Is HPV transmitted from woman to man through sexual contact and how to avoid infection?
In women, the virus enters through the cervix, rectum or oral cavity.
If there is a frequent change of sexual partners, the risk of infection increases to its maximum. The consequences of the disease can be infertility, cancer and many other ailments. The papillomavirus in men most often manifests itself on the scrotum, head of the genital organ, anus or oral cavity. In men, the disease can occur without symptoms; only after severe stress or decreased immunity can the development of papillomavirus occur.
A dangerous aspect of HPV in men is the development of cancer of the male genital organs or anus.
In order to prevent the virus from entering the human body, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene, as well as lead a healthy lifestyle and be faithful to one sexual partner.
The papilloma virus affects all areas of human life. If there are formations in the anogenital area, patients are interested in whether it is possible to have sex with HPV. It is important to know the route of transmission of the virus and the mechanism of its development.
Routes of transmission of HPV
Human papillomavirus is an infectious disease transmitted sexually with a high degree of contagiousness. The disease can be transmitted in three ways:
- Through everyday contact. Infection can occur through the common use of hygiene equipment, dishes, clothes, and shoes. You can catch HPV in public bathing areas where you can walk barefoot.
- The mother can transmit the virus to the child if at the time of birth the expectant mother has condylomas of the intimate area. As soon as the baby begins to pass through the birth canal, he comes into contact with the growths.
- Genital papilloma is transmitted through intimate contact. The most common method of infection with an infectious pathogen.
During sexual contact, the mucous membrane of the anus is most susceptible to damage. In second place is the female vagina. The least sensitive to microtraumas are the male genital organ and the oral cavity. For these reasons, infection is likely during anal sex, traditional for women. Oral contact (blowjob) is among the safest. HPV is also transmitted through condoms.
Transmission of infection from one person to another does not mean 100% development of the disease. The main role is played by the immunity status of the sexual partner. A stable immune system will not allow the infection to activate. Some people are unaware of the presence of HPV in their own body. The manifestation of papilloma virus symptoms occurs when the immune defense is weakened.
The transmission process is the same for both sexes. The human papillomavirus is transmitted to a partner during sexual intercourse through microscopic injuries caused by friction.
The virus cells are so small that they can easily penetrate minor scratches or cracks. The pathogen settles in the body. Sometimes the incubation period can take several years. Weakening of the immune defense can cause the infection to “exit” to the outside. The condition is provoked by:
- acute infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition, vitamin deficiencies;
- a woman is pregnant;
- diseases of the immune system;
- stress, nervous breakdowns.
Depending on how the infection occurred, the growths are localized. The formation of condylomas is inherent in the anal, genital and oral areas. There are two types of condylomas - pointed and broad. The first are elongated growths, on a thin stalk, which are prone to fusion. The second - flat plaques, are caused by Treponema pallidum - the causative agent of syphilis, which indicates the development of secondary manifestations of the disease.
The resulting growths contain the highest concentration of viral cells. If the growth is damaged, the infection spreads to healthy areas. In the same way, HPV passes from one sexual partner to another.
Oncogenic types pose a danger to humans, especially 16 and 18. In women, these strains are found in cervical cancer. In men, malignant processes of the prostate, head of the penis, and rectum may appear.
Condoms are an effective means of protection against most sexually transmitted diseases. To penetrate the body, the virus only needs microscopic damage to the skin, which is invisible to the eye. Synthetic materials are not an obstacle for him either. It is not recommended to consider barrier contraception as a way to protect the body from HPV. Even a high-quality condom is not able to protect against the transmission of the disease.
HPV can be transmitted through a condom. It is important to realize that the presence of the virus in the body is serious, and complications may develop in the partner. Intimate papilloma is always transmitted sexually.
Many sources claim that sex with a condom is safe, but these statements are incorrect. The presence of condylomas on the genitals, groin, anus, and oral cavity is a significant barrier to sexual intercourse.
Those who doubt whether to have sex during active manifestations of infection need to deal with two questions. Is an infected person with warts on the genitals ready for sexual intercourse in order to deliberately infect a partner? The risk that a previously healthy person will exhibit the same symptoms of the disease is not guaranteed.
Things are different if HPV is detected in the body, but there are no external manifestations of the disease. This indicates the passive presence of the pathogen or the active activity of the immune system. Taking into account that a person with this diagnosis will begin timely treatment, preventing the warts from coming out, sexual relations are allowed.
Treatment of human papillomavirus infection is a process that includes a set of measures. In severe cases of the disease, the patient is prescribed a course of antiviral and immunostimulating drugs and removal of condylomas.
Drug therapy includes the use of Interferon, Viferon, Cycloferon, Allokin Alpha. The products have a complex composition that simultaneously helps to suppress the activity of the pathogen and normalize the body’s natural defenses. You can treat the external manifestations of the disease using destructive chemicals, keratolytics, or hardware influence.
Correctly selected treatment helps to completely neutralize the infection. The virus enters a latent state, in which it is unable to reproduce and cause symptoms of the disease. After treatment, the person becomes non-infectious to others.
HPV does not apply to diseases, after which long-lasting immunity is developed. The disease can be cured, but the virus remains in the body. A person who has undergone therapy will not infect a partner during intimacy. The main condition for a person who has suffered the active phase of papillomavirus is not to allow the infection to reactivate.
