If you are breastfeeding, you must be careful about what you eat. Proper nutrition will protect your baby from abdominal discomfort. Also, most importantly, it will prevent various skin diseases that can undermine the child’s health and cause his constant whims and crying. A simple violation by a nursing woman of the nutritional rules for this period can provoke atopic dermatitis in the baby, the symptoms of which cause anxiety and panic in many parents.
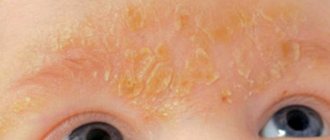
Atopic dermatitis photo in infants
The main reason for this disease in a baby may be a genetic predisposition.
Important!
Symptoms can be caused not only by diet, but also by poor hygiene or the use of medication by the mother during pregnancy.
The reasons can be completely different , but they almost always cause atopic dermatitis in the baby; a photo of its symptoms in infants was taken to warn parents about the consequences of neglecting basic rules.
Methods of treating the disease
Only after confirming the diagnosis will a specialist tell you how to cure the pathology. You should not treat atopic dermatitis on your own. Similar symptoms can be observed in other serious diseases, such as seborrheic dermatitis, lichen versicolor, microbial eczema, and contact dermatitis in children. Inadequate treatment can endanger the baby's life.
Drug therapy
The question arises: how to treat the disease? There is no clear answer. Since proper treatment takes into account the stage, form of the disease, and the age of the baby. An important factor is the involvement of other systems and organs in the course of the disease. The area of damaged skin is taken into account.
Before treating a pathology, the doctor carefully analyzes the data and develops a treatment regimen. It is based on the following drugs:
- Antihistamines. They are aimed at eliminating itching. Medicines may be prescribed: Erius, Suprastin, Tavegil, Claritin, Ketotifen, Loratodin, Fexadin, Telfast.
- Detoxifying agents. The drugs allow you to cleanse the child’s body. Medicines used: Enterosgel, Activated carbon, Polyphepan.
- Hyposensitizing drugs. Such products reduce the baby’s sensitivity to allergens. Suitable medications are: Sodium thiosulfate, Calcium gluconate.
- Corticosteroids. Prescribed for acute or chronic stages. The products have excellent anti-inflammatory effects. Medicines may be recommended: Elokom, Lokoid, Akriderm, Sinaflan, Celestoderm, Belosalik, Diprosalik.
- Antiseptics. These solutions are the answer to the question - what to smear on damaged areas? The most effective: Fukartsin, Methylene blue, Diamond green.
- Sedatives. They help calm the baby. Medicines prescribed: Glycine, Persen. A variety of soothing herbs, such as valerian and peony, are recommended for the child.
- Enzymes. Drugs are prescribed for problems with the functioning of the pancreas. These medications include: Creon, Pancreatin, Mezim.
- Antibacterial agents. In case of infection, the therapy includes ointments (creams): Lincomycin ointment, Lorinden S. Tablet medications are prescribed: Sumamed, Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Zitrolide, Rovamycin.
- Eubiotics. Allows you to save your child from dysbacteriosis. Effective drugs: Linex, Probifor.
Atopic dermatitis in infants, causes
This disease, identified by inflammation of the skin, can occur under the influence of both external and internal factors. In addition to the reasons already mentioned, its manifestation can also be provoked by:
- Difficult labor and poor prognosis during pregnancy
- Transference of various viral infections by the baby or mother before birth
- Using medications to treat the baby from the first days of birth
- Early cessation of breastfeeding and transfer to artificial feeding
- Using various household chemicals to care for a child, which are not suitable for use at this age
- Washing children's clothes with aggressive washing powder with a strong odor (failure to comply with the optimal temperature and humidity in the room where the baby is located. Lack of regular wet cleaning of the children's room. A large number of different flowering plants in the baby's room. Not using ironing of washed children's clothes)
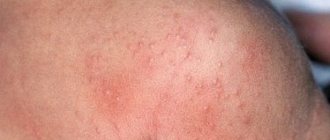
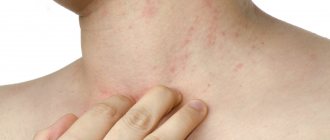
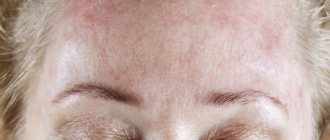
Each of these reasons individually can contribute to the development of a skin manifestation in a child, which can instantly appear in the form of a rash on the cheeks, bends of the knees and elbows, buttocks, stomach and back. The skin is dry and red in various areas. The baby does not sleep well, looks anxious and capricious due to unbearable skin irritation.
