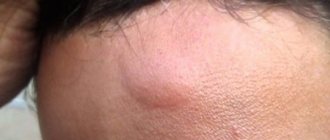
Atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle
The main function of the lacrimal apparatus is to protect the eyes from the aggressive effects of the exogenous environment.
The lacrimal apparatus also maintains the natural level of moisture in the conjunctiva and cornea. Tear secretion is excreted from the body through special pathways or through glands. The organs of the lacrimal apparatus include the lacrimal gland, small lacrimal glands and lacrimal canaliculi. In the area of the tear lake there is a so-called The lacrimal caruncle is the visible part of the surface of the eye. It is slightly convex and protrudes slightly in the inner corner.
The lacrimal caruncle is considered a vestigial component of the eye, not needed by the human body. It is believed that it was necessary as one of the receptors in the Paleolithic era, but over time it atrophied.
Neoplasms of the lacrimal caruncle are atheroma, lipodermoid, epithelioma or fibroma. These types of tumors are not dangerous to health, but they damage vision. For a correct diagnosis, a histological examination of the secretion from the neoplasm is necessary.
Patients with atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle often complain of an increase in the size of the lacrimal caruncle, its redness, burning in the eyes and a sensation of a foreign body in the area of the lacrimal caruncle.
The origin of benign neoplasms in the area of the lacrimal caruncle is still unclear. Many authors suggest that neoplasms are provoked by the development of infection when eyelashes and other foreign bodies enter the eye. Also among the probable causes of the development of atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle are acute dacryocystitis, atresia of the lacrimal canaliculi and other anomalies of the lacrimal apparatus of the congenital type.
Treatment of neoplasms of the lacrimal caruncle is surgical. The intervention is performed in an ophthalmology clinic under local anesthesia for patients over the age of 7 years. Removing atheromas in the early stages reduces the risks of inflammation and damage to neighboring eye structures.
Reception hours (on weekdays) 10:00 – 17:00
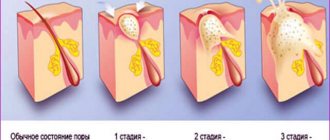
Classification
Atheromas are divided into groups according to their histological structure and reasons for their appearance. Differences in the cellular structure of cysts do not manifest themselves clinically, therefore histological classification is of interest only to researchers. In practical dermatology, classification based on the characteristics of the formation of atheromas is important. According to it, cysts from the sebaceous glands are divided into two groups:
- Congenital (primary or true). Their development is based on a genetic defect that affects the formation of the sebaceous glands and their ducts. The development of cysts from skin anlages begins in utero, which is why congenital atheromas are often detected in newborns. They are rarely larger than 0.5 cm. Usually the formations are multiple.
- Acquired (secondary or false). They develop in unchanged sebaceous glands when their lumen is blocked. They appear predominantly in adult patients against the background of previous skin damage and existing disturbances in the activity of the sebaceous glands. Over a long period of time they increase in volume, reaching significant sizes. Represented by single formations.
Squamous papilloma
An uncommon benign tumor caused by papillomavirus. Usually occurs in children and young people.
Papillomas have finger-like projections and are located on the conjunctiva of the eyelids, fornix and lacrimal caruncle (Fig. 2-5, A). They can be multifocal or bilateral.
Papillomas often heal on their own. When the size of the papilloma is large or long-standing, they can be removed surgically, but you should be aware that they can recur, becoming larger than before. Cryotherapy on the tumor bed after surgical removal significantly reduces the risk of recurrence.
A nonviral, pedunculated, broad-based form of squamous papilloma occurs in elderly patients and involves the perilimbal conjunctiva. This form is precancerous or cancerous and should be completely removed within healthy tissue, followed by cryoapplication.
Rice. 2-5. Conjunctival papilloma. A - squamous papilloma of viral origin in a child. Multiple papillary vascular trunks are visible, directed towards the tumor stalk. Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia.
Rice. 2-5. Continuation. Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia. B, Note the large, well-circumscribed, flat tumor adjacent to the limbus from 6 to 8 o'clock. Excisional biopsy revealed conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia; B - a fleshy, wide-based, slightly protruding tumor with a keratinized leukoplakic area. An excisional biopsy revealed conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia.
Rice. 2-5. Continuation. D, This HIV-infected patient had a small lesion on the superior limbal conjunctiva. Thick grayish layers of pathological epithelium rushing into the cornea indicate active invasion of the cornea in the area from 3 to 12 o'clock; D – squamous carcinoma. A large, prominent tumor is visible on the superior limbus. Actively vascularized. The tumor has taken over almost the entire area of the cornea. Conjunctival biopsy revealed squamous carcinoma.