To do this, it is recommended to pay attention to the state of immunity, avoid stress, hypothermia, and treat infectious diseases. Women need to visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year so that the doctor can notice the appearance of new formations in time. Patients who have had a strain that causes cancer have been identified in their bodies should be careful.
The papilloma virus is so common that becoming infected with it is not particularly difficult. Following certain recommendations will reduce the likelihood of disease transmission:
- use exclusively personal hygiene items;
- check compliance with sanitary standards during salon procedures and gynecological examinations;
- do not walk barefoot in public places;
- exclude contact with papillomas in another person.
The main recommendation for people who are sexually active is to have a regular lover. Based on the fact that HPV is transmitted from partner to partner through a condom, only this condition can guarantee safety.
Another way to avoid infection is vaccination. There are 3 HPV vaccines. Quadvalent Gardasil - from 16, 18, 6, 11 types. 9-valent Gardasil - from 16, 18, 6, 11 and 5 highly carcinogenic strains. Cervarix - from types 16 and 18. Vaccination occurs in 3 stages, after which the vaccination can be considered complete.
HPV is transmitted to a partner. It is important for people suffering from this disease to understand that they can easily become infected with papillomavirus. To avoid such a situation, it is necessary to identify the development of infection and begin treatment.
The papilloma virus can remain in the human body for a long time and not manifest itself in any way. It is activated only when the immune system is weakened. In most cases, the infection does not pose a particular danger, but some of its strains, under certain factors, can degenerate into cancer.
The human papillomavirus causes the formation of benign neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes. They have the appearance of a papilla that protrudes several millimeters above the surface. As a rule, such a growth appears when the body’s defenses are weakened. Usually a person lives quietly and does not even think about “whether I can be a carrier or not,” for the time being. Why papillomas form:
- frequent hypothermia or overheating;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- presence of bad habits;
- frequent stress, depression, overwork;
- lack of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients.
Methods of transmission of HPV
It is easy to become infected with the human papillomavirus because the virus can easily be transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person. Many people who have encountered this problem are concerned with the question: how can you become infected with papilloma? There are 4 main routes of transmission:
- through sexual relations;
- contact and household method;
- from mother to child;
- self-infection.
Let's consider the listed methods of virus infection separately.
Transmission of HPV through sexual contact
In most cases, papillomas are transmitted through sexual contact. The infection enters the body through open areas of the genitals, so contraception does not always provide the necessary protection. Transmission of the virus occurs regardless of the type of sexual intercourse, traditional sex, or oral, anal. After infection, benign tumors – papillomas – form on the genitals. In this regard, the question is: does a condom protect against HPV? No, it still cannot protect the body 100% from the penetration of the virus.
In cases of transmission of the virus through unconventional sex, growths may appear near the anus or in the oral cavity. Sometimes the infection can even be transmitted through a kiss or mutual caress of the genitals. After the virus enters the mucous membrane, it quickly enters the body through minor damage. HPV transmission usually occurs from men to women, and in rare cases, vice versa. Homosexuals, in particular passive ones, are at great risk of contracting the papilloma virus. Knowing how HPV is transmitted, you can protect yourself by living a sexual life with one regular partner.
Contact-household method of transmission of HPV
In addition to sexual contact, HPV is also transmitted through household contact, although such cases are uncommon. When in contact with an infected person, there is a chance of becoming infected, especially when shaking hands. The virus can be in saliva, urine, sweat. Therefore, if you kiss a person on the cheek, you can infect him. And even on public transport, by holding the handrail on which the virus is located, and then by touching your eyes, face, or any other part of the body, you can become infected with HPV. But infection with HPV in this way is quite rare, since the papillomavirus cannot exist outside the human body for a long time.
People often become infected with the virus in a swimming pool or bathhouse. Also, cases of infection in medical institutions and beauty salons are not uncommon. This can happen when a doctor examines patients without gloves. The risk of HPV infection especially increases if there are various injuries, cuts, and scratches on the body.
It is necessary to monitor hand hygiene, do not sit down to eat without washing them, and also do not use other people’s hygiene products: towels, soap, washcloths. This is the only way to at least slightly reduce the risk of infection in public places.
Mother-to-child transmission of HPV
Many women who have HPV in their bodies are wondering whether papillomas are contagious to the fetus? Passing through an infected birth canal, a newborn can contract the virus. Infection in this way leads to the appearance of papillomas on the respiratory organs. And laryngeal papillomatosis makes breathing difficult and can lead to suffocation of the child. Sometimes the virus can be transmitted during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Some resort to caesarean section in such cases. But even so, the child can become infected. Therefore, cesarean section is recommended in extreme cases or if the mother has a large number of papillomas on the genitals. HPV is not inherited; if there is a carrier of HPV in the family, then he can infect the rest of the household. Therefore, being a hidden carrier of the virus, you should think about how not to infect your partner.
Self-infection with HPV
It is possible to become infected with the virus yourself while shaving, cutting nails or epilating. And children who constantly pick off warts can transfer the existing virus to healthy areas of the skin, thereby increasing the affected area.
Is human papillomavirus transmitted by airborne droplets? This happens very rarely, but it does happen.
For example, when medical personnel become infected with HPV during an operation on a patient. But this rarely happens.
Human papillomavirus in men
HPV is the abbreviated name for human papillomavirus. Most sexually active residents of the CIS sooner or later become infected with it. There are more than 100 varieties of the virus that are transmitted through sexual contact. They can affect the male genital area, including the skin of the penis or anus and the surrounding skin. They can also affect the mouth and throat. However, when infected with HPV, the risk of developing cancer increases many times over.
