Genital herpes is an infectious disease that is caused by the herpes virus, usually type 2.
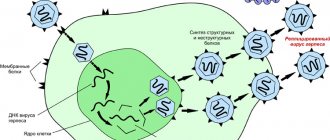
This pathogen belongs to the Herpesviridae family and includes 8 types of DNA-containing viruses.
At the same time, the herpes virus is thermolabile to high temperatures and tolerates drying well. For example, at a temperature of about 50 degrees. With HSV, it dies in 30 minutes. The virus remains viable for a long time on various surfaces. So, on metal products it lives up to 2 hours, and on plastic and wood – up to 3.
This virus has the ability to exist for a long time in a latent form in the human body, while outside the clinical manifestations of the disease, the pathogen is located in the ganglia of the nervous system, from where, after the appearance of favorable conditions for it, it successfully manifests itself.
During primary infection with the second type of herpes virus, the mucous membranes of the genitals can be affected, and in newborns, when the mother is ill, dissemination, or spread, of infection throughout the body. With recurrent diseases, the infection occurs in the form of genital herpes.
Causes of genital (genital) herpes
The source of infection for genital herpes is a sick person with a clinical course of this disease or a virus carrier who does not have a clinical picture, but has the presence of the causative agent of this disease in the body. Genital herpes is transmitted through sexual contact, as well as from an infected mother to the fetus, both in utero and when the fetus passes through the mother’s birth canal infected with herpes.
Intrauterine infection can occur in the following ways:
- transplacental - through the placenta;
- ascending route - from the vagina;
- transovarian - from the pelvis through the fallopian tubes to the fetus;
- when passing through the birth canal.
Genital herpes is transmitted not only through intercourse through the vagina, but also through sexual contact with the oral cavity and the anus and rectum. As doctors say, where herpes appeared, there was contact. Recurrence of genital herpes is possible with a decrease in immunity as a result of various diseases, for example, colds or any other.
Treatment approaches
Treatment of genital herpes is carried out when severe symptoms of the disease appear. When a primary infection is diagnosed in the last stages of pregnancy and rashes in the intimate area, delivery by cesarean section is indicated. In case of recurrent infection, it is sufficient to treat the birth canal and rash sites with antiseptic solutions, which reduces the likelihood of infection of the child to 1%. Povidone-iodine is most effective in this regard.
The condition for prescribing antiviral drugs is the predominance of the expected benefit to the mother over the risk to the child. If you have to treat herpes during lactation, stop breastfeeding while taking the drugs.
Hospitalization for acute conditions is not required. Only severe generalized forms are treated in an infectious diseases hospital. The home regimen involves maintaining personal hygiene, proper nutrition, treatment with antiseptics and taking Acyclovir. The regimen is selected by the doctor on an individual basis. The usual dosage is 200-400 mg 3-5 times a day. The duration of the course depends on the form of infection. For primary treatment, the drug is taken for 5-7 days; for relapse, 5 days are enough.
Neonatal herpes is also treated with Acyclovir. The dosage is selected by the pediatrician. Additional symptomatic therapy is prescribed based on the clinical symptoms of a particular child.
It is impossible to completely cure herpes. The virus remains dormant in the nerve ganglia; with new episodes of decreased immunity, a relapse may occur. Therefore, for a successful pregnancy, it is necessary to plan its occurrence. A preliminary examination and taking Acyclovir for prophylactic purposes during frequent exacerbations will help avoid illness in the expectant mother.
If the father has herpetic rashes, it is recommended to refrain from kissing and intimate relationships. If this does not work, he is prescribed Acyclovir in small doses throughout the entire period of his wife’s pregnancy, and sexual intercourse only with the use of a condom. It is also better to abstain from oral-genital relations.
[youtube.player]
Due to the lack of accurate data, a woman who has genital herpes during pregnancy may needlessly worry about the health of her unborn baby. Of course, there is a certain danger, but 95% of children from such mothers are born healthy.
Knowledge of where the disease comes from, how to deal with it, and when it is really dangerous will help you avoid unnecessary worries.
Difficult to determine presence in early stages of the disease
Symptoms
As noted earlier, genital herpes can be primary and recurrent.
Therefore, the manifestations of both variants of the disease will differ significantly from each other. Herpes in an intimate place is a very unpleasant thing.
Primary herpes occurs at the moment of first contact with the infectious agent. The incubation period ranges from two to fourteen days.
After this, the following symptoms of genital herpes occur:
- a sharp increase in body temperature to 38 ° C and above;
- headache;
- weakness;
- general malaise;
- itching or burning in the genital area, sometimes unbearable;
- pain in the affected area of the genitals;
- swelling of the affected area, usually swelling of the glans penis in men, swelling of the labia majora and minora in women, and similar reactions near the anus are also possible.
