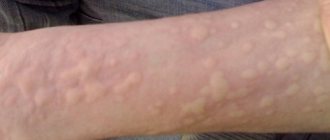
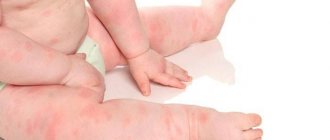
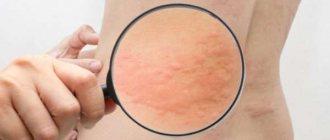
A peculiar red rash on the skin that causes itching, similar to burns from nettle leaves, this is urticaria. It is divided according to the form of manifestation and course into two types: acute and chronic urticaria.
Manifestations of urticaria are similar to nettle burns
Let's talk about the chronic form. If the rash and the accompanying sensations do not go away for a long period of time, from four to six weeks, this is a chronic form.
What caused
Factors that provoke urticaria are divided into several groups:
- endogenous - everything that is associated with pathological or inflammatory processes in organs,
- exogenous - everything that is associated with external factors.
It is the inflammatory processes in the organs and their systems that cause the protracted nature of the disease.
How does it manifest? Blisters have different shapes and sizes. With this form, the rash appears again and again, each time it can change location. Usually affects: torso, face, limbs, palms, plantar area.
The rash may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, dizziness, and general weakness.
Symptoms and signs
The external manifestation of chronic urticaria is not much different from cases when it is acute or occurs normally. You can guess that rashes have appeared on the human body precisely for this reason by paying attention to the following external indicators:
- a large number of small pink blisters;
- the rashes coalesce into one large bright spot;
- neoplasms rise slightly above skin level;
- the shape and diameter of the blisters can be completely different.
Rashes can appear on any part of the body, and the extent of the damage is quite large. The external manifestations of this disease are complemented by a number of symptoms that occur about an hour after contact with the causative factor. Symptoms that indicate that a person has chronic urticaria are as follows:
- in the affected area, the skin burns and itches severely;
- there is nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea is observed;
- irritability and sleep disturbance appear.
More often, such symptoms intensify if we are talking about focal urticaria; a chronic disease of a generalized type brings a little less discomfort. If the problem is limited to the appearance of itching and irritability, you can cope with it yourself, but the presence of more serious symptoms forces a person to visit an allergist or immunologist.
Recurrent urticaria
This type of urticaria is characterized by a wave-like course. This is due to the fact that the body becomes sensitized to the allergen over a long period of time. There are periods of exacerbation and calm. One of the main features of this disease is the sudden elimination of symptoms at the acute stage. The dermis quickly become the same as they were originally and take on the appearance as if there was nothing on them.
If there is no timely prescription of appropriate treatment, then the disease qualifies over time as chronic recurrent urticaria. This form very often becomes progressive. Then consequences such as:
- lupus,
- arthritis,
- diabetes,
- gluten intolerance,
- Sjögren's syndrome.
At the first signs, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe adequate treatment.
Sjogren's syndrome, one of the consequences of chronic urticaria
Causes of recurrent forms of urticaria
The classification of the causes of chronic urticaria includes, in addition to standard external and internal factors, other types of causes. Systematization of all causes shows that chronic urticaria can be not only an independent diagnosis requiring direct therapeutic intervention, but also a symptom of another disease, often of infectious etiology.
Possible causes of chronic urticaria:
About half of those suffering from urticarial rashes have an autoimmune diagnosis. If, after excluding probable causes, the root cause of the skin lesion is not identified, then a diagnosis is made: chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU). This diagnosis is received by 70-80% of patients.
It is difficult to establish the etiology and study the pathogenesis of urticaria as a nosological form of the disease, i.e. independent form of the disease.
In acute forms of urticaria, the ability to establish etiological causes is much higher than in the recurrent type of the disease.
In the case when urticaria is an indicator of the presence of any source of infection or disease in the body, the symptoms disappear with proper treatment of the disease and achievement of remission.
Principles of treatment of chronic urticaria
The most common cases of urticaria are when the causes are not determined, then the diagnosis is idiopathic urticaria. This type is characterized by a long course of over six months. The blisters are clearly demarcated. Accompanied by swelling, general weakness of the body, fever, and nervous disorders. Severe manifestations can lead to loss of ability to work. Treatment of chronic urticaria is a labor-intensive process, but is it possible to achieve results without effort?
