Home / Possibility of infection
Back
Published: 08/11/2020
0
0
- 1 In scraping a thread of mycelium in pityriasis versicolor
- 2 Symptoms of infection
- 3 How to treat mycelium threads on nails
- 4 What diseases does it cause?
- 5 Are there transverse partitions in the mycelium threads?
- 6 Yeast mycelium threads in a smear on the flora
- 7 Diagnostics
- 8 Treatment
- 9 Classification of fungal infection
- 10 How to protect yourself
- 11 Features of threads for candidiasis
- 12 What to do if there are mycelium threads in the analysis
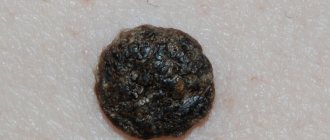
Scraping threads of mycelium in pityriasis versicolor
This is a chronic fungal disease.
It is caused by Pityrosporum ovale.
This is a yeast fungus.
It appears in places where there is increased sebum production.
Because the fungus actively metabolizes fats.
It is an opportunistic microorganism that lives on the skin of any person.
The disease does not occur due to infection.
It is called:
- increased production of sebum;
- insufficient hygiene;
- lubricating the skin with fat, for example, for medicinal purposes;
- decreased immunity;
- local use of glucocorticoids for a long time.
More often the disease manifests itself against the background of increased sweating.
Fungi prefer damp skin.
Without treatment, the disease may go away on its own within a few months or years.
It is usually not observed in patients over 40 years of age, but affects only young people.
Sometimes complicated by fungal folliculitis.
Pityrosporum ovale infection is also associated with seborrheic dermatitis.
Symptoms are usually mild.
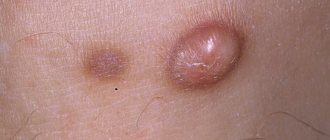
These are spots on the skin - white on tanned skin and light brown on untanned skin.
They can be of various sizes, usually round in shape.
The lesions can merge if located nearby.
Skin flakes are taken for microscopy.
They are obtained by scraping the stain.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8nc8_w2EIZM
Staining is carried out with potassium hydroxide.
In the sample, the doctor can see mycelium threads and fungal cells.
They have a round shape.
When examined under a Wood's lamp, the glow will be green.
Sometimes it has a bluish tint.
But the glow may be absent if the patient has washed immediately before visiting the doctor.
Differential diagnosis is carried out primarily with vitiligo.
With this disease there is no peeling when scraped.
Mycelium threads are also absent upon microscopy of skin scrapings.
Pathomorphological examination reveals mycelial threads and fungal cells.
They are detected in the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Increased proliferation of keratinocytes is observed.
There are signs of inflammation and dilated blood vessels.
Microsporia of the scalp
A fungal infection of the scalp is detected when a person notices a red spot on the skin. Microsporia is very easily tolerated, but can be treated for a long time. To begin medical measures quickly, you need to know how the disease manifests itself. If you notice symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
What is microsporia in humans?
Microsporia disease is a skin disease. It is caused by infection of humans with a fungus of the genus Microsporum, which is very contagious and widespread. Most of them are located in easily accessible places: in the soil, on the surface of plants and animals. These bacteria can develop their destructive activity on smooth or hairy areas of the skin. In the second case, the disease causes hair loss and marks on the skin. Microsporia is often observed in children. Children have more contact with pathogens and an underdeveloped immune system.
Forms of the disease
A person can become infected with 2 types of microsporia:
- Superficial. It is characterized by damage to the upper layers of the skin. The integument undergoes clinical changes in the form of spots with peeling, and the hair in this part is either absent or the hairs are broken. The disease, which appears as a result of the activity of anthropophilic fungi, is easily transmitted between people.
- Internal (subcutaneous), which is transmitted from animals. In this case, the fungal mycelium penetrates deeply, forming inflammatory processes, purulent formations, and a depressed state of the body.
Microsporia manifests itself in the following forms:
- affects the scalp and smooth skin;
- skin and facial hair (in men);
- purulent formations appear.
Causes and routes of infection
A person can acquire microsporia through contact with infected animals, people or household items. These fungi are very tenacious. They can remain active for several months and years. The danger of infection from animals decreases with each new carrier, since human skin is not a natural environment for this microorganism. If the species is anthropophilic, it can cover large groups. Children who have insufficient hygiene skills, weak immunity, and frequent contact with each other are especially susceptible to its influence.