Signs that cause atopic dermatitis in newborns can appear in a child as early as two months of age. The peak of development of the disease, according to experts, occurs in the period from six to twelve months. At this time, the manifestation of the disease is the most dangerous, since by scratching the skin, the baby can introduce various bacteria into the wounds, which will provoke even greater complications.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
Initially, in infants from 2 months to a year, dry red spots appear on the face, neck, buttocks, they peel off, crusts and ulcerations form. Itching occurs on the affected areas of the skin, the child is worried, touches his face with his hands, often cries, and sleeps poorly. Often the symptoms of atopic dermatitis in an infant coincide with a change in diet, the introduction of meat products, fruits and berries into the diet, as well as a transfer from breastfeeding to artificial feeding.
The spread of atopic dermatitis throughout the body is more common when an infant is overfed
If the disease is not treated in time, it gradually spreads throughout the body, and the baby’s nervous system suffers. Subsequently, allergization of the body develops, and respiratory tract diseases appear - allergic rhinitis, laryngitis, bronchitis; at an older age, there is a risk of the child developing bronchial asthma.
Important! You need to show your child to a doctor at the very first signs of illness, when treatment will be most effective.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants
When the first symptoms appear in a child, the mother should immediately contact an allergist who knows how to treat atopic dermatitis in an infant without harming the baby’s health.
Important!
Long-term failure to provide the necessary treatment leads to the spread of skin manifestations of the disease.
First of all , the doctor, with the help of the mother’s stories, tries to find out what could have triggered the appearance of skin rashes. Depending on this, he determines how to treat atopic dermatitis in infants.
Elimination of the disease without drugs is possible if the following rules are followed:
- A baby should be bathed only in the stage of exacerbation or subsidence of the disease (the water for it should be filtered, without chlorine impurities. If the doctor allows, then you can add herbal decoctions to the water for the procedure)
- You need to wash your child without a washcloth; when using soap and shampoo, their pH level should be neutral
- Fresh air should be periodically provided to the baby's room.
Cases of drug use
If baby care measures are not able to cope with the skin symptoms that appear, then the doctor prescribes creams and ointments that contain glucocorticoids. They are selected based on the baby’s age and the nature of the inflammation. Various lotions can also be used for treatment For example, Exipal M, which helps restore normal skin functioning. Despite the fact that it does not contain hormones, its effect is in no way inferior to hormonal drugs. Exipal M is available in two forms:
- In the form of a hydrolotion (moisturizes the skin, reduces its tightness and itching, suitable for the remission stage. The main advantage is the ability to use it from birth without harm to health)
- In the form of a lipolotion, which is recommended for use during exacerbations of the disease (it effectively softens the skin, allows it to breathe and retains its effect for a long time. Due to its enhanced effect, it is mainly prescribed for children from six months)
Important!
The use of lotions, creams and ointments can prevent further development of the disease without transforming into a dangerous form of manifestation.
How to treat atopic dermatitis?
It takes at least two to three months for the signs of the disease to disappear.
Parents need to be patient, follow the doctor’s recommendations, and adjust the prescriptions together with the doctor. Related article:
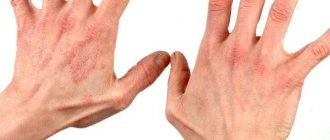
What to do with atopic dermatitis on the hands of adults and children?
Otherwise, the inflammatory process will take an irreversible form and subsequently cause bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis and other serious illnesses in a person.
Doctors have developed general approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants:
- It is necessary to eliminate contact with allergens.
- Follow a special diet.
- Take antihistamines to relieve the patient from itching.
- Remove toxins from the body.
- Take anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Use sedatives.
Treatment with medications
Neurodermatitis must be treated comprehensively. Medicines are prescribed taking into account age, stage of the disease and location of the rash. If necessary, sorbents, creams, vitamins, immunomodulators, antiseptics, antihistamines and antibacterial drugs are used.
Preparations for internal use
To remove toxins from the body, doctors often prescribe Enterosgel sorbent.
A safe and useful drug that removes allergens from the body is Smecta suspension. Doctors often use Fenistil and Zyrtec as an antihistamine. If coccus bacteria are detected on the skin of a newborn, antibiotics are used together with bifidumbacterin. Immunomodulators and vitamins are rarely used for infants.
Dr. Komarovsky strongly recommends giving babies calcium gluconate . Deficiency of this substance in infants occurs during the period of growth and appearance of teeth. Then atopy worsens. The use of calcium gluconate will help cope with exacerbation of allergic diseases.