- The first thing the attending physician does is collect an anamnesis. Frequency and circumstances play a very important role. Heredity plays a big role. Even if relatives through a generation suffered from allergic diseases, this puts the person at risk. Then a number of tests are performed. Indicators in analyzes can reveal the causes of the disease.
- Then screenings for chronic diseases are carried out.
- Afterwards, food tests are done, which can allow you to choose the optimal diet for the patient.
Urticaria is treated mainly with diets, because it is difficult to treat with medication. With the help of a properly selected diet, you can free the body of accumulated toxins and, as a result, get a long period of remission. There are two types of diets: elimination and challenge.
The first is based on the gradual elimination of allergens from the diet and monitoring the body's reaction. The second, on the contrary, is based on the gradual introduction of allergens into the diet.
First of all, the doctor will collect anamnesis
Diagnostics
To identify the diagnosis, carry out the following steps:
- Examination of the patient and analysis of all visible manifestations of the disease.
- Collection of analyzes and laboratory tests: physical tests that make provocation factors: light,
- cold,
- warmth,
- pressure,
- tension;
- herbs,
- identifying possible foci of infection,
If there is a need to continue diagnostic studies, then carry out:
- Elimination diet
– sequential exclusion of foods that are suspected as allergy triggers is made from the diet. Each time the patient is examined to determine his condition. - If the previous event did not clarify the picture, then a provocative diet
- the same as an elimination diet, but in this case foods that may have allergens are added sequentially. The body's reaction is observed.
A specialist talks about diagnosing chronic urticaria in this video:
What other actions can be taken to treat chronic urticaria?
- During the treatment process, the patient may be referred to an ENT specialist and a neurologist.
- Antihistamines are initially prescribed.
- In severe cases, hormonal agents and immunomodulators are prescribed.
- To reduce itching, external agents are prescribed, such as ointments and creams.
- Enterosorbents have a positive effect, and probiotics can improve the condition of the intestines, especially when the body’s reaction occurred in connection with taking antibiotics.
- Physiotherapy can be of considerable benefit in the treatment of this disease: PUVA, electrophoresis, ultrasound, irradiation, subaqueous baths. All this can only be used in combination. If you use one remedy, there will be no result.
Herbal treatment is often prescribed in combination if there is no allergy to them. In folk medicine, there are many remedies that perfectly help get rid of swelling, itching and flaking.
We will consider folk remedies that have already managed to show positive results in the fight against such an unpleasant disease below.
- Baths with herbal decoctions perfectly relieve nervous tension and have a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin. Most often, decoctions are used: chamomile, oak bark, celandine, string, St. John's wort, sage.
- Nettle. An excellent tool. It is taken orally in the form of tea, and lotions are made from the infusion.
- Elecampane. Its decoction is made as follows: add a tablespoon of raw material, a glass of water, and simmer for ten minutes over low heat. Take one third of a glass twice a day before meals.
- Yarrow. Drink 30-40 drops of the infusion at night, before going to bed.
- Celery is used in various variations. Drink freshly squeezed juice or make compresses with it. Squeezed leaves are also used in the form of compresses.
- The most unique remedy is aloe. It can also be used orally, and the leaves themselves can be applied directly to the affected areas. Aloe is a plant that is suitable for treating any disease. Blood cleansing procedures are also used with its juice.
Aloe leaves can be used internally and externally
Therapy
The main rule in the treatment of any type of urticaria is the elimination of the pathogenic factor influencing the occurrence of the disease. It is necessary to eliminate allergens from life, cure chronic infections and other provoking diseases. At the same time, symptoms are relieved using pharmaceutical and folk remedies, and then preventive therapy is prescribed.
Medicines to relieve symptoms
Folk remedies
Treatment of symptoms using traditional methods is also used as an additional therapy. Decoctions, solutions, infusions, compresses, baths and ointments relieve itching and swelling, accelerate skin healing, and improve immunity.
To help cure chronic urticaria:
Diet
Throughout treatment, as well as for prevention, patients must follow a hypoallergenic diet. Products that promote the release of histamine are allowed to be consumed no more than once a week.
