Many parents are familiar with urticaria, or urticaria. Most often, especially in a newborn, it manifests itself in an acute form and goes away on its own in a fairly short time. Very often, the appearance of a “nettle” rash is accompanied by itching, which worries the child, and this disease can also be accompanied by very unpleasant consequences - Quincke’s edema and transition to a chronic form. The doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment, but it is very important for all parents to know how to treat urticaria in children, how to alleviate the baby’s condition at home, and what folk remedies can reduce painful symptoms.
Symptoms and causes
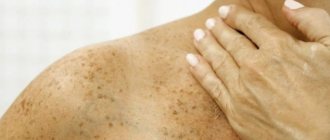
Urticaria is a rash in the form of red or pink blisters that appears on the skin and mucous membranes. Reaching several centimeters in size, the blisters have clear shapes, rise above the surface of the skin and appear singly or in large numbers. Causing discomfort with severe itching and burning, they disappear without a trace within 24 hours.
In many cases, even doctors cannot explain the nature of this disease. A significant amount of histamine is released into the blood due to too high permeability of the capillaries with their simultaneous expansion.
Increasingly, the cause of urticaria is allergies to foods, medications, and household chemicals. Rashes are common due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, infectious and endocrine diseases, and during human interaction with vegetation or insects.
Hives can be triggered by sports training, severe emotional shock, activities in dirty or chlorinated water, exposure to direct sunlight, or exposure to cold winds. This disease also affects people whose skin is extremely sensitive - when wearing tight clothes, narrow shoes, or from the strap of a bag.
Forms
Often the disease is of an allergic nature, and its symptoms appear in infancy and in children under 2 years of age. However, in some cases, the pathology is of non-allergic origin and develops under the influence of unknown factors. All types of urticaria can appear at any age, however, the acute type of the disease is more often diagnosed in young children when new foods are introduced into their diet or a change in diet.
Allergic
One type of body reaction to an allergen is allergic urticaria - a pathology that looks like “wandering” rashes on the skin, similar to a burn left by nettles (example in the photo below). The occurrence of urticaria is associated with interaction with certain allergens. Common substances and physical factors that can cause an allergic reaction include:
- fish, nuts, fruits, eggs, honey, other food;
- medicines;
- food additives (dyes, flavors, etc.);
- inhalation irritants – dust, grass and tree pollen;
- viral infections (hepatitis B, Epstein-Barr disease);
- cold, thermal, vibration, solar factors (with such allergens the disease is called dermatographic).
READ ALSO: Pimples on the penis and head: why they appeared and how to treat
Acute
This form of the disease can last from several hours to a couple of weeks. Acute urticaria appears suddenly in the form of itchy reddish blisters of various sizes and, as a rule, round in shape (rarely they have an elongated appearance). The rashes extend beyond the skin, with a matte hue in the center, and a brighter border is noticeable at the edges. The blisters may merge into one solid spot. Mostly the rash is localized in the area of the arms, butt, thighs, neck, torso, but can also occur on the mucous membranes.
In the acute form of the disease, nettle fever may develop, in which chills, headache and fever appear. Urticaria predominantly affects children as a consequence of food or drug allergies, responding in this way to an irritant. A rash often appears during blood transfusions or the administration of serums/vaccines. Acute pathology can be expressed by an atypical form of urticaria, when a blister-like strip forms on the body when a fingernail or other object is passed over it. At the same time, such a rash will not itch.
Chronic
This disease can last for years and is characterized by periodic exacerbations followed by remissions. If symptoms of the pathology appear for longer than 6 weeks, the doctor diagnoses chronic urticaria. The cause of the disease, as a rule, is an untreated infection (tonsillitis, caries, adnexitis), a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, etc. The chronic form manifests itself in the form of severely itchy rashes on the skin and is accompanied by joint pain, high fever, diarrhea, vomiting . The disease often leads to sleep disturbances.
It is often impossible to establish reliable causes of the disease, however, it is believed that in approximately half of cases, urticaria is of an autoimmune nature. In this case, the child’s body creates antibodies against its own molecules and receptors, which ultimately leads to the appearance of pseudoallergic urticaria. With long-lasting rashes, the disease develops into a papular form, which is characterized by swelling with cellular infiltration, thickening and hyperpigmentation of the skin in the bend areas of the elbows, knees, etc.
Kinds
There are spontaneous, physical and original types of urticaria.
Spontaneous urticaria appears without any visible direct impact and comes in the following subtypes:
- acute (lasting up to 6 weeks);
- chronic (more than 6 weeks).
Physical urticaria is caused by various physical influences:
- dermographic – from light scratches on the skin;
- slowed by pressure - from squeezing the skin (for example, when sitting), appears after a certain period of time (from 3 to 8 hours);
- cold - from being in cold air, in water, in the wind;
- thermal – after local influence of heat;
- cloudless – from ultraviolet rays or visible light;
- vibration - from the effects of vibration.
