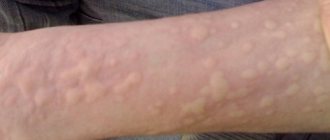
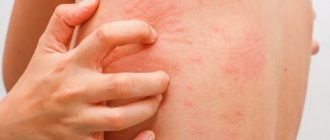
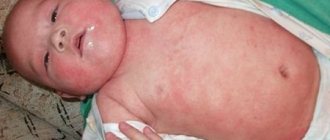
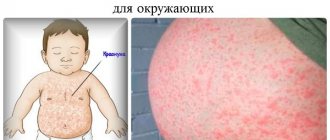
Allergy urticaria can be called perhaps the most common: according to doctors, every second person has encountered it at least once in their life. Urticaria occurs especially often in children, but adults are not immune from it either. This type of allergy got its name not by chance - the skin rashes are very similar in appearance to nettle burns.
In order for the disease not to take you or your loved ones by surprise, you need to have at least minimal information. Of course, you will have to see a doctor in any case, but it is not always possible to do this immediately. This means you must know what to do in such a situation.
Causes of allergies
The very first thing to do when urticaria appears is to understand what caused the allergic reaction. If you do not eliminate the body's contact with the allergen, trying to get rid of allergies will be as useless as fighting windmills. Of course, in some cases, only an allergist can diagnose the exact cause, but most often you can guess the cause yourself.
- Food
Food triggers allergic urticaria in about half of all cases. In principle, allergies can be triggered by absolutely any food product, but most often it is fatty fish, sweets, honey, nuts, citrus fruits, artificial preservatives and dyes. Therefore, if you encounter an allergy, carefully analyze the menu for the last 24 hours.
- Pharmacological preparations
Allergic reactions caused by taking medications account for up to 30 percent of all cases. Most often, allergies are caused by antibacterial drugs, vitamin-mineral complexes and, by the way, birth control pills. If you suspect that medications are causing your allergy, stop taking them immediately and tell your doctor.
- Plant pollen
Allergies can be caused by pollen from almost any plant. True, most often the allergy in such cases makes itself felt a little differently - runny nose, lacrimation and itching of the eyes, cough and difficulty breathing. However, the possibility of allergic urticaria cannot be ruled out - everyone’s body is different. It is quite possible that yours decided to react to the allergen in exactly this way - with skin rashes.
- Animal fur and saliva
Allergists very often diagnose people with an allergy to the saliva and/or fur of animals - cats, dogs, guinea pigs, hamsters. Moreover, there can be an allergy to any animal, or to just one. In some people, such an allergy may manifest itself as a cough, runny nose and other symptoms, and in others - by skin rashes.
- Physical impact
But physical effects on the skin very rarely come under suspicion. Which, however, is not surprising - who would think of blaming the sun or frost for the development of hives? In fact, an allergic reaction to the sun's rays - as well as to high temperature and frost - is a phenomenon that occurs very, very often. And such an allergy can occur at any time, even if nothing like this has happened before.
- Cosmetics and household chemicals
It would seem that for modern housewives in our time it is practically paradise - there are no household chemicals that make life easier. Here you can find washing powders, detergents for washing dishes, glass, floors - you can’t list everything. But very often contact with this miracle of the chemical industry leads to the development of very severe allergic urticaria.
Moreover, all of the above is true not only for household chemicals, but also for cosmetics. Cleansing gel, cream, deodorant – is there not enough cosmetics in a woman’s handbag? And almost any of these drugs can trigger allergies.
Idiopathic urticaria in children
According to the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, the incidence rate of urticaria among children under 18 years of age is 3-7%. At the same time, the following trend is clearly visible: with increasing age of the child, the duration of the disease increases. Thus, in children under 2 years old, only cases of acute urticaria are recorded, in children from 2 to 12 years old - both acute and chronic, in adolescents from 12 to 18 years old - mainly chronic forms.
The cause of chronic urticaria in children is very difficult to establish due to the difficulties of diagnosis. In order to distinguish one form of urticaria from another, special diagnostic tests are performed. However, the results obtained can be interpreted in different ways, since there are no uniform assessment criteria for children. Therefore, in most cases of long-term disease in children, idiopathic urticaria is diagnosed and the fight against symptoms begins.
The main causes of chronic idiopathic urticaria in children are:
- unreasonable use of medications, in particular treatment of viral diseases with antibiotics;
- physical factors, reaction to cold, solar radiation, water;
- autoimmune diseases.
The variety of clinical manifestations of idiopathic urticaria in children is shown in the photo; the symptoms are the same as in adults.
Symptoms of urticaria
The rash characteristic of urticaria allergies is very specific - if you see it at least once, you will never be mistaken. Well, for those who have not yet had the good fortune to see a urticaria rash with their own eyes, we will tell you about the clinical picture of this allergic reaction.
