Seborrheic dermatitis can appear regardless of age and is more often diagnosed in men. The pathology is based on inflammation of the skin in areas rich in sebaceous glands.
The disease is chronic and prone to exacerbations in the off-season (autumn and spring). The types of seborrheic dermatitis, causes and treatment of the disease are described below.
- Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
- Types of disease
- Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the face
- Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
Therapeutic diet and folk remedies
What kind of disease is this?
Other names for the pathology are seborrheic eczema, seborrhea. The inflammatory process often affects the back, face, chest, and scalp - areas richly supplied with sebaceous glands.
In most patients, sebum production is increased, and this is a favorable condition for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora.
The main provocateur of inflammation is the fungus Pityrosporum ovale, which is present on the skin of most people in an inactive state - in the form of spores.
Excess sebaceous secretions and decreased immunity provoke the proliferation of this microorganism. To cure seborrheic dermatitis and reduce the risk of exacerbations, it is important to seek help from a dermatologist as early as possible, who will prescribe effective therapy after determining the causes of the disease.
Symptomatic picture of seborrhea
Seborrheic dermatitis has characteristic symptoms, which include:
- the formation of red, inflamed spots on the face;
- the appearance of white-yellow nodules with scales;
- increased skin shine due to oil secreted through enlarged pores;
- unhealthy gray complexion;
- acne in the form of black dots;
- constant itching, burning and peeling of the skin;
- formation of bloody crusts;
- thickening of the epidermis, reminiscent of an orange peel.
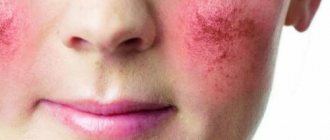
| Oily seborrheic dermatitis on the skin of the face |
Signs of seborrheic dermatitis are areas where the scalp is affected. If you examine the areas behind the ears, cheekbones, nasolabial folds, forehead, eyebrows, bridge of the nose, wings of the nose, you can see obvious fungal infections.
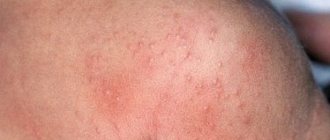
| Manifestation of dermatitis behind the ears |
The process of development of seborrheic dermatitis occurs progressively, the clinical course is similar to:
- lupus;
- skin candidiasis;
- atopic dermatitis;
- psoriasis;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- dermatomyositis.
Therefore, only a dermatologist can diagnose the disease based on the studies performed.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face (photo 1)
Factors influencing the appearance of seborrheic inflammation on the skin are external and internal. All of them directly or indirectly lead to increased production of sebum, or sebum.
Internal causes of seborrheic dermatitis are:
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- Parkinson's disease;
- endocrine disorders;
- epilepsy;
- genetic predisposition;
- immune diseases, including AIDS.
External factors:
- unbalanced diet;
- lack of zinc and vitamin PP;
- excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- frequent stress, mental shocks;
- exposure to low temperatures;
- use of soap, shampoos and household chemicals with an alkaline environment.
In most cases, it is possible to get rid of the manifestations of seborrhea by completely eliminating the cause of inflammation.
Drug therapy
Your doctor will tell you how to treat seborrheic dermatitis on the face in each specific case.
Drug treatment is considered traditional in the treatment of seborrhea, which may include the use of several groups of drugs at once:
- antihistamines;
- corticosteroid drugs;
- antifungal medications;
- immunosuppressants;
- antibiotics;
- vitamin and immunostimulating drugs;
- tranquilizers or sedatives;
- preparations containing bifidobacteria.
To eliminate the main symptom of the disease - intense itching, antihistamines are prescribed.
Medicines whose active substances are loratadine or cetirizine have proven themselves to be effective:
- Cetrin.
- Zodak.
- Claritin.
- Erius.
- Diazolin et al.
These drugs are also prescribed to the patient for allergic dermatitis.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the face with corticosteroids is prescribed when non-hormonal therapy has been ineffective.
Due to the potent active substances, the course of taking this group of medications is a short period of time.