Rice. 2-5. Continuation. E – sebaceous gland carcinoma. Mucosa of the right upper eyelid of an elderly patient with chronic blepharoconjunctivitis. Note the diffusely thickened papillomatous conjunctiva. Eyelid biopsy revealed sebaceous gland carcinoma; F - conjunctival lymphoma. The fleshy, salmon-colored tumor adjacent to the lacrimal caruncle is conjunctival lymphoma. Surgical removal of the tumor was performed along with radiation treatment; General examination revealed no systemic lesions.
Diagnostics
If a person discovers symptoms of atheroma, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. There are several similar diseases with which atheroma can be confused.
Such pathologies can be other benign tumors: fibroma, lipoma. Molluscum contagiosum, eyelid chalazion, papillomas, warts and adenomas, nevus, xanthoma and granuloma are also similar to atheroma.
To accurately diagnose atheroma, the formation is examined and felt (palpated). If there are difficulties, the doctor performs a puncture, penetrating the capsule and taking its contents. It consists of sebaceous secretion, epithelium, and bacteria.
Cysts of the eye and nose can be diagnosed using additional methods: MRI, CT or radiography.
It is necessary to differentiate the formation from a tumor of a malignant nature. Therefore, atheroma should be observed from the very beginning until complete removal.
Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia
A bilateral precancerous condition that often occurs in older patients with fair skin.
Previously, this disease was classified as a group of diseases including Bowen's disease, intraepithelial epithelioma and conjunctival dyskeratosis.
The lesions are usually located on the limbus and may involve the adjacent cornea (Fig. 2-5, B-D). There are three clinical forms: fleshy gelatinous tumor with keratinization, leukoplakic type and papillary. Treatment involves complete surgical removal of the tumor focus followed by cryoapplication.
Squamous cell carcinoma
A rare, slow-growing, invasive tumor that usually forms on the limbus. It most likely develops from conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia that grows through the basal lamina of the conjunctiva.
Papillary or gelatinous tumor. Often accompanied by a pronounced vascular network feeding the tumor (Fig. 2-5, E).
Treatment involves complete surgical removal of the tumor focus followed by cryoapplication. In some cases, layer-by-layer sclerotomy should be performed to completely excise the tumor.
This tumor can be aggressive in immunocompromised patients.
Other carcinomas
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma and spindle cell carcinoma are tumors that are in many ways similar to squamous papilloma, but they are much more aggressive and can arise not only on the conjunctiva.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare and aggressive tumor that typically affects the upper eyelid in older patients; occasionally, it may occur de novo in the form of a papillomatous growth or leukoplakic lesion on the tarsal conjunctiva (Fig. 2-5, E). This disease is often mistaken for chronic bilateral conjunctivitis or recurrent chalazion.
A series of biopsies may be necessary to make a correct diagnosis.
Methods for diagnosing education
Atheroma of the eye is diagnosed using standard visual, laboratory and instrumental techniques:
It is important that before examining the patient, the doctor asks him about everything.
- History taking and examination. The patient is asked how often he experiences acne, herpetic eruptions, and blockages of the sebaceous glands of the face.
- Palpation of the neoplasm. At the same time, pay attention to its color and density, ability to move. If the color is white, the diagnosis of atheroma will most likely be confirmed.
- Taking a biopsy followed by microscopic examination. It is performed if fibroma or lipoma is suspected. This method of instrumental diagnostics is carried out for differential purposes.
- Dermatoscopy. Using this specific technique, they find out whether there is a malignant degeneration in the formation. If tree-like growth of blood vessels is noted, the patient is sent for additional consultation with a dermato-oncologist.
Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma
A general examination of the patient by a general practitioner or oncologist should also be carried out.
Papilloma or cancer? Pregnancy.
