Liver spots form on the body due to disruption of the liver and insufficient removal of bilirubin metabolic products from it. As a result, it accumulates in the upper layers of the skin, giving it coloration. If you have problems with the liver, spider veins may form, which pulsate, protrude above the surface of the body and have radiating small vessels. They arise due to increased blood pressure in the venous bed due to ascites.
Pigment spots on the face are quite rare.
Causes of liver problems
Stars on the body due to liver disease can be caused by the following factors affecting the human body:
- viral pathologies;
- violation of the outflow of bile;
- gallstones;
- poor nutrition;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- frequent stress;
- liver parasites;
- portal vein thrombosis;
- medications;
- poor environmental situation;
- portal vein thrombosis;
- exposure to toxins and poisons;
- organ injuries;
- burdened heredity.
Return to contents
Other skin changes
As a rule, these are symptoms of violations of certain liver functions as a result of liver disease.
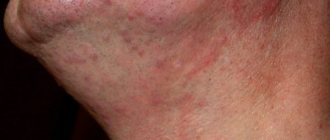
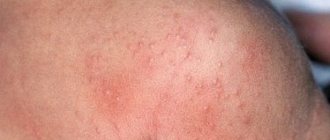
Allergic dermatitis often occurs with liver diseases. A rash, as a symptom of dermatitis, appears due to a violation of the detoxification function of the liver. Skin manifestations of dermatitis vary, but most often these are bright red spots or plaques. Dermatitis usually occurs suddenly. Treatment of allergic dermatitis is complex.
There is often a tendency to develop pustular dermatitis in the form of typical rashes - folliculitis, furunculosis. This is a manifestation of immune imbalance in response to a decrease in the synthesis of immunoglobulins by the liver.
Atrophic stripes (striae or “stretch marks”) develop as a manifestation of secondary hormonal imbalance in liver disease. They are located on the thighs, buttocks, lower abdomen, and sometimes on the arms.
The vast majority of skin and other manifestations on the patient’s body regress with treatment of the underlying disease.
Perhaps the most emotionally unpleasant manifestation of liver pathology is skin itching. Treatment of skin itching in liver diseases comes down to eliminating the root cause. However, according to the results of scientific research, drugs that inhibit the absorption of bile salts by hepatocytes (rifampicin, fusidic acid) or prevent intrahepatic cholestasis (metronidazole) can be effective. The use of these and some drugs significantly improves the quality of life of patients.
It has been established that pulse therapy with metronidazole leads to rapid disappearance of itching in patients who are insensitive to therapy with other drugs. The antipruritic effect of metronidazole is also associated with changes in the metabolism of bile acids by small intestinal bacteria. However, itching may return 4–6 weeks after stopping metronidazole therapy. A repeated short course of treatment with metronidazole eliminates itching.
It is also known that metronidazole reduces the level of low-density lipoproteins by 10–20%, i.e. improves lipid metabolism. At the same time, metronidazole derivatives have not been studied as possible drugs for monotherapy of lipid metabolism disorders.
Modern medicine has achieved certain successes in the treatment of liver diseases and their complications. However, the possibilities of medicine are not limitless, so the chances of success are much higher with timely diagnosis.
Every fall my skin became dry and itchy due to the cold weather. This time I blamed it on the same thing, but the red spots on my face, spreading to my neck, forced me to go to the doctor. I was terribly worried, but it didn’t seem to be anything terrible... I drank oats, so far everything is fine, the spots have gone away, there is no more itching. Is it probably worth keeping a diet all the time?
Attention! Information about drugs and folk remedies is presented for informational purposes only. Under no circumstances should you use the medicine or give it to your loved ones without medical advice! Self-medication and uncontrolled use of drugs are dangerous for the development of complications and side effects! At the first signs of liver disease, you should consult a doctor.
© 2020 – 2020 Editorial staff of the portal “My Liver”.
The use of site materials is permitted only with prior approval from the editor.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
What is pigmentation?
It appears mainly in older people. But when the functioning of the liver is impaired, this symptom appears quite often and is a manifestation of insufficient removal of harmful substances from the body. The spot is a limited area of hyperpigmentation, which over time changes color to a more saturated one and increases in size. These formations can appear on the entire surface of the skin. The formation of pigment is associated with the accumulation of bilirubin in the skin, which remains after the breakdown of red blood cells and must be excreted by the liver. Under the influence of the sun, the severity of age spots increases significantly, and sometimes plaques and bubbles filled with clear liquid form on their surface. Liver spots can be brown, red or brown, depending on the intensity of pigment saturation.