Hormones are available in tablet form, as well as external creams and ointments. Among systemic corticosteroid tablets and injections, Diprospan, Dexamethasone, and Prednisolone are popular. As a rule, they are prescribed for acute seborrhea.
When a fungal infection occurs, in addition to external remedies, antifungal drugs are prescribed to help relieve the symptoms of acute seborrhea on the face. These medications include: Ketonazole, Fluconazole, Diflucan, etc.
Drugs that reduce the immune response are prescribed in extremely rare cases. With intense inflammation of the skin, such medications reduce the body's allergic reaction. It is highly undesirable to take immunosuppressants without a doctor's prescription.
During the period of remission of the disease, vitamins and special immunomodulating agents (Elidel, Protopic, etc.) are often prescribed. They increase the body's defenses and help resist adverse external and internal factors.
The causes of seborrheic dermatitis on the face, associated with stress and overwork, can cause considerable discomfort to a person. In addition to the main symptoms of seborrhea, patients often report a depressed and depressed state. In this case, sedatives based on valerian, motherwort and other herbal ingredients can help. In some cases, it is necessary to take tranquilizers.
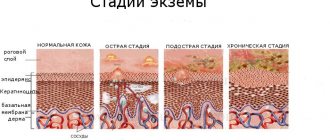
Types of disease
Seborrheic eczema is divided into three types:
- Oily – can be thick or liquid. The first is characterized by the appearance of acne and pimples, more often in boys under the age of 21, and the second is common among girls in adolescence and is localized on the face and scalp with the release of liquid secretions.
- Dry – develops with a decrease in sebaceous secretion, often before the onset of puberty. The skin dries out and cracks appear on it.
- Mixed - this form is characterized by a combination of dry and oily inflamed areas at any age, and mainly in men.
According to the severity and course of the disease, they are also distinguished:
- Seborrheic eczematide is a mild form with the appearance of slight peeling and inflammation on the face, behind the ears and head.
- Perinasal erythema - yellowish scaly spots on the wings of the nose and nasolabial folds.
- Patchy seborrheic dermatitis is a severe inflammatory process with frequent and prolonged exacerbations.
- Lichen asbestos is the most complex form of seborrhea of the scalp, in which the skin becomes covered with dense white plaques.
Ointments and creams for seborrheic dermatitis
An ointment against seborrheic dermatitis should be selected taking into account the form and severity of pathological processes. Indications for local therapy are:
- the formation of red papules and plaques covered with scales on the skin;
- peeling of the skin in the area of inflammation;
- dandruff, hair loss in the affected area;
- increase in the number of rashes;
- severe itching;
- soreness of inflamed areas.
Typically, local therapy for seborrhea is carried out with drugs containing glucocorticosteroids (hormones) or non-hormonal agents:
- antihistamines - reduce itching, redness, swelling of the skin;
- antifungal – suppress the development of pathogenic fungi;
- regenerating – accelerate the healing of affected areas;
- immunostimulating – activate local immunity and protective properties of the skin;
- antibacterial - prescribed for seborrhea complicated by bacterial inflammation.
In the treatment of the disease, both single-component products and combined drugs that have a complex effect on inflamed skin can be used.
Non-hormonal local remedies for seborrheic dermatitis include in the standard therapeutic regimen:
- Fenistil;
- Clotrimazole;
- Lamisil;
- Mikoket;
- Skin cap;
- Baneocin;
- Zinc ointment;
- Salicylic ointment;
- Fenistil;
- Apilak;
- Eplan;
- Elidel;
- Radevit;
- Losterine.
A gel based on dimethindene (a histamine receptor blocker) has antipruritic, decongestant and antiallergic effects.
One of the indications for its use is skin itching caused by various dermatitis, including seborrheic. But the gel is only a symptomatic drug - it helps eliminate unpleasant symptoms, but does not cure the disease. The drug is not prescribed for individual intolerance to the components, bronchial asthma, closed-angle glaucoma, pregnant women in the first trimester, during lactation, children under one month.