When urticaria develops, the rash rises quite strongly above the surface of the skin - by 3-5 millimeters. The rash itself looks like clearly defined blisters, exactly like those caused by contact with nettles. These blisters can range in color from pale pink to bright red. This rash is characterized by the following feature: if you press on the blister, it will acquire a normal skin color and disappear. But as soon as you let go, it will immediately appear again.
The size of the blisters can also be very different - from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters, and the number of rashes themselves can vary from single to numerous, covering almost the entire surface of the skin of the body. As a rule, if there are many rashes, they merge into huge spots, up to several tens of centimeters in diameter. It probably won’t be redundant to say that urticaria rashes are unbearably itchy.
Depending on the time during which the rash persists, doctors distinguish two forms of this disease:
- Acute form of urticaria
With this form of the disease, symptoms develop very, very quickly - within one hour after contact with the allergen. As a rule, there are a lot of blisters, they are large and very itchy. Symptoms also disappear quickly—maximum within 24 hours after eliminating the allergen.
- Chronic form of urticaria
If you are “lucky enough” to encounter chronic allergy urticaria, the picture of the course of the disease will be somewhat different. Firstly, the disease develops gradually - every day you will discover more and more new rashes, and the old ones will disappear. Although, of course, there are much fewer rashes in the chronic form than in the acute form. Such chronic urticaria can persist for a very long time - several weeks or even months. Most often, middle-aged women suffer from such allergic dermatitis.
Idiopathic urticaria in adults
- hard or watery blisters;
- itching at the site of the rash;
- temperature increase;
- chills, weakness.
Depending on where the blisters are located, other symptoms may appear. Blisters on the mucous membranes of the throat can cause nausea, diarrhea, etc.
The itching caused by the rash worsens at night, disturbing sleep. As a result, lethargy, fatigue, and irritability are noted.
Treatment can last a long time - it involves making the correct diagnosis, identifying provoking causes, relieving symptoms, prevention, and lifestyle correction. During treatment it is necessary to avoid allergens.
Pseudoallergic urticaria
Very often, doctors have to differentiate allergic urticaria from pseudoallergic urticaria. In the second case, the development of skin rashes occurs not due to exposure to allergens, but due to the presence of certain diseases. Such diseases include:
- The presence of parasites in the body.
- Hepatitis A and B.
- Tuberculosis and sepsis.
- The presence of tumors in the body - both benign and malignant.
- Problems with the endocrine system.
- Lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis.
Outwardly, this pseudoallergic urticaria is practically no different from the truth. True, the blisters are slightly smaller in size, and they are almost always localized on the back and abdomen, while with allergic urticaria the entire body is affected without exception. However, of course, only a doctor can accurately recognize the type of urticaria.
Is idiopathic urticaria dangerous during conception?
The disease has no contraindications for conception. Urticaria is dangerous only because at the time of conception and in the first weeks of pregnancy, medications pose a threat to the development of the fetus. Treatment of urticaria during pregnancy planning can only relieve symptoms.
The doctor can only prescribe medications that relieve swelling and itching. Treatment will be preventive in nature - avoidance of irritating factors, strict diet, healthy lifestyle.
You should immediately call an ambulance if your allergy causes:
- sweating;
- panic attack;
- feeling of lack of air;
- runny nose and nasal congestion;
- itching in the nasopharynx;
- difficulty swallowing.
If the disease is allergic, there is a chance that the child will have the same reactions as the parents. It is this reason that is an indication for following a strict diet during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of allergic urticaria
There is nothing complicated in diagnosing urticaria, and any medical student can distinguish it from any other skin rash. However, this is far from the most important task - it is much more important to find out why this very allergic reaction made itself felt. After all, without knowing the cause, it is difficult to limit contact with the allergen, and therefore the recurrence of an attack of urticaria.
- Location of the rash
First of all, the doctor will pay attention to where the urticaria rash is located - if it is on open areas of the body, you can suspect a cold allergy, or an allergy to the sun's rays. Of course, your medical history is taken into account - if you haven’t been outside for several days, you can hardly blame the weather, no matter what it is.
- Conversation with the patient
By the way, collecting an anamnesis is very important - the allergist must very carefully question the patient or his parents if allergic urticaria has developed in a child. Perhaps the person recently ate something unusual, some product that is not in his daily diet? Or maybe they changed the washing powder? Or purchased a new hand cream? It is very important to remember all the nuances - there are no and cannot be trifles, so tell the doctor even what, in your opinion, is not worth any attention. Very often, such a conversation allows you to quickly identify the source of trouble - the allergen that provoked allergic urticaria.
