What is scalp fungus
This is an infection that is a fungal infection of the scalp. Another name for the disease is mycosis. It is one of the causes of flaking, inflammation and itching of the scalp against the background of hair loss and brittleness. It is more difficult to treat such mycosis than in open areas of the epidermis, and it does not become noticeable immediately, but only at a more advanced stage. Infection occurs in the following ways:
- In direct contact with the carrier. The pathogen can be transmitted by hugging, shaking hands, or other interactions with an infected person.
- Household when using the patient’s personal items. Here we can also note the likelihood of contracting a fungal infection in hairdressing salons, cafes, theaters and other public places.
- Endogenous. This is what is called self-infection of a person. Fungi on the skin do not cause an infection in everyone. The inflammatory process often begins against the background of weakened immunity.
Prevention
It is possible to stop a scalp fungus from developing; there is no need to waste energy and money on treating the sore. A weakened immune system attracts more diseases than a full-fledged healthy body. The first rule for preventing fungal infections is to strengthen the general condition of the body. Exercising and eating right will help you stay in good shape and not be at risk of disease.
A decoction of medicinal herbs is an excellent remedy for prevention. Yarrow, nettle, currant and blackberry leaves, strawberry and rowan fruits are taken in equal proportions, and an alcohol decoction is added. Recipes from traditional medicine are also suitable. They are suitable for both treatment and prevention.
Do not forget that scalp fungus is transmitted through infected people and their belongings. If the following rules are followed, infection with fungal spores is unlikely: • Do not use the patient’s personal belongings and do not have physical contact with him. • Do not touch stray animals, despite their healthy appearance.
Causes
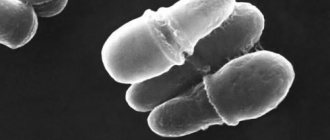
The disease is caused by pathogenic fungi that enter the scalp and begin to multiply on it. This part of the human body is affected only by certain types of microorganisms:
- Microsporum. It is the causative agent of microsporia. It is presented in two forms: zoophilic - feline or fluffy microsporum, anthropophilic - Microsporum ferrugineum. The latter causes disease only in humans. This mushroom is also called “rusty” microsporum. A person can become infected with the bestial form from animals.
- Trichophyton violaceum. This is a fungus that provokes the development of trichophytosis in humans. When the scalp is affected, it occurs in the form of ringworm. Under a microscope, the boundaries of this fungus are clear, its spores are round or oval, of the same size. They are located inside the hair in longitudinal chains, filling it completely or partially, resembling a “bag of nuts”.
- Trichophyton schonleinii. This is a Schonlein achorion fungus, which parasitizes exclusively on humans and causes favus in humans. The pathogen is easy to detect under a microscope in scales, hair, and crusts. It looks like many intertwining threads and spores of different sizes and shapes. The fungus does not destroy the hair substance, as with microsporia and trichophytosis. As a result, they do not break off, but fall out entirely.
Scalp fungus can occur not only against the background of reduced immunity. This infection has several other risk factors for its development:
- skin injuries;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- contact with an infected person;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- stress;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- washing your hair too often.
Trichophytosis (ringworm)
It is considered the most severe form of the disease.
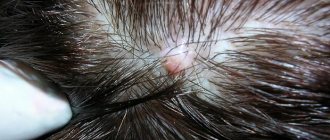
Scalp fungus is observed in children from three to twelve years of age. Symptoms include hair loss and bald patches. It is easily transmitted, so it is worth protecting the infected person from contact with people during treatment. Therapy should be started immediately. The infection has a deep stage, which is difficult to get rid of, so it is worth treating the disease in a timely manner. The incubation period for mild infection lasts a week. The skin peels and redness appears in some places. Hair becomes brittle and dull, breaking at the base. When infected, hair is short, as if the haircut was done on purpose. The areas of infection resemble a deliberately clipped hairstyle. This is where the name “ringworm” comes from. A gray coating forms, which is where the fungus accumulates.