The medicine with the active ingredient of the same name is available in the form of a gel, cream, or ointment. Clotrimazole effectively suppresses the development of pathogenic fungi, thereby affecting the cause of the disease.
Ointment for seborrheic dermatitis on the head and face is used for dry lesions. For weeping inflammation and oily seborrhea, it is better to use a cream or gel that dries the skin a little. Clotrimazole is not prescribed to children.
A medicine based on terbinafine has a pronounced antifungal effect. For use only in the treatment of adults and children over 12 years of age. Lamisil for seborrheic dermatitis is used in the form of a cream (2 weeks, 1-2 times a day) or a spray (for a week, once a day).
A topical antifungal agent based on ketoconazole is characterized by a wide spectrum of activity and suppresses the development of fungal flora. Ointment for seborrheic dermatitis on the head is applied 1-2 times a day, and the total duration of therapy is 2-4 weeks.
Cream, aerosol and shampoo based on zinc pyrithione exhibit a pronounced antifungal and antimicrobial effect and are used in the treatment of adults and children from the age of one year.
For the treatment of seborrhea of the scalp, it is better to use an aerosol and shampoo, and for inflammation of the skin of the face and body - a cream. Contraindications to the prescription of the drug are intolerance to the components contained in the drug, simultaneous treatment with glucocorticosteroids.
Treatment of inflamed lesions is carried out 2-3 times a day, shampoo is applied 2-3 times a week. The duration of therapy is on average 2 weeks.
The ointment contains vitamins A, E, D2, the action of which helps reduce inflammation and itching, accelerate the regeneration of affected tissues, and increase the protective functions of the skin. The product well moisturizes and softens the skin, used alone or in the complex treatment of seborrhea, for the purpose of prevention after corticosteroid therapy. It is not prescribed simultaneously with hormones.
Cream, gel and shampoo contain naphthalan, salicylic acid, vegetable oils, urea, Sophora extract and dexpanthenol. They have an anti-inflammatory, desensitizing effect, reduce the pain of inflamed areas. They improve metabolic processes in damaged tissues, stimulate regeneration, relieve itching, eliminate flaking, nourish and soften the skin.
The cream is applied 2-3 times a day for 15-30 days, shampoo - daily. The only contraindications to prescribing the medication are individual intolerance to the components and children under 3 months of age.
Pimecrolimus-based cream suppresses inflammatory processes, eliminates redness and swelling. The potency is comparable to glucocorticosteroids. Prescribed in cases where treatment with hormonal drugs is contraindicated or does not have the desired effect. Suitable for treating adults and children over 3 months.
In case of weakened immunity, acute viral and bacterial skin lesions, the product is contraindicated. In some patients it causes skin pigmentation disorders.
A dermatotropic drug based on glycolan has a pronounced bactericidal, regenerating, analgesic and healing effect. The product helps to quickly eliminate itching and redness, and glycerin, which is an auxiliary component, moisturizes, softens and nourishes inflamed skin. For large areas of damage, ointment is used. Eplan cream is best used after relief of acute inflammation to prevent relapse.
An ointment based on natural royal jelly accelerates the regeneration processes of damaged skin, eliminates rashes, peeling, increases local immunity and the protective properties of the skin.
For seborrhea, apply twice a day (can be under a bandage). The duration of therapy is individual, ranging from a week to two months. Ointment for seborrheic dermatitis and for other purposes is contraindicated for use by people allergic to bee products.
A product based on zinc oxide exhibits wound healing and anti-inflammatory properties. It also has an astringent, disinfecting and adsorbing effect, dries the skin, therefore it is used for the oily form of seborrhea. Zinc ointment is suitable for children and adults. With the development of purulent complications, it is contraindicated.
A product based on salicylic acid is characterized by an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, accelerates the exfoliation of dead cells, and stimulates regeneration. Used to treat oily seborrhea.