Hello! We need your opinion, because... I'm at a loss. I am a brunette, my skin is rather dark. 33 years. I still haven’t had any problems with moles; there are no papillomas. Although I have two large moles on my body, they haven’t bothered me since birth. In 2008, HPV strains were detected in me using a PCR smear, including 31,35,18. In 2010, I discovered a nevus on the lacrimal caruncle, which I didn’t have before, it somehow quickly appeared, about this I am registered with an onco-ophthalmologist; they suggested removing the lacrimal caruncle, but the doctors’ opinions were divided; I left it under observation. The nevus is not bothering me now, there is no growth dynamics, I had a fundus lens last week. Now I am worried about a papilloma that suddenly appeared during pregnancy in the shoulder area, near the armpit. At 30 weeks, on January 1, 2016, I scratched what I thought was a pimple, there was a lot of blood, it seemed to me that some kind of blood vessel had simply burst. A week later, a formation appeared that looked like a papilloma, I didn’t pay due attention to it...now it has increased in size and from a small point the size of a needle has turned into a 2mm flat red convex (without stem) oval shape with smooth edges, skin around the papilloma has changed and turned pink. The papilloma does not bleed, does not ulcerate, does not dry out, and there are no crusts. Around the papilloma last week I discovered some lumps or two under the skin. It's like some kind of small swelling that can be palpated with a finger. Along with their appearance, a burning sensation and discomfort appeared in the area of the papilloma, which intensified at night, and this alarmed me. Now I am 38-39 weeks pregnant... I am very scared, afraid of missing the degeneration of this formation, I visited 2 oncodermatologists... opinions were divided here too, which gave me sleepless nights on the eve of an important moment in my life. One said to excise now with a scalpel and send for histology, the other said to do it after birth. What could it be that no one is telling me? Maybe they don’t want to scare me? But I'm already scared! It turns out that 2 months have passed since the discovery of this formation and its simultaneous injury. Could this really be a malignant process? I can post a photo in good quality.
Thank you if you answer.
The only way to make an accurate diagnosis is to remove the suspicious formation and send it for histological examination. There is no need to wait until childbirth, since a hormonal storm during pregnancy and childbirth can provoke growth and various changes in any tumors.
Thank you very much for your answer! Yes. I am also of the same opinion - that it should be urgently removed and examined for histology. Today I saw another oncodermalogist. In appearance he said it resembles a hemangioma. It doesn’t look like it, he says it’s melanoma, although he looked without a dermatoscope. Excision with a scalpel is scheduled for February 25 and the histology result will come in 10 days. They will excise under an injection of lidocaine... which means they will cut out a little... if you do more grabbing, they said that you need general anesthesia, but I can’t do it now. If they find something bad, they will completely excise it. They also said that melanoma doesn’t hurt at all. and if it hurts, then everything is already neglected. I hope that by Thursday I will not give birth yet, because I am also afraid that such stress as childbirth will make it even worse - if there is something bad there. By the way, they wanted to take a biopsy today, but I didn’t give it. Since it was said that if there is melanoma, this cannot be done - only removal with a scalpel. I'll write back when the results come in. It is a pity that such a solemn moment in life is overshadowed by the expectation of something different and terrible.
Doctor, hello! I am very worried, please help with advice. Today I was seen by another oncodermatologist in the state. city oncologic dispensary. He said that he could not rule out the possibility that it was nodular melanoma. The fact is that a 2mm formation is too small to determine externally what type it is. It could be a hemangioma, or it could be a melanoma. Only histology will tell for sure! I read that hemangioma becomes lighter when pressed. This happens to me. But I haven’t read anywhere whether red melanoma can also react to pressure? I’ve already read about nodular melanoma... it turns out that this most malignant tumor of all melanomas gives vertical growth, i.e. can grow very deep in all its miniature area on top, progresses quickly, especially during pregnancy, appears mainly on an unchanged area of the skin (just my option)... and I don’t understand at all.. if this is such a small hemangioma, why is there such a burning sensation in stain areas? I also noticed that two weeks ago, small altered areas of skin (satellites?) appeared near the spot...one of them felt like a small island of swelling under the skin...about 1cm. Along with them, a burning sensation appeared, which at first seemed to come from them, but now it is no longer possible to understand what exactly is burning. I looked at the photo of nodular melanoma - it looks very similar to my spot. And now, I don't know what to do. At the oncology clinic they wanted to take a biopsy, but I didn’t give it to me because I read that this is absolutely forbidden to do this for melanoma. On February 25, excision with a scalpel was suggested; again, I don’t know whether to do it. After all, they will prick an area of skin with a needle for pain relief, and in the case of melanoma, this will worsen the prognosis (they will spread metastases with the needle), and they will not undertake to cut it live without anesthesia because of my situation. Again, it’s not clear... how many cm to retreat from the tumor so as not to cause harm? No one wants to give me an emergency delivery before histology by CS without a diagnosis, which, of course, no one can give me an accurate diagnosis without histology. Doing histology before birth is again scary - what if they cause damage and metastases reach the child through the bloodstream. It’s natural to give birth until the time has come... although it seems like I should already, but the due date is tentatively set at 10.03, I understand that if it’s melanoma, I can’t wait that long and so, perhaps a lot of time has been lost. What should I do? Don't get me wrong - I'm very afraid for myself and for my only child, but no one knows anything and doesn't want to help! Maybe post a photo after all? I really hope for an answer.