These include:
- exotic food;
- conservation;
- citrus;
- milk;
- chicken eggs;
- nuts;
- seafood;
- smoked, dried food;
- chocolate;
- products with preservatives.
To find out what exactly triggers the recurrence of rashes, the patient is recommended to go on a strict diet. First, a person fasts for 3 days, and then gradually introduces one product into the diet and observes the body’s reaction. This way it is possible to identify the allergen.
The prognosis for chronic urticaria is favorable. Despite the fact that the course of therapy can be long (up to 6 months), if all principles of complex treatment are followed, a long-awaited recovery occurs. But it is worth remembering that the result is also influenced by a person’s diet, regimen and lifestyle.
For quotation:
Cheburkin A.A. Chronic recurrent urticaria: syndrome or disease? // RMJ. 2011. No. 22. S. 1342
Urticaria develops as a result of the release and synthesis, mainly by mast cells located in the skin, of various inflammatory mediators. Causes of mast cell degranulation include immune, nonimmune, and idiopathic (currently unknown). In cases where the pathophysiological mechanism of chronic urticaria is not precisely known, a diagnosis of chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) is made. However, according to the results of recent studies, 25-45% of patients with CIC have IgG antibodies to the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (IgE) (FcεRI) or against IgE itself: it is believed that these antibodies are “responsible” for degranulation of mast cells and activation of inflammation. The main method of treating chronic urticaria, if its cause is identified, is therapy of the underlying disease. At the same time, urticaria is only its component - the syndrome and disappears against the background of its remission. In case of CIC, histamine H1 receptor antagonists come to the fore in treatment, among which desloratadine (Erius) stands out due to its specific properties: in addition to the antihistamine effect, its anti-inflammatory effect has been established.
Urticaria is a pathological condition of the skin that occurs against the background of an allergic reaction. The disease is characterized by the presence of pronounced symptoms and requires timely treatment.
The chronic form of the disease lasts for a fairly long period. To avoid relapse of the disease, patients are advised to completely eliminate allergens.
Chronic urticaria is characterized by the presence of pronounced symptoms that do not go away within a month and a half. During the course of the disease, the following are observed on the patient’s skin:
- Papules;
- Rash;
- Scarring;
- Swelling;
- Plaques.
Most patients during the development of the pathological process complain of itching. The rash of the disease appears as pink or red blisters. Their location can be the neck, face, arms, legs, back.
The cause of scars on the skin is an allergic reaction. They are characterized by different sizes and shapes. Quite often, scars can disappear and appear again.
Some patients develop papular chronic urticaria. In this case, papules with a white center appear on the patient's skin. An inflammatory process on the skin is observed around them.
During the development of this disease, patients complain of itching, which intensifies in the evening. During the development of an allergic reaction, patients may experience swelling on the skin.
Quincke's edema is a fairly common symptom of the chronic form of the disease.
In places where edema appears, stretching and peeling of the skin is observed. The symptoms of the disease are not always pronounced.
In some cases, signs of the disease disappear, and after a certain time they appear again. That is why, when the first symptoms of the disease occur, patients are advised to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the appearance of the pathological process is the effect on the body of a provoking factor. Against this background, the production of a special substance – histamine – is observed.
During the period of release of this protein, the capacity of the capillaries increases, which leads to the leakage of liquid through them. As a result, blisters and swelling of the skin develop.
The disease is autoimmune in nature. When exposed to an allergen, special antibodies are released and activated, which leads to an allergic reaction.
The causes of chronic urticaria and methods of treating it, see this video:
There are a huge number of provoking factors for the disease. Most often it is diagnosed against the background of impaired kidney function. With rheumatoid arthritis, the risk of pathology increases significantly.
Urticaria can be diagnosed in patients with malignant neoplasms.
If gallbladder diseases occur against the background of infectious processes, this may be the cause. The disease is often diagnosed in patients with Sjögren's syndrome.
With diabetes, a person is at risk of developing a chronic form of the disease. With lupus or lymphogranulomatosis, the development of the disease can be observed.
It is also diagnosed against the background of various diseases of the thyroid gland. The occurrence of pathology is diagnosed in patients with certain chronic diseases - caries, viral hepatitis, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism.