Pigment spots are predominantly located on the arms and upper torso.
Other symptoms
Pigmentation and the liver are associated only if there is a clinical picture characteristic of cirrhosis, which includes the following signs:
- nausea, vomiting;
- weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- yellowness of the mucous membrane, skin and sclera;
- painting the palms red;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen with the formation of ascites;
- hemorrhagic rash;
- body itching;
- dystrophic changes in the oral cavity;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- disruption of the digestive process.
Return to contents
Truly “hepatic” lesions of the skin and its appendages
Skin problems that arise from liver dysfunction are quite varied: from dermatitis and rashes to almost irreversible damage. Let's look at the most common of them.
"Hepatic" (cholestatic) skin itching
Itchy skin is an almost constant symptom of jaundice in cholestasis syndrome. It occurs due to increased levels of bile acids in the blood. Some non-obstructive liver diseases, such as hemochromatosis, sometimes begin with itchy skin. Almost never occurs in other types of jaundice (hemolytic or parenchymal). Sometimes it appears some time (even years) before the appearance of jaundice or other clinical signs of liver disease. It may also be accompanied by various rashes.
It can be short-term and paroxysmal, or persistent and painful. The most commonly affected areas of the body are the skin of the torso, arms and legs.
There are traces of scratching on the skin, a xanthomatous rash - rounded subcutaneous plaques of a yellowish color, located in the skin folds of the body, on the face around the eyes.
"Hepatic" (yellow) skin discoloration or jaundice
When the level of bilirubin in the blood increases, the skin and mucous membranes begin to turn yellow - jaundice occurs. First, jaundice (subictericity) is clearly visualized on the sclera and in the oral cavity, then the face, palms of the hands and soles of the feet are colored, and then spreads to the entire body.
Jaundice becomes noticeable when the bilirubin level is not lower than 34-36 µmol/l (2-3 mg%).
The distribution of yellow skin color on the body is, as a rule, uneven: more pronounced on the trunk and sclera, less pronounced on the limbs.
An interesting fact: acute pathology of the hepatobiliary system is often projected in the peri-umbilical zone. In acute cholecystopancreatitis, hemorrhages may appear here, and if the common bile duct is ruptured, a sharp yellow color may appear.
“Liver stars” - telangiectasia
They are the most important diagnostic sign for liver diseases. Another name is “spider veins”. They are multiple small (0.1 - 0.5 cm in diameter) pulsating vascular ectasia, which slightly rise above the skin and have a dark red color. Small vascular branches branch out from them in a radial manner, which resemble “spider legs”. Often located on the face, neck, arms, shoulders, back.
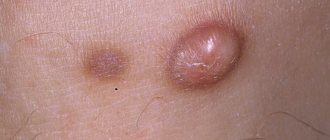
"Liver" purpura
It consists of small skin hemorrhages (hemorrhagic spots), which are located in large numbers on the skin of the body and mucous membranes. They do not disappear when pressed, which distinguishes them from some other types of rashes.
In liver diseases, their sizes can range from microscopic dots to large ones (ecchymoses or “bruises”). Nasal and uterine (in women) bleeding are also common.
Liver palms
Bright red coloration of the palms, or palmar erythema (“liver palms”) is a symptom that occurs in almost any chronic liver disease. When pressed, the red color fades, but then recovers.
In addition to erythema, smoothness of the thenar (thumb eminence) and hypothenar (little finger eminence) is noted.
The symptom also occurs in rheumatoid polyarthritis, during pregnancy, and in healthy adolescents.
Sometimes the soles of the patient's feet turn red (plantar erythema).
"Liver" tongue
In case of chronic liver diseases, the tongue becomes bright red, swollen, with a “varnished” surface. Sometimes the tongue acquires a dark red, even purple, tint and becomes dry. This sign is often a harbinger of liver failure.
The mucous membrane of the mouth and lips acquires a characteristic carmine-red color.