In adults, microsporia occurs much less frequently. They have a highly resistant immune system, internal protective factors against fungi, and carry out proper hygiene measures. Changes in the structure of the scalp help to significantly reduce the possibility of damage to this area. Ringworm does not occur in all cases of contact with an infected object. The formation of microsporia depends on the type and concentration of the fungus, immunity and other protective properties of the human body.
Symptoms of microsporia
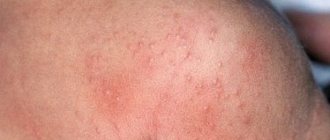
The presence of microsporia of the scalp can be determined by the following signs:
- red spots on the head;
- baldness, hair fragility;
- flat flaky patches on the skin;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- black dots;
- excessive keratinization of the skin.
Diagnostics
Microsporia of the scalp is diagnosed using the following studies:
- Laboratory. Examines hair samples, smears taken from the skin, and particles of the epidermis.
- Wood's lamps. This study is based on the fact that fungi are detected under UV light. This way you can diagnose microsporia quickly and accurately.
- Histological. Helps determine the fungal infection and the degree of inflammation it caused. For analysis, flakes of the surface layer are taken from the affected area and stained.
Treatment of microsporia in humans
Fungal diseases of the scalp are treated under the supervision of a dermatologist. Medical interventions do not require hospitalization. It is only possible to establish a diagnosis or in case of complications. The process of eliminating microsporia is often delayed, so it is important to use comprehensive treatment, which includes:
General
This part of the treatment of microsporia is characterized by the following measures:
- shaving hair at a distance of 1 cm from the border of the affected skin area;
- washing the scalp several times a day;
- control so that the skin does not become overcooled or overheat;
- providing the body with vitamins and nutrients through food and medications;
- use only personal products and hygiene items.
Systemic
Mycosis of the scalp is treated systemically with antifungal drugs, which, being absorbed in the intestines, are carried throughout the body through the blood. This ensures the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms. Systemic therapy is mandatory, since with its help you can get rid of not only the external signs of microsporia, but also the infection inside. The basis of this process are medications: Griseofulvin, Terbinafine.
Antifungal ointments for skin
How to treat fungus on the head locally:
- Ketoconazole (use 1-2 times/day, course – 4-6 weeks);
- Clotrimazole (twice daily);
- Salicylic acid and sulfur (smear the skin in the evening until the symptoms disappear).
Symptoms of infection
It is quite difficult to recognize the symptoms of the spread of mycelial threads in the initial stages, but as development progresses, a person begins to feel a number of signs.
Typically, such an infection can be identified by:
- itching, which increases significantly at night;
- redness, which indicates an inflammatory process;
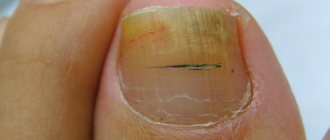
- thickening and deformation of the nail plate;
- the appearance of a cheesy coating on the skin;
- hair loss or impaired hair growth;
- peeling of the skin, which indicates the desquamation of dead cells.
If you ignore the fungus for a long time, you may develop symptoms of serious complications:
- cough - indicates lung damage;
- development of renal failure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- fever - indicates that mycelium has entered the blood.
A person can become infected with a fungal infection in different places. The most susceptible areas are areas on the skin or mucous membranes that have no protection due to their damage. When entering such zones, the mycelium begins to actively spread.
There are several ways of infection with fungal mycelium:
- Contact and household. Infection occurs when the mycelium comes into direct contact with the skin from an infected person;
- Food. The culprit of infection is the opportunistic Candida fungi, which, under favorable conditions, begin to actively reproduce;
- Air. The pathogens enter the respiratory tract, causing damage to the lungs;
- Sexual. Infection occurs during intimate intimacy with an infected partner.
Experts identify certain causes and factors that increase the likelihood of infection with fungal mycelium:
- Frequent visits to public places (saunas, swimming pools, baths);
- Using for personal purposes someone else’s manicure accessories that have not been sterilized;
- Wearing someone else's shoes or clothes, as well as using a towel that is not your own;
- Shaking hands with an infected person.
People who have a weakened immune system due to acute or chronic diseases are at risk. They deprive the human body of natural defenses that control the number of pathogenic microflora.
Mycelium is easily transferred through contaminated instruments during manicure and pedicure
Symptoms that are characteristic of a disease such as nail or skin fungus help to recognize health problems. Doctors identify the following signs of the spread of mycelium threads:
- Itching, which may intensify towards night;
- Redness of the affected area;
- Deformation and thickening of the nail plates;
- Impaired hair growth or excessive hair loss;
- The appearance of a cheesy coating on the skin;
- Peeling of the epidermis.