Like most sexually transmitted infectious diseases (STIs), the papillomavirus is transmitted only through mucosal contact from person to person.
This virus is transmitted through sexual contact. This most often occurs during vaginal and anal sex. It can also be transmitted through oral sex. Because the virus usually doesn't cause any symptoms, most men and women can become infected with it and not even know it.
Even if the infection occurred many years ago, people can still have HPV. Even men who have had only one sexual partner throughout their life can become infected.
Most men with this virus (of any type) will never experience symptoms or health problems. However, some types of virus can cause genital warts. Other varieties can cause cancer of the penis, anus, or oropharynx (the back of the throat, including the base of the tongue and tonsils).
In the CIS, about 1% of sexually active guys have genital warts at least once in their lives.
Every year in the CIS there is approximately:
- 400 men with penile cancer;
- 1,500 men with anal cancer;
- There are 5,600 men with oropharyngeal cancer, but many of these cases are caused by smoking and drinking, not HPV.
These are men with homosexual and bisexual orientation. Among them, there are 17 times more cases of anal cancer.
Another risk category is that people with weak immune systems, including those infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), are more likely to experience anal cancer. Men with HIV are also more likely to develop more severe warts, which are more difficult to remove.
Most people infected never experience symptoms.
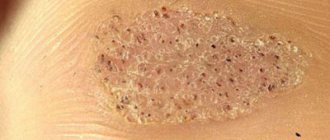
Genital warts:
- One or more occurred on the penis, balls, groin, thighs, or anus.
- They can be located singly or in groups. They can be raised or, on the contrary, be at the level of the surrounding skin. There are warts in the shape of cauliflower. They usually do not cause any inconvenience.
- They may appear weeks or months after sex.
Anal cancer:
- Sometimes there are no signs.
- Anal bleeding, pain, itching, or discharge.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the anus or groin area.
- Changes in bowel behavior or shape of feces.
Penis cancer:
- First signs: discoloration, thickening of the skin or growing tissue.
- Late manifestations: the penis is swollen or inflamed. Usually there is no pain, but in some cases the inflamed penis may hurt and bleed.
Different types of oropharyngeal cancer:
- Sore throat or ear pain that won't go away.
- Constant cough.
- Pain or problems swallowing and breathing.
- Weight loss.
- Hoarseness or changes in voice that last more than two weeks.
- Growth on the neck.
Numerous studies have identified more than 100 types of the virus. Some of them do not pose a serious threat to health, but some of them should be taken with the utmost seriousness, as they can cause the development of malignant tumors.
The oncogenic classification of the virus is divided into 3 types:
- Group 1 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 subtypes of HPV, a non-oncogenic group that does not cause the development of tumors);
- Group 2 (6, 11, 42, 43, 44 HPV has a low risk of cancer, but mutations are possible with the influence of other factors in which the risk increases);
- Group 3 (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 59, 68 have high activity in the development of cancer cells, most often bladder cancer in men).
In any case, it is important to understand what type of virus the body is infected with for further steps in treatment.
Today, there are several stages of diagnosing papillomavirus:
- Visual examination by a doctor.
- Collecting blood and secretions from the penis for testing in the laboratory.
Types of diagnostic methods:
- DNA hybridization (Digene-Test).
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
There is no cure for this virus. There is no treatment technology (medicines and drugs are not able to completely destroy the pathogen cells).
However, there are ways to get rid of the problems that HPV causes in men.
Genital warts can be eliminated through medications, surgery, or freezing. Some of these methods will require a visit to your doctor. Others can be implemented independently. None of the options listed are the best. However, they may return several months after treatment, so multiple treatments may be needed.
If warts are left untreated, they may either go away on their own, remain the same, or grow in number or quantity. They won't turn into cancer.
Cancers of the penis, anus, and oropharynx can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Often two or more treatments are used together. Patients can decide with their doctor which treatment options are best for them.
A safe and effective vaccine against the virus (Gardasil) can protect boys and men from the types that cause most anal cancers and genital warts. It is done in three doses over six months.
Condoms (if used every time you have sex, from start to finish) can reduce your chances of infecting your partner or becoming infected yourself. This also reduces the risk of HPV-related diseases. However, it is worth remembering that areas that are not protected by a condom can be infected. That is why the latter is not able to provide one hundred percent protection against the human papillomavirus.
Because this virus is so common and usually undetected, the only way to be protected for sure is to not have sexual contact at all.
If you are 26 years old or younger, you can get the HPV vaccine, which can protect you against the types of virus that usually cause problems. The vaccine (Gardasil) can prevent four common types of human papillomavirus (types 6, 11, 16 and 18).
Vaccination protects against infection, but is not a remedy against an already acquired papilloma virus or the disease caused by it. It is most effective when done to a guy before his first sexual contact (that is, before he could become infected).
The vaccine is very effective. It does not have any serious side effects. The most common side effect is arm soreness.
Research has shown that the vaccine can protect men from genital warts and anal cancer.
Partners usually infect each other. If you have been with your partner for a long time, you are most likely already infected. Most sexually active adults acquire the virus at least once during their lifetime. Although HPV is common, the health problems it causes are rare.
Condoms can reduce your chances of getting HPV and HPV-related illnesses if you use them every time you have sex, from start to finish.
If your partner has genital warts, you should not have sex until they disappear or are removed. You should check your penis for any abnormalities.
