Causes
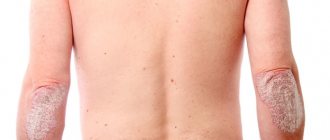
herpes on neck photo
Herpes is a chronic infection that occurs with periods of reactivation and remission. Herpes on the neck can appear for 2 reasons:
- reactivation or initial encounter with herpes simplex viruses type 1 and 2;
- reactivation of the herpes zoster virus (type 3) is a manifestation of herpes zoster.
Most often, herpes on the neck is the result of reactivation of HSV type 3 and is called herpes zoster . Cervical localization of herpes zoster is not considered widespread, since the virus is located in the nerves of the torso and head.
The cause of this disease is considered to be previous chickenpox, the recurrence of which occurs in the form of herpes zoster.
Herpes viruses primarily infect nervous tissues and exhibit their pathogenic effects on the skin. This applies to both the herpes simplex virus and the chickenpox or shingles virus.
The reason for the reactivation of herpesvirus infection is a decrease in the body’s defenses, namely the cellular component of immunity.
Against the background of hypothermia, physical injury, stress, chronic diseases, taking immunosuppressive drugs (hormones, cytostatics), both types of infection can worsen and manifest as herpetic rashes on various parts of the body.
Herpes zoster often accompanies the period after organ transplantation.
A rash on the neck, the cause of which is insufficient activity of the immune system, is described by an abundance of elements and a severe course. The same applies to oncological diseases, severe anemia, long-term use of glucocorticoids, and anticancer drugs.
Herpes on the neck, the causes of which include injury, pregnancy, hypothermia, usually occurs in a mild or moderate form.
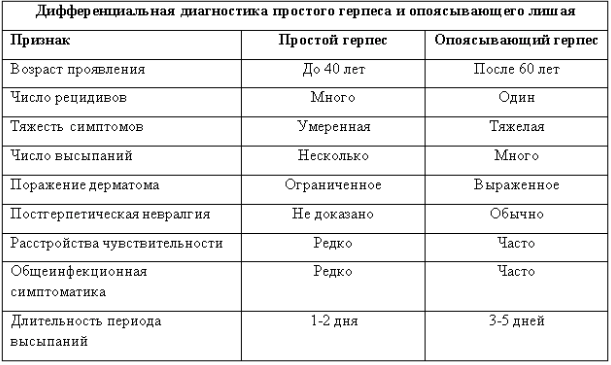
Herpes virus types 1 and 2 are most often localized on the mucous membranes of the lips, the skin of the lips, face, and occasionally rashes appear on the neck. A rash on the neck with herpes zoster appears much more often than with simple herpes.
The incidence of herpes zoster is more often recorded in the older age group. This is due to the fact that children suffer from chickenpox, and a certain time interval is required for the infection to recur.
Therefore, children who have had chickenpox in utero with herpes zoster or chickenpox in a pregnant woman may suffer a relapse in childhood. Also at risk for developing shingles are children who had chickenpox before the age of 18 months.
Frequent recurrences of a herpetic rash on the neck in an adult, the causes of which are not the presence of diagnosed tumors, taking medications, or hypothermia, require testing for HIV.
Repeated relapses of herpes zoster, as a rule, occur very rarely - no more than 5% of cases.
Treatment of herpes zoster
Treatment of herpes zoster remains a challenging task today. Despite the wide range of injections, tablets, creams and ointments for herpes, the infection is difficult to treat. The reason for this is the development of viral resistance to antiviral drugs. Viruses that persist in the body for a long time lead to a weakening of the immune system.
Treatment of herpes zoster with antiviral drugs
Chemotherapy drugs inhibit the synthesis of viral DNA, as a result of which the process of viral replication in the cell is suspended. Antiviral drugs that are nucleoside analogues currently have evidence-based activity: Acyclovir (Zovirax), Valacyclovir (Valtrex), Penciclovir (Vectavir), Famciclovir (Famvir).
Acyclovir (Zovirax) is the most commonly prescribed antiviral drug. Vacyclovir (Valtrex) and Famciclovir (Famvir) are new antiviral drugs. Famciclovir has the highest bioavailability, 77%.
Acyclovir is used 5 times a day. Famciclovir and Valaciclovir are used 3 times a day, which greatly facilitates the treatment process for the patient.
Alpizarin is an antiviral agent of plant origin.
Antiviral drugs are the basis for the treatment of herpes zoster, which should begin with the appearance of the first signs of the disease, which will significantly speed up the healing of skin lesions and reduce the incidence of postherpetic neuritis.