All these signs indicate fungal mycelium on the skin or nails. If they are detected, it is strongly recommended to immediately seek medical help. You should also limit your contacts with people and not let them use your personal belongings. This will reduce the likelihood of an epidemic starting.
If a fungal infection is ignored for a long time, its symptoms become more pronounced. They are complemented by other signs of malaise. Often people with mycelium complain of a cough, indicating the spread of infection in the lungs. Patients also notice the occurrence of obvious symptoms of such pathological conditions:
- Heart rhythm disturbances;
- Fever;
- Kidney failure.
If mycelium affects the nail layer or skin, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics. To do this, you will need to examine a sample of a piece of epidermis or toenails.
Complications of fungus
In advanced cases, mycelium of the fungus on the feet leads to complications - the development of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the epithelial layer of the nail plate, allergic reactions to spores, and a general decrease in immunity.
If onychomycosis is not treated, the fungus will spread to healthy nails and skin, and surgical intervention may be required. And when a secondary infection occurs, pus will begin to form in the affected area, causing an unpleasant odor and the spread of pathogenic flora throughout the body.
It is important to treat the fungus in a timely manner in order to avoid serious complications. It is important not to self-medicate, but to consult a dermatologist at the first symptoms of mycosis. The effect of treatment will be increased by maintaining personal hygiene, using high-quality shoes, and dry feet.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
How to treat mycelium threads on nails
Detection of mycelium in clinical material from nails is a sign of onychomycosis.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with heat rash on the face of a baby: treatment, what it looks like
This is a group of fungal diseases.
They can be caused by both yeast and mold fungi.
Typically, the distal or lateral edge of the plate is initially affected.
Then it spreads towards the center of the nail.
Pathogens:
- Trichophyton;
- Candida;
- Scopulariopsis;
- Aspergillus;
- Acremonium and many others.
You can become infected from another person.
It is possible that infection can spread to the nails from other parts of the body.
Sometimes fungal spores get onto the nail plates from the soil (molds).
In 80% of cases, the nail plates of the lower extremities are affected.
The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests.
A scraping is taken using a curette.
The material is taken from the inner plate.
From the outside it is taken if white superficial onychomycosis is suspected.
The drug is treated with 10-30% KOH.
Dimethyl sulfoxide may be added to it.
This makes it easier for a specialist to find fungi.
Using the microscopic method you can:
- confirm the etiology of the nail disease - identify that it was the fungus that provoked the disease;
- find out whether the fungal inflammation was caused by candida or dermatophytes.
But it is impossible to determine the type of mushroom by the mycelium threads.
In cases where microscopy does not give results, a histological examination of the nail area is performed.
The diagnosis is confirmed using the CHIC reaction.
If mycelium threads are detected on the nails, prepare for long-term treatment.
It continues until the healthy legs grow back completely.
Onychomycosis never goes away without therapy.
Self-healing does not occur, and more and more new nails are involved in the pathological process.
In the initial form of superficial onychomycosis, only local treatment can be used.
But systemic antimycotic therapy is more often used.
Indications for it:
- 4 or more nail plates are affected;
- the area of damage to at least one nail exceeds 50%;
- the nail is destroyed in the lateral or proximal zone.
Main pathogens:
- Trichophyton rubrum – 85%;
- candida – 10% of cases.
Drugs to which these fungi are sensitive are prescribed.
Only varnishes can be used topically - never creams or ointments.
Drugs containing amorolfine are prescribed.
Ciclopirox is used less frequently.
Terbinafine is most often used internally.
In second place is itraconazole.
It gives a lower percentage of cure.
In addition, the application scheme is more complicated.
With terbinafine everything is simpler - you drink it continuously for 3 months, 1 tablet (250 mg) per day.
Local and systemic treatment can be used in combination.
Using this scheme allows you to get rid of nail fungus in 75% of cases.
If there is no positive dynamics after 1-2 months of treatment, the fungus is inoculated on a nutrient medium.
Sensitivity to antimycotics is assessed.
Based on the data obtained, another drug is prescribed.
After this, another 15% of patients will be cured.
The remaining 10% will require surgery to remove the nail and treat its bed.
If you detect spores and mycelium threads in smears, contact our clinic.
We have experienced dermatovenerologists who effectively treat any fungal diseases.