Pathology in the fairer sex may appear due to inflammation of the appendages. Urticaria in a certain group of patients develops against the background of caries.
Chronic urticaria can occur when exposed to a variety of provoking factors. That is why a patient with a tendency to allergic reactions needs to closely monitor their health.
How is chronic urticaria diagnosed?
To ensure an effective chronic form of the disease, it is necessary to diagnose it correctly. Initially, the doctor examines the patient and also collects anamnesis.
In order to confirm a preliminary diagnosis, appropriate tests must be performed. In this case, the patient's body is tested:
These factors are allergy triggers, with the help of which the type is established. To make a correct diagnosis, an instrumental examination is recommended.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is much easier to diagnose it. That is why patients are advised to seek help from a doctor when the first signs of the disease appear.
Blood purification
In cases where long-term treatment does not produce effects, a transfusion and blood purification may be prescribed. The blood is passed through a special device that clears it of histamines. They also give injections with aloe juice and the patient’s blood. It happens like this:
- blood is taken from a vein,
- mixed with aloe (a special solution is sold at the pharmacy),
- every day the dose of the drug in the proportion increases, and the plasma decreases,
- As a result, the injection is purely a drug: the course is complete, and several such courses can cure many diseases.
You can drink decoctions from wheatgrass root. It also purifies the blood.
What is spontaneous urticaria? Among the manifestations and forms of urticaria, there is spontaneous urticaria. Its resolution occurs on its own when the irritating factor is eliminated.
But this does not mean that you do not need to undergo diagnostics. In this case, you can get by with preventive measures that will be aimed at preventing relapses in the future.
Why does chronic urticaria develop into recurrent urticaria?
In most cases, chronic urticaria becomes recurrent due to autoimmune processes in the body. What does this mean? In simple terms, the immune system, instead of directing all its forces to protect the body, on the contrary, directs them to its own cells. In fact, the human body is engaged in self-destruction. Sometimes such processes lead to irreversible changes in the functioning of organ systems.
When the body begins to fall asleep, this is precisely the result of this process. To attack one's own cells, autoantibodies are released and attach to the walls of subcutaneous cells, thereby releasing histamines and other chemicals.
Why this happens has not yet been studied. But, every year, scientists manage to learn more and more about the processes occurring in the human body and explore more factors that can provoke this or that reaction.
Everyone should know how to treat. Unlike other forms, recurrent ones must undergo long-term and complex treatment. It is aimed not only at eliminating the symptoms and the allergen, but it is also necessary to select a course of drugs that will not irritate the viruses that have already settled in the body. Antihistamines are an integral part of treatment. The next step is drugs that have a sedative effect. Corticosteroids are used in the most extreme cases.
The human immune system begins to attack its own cells, leading to hives
What hives in the chronic stage can hide behind?
In most cases, the diagnosis is idiopathic chronic urticaria, the causes of which cannot be determined. The true reasons lie very deep, so a complete examination of the body and all its systems is necessary.
This disease can be the cause of diseases such as lupus, lymphogranulomatosis, rheumatoid arthritis, malignant tumors, bladder infections, gallbladder infections, caries.
This disease is becoming common in people with alcohol intoxication and being under the influence of narcotic substances. Often, severe stress and fatigue lead to premature wear and tear of the body, as well as to pathological irreversible processes in the body. For example, sleep disturbance as a result of a nervous breakdown has very serious consequences.
Another danger posed by this disease may be secondary infection. Often the disease causes such severe itching that it cannot be tolerated.
As a result of scratching, a wound appears that becomes infected. Subsequently, the skin begins to become wet, the affected areas fester, and infection can spread to the blood.
Bladder infection, one of the complications of hives
How to tell if this rash is hives
Hives are itchy, flat, raised, pale pink blisters, similar to nettle stings. They can be large or small, red or the same color as your skin.
Blisters may come and go quickly or remain on the skin for a long time.
Manifestations of the disease can be observed throughout the body or only in one or two localized areas.
Symptoms and causes
The itching that accompanies hives can be intense or mild, long-lasting or short-term. Often the appearance of blisters caused by the disease is preceded by itchy skin. In other cases, blisters and itching appear at the same time.
Hives usually appear as clusters of blisters that can occur anywhere on the body. Its manifestations can be tiny, pinpoint or much larger. Their size and shape may also vary.