An ointment based on two antibacterial components (neomycin and bacitracin) is used in the development of infectious complications. The product is characterized by a wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity and acts on most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
One of the side effects of the drug is hearing impairment, so the ointment is not used to treat extensive skin lesions. Contraindications also include diseases of the visual system, severe renal impairment, and intolerance to aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Hormonal drugs are necessary for the treatment of advanced, severe forms of seborrhea. They instantly suppress inflammation, relieve itching, reduce redness, swelling and other unpleasant symptoms of pathology.
Most often, from this group of medications, ointments and creams are prescribed containing as an active ingredient:
Hydrocortisone has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect, eliminates itching, rashes, peeling and other unpleasant symptoms. It has many contraindications, including bacterial and viral inflammation of the skin, open wounds and ulcers, perioral dermatitis, age under 2 years, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The ointment is applied to inflamed areas 1-2 times a day. Therapy lasts from 6 to 14 days, in case of urgent need it is extended to 20 days, but no longer.
Clobetasol-based product is available in the form of cream and ointment. It is a potent drug and exhibits pronounced medicinal properties even when used in minimal concentrations. Contraindicated for the same conditions as hydrocortisone, but can be used in the treatment of children from one year of age.
Treatment of inflamed lesions is carried out 1-2 times a day for 14-20 days.
Ointment, lotion and cream for seborrheic dermatitis on the head and face contain mometasone as the main component, characterized by anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and anti-exudative properties. The drug is contraindicated for children under two years of age.
Treatment of inflamed lesions with any dosage form is carried out once a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor, based on the effectiveness, tolerability of the drug, and the likelihood of adverse reactions.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a fairly serious skin lesion that causes physical and psychological discomfort. However, the main symptoms of seborrhea (itching, redness, rash) are also characteristic of other skin pathologies. Therefore, the doctor must select a suitable ointment or cream for seborrheic dermatitis after making an accurate diagnosis and determining the main cause that caused the inflammatory skin lesion.
In addition, when choosing a remedy, it is important to take into account the stage and nature of the pathological processes. In mild cases of seborrhea, in the early stages of inflammation, antifungal agents are sufficient for treatment. In advanced forms of pathology, hormonal ointments and creams will help cure the disease. If dermatitis is complicated by purulent inflammation (pyoderma), the use of antibacterial agents will be required.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face is a skin inflammatory pathology that has a chronic course. The disease is caused by a harmful fungus that lives on the skin of almost every person. As a result, changes occur in the secretion of sebum in the skin, and the structure of the skin is disrupted. The process of inflammation develops as a result of exposure to certain factors, causing a person to suffer due to psychological and cosmetic discomfort.
Getting rid of the disease is a difficult matter, since seborrheic dermatitis develops as soon as conditions are favorable for it. But the use of complex therapy against the disease can improve the patient’s condition and the appearance of the skin.
The disease most often affects infants under one year of age, adolescents, and adults with weakened immune systems, including those with HIV infection. Men suffer from seborrheic eczema more often than women, since male hormones - androgens - are active stimulants of sebum production.
Seborrheic dermatitis is not a serious disease, but due to its chronic course, regular exacerbations occur, especially in the autumn-winter seasons. In summer, facial skin looks much better.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
According to localization, seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp and face is more common.
Symptoms on the face, photos
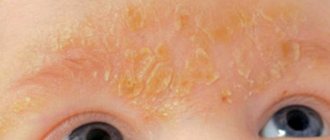
Seborrheic dermatitis on the eyebrows and face (photo 2)
Men and people with endocrine and immune disorders are prone to the appearance of lesions on the face. The skin resembles an orange peel due to enlarged pores; some areas become noticeably shiny and may acquire a grayish color over time.
Acne, pink, well-defined papules and blackheads appear. Seborrhea on the face can be not only oily, but also dry.
Seborrhea on the face, photo 5
Untimely treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the face is fraught with the addition of a secondary infection, due to which local inflammation in the form of boils or large painful pimples or pyoderma may appear on the skin.