The deep form shows no signs for the first two months. After the incubation period, general weakness of the body and swollen spots on the scalp are noticed. The body temperature rises and the lymph nodes are swollen. Peeling redness on the head is accompanied by severe itching and discharge of pus when you press on parts of the infection.
Types of fungal diseases
The classification of scalp fungus includes several forms of this disease. They differ in the type of pathogen, prevalence and speed of development. Their main difference lies in the symptoms. There are three types of fungal scalp infection:
- Microsporia. The most common form of scalp fungus. The disease is also called microsporosis. It is more common in young children, but they can also infect other family members.
- Trichophytosis, or ringworm. It is further divided into two types: superficial and deep. The latter form of ringworm is more severe. Symptoms appear 5-7 days after infection.
- Favus (scab). Mycosis of this type is less infectious to others compared to trichophytosis and microsporia. This can be seen by how in one family only one member is sick. If a person becomes infected with such an infection, it is difficult to cure it, especially in advanced cases. The risk group includes patients with vitamin deficiency and signs of tuberculosis intoxication.
Symptoms of scalp fungus
The clinical picture of such an infection depends on the type of fungus that has affected the skin. Although there are several common symptoms. These may indicate the development of a fungal infection. Most types of scalp fungus are characterized by:
- peeling of the scalp;
- the appearance of round spots with clear contours;
- loss of hair shine, dryness, dullness and hair loss;
- formation of bald spots;
- hair thinning, breaking off at the base of the follicle;
- purulent foci;
- pink plaques covered with grayish or yellowish crusts.
Microsporia
Of all fungal infections of the head, microsporia has the fastest development rate. Under favorable conditions, the spread of the fungus can be compared to an epidemic. Signs of microsporia are similar to trichophytosis. In addition to brittle hair, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- several low-inflammatory foci of redness and peeling, with borders of small blisters, on the scalp;
- whitish “stumps” of hair broken off at a height of 3-8 mm above skin level;
- grayish-white sheaths of many fungal spores surrounding hair fragments;
- lesions are located at the edge of the scalp, partially affecting smooth skin;
- The infection can also spread to the eyelashes and eyebrows.
Ringworm
The symptoms of ringworm of the scalp depend on the type of scalp. The surface form flows more easily. A white coating on the head of an adult is often associated with ringworm. Other signs of this disease:
- single or multiple round lesions (3-7 cm in diameter) of hair thinning;
- peeling and redness of the skin in the affected area;
- breaking off hairs at a distance of 1-3 mm from the skin, which is why they take on the appearance of short hair;
- small blisters along the perimeter of the lesions, covered with yellow crusts.
The superficial form of ringworm does not cause inflammation in the patient, so other symptoms do not bother him. Sometimes there is only mild itching. There is also an unpleasant aesthetic appearance of the scalp. More pronounced symptoms are characteristic of the deep infiltrative-suppurative form of ringworm:
- plaques with a diameter of 6-8 cm, painted bright red;
- swelling of the skin at the site of the lesion;
- allergic rashes;
- elevated temperature;
- discharge of pus from the mouths of hair follicles;
- purulent crusts;
- weakness;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Favus
Hair loss with favus occurs unevenly. They do not break off, retain their usual length, but become gray, dull, dry, as if dusty. In appearance, the hair resembles an old, worn wig. They are easily pulled out during washing and combing. The scuticular form of the favus is more typical for the scalp. Its main symptom is scutulae, which have the following features:
- They are yellow depressed crusts with a saucer-shaped depression in the center and penetrated with hair.
- The scutula includes elements of the fungus, cells of the stratum corneum and an admixture of leukocytes.
- If the crust is removed, there will be a shiny red surface underneath.
- After self-separation of the crusts, scar atrophy with persistent baldness remains in their place.