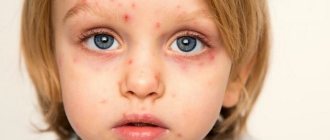
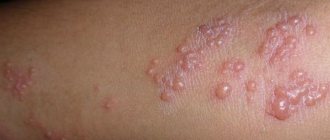
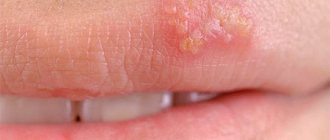
After a few days, blisters filled with clear liquid contents appear in place of the itchy and painful areas. After another couple of days, bleeding ulcers appear in place of the burst blisters, which soon become covered with a crust.
If such formations are located on the phallus, a painful act of urination is noted, if in the rectal area, a difficult and extremely painful act of defecation is noted. Sexual intercourse is also painful and does not give partners proper pleasure. When recurrent, genital herpes produces a less pronounced process. In this case, the temperature remains within normal limits, a burning sensation appears on the genitals, then blisters, ulcers and crusts form.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment, a diagnosis of this infectious disease is carried out. Genital herpes symptoms are very characteristic. Therefore, the clinical manifestations of the disease come to the fore. To confirm and differentiate from other infectious diseases, the doctor usually prescribes special research methods - MIF and PCR. These studies help determine the presence of herpes in the body. Another method for diagnosing genital herpes is serodiagnosis. Typically, this reaction is carried out in the presence of herpes in newborns to determine the increase in the titer of class G immunoglobulins, which allows us to accurately speak about intrauterine infection of the fetus. This study is also carried out in pregnant women who have negative results of other tests to detect antibodies to the causative agent of the disease. In addition, it is possible to isolate the pathogen from the contents of the vesicles by inoculating the resulting material on special culture media.
Treatment of genital herpes
Genital herpes, like herpes of any other localization, is an insidious disease. If you have it once, it will be with you for the rest of your life. It just may or may not manifest itself. This will depend on the individual properties of the body, as well as on the state of the immune system.
How to treat genital herpes? It all depends on what form struck you, as well as the extent of the damage. Thus, in localized forms, treatment of genital herpes begins with the local application of a 1 - 2% alcohol solution of brilliant green, and then the affected areas are lubricated with an ointment containing Acyclovir. If the disease has taken a generalized course, then local treatment alone will be useless. In such cases, either oral Acyclovir tablets are prescribed in addition to local treatment, or intravenous infusions of Acyclovir are given.
Main methods of treatment
The greatest danger of genital herpes appears in the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, even before its onset, if there is a virus in the body, women undergo a treatment course. To prescribe it, you need to consult a doctor. It is not possible to completely get rid of the infection, but the risk of recurrence is significantly reduced.
If the virus is present in the body, women undergo a treatment course
This course is carried out with special antiviral drugs. Immunomodulators work well (but they should not be taken by pregnant women!). If there are other diseases - liver, lungs, teeth, infections - they also need to be treated. It is better for a completely healthy woman who has undergone examinations to conceive a child.
If recurrent genital herpes does appear during pregnancy, local medications are used. They help to cope with the disease in a few days, without penetrating into the blood, and therefore without reaching the child. For rashes before childbirth, tablets may be prescribed.
Primary cases of infection are not yet a reason to terminate pregnancy. The chances that the child will be healthy are one to one. Therefore, the mother is treated, and the development of the fetus is constantly monitored. The decision will be made either by nature itself, or by a woman on the advice of a doctor.
The list of treatments for genital herpes is practically no different during pregnancy from normal situations. But these drugs can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
| Name | Action | Price |
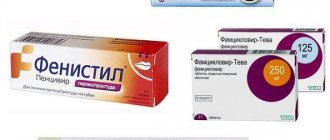
| Acyclovir tablets | Treatment of primary infection, relapse, prevention with continuous use | 90 rub. |
| Zovirax tablets | The active ingredient is the same acyclovir, but many call it more effective and safe | 647 rub. |
| Valaciclovir | A more effective drug that stops the development of the disease at any stage | 630 rub. |
| Famvir | The least dangerous drug that becomes active only in cells affected by the virus. Effective for prevention at the planning stage | 1595 rub. |
| Fenistil Pencivir cream | Famvir analogue for local use | 340 rub. |
Judging by the reviews, special measures to prevent genital herpes can, if not exclude, then significantly reduce the risk of contracting it during pregnancy.
- Sex should be protected, you need to use a condom.
- Avoid oral-genital contact.
- Take multivitamin complexes.
- From 36 weeks, your doctor may prescribe antiviral tablets.
- During childbirth, antiseptic treatment is performed.
Also find out how to avoid anemia during pregnancy.
Even if the worst thing has happened - the loss of a child, you cannot despair. The next pregnancy should be successful, because there will already be antibodies in the blood. But you should be wary if a doctor refers you for an abortion after discovering a pimple on the genitals during pregnancy, or, when the only reason for a miscarriage, without examination, calls a relapse of genital herpes. It is better to contact several other specialists and listen to their opinion.