Peeling, soreness and itching are added to the inflammatory process.
Typical areas of localization of seborrhea on the face are nasolabial folds, cheekbones, wings of the nose, eyebrows, forehead, brow ridges. If the skin of the eyelids is affected, there is a high risk of developing conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
Symptoms on the head, photo
The initial stage of seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp, photo 3
Seborrhea on the scalp is initially dry and manifests itself as dandruff. Subsequently, redness of individual areas, itching and a feeling of discomfort occur. Suppuration and wounds occur when scratching the skin.
Your hair begins to quickly become greasy, and you have to wash your hair more often than usual. Then yellowish or milky plaques appear; when scraped, the skin underneath becomes red.
Development of seborrhea on the head, photo 4
The development of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp continues with hair loss and focal alopecia (baldness). As a result of successful treatment, the hair in these areas is restored.
The symptoms of seborrhea worsen if you do not adhere to a diet, abuse spicy, sweet and spicy foods, and alcohol.
Difference from other types of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrhea on the skin is a pathological process of an inflammatory nature that develops due to a disorder of the nervous and neuroendocrine regulation of the functions of the sebaceous glands in the layers of the epidermis. Under the influence of provoking factors, a change in the composition of sebum occurs, which causes disruption in the process of skin respiration and a decrease in infection resistance.
The table shows how dry seborrhea on the face differs from other types of this disease.
| Dry form | Bold form | Mixed form |
| Insufficient sebum production | Increased work of the sebaceous glands | Symptoms of dry and oily seborrhea at the same time are characteristic. More often the scalp has decreased secretion of the sebaceous glands, and areas on the face have increased secretion. |
| Dry, cracked skin | Skin has an oily sheen | |
| White and yellowish scales on the forehead, nose and chin | Widespread rash (white head pimples) |
Dry skin does not always lead to dermatitis. In order for an inflammatory process to form, it is necessary to create a favorable environment for the disease on the skin of the face.
Diagnostics
The basis for diagnosis is the patient’s visible signs and complaints. Dermatoscopy allows you to identify the presence of hyperkeratosis (keratinization of the skin), irritation, dandruff, the degree of inflammation and the amount of sebum secreted.
Clarifying methods in the diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis:
- blood analysis;
- spectral examination of hair;
- study of hormonal levels.
They are necessary to exclude other fungal pathologies of the skin and atopic dermatitis.
Prevention
Dietary nutrition should become the norm not only during exacerbation of seborrheic dermatitis, but also during periods of remission.
To prevent the onset of symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures recommended by dermatologists:
- Take care of your face using hypoallergenic cosmetic products in accordance with your age and skin type.
- Thoroughly cleanse your skin every day and do not go to bed without washing off your decorative cosmetics.
- Treat chronic diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid stressful situations, be less nervous.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Spend more time outdoors, avoiding polluted places.
- If possible, go to the sea during your vacation.
At the first signs of seborrheic dermatitis on the face, you should not self-medicate, but consult a qualified doctor.
Correct diagnosis and timely treatment will quickly eliminate the symptoms of the disease, and the skin will again acquire a healthy and well-groomed appearance.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the face
Seborrheic dermatitis is treated by a dermatologist, but depending on the factors of the disease, the help of a gynecologist, endocrinologist, nutritionist and other specialists may be required.
Therapy for seborrheic skin lesions on the face should be comprehensive. It includes measures to eliminate the cause of the disease, diet, and the use of local medications.
Biodermia - ointment for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the face, photo 7
For skin care, you should not choose regular soap or gels with an aggressive composition. For washing, special foams or milks are used, which contain salicylic acid, tea tree oil, witch hazel, lithium salts, selenium, zinc.
Alcohol-based products are excluded.
Among the medicinal cosmetics brands that stand out are Tsindol, Sensibio, Sebovalis, Bioderma.
Among the drugs and ointments for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, the following are prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- antihistamines;
- antifungal ointments;
- immunostimulants;
- ointments and creams containing hormones;
- means for the treatment of concomitant diseases.