"Liver" smell
In liver diseases, the expression “liver odor” is often used. It's hard to describe. Some describe it as sweetish, similar to the smell of overripe fruit. Some compare it to the smell of fresh meat or liver. For others, this smell causes an association with mice - a “mouse” smell. The occurrence of such a smell is associated with a violation of the metabolism of amino acids and aromatic compounds.
This specific odor is felt when the patient breathes, as well as from his body due to the release of sweat onto the skin.
Skin pigmentation disorders
A fairly common sign of liver problems. Increased pigmentation in the form of excessive formation of age spots accompanies almost all chronic liver diseases. The color of the skin in the armpits and on the arms, especially the palms, may take on a bronze or dirty gray tint. In women, excess pigmentation is manifested as chloasma. The typical location of pigment spots on the face is the lateral surface of the cheeks with a transition to the neck.
Some doctors associate the occurrence of decreased pigmentation (vitiligo) with damage to the liver parenchyma with cholestasis syndrome and a decrease in the detoxification function of the liver. However, the mechanism of this disease is still not fully understood.
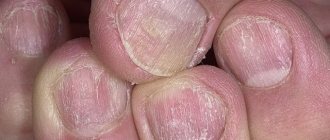
Damage to hair and nails
In men, body hair becomes thinner and may even fall out completely. Significant thinning of the hairline occurs on the head, up to complete baldness. In women, hair growth in the armpits and pubic area decreases.
Deformation of the nail plates occurs, the nails become thin, brittle, and white stripes and spots appear on them. The distal phalanges of the fingers may change (thicken) like “drum sticks”.
Diagnostic procedures
The easiest places to spot skin spots are on the arms and upper torso area. In this case, it is necessary to undergo additional tests and undergo instrumental studies to determine the condition and ability of the liver to function. It is important to do a general and biochemical blood test, as well as determine the content of basic enzymes. Ultrasound examination of the organ will help to identify structural abnormalities of the parenchyma, and angiography or Dopplerography is indicated to diagnose abnormalities in the vascular bed.
Features of treatment
Therapy, if the patient has liver pigmentation, can be aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked its appearance. For this purpose, the functioning of the liver and all organs and systems is normalized. If this method does not give a positive result, then laser removal of areas of pigment accumulation or spider veins is indicated. Alternative medicine can be used as a complement to basic methods.
Treatment of the cause
Liver spots can be removed only after the functioning of all organs and systems has been normalized and the elimination of bilirubin breakdown products from the body has been enhanced. For this purpose, it is recommended to use hepatoprotectors “Essentiale” or “Phosphoglin”, which help restore hepatocytes and normalize blood flow in the liver. Also shown are agents that enhance the removal of toxins “Sirepar” and “Hepatosan”. The amino acids “Heptor” or “Heptral” will be useful.
Herbal products “Gepabena”, “Karsil” and “Hofitol” are also used. It is possible to treat gallstones using bile acid preparations, such as Ursofalk, Ursosan, Exhol and others. Patients must be prescribed a gentle diet, limiting the consumption of fatty, fried and spicy foods. It is important to get rid of bad habits - smoking and alcohol addiction, and also to avoid stress that puts stress on the liver.
Traditional methods
In combination with drug and surgical treatment, non-traditional methods can be used. They help to significantly improve the patient’s condition and reduce the severity of pigmentation. One such method is rubbing aloe, calendula and orange juice into the pigment. This should be done 3 times a day for 2 weeks. Once a week you can apply a mask of cottage cheese, ammonia, lemon juice and white clay. Ice cubes containing frozen decoction of mint, chamomile and aloe pulp will also be useful. They need to be rubbed into your face in the morning.
Laser treatment
If it is not possible to eliminate liver stars, plaques or spots using medication, then surgical removal of these tissues is used. For this purpose, a laser is most often used. It causes minimal damage to the skin and leaves no scarring or wounds. This procedure is painful and is performed under local anesthesia. The effect is noticeable after several courses of laser removal of formations. At the same time, the problem in the liver remains and formations can develop again if their immediate cause is not eliminated.
Causes of the disease
What causes liver palms? This is a very wide list of diseases and functional disorders of the body. Such as:
- liver failure in acute or chronic form;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatitis of various nature (viral, alcoholic, toxic);
- excess vitamin A in the body;
- lack of vitamin B in the body;
- tuberculosis;
- various diseases of the thyroid gland;
- contact dermatitis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- venereal diseases;
- nonspecific colitis;
- scarlet fever and other infectious diseases;
- excess of female sex hormones in the body;
- influence of other medications.