- As the pathology progresses, the scutulae merge into solid grayish-yellowish crusts. When they are layered multiple times, a persistent “mousy” or “barn” musty smell appears.
Fungus on a child's head
In childhood, the skin is a delicate and thin covering. Due to its immaturity and weak immune status of the child, the epidermis is especially susceptible to fungal infections. In children, ringworm (trichophytosis) and microsporia are more often diagnosed, and the lesions are located not only on the scalp, but also on smooth skin. Symptoms of these diseases:
- Microsporia. Causes the appearance of concentrated red plaques on the scalp. They are surrounded by a roll of small yellow crusts and bubbles.
- Trichophytosis. Often found in young children. In addition to spots on the head, problems appear with the hair - it becomes less elastic, loses its natural shine and breaks off.
Infection of the fungus in children most often occurs during interaction with stray animals, since children are unable to assess the potential danger of such contact. In addition, the child's body is more vulnerable to risk factors for fungal infections, such as vitamin deficiency, poor environment, stress, viruses, taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs.
Favus (scab)
The spread of this disease occurs in Asian countries, but cases of infection have also been recorded in Europe. The sources of the disease are the same as those of the diseases above: stray animals and people affected by the virus. The fungus attacks the scalp, forming a crust that looks like a yellow coating with an indentation in the center from which hair often grows.
If timely treatment is not followed, the favus begins to grow, occupying new places on the body covered with hair, and more new crusts are formed. In the old affected areas, the process of suppuration begins. Hair falls out with renewed vigor, which leads to baldness.
Diagnostics
It is important to identify fungal infections at an early stage. This is especially true for the scalp. If you detect the fungus at an early stage, the chance of maintaining normal hair will be higher. Upon visual examination, the doctor may already suspect one or another type of fungal infection. To confirm the primary diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Examination under Wood's fluorescent lamp. It has a specific wavelength that allows it to illuminate fungal colonies. This way the doctor can assess the area of the lesion - it will look like a bright, unevenly outlined spot with a greenish-blue glow.
- Microscopic examination. In this study, a scraping is taken from the scalp and examined under a microscope. This way, a specialist can recognize the pathogen by the appearance of the spores. Sometimes a hair is used as a material for research. Fungal spores can also be detected in its inner part under a microscope.
- Bacterial sowing It consists of taking material from the lesion and placing it in an environment favorable for the growth of the fungus. After growing the colony, the specialist determines the type and sensitivity of the pathogen to certain antifungal drugs.
Therapy
If you identify the above symptoms, consult your doctor immediately, as treatment must occur quickly. Having established the genus of the fungus through testing, treatment will be established. A whole individual complex of pharmaceutical medications and folk remedies for external use is prescribed. Decoctions of medicinal herbs combat fungal pathogens and strengthen hair follicles, improving blood circulation.
The rule of successful treatment is consistency and systematicity. Treatment of the scalp takes half a month, in severe cases the period increases. It is important to remember that fungi get used to folk remedies that have been used for a long time. Therefore, it is worth changing the decoctions after half a month of therapy.
The main method of control is antifungal agents. The new generation of drugs is effective, but toxic. Due to existing contraindications, you need to entrust the choice of medications to your doctor. In severe cases of infection, hormonal drugs and antibiotics are prescribed. A haircut will help reduce hair loss. Short hair is easier to treat with medications.
How to treat head fungus
This disease has complex specifics, so you cannot prescribe medications yourself. The decision regarding the treatment regimen is made only by the doctor based on the results of the analysis to identify the type of pathogen. Then therapy is immediately prescribed. It must be long-term and complex, since fungus is a difficult-to-treat disease. The spores of the pathogen are stable and can persist for a long time even in unfavorable conditions. For this reason, therapy lasts until the symptoms disappear and for some time after to prevent relapses.
The main direction of treatment is inhibition of fungal activity. To stop its reproduction, antifungal drugs are used:
- Local - used for small foci of fungal infection on the head.