About the author: Borovikova Olga
[youtube.player]
When genital herpes and pregnancy are combined, this becomes a cause for concern - the expectant mother worries about whether she will be able to give birth to a healthy child, is afraid of the possibility of a miscarriage, and is not sure that doctors will be able to do something about the disease.
Most often, with timely medical assistance, all suspicions and fears turn out to be groundless. Genital herpes in pregnant women is not completely cured, but is consistently put into stable remission if taking the medicine and working with the immune system begins early enough.
Genital herpes during pregnancy
Genital herpes in women can manifest itself during pregnancy as both a primary and secondary process. Relapse is associated with suppressed immunity that occurs during pregnancy.
Genital herpes during pregnancy is a disease that is dangerous for the fetus, since intrauterine infection is possible. This may affect the skin, mucous membranes, eyes, internal organs, as well as the nervous system. In this case, the child may die from complications that arise. The development of primary genital herpes is most dangerous, especially in the last trimester of pregnancy, since the risk of infection of the child increases at this time.
If genital herpes appears during pregnancy, then treatment is carried out as in non-pregnant women. If herpes in an intimate place is a fairly common occurrence, then specific prophylaxis is carried out with Acyclovir before the onset of a planned pregnancy, as well as during its course.
Fewer complications and infections of the fetus occur with recurrent genital herpes, since it is much milder.
If genital herpes appears shortly before childbirth, a cesarean section is performed to reduce the risk of infection of the fetus. The newborn is prevented from this infectious disease immediately after cesarean section.
Causes of the disease and dangerous consequences
Why, with so many people infected with HSV, are clinical cases three times less common?
Main reason: individual immune system activity
Doctors explain this fact by the individual activity of the immune system. In many people, it produces enough antibodies to prevent symptoms. For this reason, the first detection of genital herpes can occur during pregnancy, and treatment should be prescribed only after testing.
Firstly, the virus could have lived in the body for a long time, antibodies have been successfully developed and protect both mother and child. And the rash appeared due to a decrease in immunity, which inevitably occurs in a pregnant woman. This is necessary to ensure that the body does not reject the fetus. But antibodies from the mother will pass to the child and protect him.
Secondly, if this is a relapse, treatment is prescribed only to the mother, and the condition of the fetus is monitored. If the infection is primary, completely different measures must be taken.
Relapse is indicated by the presence of IgG. The presence of IgM in the absence of IgG is detected precisely during primary infection.
Genital herpes in early or late pregnancy can be caused by both HSV type 2 and type 1. Moreover, now there is an increase in the number of cases precisely because of the first type. This is associated with the passion of some population groups for oral-genital sex.
Getting infected from a sick person:
- HSV of the second type is transmitted by contact, most often sexually;
- the first type is capable of spreading even by airborne droplets.
The risk of clinical signs increases:
- in case of any evidence of decreased immunity (hypothermia, colds, pregnancy, etc.);
- due to physical damage (scratches, chafing, etc.).
During pregnancy, it is impossible to say for sure whether genital herpes is dangerous. If this is a repeated manifestation or the first, but antibodies (IgG) are present, then the danger to the baby is low - about 5-8%. Moreover, in the absence of rashes it decreases to 0.04%. Also find out why the pubic and pelvic bones hurt during pregnancy, as well as the causes of intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
Primary infection dramatically increases the chance of transmission of the virus to the fetus. But here, too, much depends on the body’s ability to resist infections. Therefore, more complications are observed in the first weeks of pregnancy, and about 5% of children are born infected.
What can be dangerous about genital herpes discovered during pregnancy?
- Primary infection in the first trimester can cause severe developmental defects, leading to anembryony (when there is no embryo inside the fertilized egg), fetal death, and miscarriage.
- The second trimester is intrauterine infection, which results in diseases of the brain, heart, liver, lungs in the newborn, stillbirth or death in the first days of the child’s life.
- In the third trimester, the first infection with the virus is rare, but these cases account for about half of infected newborns.
- Primary infection in the later stages, about a month before birth, increases the risk of intrauterine infection by up to 50%.
- The presence of recurrent herpes in the mother will lead to infection of the fetus with a probability of only 0.02%.
Previously, it was believed that during pregnancy the most dangerous recurrence of genital herpes is just before childbirth. The explanation for this was that when passing through the birth canal, a healthy fetus inevitably becomes infected, so women were recommended to have a cesarean section. But in fact, the risk does not even reach 1%, and antiseptic treatment of the birth canal makes it even smaller.
The only real danger in this situation is premature birth. This is due to the fact that the transfer of antibodies through the placenta occurs from the 28th week. It turns out that the child does not have time to receive enough of them for reliable protection. The likelihood of complications increases dramatically.