In some cases, individual blisters merge to form very large itchy areas. The skin surrounding the area where the rash appears may appear red, swollen, or irritated.
The blister usually disappears within 24 hours, although it may appear elsewhere. The rash may remain on the body or recur for weeks, months, or even years.
Causes of urticaria
Acute urticaria that lasts less than 6 weeks may be caused by the body releasing too much histamine or overproducing it. Also, acute urticaria is a common manifestation of a true allergic reaction.
Allergies are believed to be the main cause of blisters. It can occur if you eat or drink something. Or have had contact with an environmental factor to which you are allergic.
Other factors that cause hives may include:
- medicines;
- ambient temperature;
- sunlight;
- anxiety and nervousness;
- certain bacterial or viral infections, such as streptococcal infections and urinary tract infections;
- autoimmune diseases.
In some cases, the causes of the rash may remain unidentified.
How to learn to prevent relapses
Hives will not go away on their own, and relapses will occur again and again if you do not find out how to treat them. Preventive measures:
- transition to a healthy lifestyle,
- it is advisable to make proper nutrition not just a diet during an exacerbation, but a way of life so that the body gets used to this particular diet,
- full examination and treatment of internal organs and systems,
- cosmetics should only be hypoallergenic, this applies to soaps, shower gels, shaving creams, etc.
- If possible, you should limit contact with the allergen that causes such a violent reaction as much as possible,
- It is not advisable to use household chemicals for cleaning,
- it is necessary to carry out wet cleaning in the house frequently,
- strengthen the immune system,
- the gastrointestinal tract should work like a clock: the important point is the prevention of its diseases, if you follow the diet constantly, problems should not arise,
- Naturally, you will have to exclude alcoholic beverages and tobacco products from your diet.
The use of household chemicals should be minimized
Skin rashes due to liver disease: photos of skin manifestations and rashes
The liver is the body's filter. It cleanses the blood of toxins, poisons, heavy metal salts, toxic bile pigments, breakdown products of alcoholic beverages and much more.
The patient’s skin condition directly depends on the detoxification function of the liver. If the gland works intermittently, the condition of the skin deteriorates greatly. Rashes, spider veins, areas of hyperemia, urticaria and much more may appear on it.
In addition, jaundice syndrome often develops against the background of liver and gallbladder pathologies. With it, the skin, eye sclera and mucous membranes change their color. Let's take a closer look at what symptoms can be used to recognize diseases of the hepatobiliary system and how the condition of the skin changes with them.
What liver diseases cause rashes and jaundice?
Before we look at what rashes on the skin look like due to liver disease, let’s find out what deviations cause the condition of the skin to change. Most often, a rash and other changes in the skin appear due to helminthiasis.
Various parasites can live in the liver. As a rule, Giardia, amoebas, echinococci, schistosomes, liver flukes, and roundworms settle in it. Under the influence of parasites, local inflammatory processes develop, the detoxification function of the liver is disrupted, and rashes of various types appear on the skin. Itching, burning, hyperemia and urticaria are noted.
In addition to helminthiasis, the following diseases can provoke a rash and other abnormalities:
- Viral forms of hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E, G). Liver rash is accompanied by high body temperature, hepatomegaly, dyspeptic disorders, and asthenovegetative syndrome.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. The degeneration of healthy liver cells into connective tissue leads to the patient constantly experiencing skin itching, burning, and hyperemia. Bruises, xanthelomas, and spider veins form on the skin. The color of the skin changes, the tactile and temperature sensitivity of the limbs is impaired.
- Vascular disorders of the liver. The causes of the rash may be vascular thrombosis, hepatic artery occlusion, or portal hypertension.
- Hereditary pathologies - hemochromatosis, Gilbert's syndrome.
- Autoimmune liver diseases. These include the autoimmune form of hepatitis, autoimmune cholangitis, and primary sclerosing cholangitis.
- Intoxication of varying severity.
Injuries to the abdominal cavity and organs of the hepatobiliary system can provoke skin disorders.
Xanthomas (liver plaques)
Let's look at what skin rashes are possible with liver disease. Let's start with xanthus. They appear very often in cirrhosis, fatty infiltration of hepatocytes, acute viral hepatitis, fibrosis.