If you find anything unusual, you should contact a clinic that specializes in sexually transmitted diseases.
It is believed that viruses of types 16 and 18 found in humans can most likely provoke the development of malignant oncological processes. This does not mean that such a terrible disease is obligatory; it only alerts the doctor to especially frequent, careful examination of such people. Viruses of other types (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) are not seen to be as aggressive.
Several types of HPV are usually transmitted; their combination can be detected by laboratory tests. A man gets HPV from a woman through unprotected sex; a condom (according to experts) does little to reduce the risk of infection. The use of shared hygiene items is considered a possible method of infection.
Cases of other routes of transmission of the virus from a woman to a man (kissing, handshakes, airborne droplets, associated with inhalation of particles of sputum, mucus, saliva) are controversial.
Almost the entire population (with rare exceptions) has such a “guest” in its body. Microorganisms coexist peacefully with the person who becomes their carrier.
Methods of sexual transmission in women and men
Most often, especially dangerous types of papillomavirus are transmitted from sick people to healthy people during sexual intercourse. Moreover, any type of such contact can pose a danger:
The risk of transmission of infection increases if there are visually noticeable warts on the genitals. They may appear as papillary growths, similar to cauliflower, or as flat plaques, similar to warts vulgaris.
However, you can become infected with HPV even in the absence of all sorts of external manifestations of the disease, although the likelihood of infection in such a situation is much less. In particular, doctors say that the presence of HPV in the blood in the absence of external manifestations most often does not pose a threat to others.
Are skin tags contagious or not?
Warts and papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes can also be dangerous in terms of infection. You can catch papillomavirus through simple contact with them, but the risk of infection increases:
- In case of injury to condylomas.
- If there are violations of the integrity of the skin on the human body (scratches, abrasions, skin diseases, etc.).
- With a decrease in immune activity.
It is worth noting that contact with a wart on the hand cannot lead to the appearance of genital warts on the genitals. Such tumors are caused by different strains of HPV.
Can you get infected from someone else through a kiss?
HPV can be present in various body fluids, but it is not present in pure saliva. There is a high probability of transmitting such a pathogen to another person during kissing when:
- The presence of papillomas on the mucous membranes of the mouth or throat.
- The presence of injuries to the mucous membrane.
- Oral-genital contacts.
- Severely reduced immunity.
Most often, kissing does not lead to HPV infection, since the saliva itself does not contain the virus.
Can HPV pass from mother to child?
HPV can actually pass from mother to fetus, both during pregnancy and during childbirth. The risk of infection increases if condylomas are present on the woman’s genitals. However, this situation does not become the main indication for a cesarean section, although transmission of HPV to the fetus can result in various complications, including the formation of growths in the respiratory tract. But, fortunately, such a complication occurs extremely rarely. Many scientists have come to the conclusion that infection of the fetus subsequently ends in the so-called elimination of the virus - the baby’s body independently gets rid of it during the first months of life. In the future, such children are recommended to be vaccinated against HPV.
The risk of transmitting HPV to a child can be reduced by using targeted antiviral treatment even before actively planning a pregnancy. Also, a woman needs to get rid of existing growths on her body in advance.
Can you get infected with papillomavirus through a condom?
The condom is a fairly effective method of protection against most STDs, however, it is not able to protect against the human papillomavirus. The risk of infection increases several times if the formations in the patient’s intimate area are located outside the organs that the contraceptive protects.
You can become infected with HPV during:
- Simple contact of genitals without penetration.
- Manual transfer during foreplay.
- Oral sexual contact, etc.
Today, doctors are confident that most oncogenic strains of HPV are transmitted through sexual contact. Their presence in the body can be detected using special tests, in particular PCR.
Is infection possible through household means?
The human papillomavirus is moderately resistant to environmental influences. Therefore, it can persist for some time on household and hygiene items (especially a washcloth, towel, etc.). Infection of adults most often occurs in:
- Hairdressing salons.
- Swimming pools.
- Beauty salons, in particular in manicure/pedicure rooms.
Read more After cleansing, when can you get pregnant?
Again, it must be emphasized that people who have visual manifestations of human papillomavirus infection on their bodies pose a danger from the point of view of infection.
How does the virus enter the human body?
The infection spreads through the mucous membrane or skin of a person. If there are no acute diseases, then papilloma does not manifest itself in any way, and growths do not form on the surface of the skin.
If growths of different colors have formed on the skin, then this indicates a precancerous condition, when the human skin, and the entire body, suffers a malignant disease, or the immune system is significantly reduced.
The “favorite” place for bacteria to penetrate are cuts, scratches and other skin lesions through which the virus can penetrate. The likelihood of infection increases if:
- A person has colds or other reasons for which immunity is greatly reduced.
- Dysbacteriosis of the intestines or female genital organs is observed. In this case, the beneficial microflora dies and is replaced by harmful microorganisms, in this case, papillomavirus infection.
- Presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Relapse of chronic diseases.
- Stress and depression, which reduce a person’s defense against viruses.
HPV in the body: how it penetrates and what it does
After HPV is transmitted to a woman, infected cells in the deep layers of the cervix begin to divide uncontrollably and spread rapidly. When the number of diseased cells is sufficient, signs of the disease appear on the genital mucous membranes and functional disorders of the genital organs are observed.
In men, growths usually occur on the frenulum of the penis or the coronal sulcus. Less often - on the body of the penis, the head, the opening of the urethra. Also, condylomas can be located in the urethra itself, which leads to impaired urination.