If you identify mycelium threads, contact the author of this article, a dermatovenerologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
Public health
Treatment of mycelium threads on toenails is carried out using traditional methods, under the supervision of a dermatologist. You can eliminate the infection with laundry soap, vinegar, soda, copper sulfate, aloe juice, celandine, and garlic.

Traditional methods in the fight against fungus
Traditional recipes for removing fungus from the body:
- Crush radish seeds and a few cloves of garlic, mix into a paste and apply to the sore spot for 10 minutes;
- Make an infusion of birch buds - add a spoonful of raw materials to a glass of boiling water, keep in a dark place for 4 days, treat the skin for 7 days;
- Baths with tea tree oil - add 20 drops of essential oil to a container of hot water and steam your feet, treatment course for at least two months;
- Iodine mesh - do before bedtime on the affected area, do not interrupt treatment for 10 days;
- Compresses with celandine juice - squeeze a few drops onto a cotton swab and apply to the damaged nail, do the procedure several times a day.
You can treat onychomycosis with ordinary salt and soda, take baths, and apply the solution until complete recovery. Mix the main ingredients in equal proportions, diluting with some warm water.
What diseases does it cause?
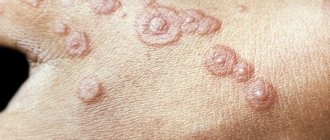
The fungus, which is produced by mycelium threads, can affect different parts of the body. There are several types of diseases that can be caused by infection with this pathogen. It can cause the following pathological conditions in humans:
- In case of damage to the mucous membranes - candidiasis, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis;
- When the superficial and deep layers of the skin are affected - pityriasis versicolor, pityriasis nigra, seborrheic dermatitis, black piedra, microscopy, trichophytosis, epidermophytosis;
- If the mucous membrane of the tongue is affected - candidiasis, actinomycosis;
- If the nail plates are affected - nail trichophytosis, rubromycosis.
Each of these diseases has its own symptoms. Discomfortable sensations, which are the main signs of the disease, help identify the mycelium, or rather the localization of the fungal mycelium. If you suspect an infection, you should immediately consult a doctor. It will help you determine the type of fungus on your skin or nails and choose an effective treatment for it.
Prevention

Proper nutrition will prevent the development of fungal infections even if the fungus gets on the skin
To prevent fungal infection, you should follow several rules:
- strengthen immunity;
- take care of the health of the nervous system;
- Healthy food;
- treat any diseases in a timely manner;
- maintain personal hygiene.
A strong immune system will not allow the development of fungal infections even if mycelium or fungal spores get on the skin, so careful attention to your own body is the key to good health and the best protection against fungal diseases.
Are there transverse partitions in the mycelium threads?
The mycelium has septa.
But septa may be absent in pseudomycelium.
It differs from true mycelium in that during the budding process, the mother cells are not completely separated from the daughter cells.
They continue budding.
Therefore, structures appear that resemble mycelium in appearance.
It is called false.
It is unseptate, that is, not divided by partitions.
When pseudomycelium is detected, the doctor sees constrictions between the cells.
The terminal cells are smaller than those located in front of them.
Sometimes pseudomycelium consists of cells of the same type.
It is called vestigial.
In other cases, cells of different types develop in pseudomycelium.
It's called complex.
Long cells - pseudohyphae - are found.
They contain buds - one or more, round or wedge-shaped.
These buds are called blastospores.
Properties of pathogenic fungi
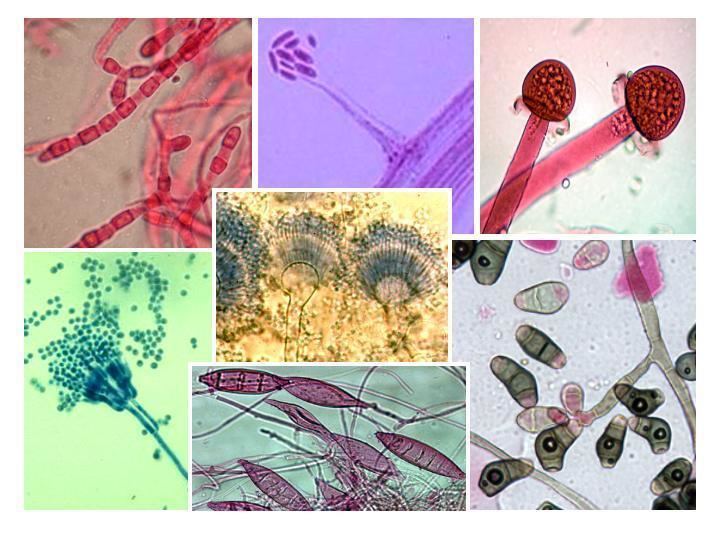
A person usually does not immediately notice that pathogenic fungi have entered his body. The spores (mushroom seeds) elongate and take the form of a tube, which continues to grow and become thinner in order to eventually turn into a hypha and become the basis of the mycelium. Already at this stage the difference is noticeable. The hyphae of higher fungi have septa, but those of lower ones do not. Hyphae from different spores grow, intertwine with each other, and ultimately mycelium grows on the substrate.