Xanthomas occur due to lipid metabolism disorders. Their occurrence is largely associated with excess levels of low-density lipoproteins in the blood and high levels of total cholesterol.
The relationship between cholesterol metabolism and liver diseases is obvious, since it is the liver that produces cholesterol fractions and regulates lipid metabolism in general. Xanthomas look like yellow plaques.
There are five types of xanthoma:
- Xanthelasma of the eyelids. Most often observed. Outwardly, it resembles a yellowish soft plaque. Located around the eyes and on the eyelids.
- Flat xanthoma. It is yellow in color and looks like raised soft papules. It can be located in the armpits, on the palms, hands, and soles.
- Eruptive xanthoma. Rarely seen. This term refers to semicircular yellow papules that have clear boundaries and are very soft to the touch. Typically, eruptive xanthoma is located in the buttocks and back of the thigh.
- Tuberous xanthoma. The size of the plaque is from 1 to 5 centimeters in diameter. May have a yellow or brown tint. Inflammatory lesions are located on the elbows, knees, fingers, and buttocks.
- Tendon xanthomas. As the name suggests, plaques affect the extensor tendons of the fingers and the Achilles tendons. They have a dense structure and a yellowish tint, and are mobile during contraction and extension of the joints.
Erythema
What other skin rashes are possible due to liver disease, besides xanthomas? Erythema is very common. It appears as a result of helminthiasis, cirrhosis, acute viral and autoimmune hepatitis. Cholecystitis, cholangitis, and cancer of the gallbladder can also cause the symptom.
What is erythema? This term refers to limited intense redness of the skin, which develops due to dilation of the blood vessels of the dermis. In medical practice, erythema is considered not only as a symptom of allergies. The occurrence of this symptom is very often preceded by diseases of the hepatobiliary and genitourinary systems.
Erythema can affect the face, leg, hands, arms and any other part of the body. The amount of redness will depend on the extent of liver damage. By the way, erythema is often a consequence of acute and chronic intoxication of the body.
Redness may appear due to prolonged exposure to cold, ultraviolet radiation, and radiation. What erythema can look like is shown in the photo.
Ulcers
When considering the types of skin rashes in liver diseases, you need to dwell on the so-called ulcers. Doctors call them abscesses. An abscess is a purulent inflammation of tissues with their melting and the formation of a purulent cavity.
Outwardly, it resembles a black or brown plaque. Around the area of inflammation, redness, hyperemia, and dry skin are observed. The abscess itself can be very itchy. The development of edema is possible. The skin involved in the inflammatory process may become “oily.”
Most often, ulcers appear due to:
- Acute viral hepatitis A and B.
- Liver cirrhosis.
- Liver failure.
- Fibrosis.
- Fatty hepatosis.
- Acute intoxication.
Ulcers are treated surgically. Physiotherapeutic measures are also used. After removing the abscess, bandages with Levomekol are applied to the skin.
Spider veins
In addition to irritation, erythema, cassanthomas, hemorrhagic rash, acne and allergic reactions, with liver diseases the formation of spider veins on the skin is possible. Stars are not a rash.
Scientifically speaking, spider veins are a locally expanded capillary network that appears through the skin. Outwardly, it resembles a red or purple cobweb.
The defect is most often located on the cheeks, wings of the nose, lower and upper extremities. Spider veins often appear during pregnancy and in older people.
Also, the deviation often develops in men and women suffering from diseases of the hepatobiliary system.
As a rule, the appearance of spider veins is preceded by cirrhosis, since it disrupts the functionality of the liver, malfunctions in the hematopoietic system develop, and portal hypertension and other vascular disorders are noted.
You can eliminate spider veins using:
- Electrocoagulation.
- Sclerotherapy.
- Laser photocoagulation.
- Surgitron device.
- Ozone therapy.
Hemorrhagic and acne rash
Hemorrhagic rash in liver diseases is observed very often, especially in autoimmune hepatitis and cholangitis, viral hepatitis. This rash is non-inflammatory in nature.
Outwardly, it appears as small granular spots of red or brown color. There are 3 types of hemorrhagic rash: petechiae, purpura, ecchymosis. They differ in the diameter of the rash. Ecchymoses with a diameter of more than 3 mm are considered the largest.