The virus enters the body through microdamage to the skin and mucous membranes. The wounds can be so small that they cannot be seen with a simple glance. Let's figure out how this happens.
The skin is a rather complex organ. Its main task is to protect the body from any external influence. In addition to skin cells, other forces are involved in protection - bacteria that live on the surface of the skin, and cells that are responsible for immune defense (for example, macrophages and white blood cells).
But all this works as long as the skin barriers remain strong. Any, even the most minor damage or inflammation of the skin, breaks the barrier, and infection can enter the body. Especially if it's a tiny virus.
Once in the body, the papillomavirus invades the cells of the epithelium (the upper layer of the skin) and mucous membranes. HPV only affects these cells—it does not live in internal organs or in the blood.
The epithelium consists of several layers. The virus invades young skin cells, which are created in the lowest layer of the epithelium. There the infection remains hidden for some time. It is impossible to say exactly how long her “sleep” will last - it could be several weeks or several years. But after hibernation, HPV begins to multiply.
As the epithelial layers are renewed, all young cells gradually “rise” to the surface of the skin. Together with the cell, HPV also rises, layer by layer. As a result, it ends up at the top and grows into a wart.
The word “multiply” doesn’t really apply to viruses. Not being full-fledged living organisms, viruses do not reproduce themselves, but simply force the host cell to produce new viral particles. This process is called "replication".
Types of papillomas
Often, a person’s immune system completely clears the body of the virus. The time required for this may vary: it depends on the type of virus and the strength of the immune defense, but is usually 1-3 years. Sometimes, although less frequently, HPV lingers in the skin for a long time. In such cases, doctors talk about the chronic course of the infection.
Cells that are damaged by the virus also react differently to its activity. Some cells simply die and are replaced by new ones. In other cells, complex changes in their structure and functions occur - for example, this is how precancerous changes occur in the cells of the cervix. Still others, under the influence of the virus, begin to divide randomly and cause tissue proliferation - papillomas and condylomas appear.
Another scenario has been described and proven - when the virus enters the body, but does not cause any changes in the cells, and after a while it completely disappears.
After infection, the virus initially does not manifest itself in any way. Papillomavirus can remain latent in the body for a long time, from several weeks to 20 years. The infection is activated when favorable factors for this occur. Typically, this factor is considered to be reduced immunity, which is no longer able to fight the virus. Other factors that provoke the development of the virus include:
- constant stressful situations;
- presence of bad habits;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
People who are highly susceptible to HPV are:
- often change sexual partners;
- live in a place with a low level of economy;
- give birth at an early age;
- had abortions;
- socially unadapted;
- prefer unconventional types of sex.
Women become infected with HPV during sexual intercourse, even during their first sexual experience. The presence of the virus in the body can be determined during a routine examination by a gynecologist, so it is not recommended to postpone going to the clinic until later.
That is, it often happens that a man is a hidden carrier and transmitter of the virus, although he himself does not even know it. But, knowing how human papillomavirus infection is transmitted, what human papillomatosis is, how to get rid of it, you can protect yourself from infection. Therefore, it is necessary to engage only in protected sexual contact and to enter into sexual relations with only one trusted partner.
Pinworms
Other parasites
Pinworms
What is HPV infection?
HPV infection is a group of viral diseases provoked by the papilloma virus. To date, more than 100 types of virus have been studied and described. Scientists have been studying the morphology of the pathogen for a long time, which made it possible to determine which types of viruses provoke which pathologies. A separate group of HPV with a high risk of oncogenicity was identified.
Due to the fact that HPV primarily affects the reproductive system, gynecologists pay considerable attention to studying the problem. Talking about what HPV is in gynecology, it is necessary to note the high risk of developing cervical cancer. Experts have found that this virus itself, or more precisely, its types 16 and 18, provokes the development of an oncological process in the female reproductive system.
How to avoid getting infected with papillomavirus
How to avoid getting infected with HPV (papillomavirus):
- avoid frequent changes of sexual partners;
- protect yourself during intimacy;
- do not use other people's things;
- do not wear other people's clothes;
- avoid visiting public baths, saunas, swimming pools (or at least carry a personal towel and spare shoes with you);
- do not drink drinks or eat food from infected people;
- carefully approach the choice of cosmetology, clinic, hairdresser (you must be sure that the institution complies with all sterilization rules);
- do not come into close contact with carriers of the virus.
If you do develop papillomas, consult a doctor. He will conduct the necessary diagnostics, determine the strain of the pathogen and, if necessary, prescribe effective treatment.
If you do develop papillomas, consult a doctor
Mother-to-child transmission of the virus
Papillomavirus is most often diagnosed in people aged 18 to 45 years. Since this period is accompanied by the highest sexual activity, a completely logical question arises: is sex possible with HPV? Considering that the infection is in most cases sexually transmitted, there is a risk of intensifying it in your own body, as well as infecting your sexual partner. How to have sex with papillomavirus, what risks exist, and what safety measures should be followed?
All about HPV
Three routes of infection are considered:
- Sexual is the most common. HPV is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person during sexual contact through secretions or microtrauma. Infection can also occur during petting or oral sex.
- Household is the second most popular route of infection. The papillomavirus enters the body of a healthy person through contact with personal hygiene items of an infected person. This often happens when shaking hands or kissing. Note that our hands are a carrier of bacteria. It is enough to rub your eyes or mouth with your hands after contact with the pathogen, and the result is infection.