- Systemic - with a large area of lesions, when the fungus has penetrated into the deeper layers of the skin.
Regardless of the chosen regimen, when treating scalp fungus, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- normalize sleep, do not overwork;
- give up sweets and products containing yeast (beer, baked goods);
- introduce into the diet more foods enriched with nicotinic acid, zinc, selenium, vitamins A, B and C;
- use only your own household items;
- do not neglect personal hygiene;
- disinfect bed linen once a week;
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun;
- refuse hats in the warm season;
- give up decorative cosmetics for hair styling, including hairsprays, mousses, etc.
Treatment is aimed not only at eliminating aesthetic imperfections, but also at normalizing the functioning of the sebaceous glands in the scalp area. Antifungal shampoos are used for this. In addition to the fungicidal effect, they exhibit an exfoliating effect, so they are not suitable for long-term use. Such shampoos are used strictly according to the instructions.
Articles on the topic
- Antifungal tablets - inexpensive but effective drugs
- Fungal diseases in humans
- Antifungal shampoo for hair and body - a review of the best treatments and how to use them
Treatment at home
Hospitalization for adults with scalp fungus is rarely required. Following all medical recommendations, the patient recovers within a period of several weeks to several months. At home, the patient should change his pillowcase and underwear daily. Doctors do not recommend putting your hair in a bun, so as not to provoke increased sweating of the scalp. You should not use the same shampoo for a long time. It is better to buy several at once and alternate them. This applies to regular, not antifungal shampoos.
You shouldn't wash your hair too often. For example, antifungal shampoo Sebozol can be used 2 times a week. With each wash, you need to thoroughly rinse not only the skin, but also the hair itself, since it may also contain a pathogen. Possible treatment regimens for common fungal infections of the scalp:
- For microsporia, local medications are used, such as Termicon ointment or Terbizil. They are applied to the affected areas 1-2 times a day, applying a thin layer and gently rubbing. Treatment for scalp fungus lasts 2-4 weeks. To enhance the effectiveness of therapy, Griseofulvin is additionally prescribed orally, 1 tablet 3-4 times a day. The medicine is washed down with 1 tsp. vegetable oil. Treatment lasts on average 1-1.5 months.
- For trichophytosis, the same ointments are used as for microsporia. Mikospor can also be used. Twice a day, compresses with salicylic or salicylic-zinc ointment are applied to the lesions. After this, the stratum corneum is removed using a blunt scalpel, and the blackheads remaining from the hair are removed using tweezers.
Antifungal drugs
At an early stage, mycosis of the scalp is treated mainly with local remedies. These include ointments, creams, gels, and shampoos. All of them must have an antifungal effect. The products are applied to the affected areas. Hair often has to be shaved off. They are removed only in the affected areas, if there are single spots on the head. Otherwise, you have to shave your head. Among ointments, creams and gels, the following drugs are considered effective:
- Clotrimazole;
- Mycosporus;
- Stop asset;
- Tinedol.
The latest ointment for fungus on the head contains the active ingredient climbazole. This substance has a fungicidal effect. The advantage of Tinedol is that it additionally has a moisturizing and soothing effect and helps get rid of unpleasant odor. Among the disadvantages, one can note the thinning of the skin after applying the ointment. Another disadvantage is the high price of 990 rubles. In addition to fungal infections of the scalp, Tinedol can be used to treat:
- painful peeling of the upper layer of the epidermis;
- peeling, deformed nails;
- to prevent recurrence of fungus on the feet.
If local therapy does not help, then systemic drugs, which are capsules and tablets, are added to it. They act on the pathogen from the inside. Compared to topical medications, tablets have more side effects. For this reason, systemic remedies are used only in advanced cases of fungus. Examples of effective drugs:
- Griseofulvin;
- Miconazole;
- Terbizil;
- Thermikon.