A diseased liver can also cause acne. It is quite rare. As a rule, acne on the skin occurs due to the acute course of viral hepatitis.
But their appearance cannot be ruled out in non-infectious pathologies of the hepatobiliary system. Acne often occurs when the liver is damaged by helminth infections. The rash is dark red or black in color.
Acne has a way of accumulating into large conglomerates.
Dark spots
Hyperpigmentation develops due to the fact that melanin is unevenly distributed in the human skin. It is this substance that gives the skin its specific color. Pigment spots are large, uneven in shape, and appear suddenly. It is extremely difficult to get rid of them.
According to experts, the appearance of age spots is the first “alarm bell” that indicates that the liver or other organs of the gastrointestinal tract are not in order. Skin pigmentation is impaired in diseases such as:
- Cholecystitis (any form).
- Cirrhosis.
- Fatty hepatosis.
- Fibrosis.
- Liver failure.
- Gilbert's syndrome.
- Cholangitis.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Steatohepatitis.
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Hepatosplenomegaly.
- Liver or gallbladder cancer.
- Hepatitis of any etiology.
The color of age spots varies from light to dark brown. If there are abnormalities in the functioning of the liver, even chloasma or melasma - large pigment spots - can form on the skin. They have an irregular shape and tend to merge.
Jaundice and other symptoms of hepatobiliary disorders
Jaundice is a problem that perhaps most people with chronic pathologies of the hepatobiliary system face. Let us immediately note that jaundice is not a diagnosis, but just a sign.
This term refers to a condition in which the skin, mucous membranes and eye sclera become yellow. Jaundice develops due to increased bilirubin content in the blood and tissues.
There are 3 types of jaundice:
- Hemolytic. Develops due to increased synthesis of bilirubin.
- Parenchymatous. It progresses due to the fact that the liver cannot secrete indirect bilirubin into bile, and it enters the blood again. With parenchymal jaundice, the level of total bilirubin increases.
- Mechanical. It is observed in diseases in which the outflow of bile through the extrahepatic bile ducts is disrupted.
In addition to jaundice and the above symptoms, liver disease can cause other symptoms. For example, with cirrhosis and hepatitis of viral etiology, bruises often appear on the patient’s skin for no reason. The tactile and temperature sensitivity of the limbs changes. Even atrophy of muscles and limbs and modification of the nail plates cannot be ruled out.
In addition to skin manifestations, pathologies of the hepatobiliary system are characterized by:
- Dyspeptic disorders. Manifestations of liver diseases and gallbladder are considered to be bitterness in the mouth, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, sour or bitter belching, flatulence, heaviness after eating food. The color of stool changes - it becomes discolored.
- Asthenovegetative syndrome. If the liver is unhealthy, the patient begins to get tired quickly, he experiences mood lability, insomnia, apathy, and a tendency to depression.
- Pain of varying intensity in the right hypochondrium. They can occur spontaneously, or after consuming junk food and alcoholic beverages.
- Increased bleeding of gums, nosebleeds, varicose veins of the esophagus and rectum. The liver can influence the functionality of the hematopoietic and cardiovascular systems, so these signs are very common.
- Lack of appetite, causeless weight loss.
- Redness of the phalanges of the fingers on the palmar side.
- Swelling of the face, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. The signs are explained by the fact that a diseased liver has a negative effect on the kidneys.
If the above symptoms are present, a comprehensive differential diagnosis is indicated. A biochemical blood test, ultrasound, MRI, CT, biopsy, duodenal intubation, fecal occult blood test, blood test for hepatitis markers, and PCR help to assess the condition of the hepatobiliary system.
Source: https://blotos.ru/vysypaniya-na-kozhe-pri-bolezni-pecheni-foto
Can chronic urticaria be cured?
Many people who have encountered this problem in practice are interested in this issue. Recurrent urticaria is a very dangerous disease; it cannot be cured. However, it is possible to reduce the frequency of relapses using preventive measures. With individual selection, herbal infusions can also help with this. This disease is characterized by a high risk of developing Quincke's edema.
If a patient diagnosed with urticaria begins to breathe heavily, urgent medical intervention is necessary. There is no need to postpone treatment and visits to the doctor; the processes of treating the disease should become part of the life process.