Sometimes adolescents experience palmar erythema of a symptomatic nature, that is, not associated with any disease. The cause is puberty.
If symptoms of liver palms are detected, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory diagnosis of the person’s condition, on the basis of which the doctor will be able to establish the mechanism of their occurrence, establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Is it possible to warn?
It is possible to prevent the development of spots in liver disease if it is possible to promptly begin treatment of the pathology by replacing the functional capacity of the liver filter. It is important to avoid stress, adhere to the correct daily routine and get enough sleep. You need to engage in light sports, but avoid excessive physical exertion. Fatty, fried and spicy foods, as well as contact with toxins and poisons, are dangerous for the liver.
It’s not for nothing that people call the liver the “filter” of our body. It performs a number of important functions, such as neutralizing toxins and other harmful substances, producing glycogen (“gasoline” for our body), and also participates in digestion, synthesizing bile, which helps absorb nutrients, break down fats, etc. Thus, thanks to the liver, we can drink and eat whatever we want in unlimited quantities.
However, everything in this world is not eternal. And our liver too. If you have an unhealthy diet, frequent consumption of alcohol, etc. the organ wears out and begins to malfunction, allowing harmful substances into the body. This is how various kinds of diseases arise that can harm a person to varying degrees, ranging from unpleasant sensations to a serious condition or even death. The skin is one of the organs that first gives signals about liver disease. And if you have a rash for no reason, you should think about whether these could be spots on the body due to liver disease?
Yellow spots
The appearance of yellow spots is the main symptom of gland disease.
Yellowing of the skin begins as a result of bilirubin, which is contained in the blood above normal; this substance is formed in the body during the processing of damaged and destroyed red blood cells.
Cholestasis syndrome occurs, which is divided into several stages: functional cholestasis, morphological cholestasis and clinical cholestasis - with such pathological complications, bilirubin stops being excreted from liver cells. The liver releases it into the blood, and accordingly, in its excess it appears in the skin as a lemon-yellow or orange tint.
With cholestasis, a certain obstruction occurs that makes it difficult to secrete bile. It is possible in any specific area between the liver and the initial part of the small intestine. Bile, encountering such an obstacle, stops entering the intestines, but the liver continues to produce bilirubin, which directly enters the blood. An unhealthy sensation occurs - a burning sensation in the liver.
This pathology is popularly called jaundice and its progression is determined by the degree of liver damage. Yellow spots cover both the skin and the nails on the hands and feet, as well as the mucous membrane.
The nerve nodes excited by bilirubin cause intense itching, which is why the rash with hepatitis and in patients with such serious diseases as cirrhosis of the liver itches terribly.
The skin with cirrhosis of the liver constantly dries, peels and becomes decrepit; the rash in diseases of this type takes on a jaundiced tint. Itching in liver cirrhosis is incessant. This leads to depression, neurosis and sleep disorders.
READ ALSO: The child has red spots on his body, like bites - what kind of pimples are they (photo of the rash)
Treatment is required only if the level of bilirubin in the blood is above the limit. It is carried out in two stages. The first step is to eliminate cholestasis with the drug Heptral. The active substance of this drug (Sademetionine) is optimized in the composition of tissues and body fluids.
Then, as part of an intravenous drip infusion, vitamin complexes, a drip with saline solution, antioxidants and hormonal drugs, and a strict diet are introduced, excluding all fatty foods in the diet.
Diseases affecting the appearance of spots on the body
The main diseases that cause redness and spots on the skin are:
- Hepatitis. Hepatitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the liver. They are usually accompanied by a variety of skin manifestations. This may include hives, changes in skin color, red-brown rashes, large pinkish-red spots, etc. The rash appears immediately after infection or during the transition to a chronic disease.
- Parasitic infections. Such diseases are divided mainly into echinococcosis, ascariasis, amoebiasis, etc., depending on the causative agent of the infection. Parasites and helminths not only damage the structure of the organ, but also stimulate neoplasms, disrupting the normal functioning of the liver. In this case, there is no jaundice, only red spots in the gland area and acne. Common symptoms are chronic fatigue, lethargy, exhaustion, sleep disturbances, bad breath, right upper quadrant pain, and enlarged liver.