If seborrhea affects the skin of the eyelids, rinsing with antiseptic solutions and using eye ointments and drops with antibacterial properties is indicated.
Physiotherapeutic procedures - darsonval, cryotherapy, ultraviolet irradiation - effectively complement the treatment of seborrhea on the face.
Complex treatment
To treat this disease, you can use both medication and folk remedies. Treatment with medications is prescribed by a dermatologist. If the disease is associated with other diseases, then other specialists should be involved: a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist or gynecologist.
As a rule , treatment of dermatosis is complex:
First of all, the attending physician prescribes an appropriate diet. The food you eat should be rich in vitamins, selenium, and zinc.
- The following antifungal drugs are recommended: Nizoral, Nisorex, Sebazol, Dermazol and others. They can be in the form of an ointment, shampoo or gel.
- The following are used as antifungal antiseptics: zinc paste, tar soap, tea tree oil and others.
- Traditional medicine is used.
In addition to the above, the underlying disease, which became the root cause of the development of seborrhea, is treated, and factors that can cause this disease are eliminated - stress, poor diet, hypothermia, etc.
Treatment of this disease also involves the use of special shampoos, such as: Nizoral, Danex, Sulsena, Ketoconazole and many others.
These shampoos help:
- reduce sebum production;
- significantly reduce the number of fungi on the hair and scalp;
- remove scales already on the skin;
- slow down cell division, which leads to the formation of new scales.
Good antifungal shampoos contain components that fight fungus, stop inflammatory processes and moisturize the scalp.
Typically, medicated shampoos should be used for two weeks to a month . How often they need to be used depends on the severity of the disease. Sometimes doctors recommend using two types of shampoo at once. One of them must contain zinc, and the other must contain an antifungal drug.
Please note that such medicated shampoos should not contain substances that irritate the skin, such as aromatic fragrances, parabens, etc.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
An integrated approach is also needed here, including, in addition to diet, the following means:
- antifungal gels and shampoos (Nizoral, Ketoconazole, Nisorex, Kelual DS, Sulsena);
- antiseptics (tar soap, tea tree phytoessence, zinc paste);
- vitamin therapy;
- creams and ointments for seborrheic dermatitis (Lamisil, Zinocap, Advantan).
Kelual DS shampoo for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, photo 8
Shampoos for seborrhea usually contain ketoconazole, ciclopirox, selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione or medical tar as an active therapeutic substance.
They have an antiseptic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory effect, remove keratinized scales from the surface, moisturize and reduce flaking.
Medicinal shampoos are used in courses of 15-30 days, and the frequency of hair washing is determined by the severity of seborrhea.
Therapeutic diet and folk remedies
Some foods can provoke the growth of fungal flora and increase the production of sebaceous secretions of the skin, so diet in the treatment of seborrhea is of great importance.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- marinades, pickles, spicy, spicy dishes and smoked meats;
- excess simple carbohydrates (chocolate, sweets, baked goods);
- fast food;
- fatty and fried;
- possible allergens (citrus fruits, strawberries, nuts, honey, eggs);
- alcohol.
The menu should include vegetables and fruits, complex carbohydrates (cereals, cereals, legumes), enough drinking water, lactic acid products, lean meats, and vegetable oils.
It is better to cook by steaming or baking.
Among folk remedies, decoctions of calendula, nettle, dandelion, string, chamomile, and tar ointments can be considered as an addition to the main treatment.
Treatment methods
Photograph showing symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp
Various medications are used to treat seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp. Is it possible to become infected with the disease? No. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid of contact with sick people. On the contrary, they should be supported psychologically during the fight against the disease, since seborrheic dermatitis often negatively affects a person’s psycho-emotional state. He is very worried about the way he looks.
If you are affected by seborrheic dermatitis of the head, treatment must be agreed with your doctor. He may recommend treatment with folk or pharmacological remedies. Don't forget how important diet plays in seborrheic dermatitis.