Products for topical use
Creams and ointments play an important role in the treatment of eczema in infants. They relieve irritation, moisturize, restore and nourish the skin. In acute cases, a hormonal ointment based on glucocorticoids is used.
Emolium has become widely known .
For local treatment of inflamed skin, pharmacies have lipolotion and hydrolotion Excipial m. These non-hormonal lotions effectively treat and protect irritated skin of various types. A good product for dry skin is Mustela brand cream. They are advised to lubricate the baby's skin after bathing. The product penetrates deeply into the skin, softens it, and relieves irritation.
Important! Please read the instructions before using baby care products.
Treatment with traditional medicines
It is impossible to cure atopic dermatitis with traditional medicines . Creams and ointments prepared according to folk recipes are used in infants to ease the course of the disease.
Soothe itchy skin:
- a compress of finely grated raw potatoes;
- lotions made from prepared black tea;
- warm baths with the addition of flax seed.
Related article:
What are the dangers of pyoderma?
Infusions of water from bay leaves, pear leaves, birch buds, and nettles can be used as rubs. They relieve inflammation, itching, and prevent the proliferation of bacteria.
Sea buckthorn oil mixed with brilliant green is suitable for lubricating painful areas of skin in infants. It was noticed that when using this remedy, the symptoms of the disease disappeared within two days.
Important ! The use of folk remedies without the consent of the attending physician is not recommended.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants - video
Mom's diet for atopic dermatitis in infants
The hypoallergenic diet of the mother of the child is based on the removal of salty, smoked foods, spices and herbs from the diet. The doctor also gives a list of foods to which the baby has had an allergic reaction. This list is always individual, because even a neutral food component can provoke strong negative manifestations in a small organism.
In order for such a list to be as complete as possible, the doctor advises the nursing mother to keep records in which she should note the foods eaten during the day, the time of meal and the reaction of the baby’s skin to them. At the beginning of making such observations, the diet should be as restrained as possible, then the diet should be gradually diversified, alternately and at intervals of several days, adding a variety of foods.
Sample menu for a nursing mother
- Monday. Kefir product, boiled rice, boiled lean pork, pear compote, buckwheat bread, steamed cauliflower
- Tuesday. Kefir product, buckwheat with butter, boiled piece of lean pork, cornbread, sweet tea, boiled potatoes
- Wednesday. You should combine dishes from Monday and Tuesday at your discretion
In the case where the food over the previous three days has not affected the baby’s skin in any way, then from Thursday you can begin to introduce a new product into the diet. It should be eaten in the morning in a minimal amount. In the absence of a negative reaction from the baby, the amount of the new product on Friday, Saturday and Sunday should be increased incrementally to the usual serving size. If there are no manifestations, on Monday morning, the nursing mother can already introduce another new product into her menu.
Skin symptoms of atopic dermatitis
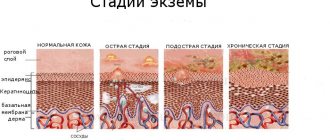
Healthy skin is characterized by tightly packed epidermal cells (the outer layer of the skin) that form a natural protective barrier against external factors. Children with AD experience disruption of the structure and function of the epidermal barrier as a result of the action of genetic factors and chronic inflammation. The main role is played by a violation of the formation of epidermal lipids, the main of which are ceramides (some of them have an altered structure or are produced in insufficient quantities). A decrease in the content of epidermal lipids leads to the fact that the binding of water is disrupted, and it begins to evaporate in greater quantities, which leads to dryness and cracking of the skin. In such a situation, allergens or other substances penetrate deep into the skin without much difficulty, causing inflammation. In addition, antioxidant protection in atopic dermatitis is impaired, and excessive permeability of the skin barrier to water and allergens is revealed.
Atopic dermatitis has different symptoms, but the most typical are persistent itching of the skin, dry skin and rashes of an exudative or lichenoid nature, which in severe cases affect the entire face, scalp, trunk and limbs. Itchy skin in children suffering from atopic dermatitis is not a very severe symptom, but it leads to scratching and worsening of the skin condition. Itching may occur before the rash appears. When the changes are not very pronounced, the child instinctively rubs the skin, increasing the symptoms of atopic dermatitis. A similar vicious circle also applies to the process of water loss. When your baby's skin sweats and loses moisture, it becomes dry and itchy, causing your baby to scratch, which can lead to a bacterial infection in and around the rash.