- Perinatal – causes a lot of controversy among specialists. The child becomes a carrier of the virus not in the womb, but during passage through the birth canal. It is at this moment that bacteria can enter the baby’s body.
Today, papilloma infection lives in most people, but not everyone has it in the active phase. For the inflammatory process to begin, the body must be affected by negative factors. These include:
- environmental situation - harmful emissions, radiation, excess ultraviolet radiation;
- bad habits – alcohol abuse, tobacco smoking, hookah smoking;
- overweight and obesity, causing endocrine system disorders;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- decrease in the body's defenses and immunity;
- hormonal changes and surges;
- taking hormonal medications;
- stress, overwork, nervous exhaustion.
Papilloma itself is not dangerous; it is benign and consists of overgrown cells. The growth becomes malignant during mutation, under the influence of negative factors.
Having sex if you have HPV is not prohibited. The decision whether or not to have sexual intercourse with this disease must be made solely by the person himself. However, it is important to understand that an active intimate life with papillomatosis becomes quite problematic.
The fact is that it is impossible to completely cure the disease. Therapy only suppresses viral manifestations, blocks their activity and puts the infection into a dormant state. As a result, there is a high risk of relapse, and patients turn to the doctor again and again.
With regular sexual intercourse during the activity of the papillomavirus, growths are injured - both on the skin (especially in the genital area - on the labia majora in women, on the testicles, scrotum, penis - in men) and on the mucous membrane (labia minora, vagina ). They are combed, rubbed, undermined.
Naturally, with frequent trauma, neoplasms begin to progress, and their number becomes much larger. This leads to multiple papillomatosis, which interferes with normal intimate contact. The situation may reach the point where oral sex and petting will be strictly prohibited. Also, growths with constant trauma tend to degenerate into malignant tumors.
Another negative factor is that an infected person is dangerous to his healthy partner. And it doesn’t matter whether we are talking about a permanent partner or a casual one.
The only way to protect yourself and your partner is to use contraceptives. They not only prevent unwanted pregnancy and resist STDs, but also protect against HPV by 75%. Studies have shown that when having sex with a condom, the likelihood of becoming infected with the papilloma virus is only 25%. With unprotected contact, this figure fluctuated around 95%. Moreover, it is easier to catch HPV during anal sex than vaginal sex.
A few words about oral sex. Some people do not understand the dangers of HPV infection. The causative agent of papillomavirus is found in human biological fluid: saliva, secretions and others. During oral sex, these fluids are exchanged. If there is a concentration of infection in the mouth or genitals, then, accordingly, there is a risk of infection. To protect yourself, it is enough to use male and female condoms during oral sex.
An important point: if infection has already occurred, then barrier contraceptives do not affect the course of the disease.
Experts recommend removing papillomas before they mutate into malignant tumors. However, a referral for removal is given exclusively by a doctor after all tests and diagnostics. There are two types of treatment for growths of this nature: medication and surgery.
Drug therapy is a conservative technique used in the early stages of papillomatosis. Its main task is to neutralize the virus and restore the body’s protective functions. Interferon drugs, immunomodulators, antiviral, chemotherapy, and hormonal drugs are used.
Surgical therapy involves complete abstinence from sexual activity. Both vaginal and anal sex are prohibited. Such procedures, despite their ease, are poorly tolerated by the body. He needs a long recovery. After surgical removal of the tumor, the tissue or mucous membrane should heal well. During sex, there is a high probability of injury, which is very undesirable.
Surgical techniques include:
- Electrocoagulation is the removal of a tumor using current. Having sex is allowed 2-3 weeks after the procedure.
- Cryodestruction - freezing the growth and destroying it with liquid nitrogen. You should not resume sexual activity earlier than a month after removal.
- Laser vaporization is the “evaporation” of a tumor using a high-tech laser. Sex is possible after 14-20 days.
- Radiosurgery is a popular technique that allows you to be sexually active 3-4 weeks after its use.
- Surgical excision is a rather “bloody” procedure, but effective. It is often used when there is a suspicion of cancer. The growth is excised along with nearby tissues. You can have sex after the wound has completely healed. This usually takes up to 1.5 months.
After any surgical treatment, sexual activity should be started gradually. It is important to understand that there is a healing wound at the site of removal. The skin and mucous membranes should fully recover after surgery. You should not give in to passion and engage in traumatic sex.
It is recommended to use a condom during sexual intercourse for six months after HPV treatment, both with a regular partner and a new one. This is due to the fact that the epithelium at the operation site is still very weak, prone to ruptures and cracks, so it is very easy to catch the infection again. It would be a good idea to refrain from casual relationships.
Security measures
Using a condom does not always protect against HPV infection. The main precaution is to avoid contact with infected people. However, in the realities of modern life this is very difficult. It is recommended to have one trusted sexual partner and not lead a promiscuous lifestyle.
Virus carriers should follow some rules in intimate life:
- Always use contraception. The method does not solve the problem of infection, but significantly reduces the risks.
- Warn your sexual partner about the disease. This is not just a rule of good manners, but a necessity. The person may not be aware of the consequences of the infection. You shouldn’t hide information about your illness; you need to value your partner’s health.
- Temporarily limit or abstain from sexual activity. Until a course of effective treatment is completed that will prevent the infection from spreading.
- Do not change sexual partners frequently. It is impossible to check everyone. And it is very easy to become infected during another sexual intercourse with a stranger.