- Cancer. The formation of metastases and tumors in liver cells leads to disruption of its functioning, and without treatment, to the death of a person. The development of such malignant neoplasms can be confused with other liver diseases, since their symptoms are similar: an unpleasant feeling of bloating, weakness, sometimes vomiting, loss of appetite, constant malaise. At a later stage, tumors inside the diseased organ reach such a size that they block the flow of bile into the intestines, and it goes straight into the blood. As a result, yellowing of the sclera and skin, darkening of urine, and itching occurs.
- Cirrhosis.
They are divided into: • Alcoholic; • Stagnant; • Viral. The vast majority of people get sick due to prolonged alcohol intoxication. The last two are much less common.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cholangitis are all diseases of the gallbladder. Basically, they are all associated with the formation of stones in the cavity of the bladder and its ducts.
Signs of the disease: • Itching of the epidermis; • Belching and bitterness in the mouth; • Heaviness under the right rib.
- Liver failure. This disease occurs due to an overdose of alcohol or medications, or severe poisoning. It can manifest itself in the form of yellow spots, a purulent rash, spider veins, bitterness in the mouth, and general lethargy.
Associated symptoms indicating liver disease are:
- General weakness;
- Bitterness in the mouth;
- Fatigue quickly;
- Congestive acne;
- Hair loss and brittle nails;
- Weight loss;
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Feverish state;
- Dry mouth;
- Yellowness of the sclera;
- Discomfort while eating;
- Smell of overripe fruit on the breath;
- Indigestion;
- Unpleasant smell of sweat.
Liver spots on the palms and tongue
Red palms are a sign observed in cases of serious liver ailments. If you press on them, the red color fades, but then, again, the inner surface of the palm returns to its previous state.
Often the patient’s tongue also turns into an unhealthy crimson tone with swelling, until it acquires a garnet color. Dry mouth appears. The mouth and lips become purple in color.
This is a sign that the liver is not working properly, there is something wrong with the liver - a sign of liver failure.
This can only be treated in one way: it is important to identify and urgently prescribe treatment for liver pathologies that cause such increased pigmentation. Medicines are prescribed that neutralize bile salts and prevent the development of cholestasis in the liver. For example: “fusidic acid”, “metronidazole”, “rifampicin”, etc. These drugs can effectively affect the patient’s recovery.
READ ALSO: Wen in newborns (on the face, on the nose), treatment in infants
Where do spots appear on the body due to liver disease?
With diseases of the gland, the skin becomes a non-standard color, and this should never be ignored. Yellowish skin with an orange color indicates internal liver problems; lemon tint - about hematological disorders; brown means mechanical damage to the organ.

Basically, liver spots are localized throughout the body, depending on the disease and its manifestations:
- Rash – face, neck, chest, back;
- Red spots – in the liver, abdomen;
- Yellow spots – oral cavity, sclera, with transition to other parts;
- Bright red spots – palms;
- Pigment spots – palms, arms, face, neck;
- Yellow plaques – armpits, eyelids, arms, legs, feet;
- Spider veins – neck, back, arms, face;
Age-related spots on the skin
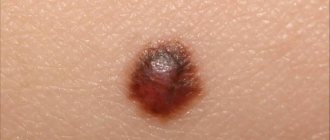
The concept of “liver” spots refers not only to changes on the skin that appear as a result of liver diseases, but also age-related changes that are characterized by a violation of skin pigmentation. We will talk about them below. You can see what such spots look like in the photo below.
Age spots are called differently:
- senile;
- pigmented;
- solar (senile) lentigo;
- hepatic.
Moreover, the latter name has nothing to do with liver diseases, it’s just that age spots are distinguished by a brown rash, which in color resembles the shade of the liver.
On the surface of the skin, age spots can look like this:
- flat;
- slightly raised oval shape;
- in the form of light or brown plaques.
As a rule, such rashes appear in people over 40 years of age and are located on open areas of the skin:
- on the face;
- on hands;
- on the shoulders and forearm.
Basically, these heels are a consequence of aging and long-term exposure to ultraviolet rays. Many people confuse them with moles; they are also distributed throughout the body, including the face and hands, and the color of moles is also brown. Only a qualified dermatologist can distinguish lentigo from a mole.