The price of Griseofulvin is 220 rubles. The drug is based on the component of the same name, which exhibits a fungicidal effect against trichophytosis, microsporia, and epidermophytosis. Plus Griseofulvin is well absorbed through the intestinal wall, so the effectiveness of the drug is high. The disadvantages include possible adverse reactions in the form of dyspepsia, headaches, dizziness, photosensitivity. General indications for the use of Griseofulvin:
- trichophytosis;
- favus;
- athlete's foot;
- microsporia;
- onychomycosis.
Antibiotics are used only when a bacterial infection is associated, as indicated by purulent formations on the scalp. In addition to antibacterial and antifungal agents, the patient is prescribed immunomodulatory drugs:
- Aflubin;
- Immunal;
- Echinacea.
Medicinal shampoos
Local treatment is carried out not only with ointments and creams. Your doctor may prescribe antifungal shampoos. Such agents additionally have keratolytic properties. This means that shampoos cause active exfoliation of dead cells from the surface of the skin. The following remedies have this effect:
- Nizoral;
- Keto Plus;
- Mycozoral;
- Sebozol.
The active ingredient in the latest shampoo is ketoconazole. When used externally, this substance has antifungal and antimicrobial effects. Sebozol shampoo costs about 100-150 rubles. The product belongs to the category of cosmetics because it is effective for the prevention and removal of dandruff. The advantage of Sebozol is that it is suitable for everyday use and any hair type. The drug is safe and causes virtually no side effects.
The disadvantages include the impossibility of using this shampoo during pregnancy and lactation. General indications for the use of Sebozol:
- damage to the skin, nails and hair by yeasts, dermatophytes;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- systemic mycoses;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- folliculitis;
- trichophytosis;
- leishmaniasis.
The cost of Nizoral shampoo is about 350 rubles. The basis of the product is also ketoconazole, which has antifungal activity. The plus of the shampoo is that it additionally reduces the flaking and itching that accompany fungus on the head. Among the disadvantages, the following can be noted - compared to Sebozole, Nizoral needs to be used more often. Indications for use of the latter shampoo are somewhat different:
- pityriasis versicolor;
- dandruff;
- seborrheic dermatitis.
Treatment with folk remedies
Fungus on the scalp can only be cured with properly selected drug therapy. As a supplement to it, it is allowed to use folk remedies. Before using them, you should consult your dermatologist. After its approval, you can use the following folk recipes that have good reviews:
- After each wash, rinse your hair with warm vinegar solution. To do this, dissolve 2 tbsp in 1 liter of water. l. vinegar 9%.
- Place a few drops of essential oil, such as eucalyptus, onto the comb. When combing, the product will have a nourishing and antimicrobial effect on the hair.
- Grind 300 g of celandine root, pour 0.5 liters of vodka into the raw material, leave for 1 week in a dark place. Then strain the tincture and use for compresses. To do this, moisten a cotton swab with the product and apply it to the lesion. You need to wrap the top of your head in cellophane and put on a hat. The compress is left for 1 hour and then washed off.
- Brew 2 tbsp with a liter of boiling water. l. crushed calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort or their collection. Rinse your hair with warm broth after each wash.
- Peel 4 lemons, chop their peels, then add 1 liter of water and boil. Simmer over low heat for 15 minutes, then cool and filter. Use to rinse your hair after each wash.
- Squeeze the juice from 2 cloves of garlic, add 1 tsp. olive oil. Rub this product into the scalp and leave for 1 hour. Then wash your hair with antifungal shampoo. Repeat the procedure every time you wash.
Preventive measures
It is much easier to prevent fungal infections than to treat them for a long time. Since this disease is contagious, you should limit contact with people and animals with this infection. Other preventive measures:
- use personal household items;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- have your own personal comb;
- when visiting the pool or sauna, wear a personal cap;
- Healthy food;
- exercise;
- wash your hands thoroughly after visiting public places;
- use high-quality hair cosmetics;
- periodically take a course of immunomodulators;
- do not stay in the sun for a long time.