Monitor your health closely and do not give up sex life.
People often mistake growths on the skin for harmless and treat them with traditional methods. This mistake can have dangerous consequences - abnormal proliferation of epithelial tissue aggravates the spread of papillomavirus throughout the body, and some of its strains provoke cell mutation with the formation of various types of cancer.
More than 80% of the world's population are carriers of the human papillomavirus, regardless of age and race.
With a sharp decrease in immunity, a previously dormant disease makes itself felt by the appearance of a large number of genital warts on the skin.
How is the human papillomavirus transmitted? The microorganism enters the human body through mucous membranes or skin. In a benign course of the disease, it does not manifest itself in any way: the epithelium retains its shape unchanged.
Household route of transmission of the virus
When diagnosing the papilloma virus in a person, it can be said with 85-90% probability that the disease was transmitted through household contact to all members of his family. How does infection occur at home?
- in the presence of damage to the skin, pathology occurs when sharing towels, bed linen, cosmetics, soap, and washcloths;
- You can become infected through saliva by sharing the same dishes or toothbrush with a carrier of the disease;
- Wearing clothes of someone who is sick increases the risk of transmitting the virus. If you wear the underwear of an infected person, the possibility of infection increases dramatically;
- self-infection often occurs when shaving or epilating the bikini area. Having accidentally damaged a genital wart or a wart, a person provokes the development of several epithelial neoplasms in the adjacent area.
How you can become infected with the virus in public places:
- When visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or swimming pool, it is quite difficult to become infected with the virus, because need physical contact. But this option cannot be ruled out;
- Frequent handshakes provoke the transmission of viruses in cases where there are microcracks in the upper layer of the epithelium.
What other routes of transmission of the virus exist:
- The medical literature describes cases of infection with the human papillomavirus through donor blood transfusion.
- When performing an operation to remove genital warts, doctors and junior medical staff may inhale viral particles, which begin to actively multiply on the nasal mucosa.
- Poor sterilization of manicure instruments in beauty salons can cause infection among clients.
In order to prevent the papilloma virus from entering the body, it is necessary to take precautions when visiting public places, remain faithful to one partner and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Transmission of the papilloma virus through a kiss is not a myth, but a very real way of contracting HPV from a sick partner, along with sexual intercourse. Here we are talking mainly about intimate relationships in which people are a couple. Accordingly, adults are more susceptible to this; children, depending on their age, are usually spared this problem.
How does HPV infection occur?
HPV infection occurs through direct contact of mucous membranes and genital skin. During sexual intercourse, microcracks and damage to the mucous membranes often occur, which only increases the risk of HPV infection. However, there are some differences in the mechanisms of transmission of the virus in women and men.
The likelihood of HPV infection in men directly depends on the number of regular sexual partners. Frequent promiscuity increases the likelihood of infection several times. At the same time, the man himself in most cases is unaware of the presence of the HPV virus in the body. As a result, the virus spreads further. In 90% of cases of sexual intercourse, the partner, who was previously completely healthy, becomes infected.
The routes of HPV infection in women do not differ from those typical for men. In the first place is sexual. However, certain factors also increase the risk of infection in women.
Among these, gynecologists distinguish:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- performing abortions;
- history of traumatic birth;
- gynecological diseases;
- stress;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives.
Knowing about the presence of HPV in the body, women planning a pregnancy in the near future are wondering whether the human papillomavirus is transmitted from mother to baby. Experts say that there is a risk of infection for the child. However, HPV is rarely observed in children; the modes of infection differ from those in adults. Transmission of infection most often occurs at the stage of the fetus moving through the birth canal: the virus passes from the mother’s mucous membrane to the baby.
It is worth noting that the danger from such infection is low. In most cases, the baby’s body manages to get rid of HPV during the first 2-3 months of life. This happens due to the entry of antibodies into the infant’s body along with mother’s milk. The main danger of HPV for children is damage to the respiratory tract - the formation of polyps. Such cases are rare and are considered rather as exceptions.
Routes of infection
The papillomavirus is transmitted only through contact from person to person, the source of infection is the patient’s epidermal cells, blood is safe. It is even capable of living and developing for some time in the external environment, but for a full life cycle it needs a cell. There are varieties of HPV that infect only animals; they are not dangerous for humans.
The virus enters the human body through damage to the mucous membranes or skin. Having penetrated into the deep layers of the epithelium, the infection remains dormant for some time, during which time foreign cells mature, along with which harmful microorganisms appear on the surface and begin to reproduce uncontrollably. The virus has the unique ability to quickly integrate into cellular DNA and transform its structure - it is integration into the cell genome that provokes the occurrence of oncological pathologies.
The main routes of infection with the virus are:
- Vertical - infection occurs in utero from mother to fetus.
- Contact and household - through touch, kiss.
- Sexual – during genital, oral or anal intercourse.
- Self-infection - papillomas are contagious, so you need to be very careful when shaving or epilating.
The vertical method of infection should not be confused with the transmission of the virus “by inheritance,” since this is impossible. Typically, transmission from mother to fetus occurs if there is damage to the placenta or there are pathological changes in it. As a result of transplantation infection, the baby develops respiratory papillomatosis, treatment of which should begin as soon as possible after the birth of the child. Unfortunately, due to the low effectiveness of drug treatment, surgical intervention is usually performed.
Infection is also possible during childbirth, which also causes breathing problems and decreased immunity.
Another factor in infecting a child from the mother is breastfeeding, which can cause respiratory papillomatosis.