Age spots and moles are mostly not dangerous and painless; they do not necessarily need to be treated, only if the doctor has prescribed their removal using laser or cryotherapy.
You should consult a doctor if the spots begin to change their appearance and shape. This will make it possible to prevent their degeneration into a malignant form in time.
What do liver disease spots look like?
There are different formations.
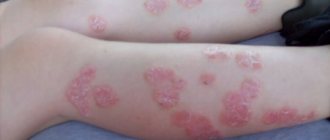
- Spider veins. They are blood vessels that rise above the skin level. They also have branches - vascular branches. The stars are usually dark red in color. The size can reach 15 cm. The photo shows blood spots on the body due to liver disease.
Upon palpation, you can notice how the stars pulsate. Sometimes they are quite painful and do not go away throughout the illness.
- Rash. It is not uncommon for a rash to appear with such diseases. It can be pustular, acne, or papulous. The main places of its concentration are the face, neck, back and chest.
The rash can also appear as an allergic reaction. For example, this happens with parasitic infections or an overdose of medical or other substances.
- Liver plaques. Most often they are a consequence of chronic diseases. They look like traces of healed burns and have clear edges.
At the first stage, they appear as round red lumps, then develop into blisters. After their breakthrough, a whitish spot with a red border remains in this place.
- Red palms. This phenomenon occurs in chronic liver diseases. The diseased organ cannot cope with the processing of hormones, so the bloodstream mixes on the surface of the palms, which is why the limbs acquire a bright red tint.
When pressed, this disappears, but after a while the previous color appears again. Redness of the palms is often accompanied by fever and can spread to the feet.
Outwardly, this phenomenon looks like a scattering of hemorrhagic spots. They can be either small or reach quite large sizes. Distributed throughout the body. They disappear when the disease that caused them, liver failure, is eliminated.
Basically, pigment spots are age-related rashes, typical for people over 40. But you should pay attention to them if: • There are too many of them; • The shade of the spots changes – it becomes gray or bronze; • The spots begin to spread.
In this case, this may be a signal that the liver is not healthy. Some doctors are of the opinion that the gland's ability to process and remove toxins deteriorates, which can result in a disease such as cholestasis.
Skin pathologies in liver diseases
With liver disease, a rash appears in the form of spots. The spots that appear on the skin in liver diseases are the main sign of its pathologies - “liver spots”: bruises, plaques, spider veins, hepatic palms (redness of the palms), yellowing, itching. Sweating increases, and the sweat discharge has a very pungent and antipathetic odor. In such cases, you should immediately go to the doctor without hesitation.
When a patient consults a doctor, a diagnosis is strictly made that is directly related to dysfunction of the liver. Liver spots (see photo) make it clear that it is time to take measures to treat this disease.
Why does the body itch? What are the causes of this itching?
There can be many reasons for skin itching. This annoying phenomenon, which causes a person both physical and psychological suffering, can be associated with an allergy to something, and with dermatological dysfunction, but the motivation for this can also be disorders in the liver itself.
Hepatic itching has a distinctive feature; it manifests itself strongly and painfully, and occurs at night.
In despair, the patient complains to the doctor: “I itch until I bleed, but it doesn’t bring relief. Taking antihistamines is also futile.” The point is that this very itching is not the disease itself, but a symptom of a disease of the internal system.
READ ALSO: Rash on the body of an adult: how to treat if it itches, red rashes all over the body and allergies
And if it does not disappear over a certain period of time, then you need to immediately take measures related to going to the doctor, otherwise the disease in its stage may intensify.
Itching of the skin due to liver diseases can be treated with the help of certain medications , such as metronidazole, which instantly and effectively eliminates the harmful phenomenon.
This drug accelerates metabolism and normalizes lipid metabolism. Sometimes itching due to liver diseases may return after some fairly long time has passed after stopping the medication.
In this case, you need to repeat the therapy. Compliance with the rules of necessary hygiene, a strict diet, and avoidance of overheating of the skin in any form also only helps to speed up recovery. You should categorically avoid baths and saunas, and take a cool shower in the summer months.