Rice. 21. The photo shows the antiviral drugs Acyclovir and FamVir.
Treatment of herpes zoster with immunostimulants
One of the important directions in the treatment of herpes zoster, in addition to antiviral therapy, is the correction of specific and nonspecific immunity, which is achieved by the use of immunoglobulin, interferon inducers, interferon preparations and stimulation of T and B-cell immunity and phagocytosis.
Antiviral gamma globulin
Immunoglobulin for the treatment of herpes zoster contains antiherpetic antibodies that neutralize varicella-zoster viruses. The maximum effect is achieved when immunoglobulin is administered in the first 72 hours from the moment of contact with the patient. The patient’s condition is mandatory for administering the drug when they are taking corticosteroids, cytostatics, immunosuppressants, for HIV infections and leukemia.
Vaccine against varicella-zoster viruses
The herpetic vaccine activates cellular immunity. It can prevent the development of a primary infection, the emergence of a state of viral latency and alleviate the course of an existing disease. The vaccine stimulates specific reactions of antiviral immunity and restores the functional activity of immunocompetent cells.
A combination of antiviral drugs and vaccine therapy provides a stable effect in the treatment of herpes zoster.
Treatment of herpes zoster with interferon inducers
Interferon inducers have an antiviral effect, as they regulate the synthesis of cytokines - regulators of intercellular and intersystem interactions. Interferon inducer drugs cause the synthesis of their own α, β and γ interferons in T and B leukocytes, enterocytes, macrophages, liver cells, epithelial cells, tissues of the spleen, lungs and brain, thereby correcting the immune status of the body. Interferon inducers are represented by Amiksin, Neovir, Ridostin, etc.
They have antiviral activity and are interferon inducers; herbal preparations: Alpizarin and Helepin-D.
Natural and synthetic compounds are capable of inducing the production of endogenous interferon: Levamisole (Dekaris), Dibazol, Vitamin B12, Pyrogenal, Prodigiosan.
Local treatment of herpes zoster
Local treatment of herpes zoster occupies a special place in the complex treatment of the disease. Its importance increases many times in cases of development of resistance to antiviral drugs. The local use of antiviral drugs ensures a high concentration of the drug in the lesions. In this case, there is no toxic effect of drugs on the entire body.
READ ALSO: Fenistil instructions - Rashes (rashes)
Antiviral drugs
Contain the antiviral substance acyclovir, preparations for external use: Acyclovir ointment, Acyclovir HEXAL cream, Acyclovir Belupo, Zovirax (UK), Supraviran, Ciclovir (India), Virolex (Slovenia), an analogue of Famvir. Creams are applied 5 times a day (every 4 hours) for 5 - 10 days.
Rice. 22. The photo shows Acyclovir ointment for herpes and Acyclovir HEXAL cream.
Vectavir cream. The drug contains the antiviral substance penciclovir. It is used for herpes zoster at any stage of the disease from the age of 16. The cream is applied 5 times a day (every 4 hours) for 4 days.
Rice. 23. In the photo, Vectavir herpes cream for external use with antiviral activity. Can be used at any stage of the disease.
Antiviral drugs of plant origin
The ointment is prepared on the basis of alpizarin, obtained from the herb of 2 types of alpine kopek, alpine kopek, legume family, or technical mangiferin, obtained from mango leaves, sumac family. 5% ointment is used in adults for 3 - 5 days. Treatment can be extended to 3 - 4 weeks.
Rice. 24. The photo shows an ointment for the treatment of genital herpes of plant origin Alpizarin.
Interferons
Ointment and gel for herpes Vireferon contains interferon alpha-2b (hydrogel-based ointment). The ointment is applied to the skin and mucous membranes in a thin layer. Then dry the greased areas for 15 minutes. During this time, a protective film is formed. Ointment for herpes Interferon alpha-2 recombinant is used 2 times a day (every 12 hours) for 3 - 5 days.
Rice. 25. The photo shows an ointment for herpes with interferon Vireferon.
Stages of development
herpes photo
Primary infection with type 3 herpes viruses occurs through airborne droplets. The infection is considered highly contagious, meaning there is a high chance of infection since the virus is volatile. After chickenpox, the virus lies dormant in the dorsal roots of the spinal cord.
Depending on the specific location of the viral particles, recurrences of chickenpox in the form of herpes zoster can occur in different anatomical areas and most often affect the chest, abdomen, back and lower back.