During sexual transmission, the source is 75% male; the likelihood of infection increases if sexual relations began too early, there is a frequent change of sexual partners, or the partner has obvious signs of pathology - warts and condylomas.
During oral sex, infection can occur if the partner has a deformation of the oral mucosa; in case of infection with virus types 16 and 18, there is a high probability of throat cancer.
Unfortunately, a condom cannot always prevent HPV infection, since it can be transmitted through contact with a partner’s skin if there are microtraumas on it.
The household route of transmission of the virus is dangerous because if the disease is diagnosed in one family member, then there is a high probability that all family members will be infected. Infection occurs as follows:
- general use of washcloths, bedding, soap, cosmetics;
- through saliva when sharing dishes or a toothbrush;
- wearing underwear or clothing of an infected person.
You can also become infected through contact and in public places:
- baths, saunas, swimming pools (although the probability is extremely low);
- when shaking hands, if there are microcracks on your hands.
HPV transmission can occur in nail salons and tattoo parlors if instruments are not properly disinfected.
HPV – how long does it take to appear after infection?
Having learned about how the human papillomavirus is transmitted, many patients are interested in the timing of the first symptoms. Doctors cannot say for sure how quickly it manifests itself after HPV infection.
The following factors are of decisive importance:
- patient's age;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the body;
- state of the immune system.
In practice, the timing of clinical manifestations of HPV varies. The appearance of condylomas and changes in the affected cells can be observed both after a few weeks and after months. In some cases, the first lesions on the skin in the groin and genital area are detected a year after the papilloma virus enters the body. The exact time at which HPV entered the body can be determined based on laboratory tests.
Even those who know how the human papillomavirus is transmitted cannot always avoid infection. After treatment, in order to exclude re-infection with HPV and prevent the development of a relapse, doctors vaccinate against the papilloma virus. Vaccinations prevent the development of viral infection for 15 years or more. Among the vaccines used:
- Cervarix - effectively protects the body from types 16 and 18 of HPV. Helps prevent a number of diseases caused by HPV: cervical cancer, cancer of the oral cavity and larynx. Vaccination is possible from 9 years of age.
- Gardasil-4 – protects against four types of HPV: 6, 11, 16, 18. Vaccination of girls and women is carried out from the age of 9 to 45 years, boys and men - from 9 to 26 years.
Sexual method
Previously, we figured out how you can become infected with a benign neoplasm (papillomavirus). It became clear that HPV is most often transmitted through intimate intimacy (sexual contact). Moreover, you can become infected through all types of sex (vaginal, oral, anal). Papilloma through intimate contact (sexual contact) is transmitted through contact between mucous membranes if they are damaged. Moreover, the risk of infection is higher during anal sex, since it is more traumatic.
Considering that the risk of infection increases during intimate contact, the question arises: is it possible to have sex with HPV if one partner has it? Moreover, during sexual intercourse, infection with oncogenic strains of the virus often occurs.
Sex with HPV is acceptable, but you should always use a condom during it
Sex with HPV is acceptable. But during it you should always use barrier contraception (condoms). According to statistics, protection helps men and women avoid infection in 2 out of 3 cases. Without contraception, the risk of infection increases to 90%. If one of the people entering into intimate intimacy is infected, it is necessary to regularly undergo diagnostic testing for the oncogenicity of the pathogen (a healthy partner for the presence of HPV).
Read more How to treat endocervicitis
However, during sexual intercourse, even with a contraceptive, undesirable events can occur. During sex, the growth may become injured. As a result, another infection or blood poisoning may occur in the wound. Also, damage to the tumor can cause it to degenerate into malignancy. Thus, it turns out that having sexual intercourse while being treated for HPV is undesirable. If you do do this, be extremely careful. But it is still better to have contact only after treatment. Sexual life after removal of papillomas is less risky.
There is an opinion that the papillomavirus can be activated during masturbation. Allegedly, this is inferior sexual intercourse, resulting in hormonal imbalance and weakening of the immune system. This opinion is wrong. Masturbation does not in any way affect the body's protective functions.
Signs of HPV infection
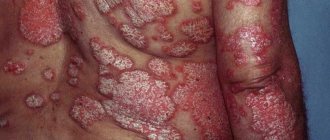
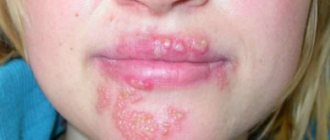
Symptoms of HPV infection include lesions on the genitals. In most cases, the virus leads to characteristic skin lesions. Patients report the appearance of vulgar papillomas and genital warts. Externally, these growths resemble cauliflower, so it is difficult to confuse them with other skin manifestations.
In women, pale pink papillary growths are localized:
- in the area of the labia minora;
- in the groin;
- on the clitoris;
- near the external opening of the urethra;
- in the vestibule of the vagina.
In some cases, condylomas form in the anus if a woman practices anal sex. The strong growth of such formations leads to the appearance of bloody discharge and pain during sexual intercourse. In men, such formations are localized in the pubic area, perineum, and less often on the surface of the penis.
Does a condom protect?
If one of the partners has HPV, it is necessary to use a condom during sexual intercourse. However, a contraceptive is not a 100% guarantee that the infection will not be transmitted. Of course, the pathogen will not be able to break through the condom, but infection can occur in another way.
Infection can occur during foreplay. Through microcracks in the skin or in the oral cavity. In this case, a barrier contraceptive will not help.