Among the original types of urticaria are:
- cholinergic – from stress of a physical or emotional nature, leading to an increase in body temperature;
- adrenergic – caused by adrenaline released by the body during stress;
- contact – from the interaction of the skin with an allergen substance (dust, animal fur, plant pollen, metals);
- aquagenic - from contact of the skin with water (when the allergen appears in the skin of people, and water acts as a solvent for it).
Pay your own attention to how allergies to sweets manifest themselves in adults and children and how to treat them https://woman-l.ru/simptomy-i-lechenie-allergii-na-sladkoe/
Treatment
Since the cause of the disease in 90% of cases remains unclear, the main means of treatment for urticaria are antihistamines, which have virtually no side effects, but have a long-lasting effect.
If the disease is severe, steroid hormones may be used, but only under the supervision of a doctor. Hormonal therapy is associated with a considerable number of side effects, due to this it takes a short course.
Ointments are used as an additional remedy, in many cases they are prescribed after the use of injections or tablets. However, in mild cases of the disease, the situation can be resolved with the help of ointments alone. Remedies are divided into hormonal (much better) and non-hormonal (weaker, but safer).
In severe cases of urticaria with complications, for example, with Quincke's edema (when the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract swells, breathing is difficult, a whistling paroxysmal cough appears), the patient is placed in a clinic, where they are treated with histamine blockers and hormonal drugs, and the allergen is removed from the body using sorbents and droppers , gastric lavage.
What you need to know about Quincke's edema?
Acutely developing local swelling of the skin is a dangerous complication of simple urticaria. This condition can be life-threatening, because suffocation occurs with swelling of the larynx. Therefore, it is so important to seek medical help when the first signs of hives appear in a child.
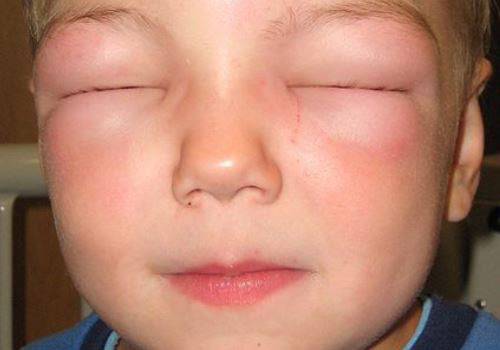
Quincke's edema is a dangerous complication of urticaria
The problem is that Quincke's edema usually develops acutely. The child may not be bothered by anything, but after a few minutes the lips increase in size and swelling appears under the eyes. What to do if a child’s well-being rapidly deteriorates? First of all, it is necessary to limit contact with the allergen. Then you should lay the child down and raise your legs. You should immediately call an ambulance. While the doctor is on the way, you should give the child plenty of water. In this way, it will be possible to speed up the process of eliminating the substance that provokes a complex allergic reaction. Before the specialist arrives, you can give your child an antiallergic drug.
Prednisolone helps relieve complex allergic manifestations (suffocation, bluishness of the face). Parents of allergy sufferers should keep this medication in their medicine cabinet. Even if Quincke's edema was managed on the spot, the specialist will recommend going to the hospital for a full examination of the child.
How long does the unpleasant condition last? Everything here is individual. With timely medical care, swelling can be completely removed within a few hours.
Diet
A carefully selected diet reduces histamine production. If you have urticaria, exclude from your diet:
- products containing preservatives, flavorings, artificial sweeteners, dyes and other chemical additives;
- berries, vegetables and fruits of red and orange colors, citrus fruits;
- fatty fish and seafood, caviar;
- fatty meats;
- chocolate, cocoa, coffee;
- baked goods and confectionery products;
- honey and nuts;
- eggs;
- milk;
- spices.
Instead of fried foods, foods are boiled or baked. Allowed:
- lean meat (no skin);
- low-fat fish;
- vegetable soups (meat broth is not allowed);
- vegetables and fruits of white and green colors;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- durum pasta products and cereal porridge (not counting semolina);
- whole grain bread and bran, biscuits;
- vegetable (olive and sunflower) oils;
- sugar in a minimal amount (much better, fructose).
When the skin is cleansed, you can gradually add familiar foods to your diet.
In children
The immune system of a child under 6 years of age is not sufficiently developed, and therefore up to 25% of children do not always develop urticaria. Many medications are contraindicated for children, so it is not recommended to treat her without consulting a doctor.
The causes of the disease and the principles of treatment of childhood urticaria are similar to those in adults. However, the following recommendations will be useful for parents:
- cut your child’s nails short to avoid scratching the affected, itchy skin areas;
- for a specific period of time, isolate the child from pets living in the house;
- bathe your child in cool water instead of a hot bath;
- To reduce itching, apply baby cream with panthenol and similar substances to the skin.
If the rash is accompanied by significant fever, nausea or vomiting, increased breathing and heart rhythm disturbances, swelling (especially in the face), you should immediately call a medical team.
Prevention measures
A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention of any disease. Urticaria is no exception. A child who spends a lot of time outdoors, sleeps well and eats well will be less likely to encounter trouble. Prevention of urticaria in children also comes down to timely treatment of any infectious conditions. A baby under one year old should be brought to the pediatrician for a preventive examination every month.