I decided to write again... to share my thoughts... how true are they? Having very superficially understood my problem (as much as the lack of medical education and the presence of home Internet can allow), I realized that I needed a dermatoscopy, first of all. For some reason we have problems with this in our city. Tomorrow will be the 4th oncologist (I’m already on edge) - let’s see if he has this device in stock. How did I happen to know that hemangioma can be easily diagnosed only with the help of a dermatoscope. There are characteristic features that are unique to her. More specifically, the presence of lacunae and white partitions between them, while in non-pigmented melanoma the vessels inside look like nodules. It’s probably better to do a dermatoscopy first, so that later you can understand how much to capture healthy tissue and under what anesthesia and how quickly it needs to be done.
Alina, removal of the tumor does not carry a high risk of immediate metastasis; if melanoma is histologically confirmed, it will be possible to resect the surgical scar.
Hello! We need your opinion, because... I'm at a loss. I am a brunette, my skin is rather dark. 33 years. I still haven’t had any problems with moles; there are no papillomas. Although I have two large moles on my body, they haven’t bothered me since birth. In 2008, HPV strains were detected in me using a PCR smear, including 31,35,18. In 2010, I discovered a nevus on the lacrimal caruncle, which I didn’t have before, it somehow quickly appeared, about this I am registered with an onco-ophthalmologist; they suggested removing the lacrimal caruncle, but the doctors’ opinions were divided; I left it under observation. The nevus is not bothering me now, there is no growth dynamics, I had a fundus lens last week. Now I am worried about a papilloma that suddenly appeared during pregnancy in the shoulder area, near the armpit. At 30 weeks, on January 1, 2016, I scratched what I thought was a pimple, there was a lot of blood, it seemed to me that some kind of blood vessel had simply burst. A week later, a formation appeared that looked like a papilloma, I didn’t pay due attention to it...now it has increased in size and from a small point the size of a needle has turned into a 2mm flat red convex (without stem) oval shape with smooth edges, skin around the papilloma has changed and turned pink. The papilloma does not bleed, does not ulcerate, does not dry out, and there are no crusts. Around the papilloma last week I discovered some lumps or two under the skin. It's like some kind of small swelling that can be palpated with a finger. Along with their appearance, a burning sensation and discomfort appeared in the area of the papilloma, which intensified at night, and this alarmed me. Now I am 38-39 weeks pregnant... I am very scared, afraid of missing the degeneration of this formation, I visited 2 oncodermatologists... opinions were divided here too, which gave me sleepless nights on the eve of an important moment in my life. One said to excise now with a scalpel and send for histology, the other said to do it after birth. What could it be that no one is telling me? Maybe they don’t want to scare me? But I'm already scared! It turns out that 2 months have passed since the discovery of this formation and its simultaneous injury. Could this really be a malignant process? I can post a photo in good quality.
[youtube.player]
Neoplasms require mandatory diagnosis and treatment (both surgical and medicinal), because otherwise they can grow quickly, become inflamed, become injured, cause persistent discomfort to the patient, cause visual impairment, dry eyes or tearing, and in some cases, degenerate into cancerous tumor.
Atheroma symptoms, complications, removal methods
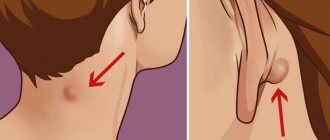
Atheroma is a benign subcutaneous formation that has a round shape, is dense and mobile to the touch, and does not exceed 5 centimeters in size. The color of the skin around the atheroma does not change; sometimes, if you look closely at it, you can see a small dark dot that clogs the outlet of the sebaceous gland duct. Atheromas develop in the sebaceous gland duct. Such tumors are often called a fatty cyst. Atheroma is usually located in those areas of the body where there are sebaceous glands - on the face, on the scalp, on the back of the neck, between the shoulder blades, in the armpits, on the scrotum, labia, perineum, chest and upper back. Sebaceous glands are found on almost the entire surface of human skin, except for the feet and palms. The main difference between atheroma and lipoma is that atheroma is always formed from the sebaceous gland located under the skin, due to blockage of its duct or thickening of sebum. If something interferes with the removal of sebum to the surface of the skin, then it accumulates in a kind of bag (capsule) - this is atheroma. The composition of atheroma is always the same: fatty substances (sebum), epithelial cells and the sebaceous gland. One of the reasons for the appearance of atheroma may be a rupture of the sebaceous gland, which can be the result of skin inflammatory diseases and skin damage of varying severity. It has been noted that multiple atheromas can appear in people suffering from Gardner's syndrome (a very rare genetic disease). Atheromas appear more often in men than in women. People who have previously suffered from acne are especially susceptible to the appearance of these wen.