For diagnostics and drug production, pathogenic fungal species are grown on nutrient media such as Sabouraud, Chapeka-Doxa, wort and wort agar. A prerequisite is a pH below seven.
Fungal cells are covered with a wall of carbohydrates, but the substance by which the species can be determined is chitin. It does not interact with penicillins and lysozyme, therefore it is more virulent for the human body.
The pathogenic fungus is resistant to physical and chemical disinfectants. Treatment for them can cause irreparable harm to human organs and systems, since a high concentration of drugs in body fluids is required. Microspores are the most sensitive to therapy, and candida is the least sensitive. The selection of drugs is complicated by the fact that one type of fungus can have different combinations of antigens, and toxins, enzymes and other pathogenicity factors still remain unknown.
Yeast mycelium threads in a smear on the flora
Spores and mycelium threads are found in candidiasis.
Only these mushrooms do not form mycelium, but pseudomycelium.
Candida can be detected in smears from:
- vagina;
- penis;
- mouth;
- anus;
- skin;
- nails
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Papilloma on the nipple of the breast
Candida can affect various structures and organs of the human body.
Inflammation can develop:
- on the genitals;
- in the folds of the skin;
- under occlusive dressings;
- in hair follicles;
- rectum;
- in the mouth and throat;
- on the nails.
In severe cases, invasive candidiasis develops.
It affects internal organs.
This is possible against the background of immunodeficiency, for example, with HIV.
Candida can be detected in a vaginal smear.
This study is called a flora smear.
Because it identifies not only mushrooms.
This smear also helps detect a number of other microorganisms.
These are opportunistic bacteria and some sexually transmitted pathogens.
The smear may reveal kidneys.
They are also called rudiments.
These are Candida spores that have just begun to grow.
Externally, this microscopic feature looks like an oval cell, on the surface of which another smaller oval began to grow.
It is located at one of the poles.
Yeasts reproduce by fission.
They form buds.
With the further formation of a large number of primordia, they form and elongate without cell separation.
Then pseudomycelium is formed.
It looks like thread.
Another name: pseudohyphae.
With candidiasis, threads of varying lengths are detected.
The mycelium threads can be best visualized at high magnification of the microscope.
In this case, they can be examined in detail.
Diagnostics

To determine the type of mycelium, laboratory tests will be needed
Diagnosis of suspected infection with fungal mycelium is limited to standard measures. They allow you to correctly determine the type of pathogen and determine its sensitivity to drugs.
Detection of mycelium is carried out in the following ways:
- Microscopic examination of skin scrapings. This procedure easily reveals yeast, that is, the presence of yeast fungus. It is usually found in a smear taken from an infected mucous membrane;
- Culture method. This study requires inoculating biomaterial taken from the patient onto nutrient media. This is carried out to obtain active mycelial growth and identify the type of pathogen.
After all the required diagnostic measures have been carried out, and the doctor has become familiar with the test results, he will be able to give the patient the correct diagnosis.
Treatment
When threads appear, treatment includes the use of antifungal drugs.
Different diseases are treated differently.
For dermatophytosis of the skin, the use of local antifungal drugs is usually limited.
Ointments and creams are used.
They may contain:
- ketoconazole;
- miconazole;
- terbinafine;
- amorolfine;
- ciclopirox and other drugs.
In severe cases, oral medications are also used.
For candidiasis, clotrimazole is used externally.
Fluconazole can be prescribed orally.
In the recurrent form, treatment can be very long.
Treatment of skin diseases caused by fungus depends entirely on the degree of damage and the individual characteristics of the body. Despite this, in all cases it is necessary to carry out antifungal therapy: both external and general. For local treatment, it is necessary to use various antimycotic creams, such as Miconazole, Exoderm, zinc or salicylic ointment.