Special attention should be paid to children who have already developed urticaria once. Contacting an allergist will help prevent exacerbations. The doctor will examine the baby and tell you what measures will help avoid trouble in the future.
In pregnant and nursing mothers
Changes in hormonal levels and reduced immunity in pregnant women do not always lead to hives. It almost always appears in the third trimester and often continues until childbirth. The disease has absolutely no effect on the child, but causes some discomfort to the expectant mother (itching, nervousness, sleep disturbance).
It is not uncommon for hives to appear after childbirth. This is caused by hormonal imbalance in the body and stress. Despite the assurances of the nursing mother to be patient, it is necessary to carry out treatment.
A significant number of medications are contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation. Antihistamines can penetrate into the blood and breast milk, adversely affecting the baby's health. It is not best to carry out any treatment, even homeopathic and folk remedies, without the approval of a doctor.
The main thing is not to allow contact with all possible allergens (cosmetics, household chemicals, medications, pets and flowering plants). Pregnant women and nursing mothers should adhere to a strict hypoallergenic diet.
If the symptoms of urticaria do not disappear, treatment continues with medications. If the use of hormonal drugs is required, breastfeeding ends until complete recovery.
Diagnosis of urticaria
A specialist will be able to determine what pathology you have encountered without much difficulty. However, this is not enough to prescribe appropriate treatment. It is important to understand what triggers a child’s allergic reaction. It is possible that the small patient suffers from chronic diseases that need to be treated first.
For urticaria, allergy tests must be performed
The examination of the child will be carried out in several stages. First of all, the doctor farrows the parents. It is important to find out when and under what circumstances the first signs of urticaria appeared.
The patient is given an appointment to conduct research:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- blood sugar test;
- stool analysis for oviworm.
It is important to exclude the development of autoimmune diseases and HIV. Allergy tests are required to determine what exactly the child is developing a negative reaction to.
Treatment with folk remedies
Home-made remedies have a fairly good effect in curing urticaria. Ointments and lotions will help save you from constant itching and redness of the skin:
- Basil ointment: wash 10-15 fresh leaves of the plant and grind to a smooth paste, add a little aloe juice. Apply to the rash several times throughout the day. Basil leaves can be replaced with sandalwood leaves.
- Oat ointment: soak 20 grams of cereals for 60 minutes in 200 milliliters of hot boiled water. Mix the resulting mixture and leave for another 30 minutes. Apply to skin a couple of times during the day.
- Oatmeal ointment: mix 0.5 cups of small flakes and 0.5 cups of corn starch, add 50 milliliters of apple cider vinegar. If the ointment comes out juicy, lightly dilute it with warm water. Apply to skin and leave for 15-20 minutes.
- Ointment based on soda and water in a ratio of 3:1. This product should not be used if the skin is severely irritated or damaged due to combing.
- Nettle lotions: place 30 grams of leaves in 0.5 liters of water, boil, boil for 3-5 minutes, leave for 1 hour, then strain. Apply gauze or cloth soaked in the broth to the affected areas.
- Thyme lotions: pour 15 grams of raw material
with 1 glass of water, then bring to a boil, cover the container and cool. Apply lotions for 10-15 minutes to reduce itching. - Oatmeal bath: pour 100 grams of cereal with 2 glasses of hot water, stir and leave for 15 minutes. Pour the resulting mixture into a bathtub with cool or warm water and stir. Similar baths are very calming for the skin, and children can also take them.
- Cosmetic mint ice: pour 200 milliliters of hot water , cover the container, cool and strain. Pour the infusion into molds and preserve. Mint ice is harmful for cold urticaria.
- The affected skin can be treated with mild soap, dried and coated with an insufficient amount of lemon juice. After 10 minutes, apply 1 tbsp. a spoonful of honey mixed with 1 teaspoon of small sea salt. Leave for 15 minutes and rinse with warm water.
Decoctions and infusions for urticaria are productive not only for finishing the outside of the skin, but also when taken orally:
- Raspberry decoction: pour 100 g of plant rhizomes into 500 milliliters of water, boil for 20 minutes over low heat and leave for 1 hour. Drink 100 milliliters of strained broth several times during the day.
- Infusion of nettle flowers: pour 4 teaspoons of dry raw material into 1 glass of hot water
, cover for 30 minutes and strain. Drink 100 milliliters warm 4-5 times throughout the day. - Yarrow infusion: pour 20 grams of herb into 200 milliliters of hot water, leave for 45 minutes. Take 1/3 cup 3 times during the day.
- Infusion of the series: pour 15 grams of raw material into 150 milliliters of hot water
and, when the color of the infusion turns golden, strain. Drink 3-4 times during the day. - Celery juice: grind the roots using a meat grinder or on a grater, squeeze, take 1-2 teaspoons before eating.
- Celery infusion: place 2 tablespoons of chopped roots in a glass of cold water, leave for 2 hours and strain. Drink 70 milliliters of infusion before meals 3 times a day.
- Calamus root: crushed rhizomes take 5 grams daily before going to bed with water.
If after 6 weeks of treatment with home methods the disease has not subsided, you need to go to the doctor.