Complications of atheroma
Typically, these small, painless lumps are harmless and almost never turn into anything cancerous. Any complications are associated with atheroma damage. Dangerous complications of atheroma are:
- Inflammation. Since the contents of atheroma are a breeding ground for bacteria, if they penetrate the atheroma capsule, inflammation develops very quickly and pus appears. Pus may break out. If it spreads under the skin, it can cause soft tissue phlegmon. It happens that atheroma becomes inflamed without infection. In this case, before removal, it is first necessary to relieve inflammation. For these purposes, Vishnevsky ointment and Levomekol are used.
- Break. Rupture of atheroma requires immediate medical attention, as an abscess may develop.
- Discomfort. Atheromas can cause serious physical discomfort. For example, atheroma on the genitals can interfere with normal urination or sexual intercourse.
Removal of atheroma
Due to the fact that atheroma and lipoma are very similar, an accurate diagnosis can only be made after a morphological or histological examination of the tumor tissue. These studies will rule out the presence of lipoma and malignant tumor. Modern medicine knows only one way to treat atheroma - removal. Therapeutic and traditional methods of treating atheroma have not proven effective. Removal methods can be different: surgical, laser and radio waves. The patient can choose the method of atheroma removal himself, since all of them can be used to remove atheromas of any size. Typically, patients prefer two methods: laser and radio wave, since their advantages are the absence of a rehabilitation period and a high cosmetic effect. However, if the wen is inflamed and suppurates, then only surgical intervention will help. In this case, the atheroma is opened, cleared of contents, and then subjected to drug treatment. The operation to remove atheroma is simple, it is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis and lasts about 15 minutes. The atheroma is removed only together with the capsule, since if even a fragment of the capsule remains under the skin, this will inevitably lead to a relapse of the disease. Doctors recommend removing atheroma without waiting for it to grow or break through - this can significantly complicate treatment and reduce the cosmetic effect.
Prevention of atheroma
Since atheroma is a wen and occurs due to the impossibility of sebum flowing through clogged pores, the main preventive methods are aimed at carrying out cosmetic procedures to clean the pores. They can be special masks, scrubs, steam baths. To reduce the greasiness of the scalp, you can use drying shampoos. Also preventing atheroma is establishing proper nutrition. If atheromas appear frequently, you should consult an endocrinologist. This article will tell you more about lipomatosis.
Causes
Papilloma on the eyelid is an external manifestation of an internal problem of the body: its infection with the HPV virus. This pathology is transmitted in one of three ways:
- in intimate relationships between a man and a woman (the most common way, from which contraception does not protect 100%);
- when using personal belongings of an infected person;
- during childbirth from mother to baby.
If HPV enters the patient’s body, this does not mean that growths will immediately begin to appear. Papilloma on the mucous membrane of the eye forms in the presence of the following provoking factors associated with decreased immunity:
- hormonal disbalance;
- exacerbation of chronic ailments;
- viral, colds;
- frequent hypothermia;
- states of immunodeficiency caused by mental or physical overload, stress;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- poisoning of the body with toxic substances (alcohol, nicotine, drugs);
- diabetes mellitus, etc.
If you have a strong immune system, the body resists the virus and papillomas do not form.
Reasons for appearance
First of all, atheroma occurs as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland and thickening of the consistency of the sebaceous secretion of the skin. In some cases, such a cyst can be a complication of the underlying disease, increasing its symptoms and clinical manifestations.
The main causes of atheroma are:
- predisposition of the body at the genetic level associated with impaired fat synthesis,
- congenital pathologies of the sebaceous glands,
- hormonal imbalance and metabolic disorders,
- weakening of the protective function of the immune system,
- inflammatory processes in the structures of the epidermis,
- increased sebum secretion due to disruption of the nervous and neuroendocrine regulation of the exocrine glands (as a consequence, the development of seborrhea),
- puberty in adolescents, which is characterized by increased secretion of the sebaceous glands,
- pimples, blackheads, acne and other dermatological skin diseases,
- improper use of skin care products,
- excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis).