- Allergy tests
If the conversation with the patient is unsuccessful, the doctor will most likely decide on the need to conduct allergy tests. This may be a blood test that will identify allergens, or skin tests - it depends on the specific case. Skin tests are done as follows: using a special needle, the doctor makes scratches on the surface of the skin. Then a saline solution containing various allergens is applied to them. After about 20 minutes, the doctor will evaluate the results - if the skin around the scratch is red and/or swollen, the person is allergic to the substance dissolved in this liquid. Unfortunately, there are often cases when the true cause of an allergic reaction cannot be established.
If a person suffers from chronic urticaria, the diagnosis should be more extensive. Firstly, it is necessary to undergo a general analysis of urine and blood, liver tests, tests to ensure the absence of parasites, exclude dysbiosis, conduct an ultrasound examination of internal organs, an X-ray examination of the lungs and a number of other studies. Such a detailed examination is necessary in order to identify the disease that provokes the development of urticaria.
Idiopathic urticaria in children
In children, the disease may be accompanied by a number of others:
- digestive system problems;
- ENT organs;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diseases of the nervous system.
Children sleep restlessly; scratching the blisters often leads to their inflammation and a rise in temperature at night.
Treatment is also aimed at strengthening the immune system and relieving symptoms. It is important to protect the child from provoking factors. It is necessary to limit contact of the child’s skin with synthetic fabrics and household chemicals. Many of your child's toys may contain allergens, which is important.
Choose clothes and bedding made from natural fabrics, replace soaps and shampoos with hypoallergenic ones. Parents should help the attending physician collect a complete picture of the disease, which will help identify the allergen. During treatment, it is necessary to protect the child from chocolate, allergenic fruits, and junk food.
Both children and adults can be referred to physiotherapy procedures - electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, UHF therapy.
A doctor practicing dermatovenerologist talks about the causes, diagnosis, symptoms and treatment in the video:
Treatment of allergic urticaria
Allergic urticaria should not be ignored under any circumstances - treatment should begin immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear. We have already said above that it is not so difficult to get rid of true allergic urticaria in its acute form if you know what to do.
- Avoiding contact with the allergen
The first and most important condition for treating urticaria is eliminating the allergen. Of course, this can only be done for sure if you know exactly what you are allergic to. Otherwise, eliminate all possible allergens that have already been mentioned.
- Antihistamines
If there are a lot of rashes, you should not stop taking antihistamines. Ideally, an allergist should help you choose a medicine. But if you don’t have the opportunity to consult a doctor, buy Tavigil or Suprastin at the pharmacy. Strictly follow the recommended dosage - exceeding it has a negative effect on the body. Moreover, taking the drug should be a one-time use, as an emergency aid. You can continue treatment only after visiting a doctor, if necessary.
- Local remedies
The rash causes very severe itching, which is very, very difficult to tolerate. In order to get rid of it, you can use regular zinc ointment, which is sold in every pharmacy. Simply apply a thin layer of ointment to the rash and leave for 20-30 minutes, then rinse with water. If the situation is critical, the doctor will prescribe you more potent ointments that contain corticosteroids.
There are many different traditional medicine recipes that promise quick relief from allergic urticaria. Doctors are categorically against this type of treatment, because almost all recipes are based on the action of certain medicinal plants. And any plant without exception is a potential allergen. Moreover, with hives, even a well-known plant that you have already used several times can cause an allergy. Therefore, give up traditional medicine.
The only remedy that is worthy of your attention is compresses with baking soda, which very well relieve even the most severe itching. The compress is easy to make - you only need a gauze cloth and baking soda. Cut several small napkins from gauze and prepare a saturated soda solution - dissolve five teaspoons of soda in a glass of water and mix thoroughly.
Soak a gauze pad in the soda solution and apply to the blisters, leave for 10-15 minutes. If the napkin dries out early, change it to a damp one. After finishing the procedure, do not shower for at least another hour. The itching will disappear fairly quickly and will return in about 3-4 hours. If this happens, you can make a soda compress again - it is completely safe for health.
Treatment of chronic allergic urticaria is a rather labor-intensive and lengthy process, sometimes taking more than one month. It goes without saying that the treatment regimen should be selected exclusively by an allergist. Most often this means taking antihistamines, external agents, restorative measures and, of course, eliminating contact with the allergen. In any case, treatment will be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the specific situation.
Idiopathic urticaria. How to treat if you don’t know the cause?
Urticaria is a systemic disease, the external manifestation of which is an inflamed itchy rash on various parts of the body. The disease affects various categories of the population and is among the top 20 most common dermatological diagnoses.
In most cases, the cause of the disease is identified quite simply, and the disease can be stopped in the early stages. However, in 20-30% of cases, the disease lasts more than 6 weeks and smoothly passes from acute to chronic or relapsing phases.
Sometimes, even the most modern diagnostic methods do not allow us to establish the root cause of the disease or its provoking factors. It is this variant of the disease that is commonly referred to as idiopathic urticaria. That is, incomprehensible, inexplicable, arising spontaneously.