Important!
If the zoster virus affects the dorsal roots of the cervical part of the spinal cord, the rash will be localized on the neck.
Infection with herpes simplex occurs through contact and household contact. The virus penetrates microcracks and wounds, which leads to the appearance of a characteristic rash. Next, the herpes virus enters a latent stage and the number of relapses is determined by the state of the immune system.
Herpes simplex affects the skin of the neck in two ways:
- in the presence of injuries to the skin of the neck and contact penetration of the virus into the wounds, a rash develops on the neck;
- with an exacerbation of herpes simplex on the face and a marked decrease in the tension of immune forces, the rash can spread to the neck.
Stages of development of a rash on the neck during infection with HSV types 1 and 2:
- Penetration of the virus into the epithelial cells of the skin of the neck.
- Active reproduction in cells with their destruction, tissue inflammation and the formation of a rash. This stage is accompanied by typical symptoms: burning, itching, redness, papule, vesicle.
- New viral particles enter the blood.
- Herpes settles in the nerve ganglia.
- When immunity decreases, viral particles multiply and penetrate the skin along the axons of nerve cells and cause a relapse.
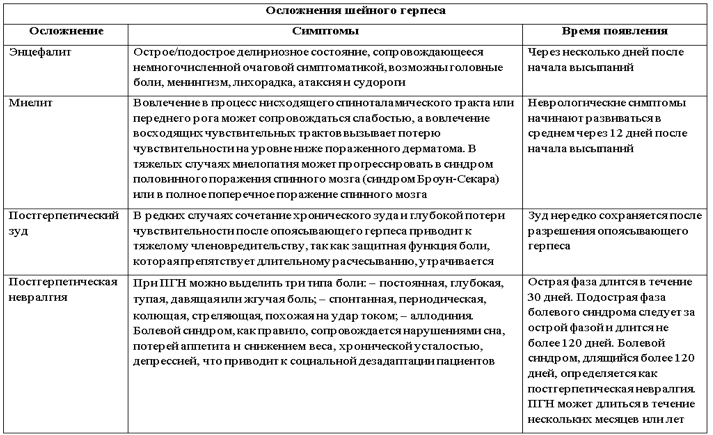
Complications of the virus
Lack of therapy leads to various complications of herpes. More often they occur against the background of a weakened immune system or in patients over 50 years of age. The virus can affect the eyes, ears, and meningitis. Deep erosions that appear after the vesicles open contribute to the spread of the virus throughout the nervous system. Encephalitis develops.
Death is recorded in 60% of cases. Paralysis of the respiratory muscles is fatal. Prolonged pain localized in the head area provokes postherpetic neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve. The disease negatively affects the patient’s psycho-emotional state and performance.
Herpes during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage, abnormal development of internal organs, and blood poisoning. Ramsay-Hunt syndrome is considered a dangerous complication of herpes on the head. The patient complains of ear pain, dizziness, and weakness of the facial muscles. The virus can affect different nerves in the head.
To eliminate the syndrome, taking antiviral drugs is indicated. Early therapy increases the patient's chances of complete recovery.
In other cases, the prognosis is negative:
- hearing loss;
- facial paralysis
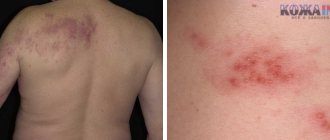
Symptoms
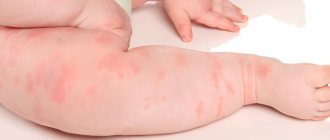
rash on neck photo
The clinical picture of lesions of the skin of the neck by herpes viruses depends on the individual characteristics of immunity, which is determined by the presence of immunosuppressive factors.
Herpes zoster on the neck is manifested by the following types of clinical signs:
- vesicular variety;
- atypical (bullous, hemorrhagic, ulcerative-necrotic, gangrenous, abortive);
- herpes zoster on the neck without rash;
- complicated by encephalitis, neuralgia, myelitis, itching.
Symptoms of the vesicular variety:
- pain in a certain area of the neck or around the neck, corresponding to a nerve affected by viruses;
- the pain is periodic, paroxysmal or constant, occurs when touched, has a burning, stabbing, pulsating, shooting character;
- skin itching, tingling;
- papules, quickly replaced by vesicles filled with clear liquid;
- the location of the rashes is linear and can encircle the entire neck;
- temperature increase;
- severe symptoms of intoxication (headaches, weakness, chills).