Itching and itchy spots
Almost all liver diseases are accompanied by itching on the epidermis. It especially manifests itself in combination with irritation and yellowness of the skin. This happens because bilirubin, which the liver should, but cannot, neutralize, lingers in the layers of the skin, irritating it. Thus, the body begins to itch due to stagnation of bile and, as a result, the occurrence of jaundice.
All skin rashes that appear on the skin as a result of liver disease, be it hives, plaques or red spots, are not without itching. It happens that itching occurs against the background of allergies, then in order to distinguish liver irritation from allergic irritation, you need to know that hepatic irritation is not eliminated by antiallergic drugs.
The appearance of age spots on the skin
As mentioned above, various pathological complications of the hepatic gland lead to the appearance of pigmentation on the skin. This is caused by a slowdown in metabolism and aging of the body.
To prevent these complications, the following medical procedures are necessary:
- from the vitamin complex are prescribed: ascorbic acid, multivitamins, methionine, parabenzoic acid,
- It is also necessary to conduct several sessions of oxygen therapy.
The first step and unconditionally is to identify the cause of the internal organ disease that caused the deposition of this pigment, and begin treatment with it. Is it the liver or endocrine glands?
For cosmetic treatment of the spots themselves, all kinds of creams, salicylic alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and bodyagi masks are used. All procedures must be performed only in a clinical setting, under the supervision of medical staff. It is imperative to do tests on the tolerability of the various components contained in these products.
Treatment of liver spots
The most important thing is that you should not self-medicate. If you have liver spots, you should definitely contact a specialist who will examine you and prescribe the correct treatment.
A large number of cosmetic companies offer various medications and cosmetics for removing stains. However, the problem is within you, and after some time they will return again. It is better to focus efforts on combating the source of the problem than to mask it.
The liver is an amazing organ. She is capable of self-regeneration even in the most advanced cases, so if you help her, recovery will go faster. You should take medications as directed by your doctor, undergo procedures and follow a diet. Treatment of any of the diseases is carried out in various ways:
- In case of cirrhosis, treatment is aimed at stopping the processes of decay of organ structures. It includes the use of medications and diet.
- To get rid of diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts, you need to methodically take choleretic drugs. Also, one of the methods of non-surgical treatment is remote ultrasound lithotripsy. However, if the stones are too large, then only surgery will help. Now medicine offers the most modern methods of removing stones: crushing them with a laser, endoscopic cholecystectomy or open abdominal surgery.
- If a person has parasites, they are treated with antiparasitic drugs. If they do not help, surgical excision is used, then restorative measures.
- In the case of hepatitis, antiviral medications and a strict diet are used.
One way or another, the best option is to turn to a professional, if only to avoid making things worse. After all, health is one thing, and you need to preserve it with all your might. Take care of yourself!
So-called liver spots most often appear on the face and hands. And despite the fact that this is not the most serious problem, you can make them less visible if you consider them unsightly.
Today we will tell you about several natural remedies for liver spots. With their help, you can restore youth and beauty to your skin.
Treatment options
Self-medication of such forms of the disease is fraught with consequences. Since the face and hands suffer more often, i.e. visible places on the body, experts recommend not to take risks, but to go to the hospital. After a thorough examination of the skin, tests are prescribed. Do not forget that rashes can be caused by diseases such as scarlet fever, measles and other infections, and their treatment requires special care and conditions.
Erythemas associated with sun rays require first aid. In such cases, it is necessary to apply cold to the damaged areas of the skin or resort to the use of aerosols that contain panthenol.
This is followed by contacting a specialized department. Treatment of erythema nodosum requires an integrated approach to eradicate the problem. The main condition remains bed rest. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are also used. Be sure to use:
- ointments;
- compress;
- dimexide application.
But it is worth remembering that patients with erythema nodosum are strictly prohibited from sunbathing, using massage and dieting. Meals should include foods moderately rich in fats and proteins. Exudative erythema (pathogens of this type are unknown) requires specific treatment.
- Initially, all dosage forms that can cause rashes should be discontinued.
- Next, ointments are selected that have no contraindications at all. As usual, specialists prescribe cooling mixtures or indifferent pastes and ointments. For example, zinc ointment. Quite cheap, but effective. It has been used for more than 50 years for diseases such as eczema, allergic rashes, dermatitis and, of course, erythema.
Zinc ointment is an inexpensive and effective remedy