Miconazole Exoderm Zinc ointment Salicylic ointment
It must be remembered that all medications have a number of contraindications, for this reason it is best to entrust the choice of medication to your doctor. Also try to regularly change clothes on which pathogenic spores accumulate. Only with an integrated approach will it be possible to get rid of the disease.
If you have inflammation, then drug therapy must be supplemented with combination drugs. Do not forget to apply an iodine solution to the skin, which helps prevent the infection from spreading to other areas of the body. In the initial stages, it will be possible to cope with the lesion with the help of traditional medicine - however, if there are no results for a long time, you should still consult a doctor. Read more about the use of iodine for fungus...
To prevent infection, try to follow all the rules of personal hygiene, do not contact other people's animals and do not wear other people's clothes. Also, do not forget to take vitamin complexes regularly.
It is up to a competent specialist to decide how to treat fungal mycelium, with whom you need to make an appointment at the first suspicion of infection. If this pathogen is detected, it is necessary to undergo a course of drug therapy. This is a mandatory measure that will help get rid of fungus on the skin, mucous membranes or nails.
Treatment of mycelium threads is usually carried out with topical medications. You may also need to take pills to fight the infection from the inside. For such problems, doctors prescribe:
- "Nystatin";
- "Fluconazole";
- "Ketoconazole";
- "Clotrimazole";
- "Triderm";
- "Miconazole".
The choice of medicines should be trusted to a specialist. For therapy to be more successful, it must be carried out in accordance with certain rules. Before applying medicinal compositions, you need to thoroughly wash the problem area. In this case, treatment of the fungus is more effective, since nothing prevents the active substances of the ointments from penetrating into the deep layers of the epidermis.
If the patient uses topical medicinal products according to the instructions, clear improvements will become noticeable after about 2 weeks. If no changes are visible, then the treatment regimen will have to be adjusted or completely replaced with a more effective one. All these questions must be discussed with a dermatologist.
Conservative therapy does not always achieve the desired result. In this case, more radical methods come to the aid of patients with fungal mycelium. Laser treatment of the affected areas helps to cope with the disease. To achieve optimal results, it is advisable to undergo 3-10 sessions of this procedure.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a photo of a rash on the body of an adult with explanations of what it could be
A good helper for this disease is therapy that uses wave radiation. This is a fairly effective method of combating fungal mycelium. However, such treatment is required for 2-3 months.
The methods listed above are used in medical practice only in rare cases.
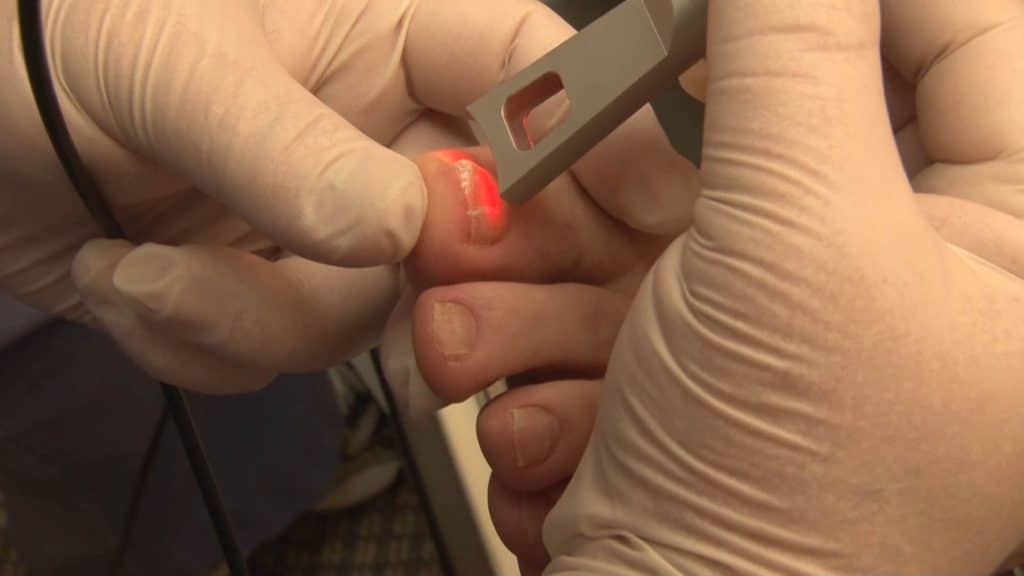
Drug treatment can be supplemented with laser
Reasons for appearance
If tests show that you have fungal mycelium, you should immediately consult a doctor to determine the most effective method of treatment. Remember, the sooner you start drug therapy, the easier and faster it will be to get rid of the lesion. It must be taken into account that such a lesion is a reason for serious drug therapy, which will help prevent the development of complications in the future.