Itching and pain last for 2-3 days, then rashes appear.
Unlike simple herpes, with herpes zoster the rash around the neck appears without the stage of erythema - redness.
A rash on the neck of an adult lasts 3-4 days, then it drains, and after a week it suppurates. A small pustular rash on the face and neck caused by herpes appears a few days after the onset of the disease.
If pustular elements appear immediately, a differential diagnosis should be made with pyoderma and streptococcal skin lesions.
Erosion and crusts form at the site of the rash.
Important!
If new rashes appear on the neck for more than 7 days, immunodeficiency is suspected.
The crusts fall off during the 3-4th week of the disease, then peeling and changes in pigmentation remain.
How to cure herpes on the head with folk remedies?
Folk remedies can be used either alone or in combination with traditional medicines for herpes on the head. What does traditional medicine recommend to use?
- A composition made from almond oil, a clove of garlic and valocordin to lubricate the rash.
- Plantain leaves to apply to the affected area of the skin.
- Tinctures of ginger rhizomes and willow bark for immunity.
- Decoctions of peppermint, lemon balm, immortelle herb and other herbs for lotions.
- Compresses made from infusions of oak bark, burdock, chamomile and calendula to relieve burning and itching.
- Alcohol tinctures of calendula and lemon balm also effectively fight herpetic inflammations.
MORE ABOUT: Incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
You can also use stems of prickly tartar or violet leaves to treat herpes on the head. The juice of these plants can be wiped over the affected surface up to several times a day. As a result, the blisters will dry out and the irritation will subside.
In addition to treatment, you also need to take proper care of your scalp. Try not to wash your hair frequently, and do not use shampoos with fragrances, which can unnecessarily dry out the scalp and cause irritation.
It is better to prefer fragrance-free baby shampoos for washing your hair during herpes. And after washing your hair, you need to treat blisters and ulcers on the skin with brilliant green or hydrogen peroxide.
As for combs, you need to use them very carefully during illness, trying not to touch the inflamed skin with the teeth. It would also be a good idea to treat the comb with an antiseptic or alcohol before each use.
Forms of herpetic rash
Atypical forms are described as follows:
- Zoster without rash is described by the complete absence of rash elements, with only pain present among the symptoms.
- The abortive form is characterized by the presence of papules without the formation of vesicles.
- The hemorrhagic form of the rash on the neck is described by the bloody content of the vesicles, deep skin lesions and a more severe course.
- The necrotizing variety involves damage to the skin deeper than the dermis, with the formation of deep, long-term non-healing ulcers that form scars.
The intensity of the rash with herpes zoster on the neck varies. The rash may surround the entire neck, may be represented by single blisters, but with severe pain.
The spread of herpes to other areas innervated by the thoracic and lumbar nerves occurs with HIV infection. In addition, the likelihood of developing a generalized form increases with age.
Herpes zoster is characterized by the involvement of only one dermatome in the process - the area of the skin innervated by the affected nerve. Spread of the rash to other anatomical areas has been described in severe immunodeficiency.
Herpes simplex on the neck is characterized by a milder course, a limited number of rashes, which are located in small groups.
Relapses are recorded quite often. The sequence of development of the elements of the rash is the same as with the shingles variant, but the stage of redness of the skin area lasts longer.
Complications of herpes of the skin of the neck, initiated by different viruses, have a similar list.
A herpetic rash on the neck in a child, initiated by HSV type 3, is milder than in adults, which is due to a more intense immunity to this infection.
Forms of clinical manifestations of herpes zoster
Typical (vesicular) form
The typical form is characterized by blistering rashes and the presence of pain symptoms. The rashes are unilateral (common in chickenpox).
Bullous form
In the bullous form of herpes zoster, the blisters merge and reach the size of a plum.
Abortive form
In the abortive form of the disease, papules do not turn into vesicles.
Hemorrhagic form
The hemorrhagic form is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process deep into the skin (dermis), the contents of the vesicles mix with blood, causing the crusts to become dark brown.
Gangrenous form
The gangrenous form is characterized by the development of a gangrenous process at the bottom of the vesicles. After the wounds heal, scar changes remain.
Herpes zoster without blistering rashes
It is assumed that there is a form of the disease without blistering rashes.
Herpes zoster without pain
There is a form of herpes zoster with skin rashes, but without pain.
Immunity inhibits the development of the disease. A good immune system prevents the spread of viruses in the patient's body.