The risk of atheroma increases significantly in overweight people who have a tendency to increase the secretion of skin secretions. A fairly rare occurrence is a cyst in newborns. However, in this case, it may appear due to intrauterine damage to delicate and sensitive skin.
Very often, the cause of the appearance can be the most common disregard for personal hygiene rules. The skin is not cleansed, so the skin pores become blocked and dirty. This contributes to the disruption of the natural outflow of the secretion product of the glands, which can lead to unwanted infections and viruses entering the body.
Symptoms
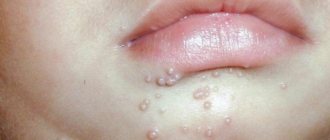
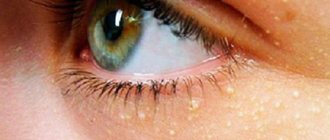
Neoplasms caused by papillomavirus are most often localized on the upper eyelid, somewhat less often - in the corners of the eye, on the conjunctiva. These are growths that have a thin and long or small thick stem. If they are concentrated on the eyelid in large numbers, they are called papillomatosis.
The problem has the following symptoms:
- inside the growth there is a feeding vessel through which it receives the substances necessary for its functioning.
- Neoplasms can cause discomfort when closing the eyelids and provoke the sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
- Their diameter varies from millimeter to centimeter.
- Their color matches the surrounding skin or is slightly different from it (for example, red, dark formations are possible).
Depending on the appearance of papillomas on the eyelids, there are two types:
- keratome – elongated, long, granular. Touching them causes the patient severe discomfort. This type of growth appears mainly in older citizens.
- Fibroid - homogeneous in structure, similar to drops of a more elongated or flat shape. They occur in patients of all ages.
Any type of papillomas on the eyelids can provoke dry eyes or increased lacrimation, causing constant itching, which poisons the patient’s life.
Treatment of pathological formation
Often patients try to treat the so-called pimple in the eyes on their own. But treatment of atheroma of the lower or upper eyelid must be performed by a qualified specialist in order to avoid serious complications. Conservative therapy consists of treating the tumor with antiseptic solutions and anti-inflammatory drugs in ointment dosage forms. But if signs of suppuration have already appeared, immediate surgical intervention is required. When the operation is performed as planned, there is a chance to avoid the formation of a rough keloid scar. If pus breaks out from the atheroma, the wound heals by secondary intention, after which a keloid is formed. Surgical intervention consists of excision of the epithelial surface of the formation, drainage of pus and suturing of the wound defect. After this procedure, the patient is given a patch with an antiseptic and an antibacterial drug is placed in the wound.
A new technique for removing a tumor using a biopsy is quite effective. To do this, a needle is inserted into the tubercle area, through which the caseous contents are drawn out.
What is the danger of papillomas appearing on the eyelid?
Papillomas on the upper eyelid, single or multiple, are a serious cosmetic defect that can ruin your mood and affect self-esteem. For neoplasms located in this area, there is a high probability of injury, which leads to inflammation, suppuration, and bleeding. Lack of therapy can cause:
- constant feeling of discomfort, itching, pain in the eyes;
- dry eyes, tearing when growths of the inner eyelid appear;
- negative effects on vision: growths cause conjunctivitis, blepharitis.
If left untreated, papilloma under the eye can degenerate into a malignant tumor, increase in size, and the damaged area often grows. The HPV virus, which causes papillomatosis, can provoke cancer of the cervix in women and the penis in men. In order to prevent fatal consequences, it is important not to self-medicate, but to undergo a charming medical diagnosis.
Diagnostic measures
Papillomas on the eyelids are not just a cosmetic defect. This is a good reason to go to a dermatologist for diagnosis. The specialist will prescribe two types of studies for the patient:
- PCR test - allows you to determine whether there is an HPV virus in the body, what type and in what concentration.
- Other tests that reveal the condition of the body and its immune forces (for example, a general blood test).
If there is a suspicion that the neoplasm near the eye is of a malignant nature, the patient will be referred to an oncologist who will take an element of the biomaterial for histology.
Depending on the characteristics of development, papillomas are divided into two types:
- inactive - they practically do not increase in size, do not cause discomfort, and their color matches the shade of the surrounding skin.
- Highly active - they grow quickly, cause discomfort when accidentally touched or provoke itching, and when injured they can develop into malignant formations.