Dermatologists recommend using complex treatment methods, prescribing different products aimed at performing specific functions.
- Shampoos with medicinal composition. We are talking about shampoos that are sold in pharmacies. They are developed on the basis of special components that help restore skin and hair.
- Nutrition. A diet for seborrheic dermatitis involves eating healthy foods and avoiding all kinds of allergens or foods that provoke the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Boosting immunity or fighting chronic diseases. Based on what was the provoking factor in the development of the disease, appropriate medications are prescribed.
- Local therapy. The doctor may prescribe a special ointment for seborrheic dermatitis on the head, which will help eliminate symptoms, redness or itching. But you cannot buy ointment or cream on your own without prior approval from your doctor. Otherwise, you may experience complications of seborrheic dermatitis.
Useful to know about shampoos
Let's look at a few basic points that will be useful for you to know in the fight against seborrheic dermatitis.
- One of the most important conditions for treating scalp disease is the correct selection of medicated shampoo;
- Most shampoos against seborrheic dermatitis are based on salicylic acid, tar, zinc, selenium sulfide and ketocanozole;
- The use of medicated shampoos is a mandatory daily activity;
- Rely on the specific instructions for the purchased shampoo;
- Having completed successful treatment, it is recommended to continue using the shampoo as a preventative measure for several weeks. But now shampoo is applied no more than 2 times a week;
- The shampoo needs to be changed periodically, since in case of complex disease, the fungus gradually adapts to the drug. Changing the active components promotes faster recovery;
- The most effective shampoos are those based on ketonazole, as they have an antifungal effect. A prominent representative of this category of shampoos is Nizoral cream for seborrheic dermatitis;
- When the disease begins to subside, try not to use aggressive detergents. It is better to replace them with oak or herbal decoction. Oak bark, used to prepare rinses, perfectly promotes recovery and maintenance of the scalp after seborrheic dermatitis.
This is an unpleasant skin disease that should never be ignored. It is better to solve problems when the first symptoms appear, rather than later switch to dangerous hormonal medications full of side effects.
Prevention of seborrheic dermatitis
The likelihood of developing seborrhea is reduced by preventive measures:
- maintaining hygiene;
- refusal of frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages;
- maintaining normal weight;
- for women – regular examination by a gynecologist;
- control of hormonal levels;
- minimizing the impact of stress;
- lack of overwork;
- timely treatment of any diseases;
- annual testing, at least blood and urine;
- maintaining immunity.
In the prevention of seborrhea, it is also important to adhere to a plant-dairy diet without excess fat and simple carbohydrates and take vitamins.
Local treatment of seborrhea
Products applied locally are designed to degrease the skin on the face and reduce sebum secretion. In the absence of pustules, comedones - blackheads - can be removed. For this purpose, there is mechanical cleaning or salt compresses. Cleaning is carried out by cosmetologists; the procedure includes a steam bath, paraffin mask, and mechanical removal of comedones.
If acne and pustules are present simultaneously, the doctor recommends the use of ointments with an antibacterial composition. The affected areas can be wiped with sodium tetraborate, sodium bicarbonate, purified sulfur 3-5%. As soon as the inflammatory processes subside, you can switch to alcohol tinctures of valerian, lily of the valley, hawthorn, boric acid and salicylic alcohol - wipe your face with them.
For dry seborrhea of the face, the damaged areas of the skin are wiped with salicylic, boric or citric acid, or sodium bicarbonate solution. After wiping, the skin is lubricated with “talks” with sulfur and ichthyol. Patients are prescribed medications to help exfoliate the skin. It is useful to apply cream with vitamins and medicinal herbs. The American-made MG 217 medicated Tar moisturizing medicinal composition performed well. There is shampoo and oil.
When treating seborrhea, it is important to adjust the diet, then the effect of the drugs used will be noticeable faster. It is necessary to limit salty, fatty foods, spicy and fried foods. Smoking and alcohol aggravate the disease, affecting all human organs.