Rice. 19. The photo shows a hemorrhagic form of herpes zoster.
Rice. 20. With widespread rashes, the course of the disease is often complicated by the addition of a secondary infection. Treatment of herpes zoster in this case is significantly difficult.
Diagnosis and treatment
herpes on the neck treatment photo
Diagnosis of cervical herpes is not difficult. Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following skin diseases:
- staphylococcal skin diseases;
- streptococcal infection, including erysipelas;
- contact dermatitis;
- Dühring's dermatitis;
- pemphigus;
- pemphigoid.
To determine the treatment protocol and prognosis of the disease, a differential diagnosis is made between HSV types 1 and 2 and herpes zoster.
To verify the virus, a PCR study is carried out. If necessary, perform a blood test for antibodies to herpes viruses types 1-3. Pustular rashes are subject to bacteriological examination.
Several groups of drugs are used to treat neck herpes:
- antiviral block;
- painkillers;
- glucocorticoid agents.
What is herpes
Herpes is classified as a viral disease.
Herpes is one of the most common viruses on our planet. Its causative agent is Varicella Zoster or chickenpox virus. When it enters a child's body, it provokes a disease popularly known as chickenpox.
This disease is easily treated, as a result of which, in most cases, the body develops a strong immunity to it. However, the virus itself does not disappear from the body, that is, once infected, a person becomes its carrier for life.
Prevention
Primary prevention of herpes on the neck is based on compliance with measures aimed at reducing viral infection:
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures: use of separate utensils, hand hygiene, routine cleaning of premises in the outbreak of an infectious disease;
- isolation of sick people, use of protective equipment to prevent infection (masks and respirators, gloves);
- excluding contact of infants with a large number of older children and adults.
Many patients are concerned if herpes on the neck is diagnosed, how to treat it in order to prevent relapse and progression of the disease. During the treatment process, you should also think about prevention, for which you need to:
- rationally take prescribed antiviral medications: at regular intervals, observing the dosage and duration of treatment;
- avoid drinking alcohol and smoking;
- eat a balanced diet: eat enough animal protein (meat, dairy products), healthy fat (vegetable fats);
- do not wet the area of the rash;
- avoid sudden temperature changes.
The main preventive way to combat the recurrence of cervical and other forms of herpes is vaccination.
Vaccination against HSV 1,2 type Vitagerpavak. The drug is presented with an inactivated virus. The vaccine modulates immunity and enhances the immune response.
The regimen consists of 5 injections at weekly intervals; after 6 months, if necessary, the course can be repeated. To prevent chickenpox and, accordingly, shingles, the Varilrix vaccine is used, which protects against the disease for at least 7 years.
Herpes of the scalp: why it occurs
Infection with the virus occurs through direct contact with a sick person, with household items and cutlery. Very often, the infection is transmitted during fetal development or during childbirth from an infected mother.
- weakened immunity;
- poor nutrition and lack of vitamins;
- living in poor environmental conditions;
- abuse of bad habits;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- frequent stress and nervous tension;
- severe hypothermia;
- ARVI and influenza.
How to avoid getting herpes
- Strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene. Labial herpes is an infectious disease! Wash your hands thoroughly with soap before and after handling herpes, and after applying antiviral cream.
- Don't touch your eyes with your hands! This is especially true for women because they wear makeup.
- Do not use saliva to wet contact lenses.
- Do not touch areas affected by herpes! Despite the severe itching and pain, do not touch the herpetic rash under any circumstances, do not kiss, especially with children, do not use someone else's lipstick and do not lend your own to anyone, do not share a cigarette with a friend.
- Do not try to get rid of blisters or remove scabs to avoid spreading infection to other areas of the body.
- Use separate towels and utensils, and do not drink from someone else’s glasses.
Signs of the disease
Herpes manifests itself as numerous blisters located on the back of the neck. They are grouped in pairs. The patient experiences an irresistible urge to scratch an itchy area of the body.
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by redness of the skin around the rash. The patient notes the appearance of tingling throughout the body, an increase in temperature, and the contents of the bubbles become cloudy. After opening them, a wet surface is exposed.
The development of the disease is influenced by:
- state of the nervous system;
- dysbacteriosis;
- thyroid function.
Modern diagnostic methods help the doctor prescribe the correct treatment for herpes on the neck - the causes of the disease are largely related to weakened immunity. Therapy is carried out at home and depends on the stage of the disease. Symptoms of damage to the body by a dangerous virus are especially pronounced in HIV-infected patients.