A person can pick up mycelium threads absolutely anywhere. Even if you constantly wash your hands and practice personal hygiene, this does not guarantee you 100% protection from infection. Despite this, some people are much more susceptible to this condition than others. Those who suffer from excessive sweating, wear tight and synthetic clothes or shoes, have a weakened immune system or have serious chronic diseases should be especially attentive to the condition of their skin. Also among the factors that can trigger the development of mycelium on the skin are:
- Regular visits to baths, saunas and swimming pools - places where humidity and temperature are constantly increased. In such an environment, the fungus feels as comfortable as possible; it quickly begins to multiply and spread. Don't forget to wear rubber flip flops when visiting these places.
- Using someone else's or dirty manicure tools.
- Contact with an infected person.
- Wearing someone else's clothes, shoes, sleeping on used underwear.
- Using someone else's towels.
Fungus is a disease that can await you absolutely anywhere. You can even pick it up on public transport or in a store. It is impossible to determine at what exact moment the infection occurred. For this reason, you need to approach the issue of personal hygiene as responsibly as possible. If the first signs of infection appear, consult a doctor immediately.
The disease is activated in the process of reducing the body's defenses, disruption of the endocrine system, and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Additional factors include frequent exposure to a humid environment, excessive sweating, poor diet and constant stress.
The fungus can attack a person with long-term use of antibacterial drugs, diabetes, foot injuries, or close contact with the hygiene items of an infected patient.
Classification of fungal infection
Sometimes inexperienced laboratory technicians confuse mycelium threads with villi.
They can get into the vagina from tampons.
Then these are the lint of cotton fabric.
But they can be distinguished from threads of mycelium or pseudomycelium by certain parameters.
Firstly, in size.
The villi are always larger and thicker than the hyphae.
Secondly, due to the absence of kidneys.
Unlike mushrooms, cotton threads cannot reproduce by division.
Therefore, rudiments never form on their surface.
Mycoses are a large group of skin diseases. It can be caused by a huge number of different pathogens, which determine the course of the disease and the method of treatment. Based on the type of pathogen, this disease can be divided into:
- trichophytosis - lesions of the skin, nail plates and mucous membranes;
- candidal infections - affect the mucous membranes;
- cryptococcosis - affects internal organs and lungs;
- aspergillosis - reduce immunity and cause an infectious process in the lungs.
Based on localization, fungal infections can be divided into two separate categories:
- superficial – infection occurs without the infection spreading through the internal organs;
- systemic – the internal organs are primarily affected.
It should be noted that fungal mycelium always develops against a background of weakened immunity. It is when the body is weakened that pathogenic spores begin to multiply and cause serious damage. It is very important to monitor your body to prevent serious damage.
Definition
Pathogenic fungi are causative agents of deep and superficial mycoses in humans and animals.
These creatures belong mainly to the class of dermatophytes, that is, they feed on skin. Less common among them are lower fungi and actinomycetes. They have a certain affinity for animal tissues. This means that dermatophytes prefer the epidermis with the scalp, yeast prefer the lymphatic system, candida prefer parenchymal organs, aspergillus live in the respiratory system, and actinomycetes love to settle in the bones.
Knowing these features, the doctor can differentiate diseases and prescribe specific treatment.
Fungi are heterotrophic microorganisms that are incapable of forming nutrients through photosynthesis. All pathogenic fungi are divided into two large groups: saprobionts, which feed on organic debris, and biotrophs, which parasitize living cells of the host.
Mushrooms can be beneficial or harmful to people. Fungal microorganisms inhabit the human body, creating an opportunistic environment. Under favorable conditions (for example, decreased immunity), the fungus can pose a threat, causing various infectious diseases. All pathogenic fungi are classified into genera and species, families and classes with subclasses. According to the method of reproduction, pathogenic fungi comprise eight classes, but only four are dangerous from a medical point of view:
- Ascomycetes. The most numerous class, including dermatophyte fungi, yeast-like and mold fungi.
- Zygomycetes (Mucor) - each genus of these fungi is pathogenic and dangerous to humans.
- Basidiomycetes. The causative agent of a serious disease, Cryptococcus neofarmans, is isolated separately.
- Deuteromycetes. These imperfect fungi (non-sexual reproduction) are the causative agents of skin mycoses.