With the first type of growths, resection is at the discretion of the patient, with the second it is mandatory.
In addition to surgical intervention, medication is required, which is selected for the patient individually, taking into account the condition of his body.
How does this education manifest itself?
Atheroma on the eye is visible to the naked eye. When the patient looks in the mirror, he notices a yellowish or white spot on his eyelid, rising above the surface of the skin.
With this disease the following clinical symptoms occur:
The formation may have a yellowish tint and is absolutely painless for humans.
- The appearance of a whitish or yellowish tubercle on the upper or lower eyelid, inactive on palpation.
- Release from fluid formation. It is serous or purulent in nature with an unpleasant odor.
- Absence of painful sensations when pressing and neoplasm.
- The appearance of a focus of inflammation above the atheroma during suppuration. It is accompanied by redness and a local increase in temperature.
- Breakthrough of a suppurating formation with the release of a certain amount of foul-smelling fluid.
- Ulceration with rapid growth of the tumor.
Treatment methods
- immunomodulators;
- local or general antiviral agents;
- vitamins
Ignoring the effects of medication can reduce the results of surgery to zero: the eyelid from which growths have been removed will again become covered with tumors when the patient’s immunity first weakens.
In addition to drug therapy, the doctor gives advice to remove general factors that favor the development of HPV. For example, the patient is advised to get enough sleep, walk more in the fresh air, provide himself with a balanced and varied diet, eliminate stressful situations, treat a chronic illness, if any, and stop taking pharmaceutical drugs without a doctor’s prescription.
This is a classic method that allows you to get rid of papilloma on the eyelid by excision with a scalpel. It is used for those tumors for which other removal methods are not applicable: large defects, malignant growths.
Surgical excision of papillomas from the eyes proceeds according to the following scheme:
The disadvantages of the surgical technique include a long recovery period, the need for the patient to go to dressings, and then attend the procedure for removing sutures. The method is associated with a high risk of relapses, the appearance of scars and scars on the treated area.
An important advantage of the technique is the possibility of its use in the presence of contraindications for removal, characteristic of other methods, in case of large size or malignant nature of papillomas. The surgeon retains material that can be submitted for histology.
Removing papillomas from the eyelid with a laser is a process of evaporating them with a laser beam. This method appeared relatively recently, but has already earned positive reviews from doctors and patients. Its advantages include:
- minimal risk of relapse;
- absence of scars, cicatrices;
- non-contact exposure ensuring complete sterility;
- bloodless removal;
- minimum number of contraindications;
- targeted impact: harm to vision is excluded, the likelihood of harming healthy tissue is minimal.
Laser coagulation is not used for pregnant women and nursing mothers, people with cancer and skin diseases, inflammatory processes in the acute phase, and those who have recently been actively sunbathing.
Before removing the papilloma, the doctor treats the eyelid with an anesthetic and administers a local anesthetic. Then a laser beam is directed at the growth, removing the tumor layer by layer. Thanks to high-precision automation, the strength and direction of the impact is regulated. In one session you can get rid of several tumors at once.
After laser coagulation, the patient is left with a small wound on the eyelid, which is treated with a disinfectant and wound-healing agent. After resection, you should avoid sunbathing for a week, refuse to visit the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, apply cosmetics to the treated area, and use contact lenses.
The disadvantage of the method is that the neoplasm is completely evaporated, leaving no material for analysis. If there is any doubt about its benignity, a puncture should be performed before resection.
Removal of papilloma on the lower eyelid is possible using liquid nitrogen. High temperatures cause the neoplasm to turn white, gradually die, and then fall off naturally. If the growth is located in close proximity to the eye, it is important to choose a highly professional doctor or a clinic with modern equipment to avoid harm to vision.
Liquid nitrogen is applied to the neoplasm in one of two ways:
- applicator;
- with a special device – a cryodestructor.
During the procedure, the patient experiences a minimum of discomfort. They boil down to a slight burning and tingling sensation. After the session, the neoplasm turns white, which means that the nitrogen has taken effect. The treated area is treated with an antiseptic and covered with a gauze bandage for 1-2 days.
Cryodestruction is contraindicated for persons with individual cold intolerance, patients with malignant tumors, and those suffering from acute diseases and skin ailments.
After the procedure, the patient should not use cosmetics or allow the tumor to come into contact with water.
You should refrain from sunbathing and visiting the sauna. Practice shows that the growth disappears after 2-3 weeks.
