Avoid stress and emotional overload.
- Maintain a work and rest schedule.
- Adjust your diet to include foods high in vitamin D.
- Combat dry skin with moisturizing creams.
- Avoid contact with household chemicals.
The listed preventive measures cannot replace drug treatment; they can complement it, prolong the period of remission and prevent the occurrence of a new attack of exacerbation.
Causes of appearance and provoking factors
Pustular (translated from Latin pustule - “pustule”) form of psoriasis more often (in 60% of cases) occurs against the background of an ordinary (vulgar) disease. The exact reason for the progression of the problem has not yet been established.
Nevertheless, scientists identify a number of factors that provoke the development of this form of psoriasis:
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Excessive exposure to direct sunlight.
- Injuries, infectious skin lesions.
- Decreased calcium concentration in the blood.
- Long-term treatment with hormonal ointments, salicylic acid.
- Concomitant liver damage, among which obstructive jaundice is most often noted.
The more factors simultaneously affecting the patient, the higher the chance of developing pustular psoriasis.
In 40% of cases of pustular psoriasis, it is preceded by the usual, vulgar form. Let's consider the sequence of reactions occurring in the skin, which determine such a development of events:
- Immune system dysfunction. T lymphocytes (killer and helper cells) penetrate the epidermis. There they provoke a massive release of inflammatory mediators, which cause the occurrence of the phenomenon.
- There is a disorder in the functioning of keratinocytes. They stop ripening, but quickly divide. Their proliferation begins and, in parallel, leukocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells migrate into the epidermis, aggravating the course of the disease.
This is how common psoriasis develops. The pustular form is additionally accompanied by the appearance of specific bubbles with liquid inside. When they are damaged, a bacterial skin infection with characteristic symptoms occurs.
According to medical statistics, in 40% of cases the disease occurs in completely healthy people for unexplained reasons. In another 60% of patients, it develops in response to improper treatment of conventional forms of psoriasis and is localized in the same affected areas.