In the etiology of skin fungal infectious diseases, the main role is played by yeast-like fungi, as well as molds and dermatophytes. The most common are fungi of the genus Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epidermophyton, Candida, Pityrosporum, Torulopsis, Exophiala werneckii, Piedraia hortae.
Dermatophytes are causative agents of diseases of the skin, hair and nails. Medicine knows about fifty species of pathogenic fungi that can lead to the development of infectious diseases. Some pathogenic fungi affect only the skin, the other part affects the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Mycoses are caused by opportunistic fungi that are active in some human immunodeficiency states.
How to protect yourself
If a person wants to protect himself from infection with fungal mycelium, he should adhere to certain rules in everyday life. To prevent mycosis infection, it is recommended:
- Get a personal towel, washcloth and other accessories necessary to maintain personal hygiene;
- Air your shoes every day. Don't forget to change your socks regularly;
- When visiting the swimming pool, baths, saunas and other similar places, wear slippers on your feet;
- Use special foot powders. This rule is relevant for people who suffer from excessive sweating in the feet;
- Choose underwear and clothing exclusively from natural materials. It is not advisable to wear something that is too tight to the body.
To avoid illness, you need to take care of your own nutrition. It must be healthy and complete. It is necessary to include in your diet yoghurts with live bacteria, garlic and foods that contain vitamin B. As for sugar, milk, tea and coffee, it is best to start limiting yourself in this.
Features of threads for candidiasis
In candidiasis, the filaments are pseudomycelia rather than mycelium.
They do not have partitions.
But there are thickenings on the threads.
They appear in those areas where there are branches of pseudomycelium.
The fiber can have different lengths.
Sometimes the threads become twisted or intertwined.
Pseudohyphae can be detected in a native smear.
That is, not painted with anything.
But sometimes there are so many cells in the material that fungi are poorly visualized.
Then potassium hydroxide is added to the preparation.
The sample appears lighter when examined microscopically.
Elements of fungus become much more visible.
They are visible with a microscope magnification of 100 times.
A magnification of 400x is required to see the details.
This way the laboratory assistant can identify small and short filaments of pseudomycelium.
Budding cells and blastospores are also detected.
They are otherwise called blastoconidia.
They look like oval cells, corresponding in size to epithelial cells.
The appearance of budding forms is associated with the proliferation of fungi.
Their number may vary.
But it does not reflect the real quantitative indicators of the fungal process in the vagina.
It also does not correlate with the severity of symptoms.
Therefore, a smear on the flora cannot be used to assess the dynamic course of the disease.
This is an exceptionally high-quality test.
He gives a yes or no answer.
If mycelium threads are found, this indicates a fungal disease.
If they are not detected and the smear is clean, then the person is healthy.
Age factors of distribution
Candidiasis on the tongue most often occurs in newborns. Moreover, treating a disease in a child is much simpler and faster than in an adult patient. The younger he is, the easier the disease is to treat.
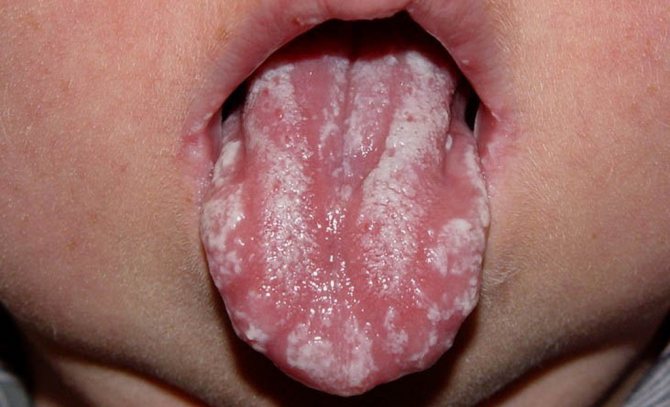
Most common in childhood
“My daughter, when she was not yet a year old, was diagnosed with candidiasis. I noticed a white coating on my tongue, at first I thought it was a nutritional mixture. I tried to wash it off with water, but nothing happened. The doctor said that there was nothing wrong with it; fungus in the mouth is often found in infants. We were prescribed Fluconozol and a general strengthening multivitamin complex. The plaque disappeared quite quickly, literally within a week, and did not appear again.”
Karina88, Moscow, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Quite often, older people have to deal with candidiasis. According to statistics, about 10% of people over 60 years of age experience this unpleasant disease 1. This trend is primarily associated with wearing prosthetic structures in old age, which often create ideal conditions for the rapid spread of fungus.