Cryodestruction is not used for papillomas located on the ciliary edge. Practice shows that for the fight against neoplasms on the eyelids, this method is less in demand than laser resection due to the lower precision of the effect.
Experts are unanimous in their opinion that removing papillomas in the eye area using folk remedies is unacceptable. Such recipes can be used exclusively as additional therapy after consulting a doctor. Effective techniques are based on increasing the body's immune forces. To do this, use rosehip decoctions, echinacea tincture, use natural honey, chamomile tea, St. John's wort, etc.
If you have your doctor's approval, you can use the following recipes to remove papillomas:
To prepare it, the stems of the plant are passed through a meat grinder, the juice is squeezed out of them, which is combined with baby cream or glycerin in a ratio of 1:4. The composition is applied to the growth around the eyelid 1-2 times a day for 3-4 weeks.
It has regenerating, local immunostimulating properties and increases cellular metabolism. The product is applied with a cotton swab to the affected area, the procedure is repeated daily in the morning and evening. It takes at least a month to completely get rid of the tumor.
A cotton swab is moistened with freshly squeezed plant juice and applied to the eyelid with papilloma for 15-20 minutes. This natural remedy can fight the HPV virus at the local level.
Traditional medicine suggests lubricating the eyelid where the tumor is located and leaving it until it dries. Recovery occurs due to the immunostimulating properties of the product.
It is used for the lower eyelid, because in this case the likelihood of the substance getting into the eye is minimal. The product is applied to the affected area and left until dry.
To combat papillomas on the eyelids at home, it is strictly forbidden to use aggressive agents (for example, laundry soap, Supercleaner, the use of cauterizing ointments), because if they get into the eye, there is a high probability of losing vision.
Treatment of suppurating atheroma
This condition requires immediate treatment, as it poses a danger to human health and life. Formations larger than 5 cm are subject to emergency surgical removal.
If a festering atheroma on the neck has opened on its own, then it is necessary to apply a sterile bandage to it and go to a medical facility, where a specialist will take care of the wound.
The only generally accepted effective method of dealing with cysts is surgery. Conservative treatment in this case is not possible, since the capsule remains inside. which periodically fills with secretions and becomes inflamed. In case of an inflammatory process, antibacterial therapy is carried out inside, pus is cleaned out and the capsule is cut out.
The best methods for removing wen:
- Laser. Used to treat small cysts. The bubble is opened with a beam and its internal surface is treated in order to neutralize the internal structures.
- Surgical. Using a scalpel, an incision is made in the area of the lump and the atheroma is removed along with all its contents. A relapse in this case is possible, but only if the doctor does not clean the wound well and a secretion remains in the subcutaneous tissue.
- Radio knife. The most effective, painless and safe. Eliminates the risk of bleeding and further relapses. It is most preferable for treating atheroma on the neck and head.
When choosing a removal method, it is important to consider contraindications:
- Pregnancy.
- Heat.
- Oncological diseases.
- Pacemaker.
- Acute inflammatory processes of the skin in the area of intended treatment.
- Metal implants.
Possible complications
A patient who decides to remove papillomas around the eyes should be aware of possible complications. These include the following:
- the appearance of a hypertrophic scar at the site of papilloma after laser resection. This red spot, which does not go away on its own, only loses its brightness over time.
- Frostbite of deep tissues during cryodestruction, which looks like intense redness of the eyelid and goes away after 2-3 days.
- Severe bleeding, the appearance of an eyelid scar and infection are the unfavorable consequences of cryodestruction.
- Swelling of the eyelid that occurs after any type of papillomas removal.
- Suppuration, an inflammatory process after the patient attempts to forcibly tear off a scab.
To avoid possible complications after removal of papillomas on the eyelids, you should prepare for the resection procedure 1-2 weeks in advance. You need to stop tanning, temporarily stop using cosmetics, and regularly apply sunscreen to your skin in the summer.
Preventive measures
Eliminating papillomas on the eyelids and eyes is a difficult undertaking, fraught with possible side effects. To avoid the need to resect tumors, you should take care in advance to prevent the HPV virus. Experts recommend taking the following precautions:
- be sure to wear slippers in the pool, public shower or bathhouse;
- carefully choose sexual partners, do not neglect contraception;
- use preventive pharmaceutical drugs (for example, Epigen Spray);
- do not wear personal belongings of a person infected with papillomatosis, do not use his hygiene products: HPV is often transmitted through contact and household contact;
- wash your hands after visiting public places.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
We will definitely fix it, and you will get + karma [youtube.player]